How Middle Ear Infections Are Treated
Most ear infections clear up within three to five days and don’t need any specific treatment. If necessary, paracetamol or ibuprofen should be used to relieve pain and a high temperature.
Make sure any painkillers you give to your child are appropriate for their age. Read more about giving your child painkillers.
Antibiotics aren’t routinely used to treat middle ear infections, although they may occasionally be prescribed if symptoms persist or are particularly severe.
Read more about treating middle ear infections
When Are Antibiotics Prescribed
Antibiotics are typically only prescribed to treat AOM and swimmers ear. This is because OME and COME occur after the bacterial infection has passed antibiotics are not effective against the fluid buildup alone.
Your doctor will examine your ear with an otoscope and evaluate your symptoms to determine what type of infection you have and whether antibiotics will be effective. If your symptoms are mild, they may recommend taking a wait-and-see approach. If symptoms dont resolve on their own or if theyre severe, then antibiotics will likely be prescribed.
Antibiotics And Other Prescriptions
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , using antibiotics by mouth to treat ear infections may not help certain cases of middle ear infections. Antibiotics are not effective against outer ear and viral infections.
The main treatments for outer ear infections are manual cleanings and ear drops. The type of ear drop will depend on what is causing the infection. In the case of malignant otitis externa, intravenous antibiotics are the primary treatment.
Recommended Reading: Vaginal Yeast Infection Or Uti
What Causes A Middle
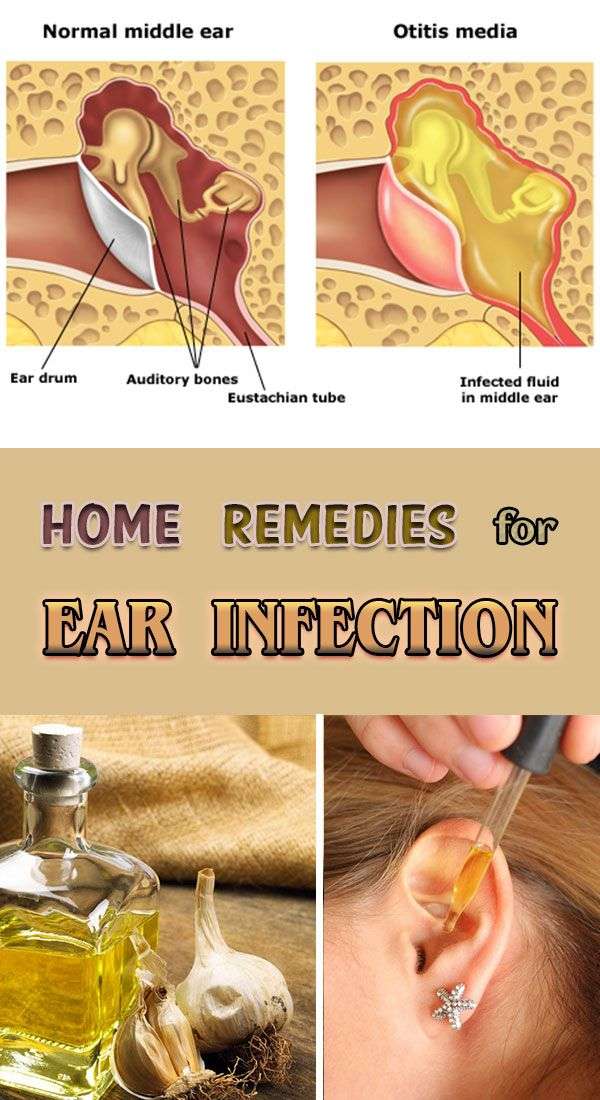
The middle ear connects to the throat by a canal called the eustachiantube. This tube helps even out the pressure between the outer ear and theinner ear. A cold or allergy can irritate the tube or cause the area aroundit to swell. This can keep fluid from draining from the middle ear. Thefluid builds up behind the eardrum. Bacteria and viruses can grow in thisfluid. The bacteria and viruses cause the middle-ear infection.
When Should I Call The Doctor
- has other serious medical problems,
- vomits over and over,
- is younger than 6 months old,
- is older than 6 months old and has had a fever for more than 48 hours,
- has redness and swelling behind the ear,
- is very sleepy,
- has a skin rash,
- isnt hearing well or at all,
- remains in a lot of pain despite at least one dose of acetaminophen or ibuprofen, or
- still has an earache after 2 days of treatment with acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Read Also: How Long For Bladder Infection To Go Away
Fast Facts On Ear Infections:
Here are some key points about ear infections. More detail and supporting information is available in the main article.
- Ear infections are more common in young boys than young girls.
- Most ear infections improve without treatment.
- Vaccinating a child against the flu can help prevent ear infections.
- Biofilms of antibiotic-resistant bacteria may be to blame for prolonged and repeated cases of ear infection
- Secondhand smoke increases the risk of ear infections.
An ear infection is a bacterial or viral infection of the middle ear. This infection causes inflammation and the buildup of fluid within the internal spaces of the ear.
The middle ear is a air-filled space situated behind the eardrum. It contains vibrating bones that convert sound from outside of the ear into meaningful signals for the brain.
Ear infections are painful because the inflammation and buildup of excess fluid increases pressure on the eardrum.
An ear infection can be acute or chronic. Chronic ear infections may permanently damage the middle ear.
In adults, the symptoms are simple. Adults with ear infections experience ear pain and pressure, fluid in the ear, and reduced hearing. Children experience a wider range of signs. These include:
- tugging or pulling at the ear
- ear pain, especially when lying down
- difficulty sleeping
Ear infections are generally divided into three categories.
How Are Ear Infections Treated
To treat an ear infection, health care providers consider many things, including:
- the type and severity of the ear infection
- how often the child has ear infections
- how long this infection has lasted
- the child’s age and any risk factors
- whether the infection affects hearing
The type of otitis affects treatment options. Not all kinds need to be treated with antibiotics. Because most ear infections can clear on their own, many doctors take a “wait-and-see” approach. Kids will get medicine for pain relief without antibiotics for a few days to see if the infection gets better.
Antibiotics aren’t routinely prescribed because they:
- won’t help an infection caused by a virus
- won’t get rid of middle ear fluid
- can cause side effects
- usually don’t relieve pain in the first 24 hours and have only a minimal effect after that
Also, overuse of antibiotics can lead to antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which are much harder to treat.
If a doctor does prescribe antibiotics, a 10-day course is usually recommended. Kids age 6 and older who don’t have a severe infection might take a shortened course for 5 to 7 days.
Some children, such as those with recurrent infections and those with lasting hearing loss or speech delay, may need ear tube surgery. An ear, nose, and throat doctor will surgically insert tubes that let fluid drain from the middle ear. This helps equalize the pressure in the ear.
Recommended Reading: Chicago Fire Infection Part 2
Infections Inside The Ear
Antibiotics are not usually offered because infections inside the ear often clear up on their own and antibiotics make little difference to symptoms, including pain.
Antibiotics might be prescribed if:
- an ear infection does not start to get better after 3 days
- you or your child has any fluid coming out of the ear
- you or your child has an illness that means there’s a risk of complications, such as cystic fibrosis
They may also be prescribed if your child is less than 2 years old and has an infection in both ears.
If antibiotics are not prescribed, eardrops containing a painkiller and an anaesthetic might be prescribed.
What Home Remedies Relieve Ear Pain And Cure Ear Infections
Natural and over-the-counter nonprescription remedies for ear infections:
Which parts of the ear can become infected?
Also Check: Infected Gum Around One Tooth
What Are The Symptoms Of A Fungal Ear Infection
An explanation of the different types of ear infection and which parts of the ear are involved can be found in the .
This leaflet is about infection of the ear canal with a fungus. Other causes of otitis externa can be found in the .
Typically, the ear starts to look red and the skin on the outer part of the ear becomes scaly. It may start to itch and become quite uncomfortable. You may notice discharge beginning to leak out of the ear.
The itching is often worse with fungal infections than with other types of ear infection. Apart from this the symptoms of a fungal ear infection are often identical to ear infections caused by germs . This means your doctor may prescribe antibiotic ear drops to start with and may only suspect a fungal infection when the treatment doesn’t work.
How Long Does It Take For An Ear Infection To Heal
On average, an ear infection can last one to two weeks depending on where it is located and how it is treated. Middle ear infections tend to go away the fastest without treatment. Inner ear infections can last a few weeks. The use of antibiotics or other treatment methods can help speed up the healing process.
Also Check: Can Tmj Cause Ear Infection
What Is Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is a penicillin antibiotic that fights bacteria.
Amoxicillin is used to treat many different types of infection caused by bacteria, such as tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, and infections of the ear, nose, throat, skin, or urinary tract.
Amoxicillin is also sometimes used together with another antibiotic called clarithromycin to treat stomach ulcers caused by Helicobacter pylori infection. This combination is sometimes used with a stomach acid reducer called lansoprazole .
There are many brands and forms of amoxicillin available and not all brands are listed on this leaflet.
How Is A Middle
Your health care provider will take a medical history and do a physicalexam. He or she will look at the outer ear and eardrum with an otoscope.The otoscope is a lighted tool that lets your provider see inside the ear.A pneumatic otoscope blows a puff of air into the ear to check how wellyour eardrum moves. If you eardrum doesnt move well, it may mean you havefluid behind it.
Your provider may also do a test called tympanometry. This test tells howwell the middle ear is working. It can find any changes in pressure in themiddle ear. Your provider may test your hearing with a tuning fork.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Rid Of A Tooth Infection At Home
Treating Inner Ear Infections
The inner ear is located next to the middle ear within the temporal bone. The inner ear contains the semicircular canals, which are essential to balance and equilibrium.
Inner ear infections are much more likely to be caused by a virus than a bacterial infection. They are much less common than outer ear infections or middle ear infections.
The most common inner ear infections include labyrinthitis or vestibular neuritis, which are slightly different conditions.
Labyrinthitis affects the labyrinth, which is a system of fluid-filled sacs that helps you hear and gives you a sense of balance. Labyrinthitis can cause both hearing changes and dizziness, or vertigo.
Vestibular neuritis is an inner ear infection that affects the vestibular nerve and usually causes dizziness and balance issues but no hearing changes.
There is no specific diagnostic test to identify an inner ear infection, so misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis is common.
Which Antibiotic Is Best For An Ear Infection
Two classes of antibiotics are commonly used to treat an ear infection.
Aminoglycosides
Aminoglycosides have been the main treatment for bacterial ear infections for decades. Two aminoglycosides used in ototopical preparations are:
Though both of the above are commonly used in the United States, only neomycin has FDA approval. Neomycin is effective for gram-positive bacteria but its effectiveness against gram-negative bacteria has declined over years, especially against Pseudomonas, the most common bacteria in ear infections.
Tobramycin is effective for Pseudomonas and other gram-negative bacteria.
Quinolones
Quinolones are the most recently introduced ototopical antibiotics. Most quinolone antibiotics in use are fluoroquinolones, which also contain an atom of fluorine. Fluoroquinolones are considered the best available treatment now for ear infections for two reasons:
- Broad spectrum of activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
- Lack of ototoxicity
Following are some of the FDA-approved fluoroquinolone solutions for external ear infection from Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa:
Ciprofloxacin
Read Also: Most Common Opportunistic Infection In Hiv
Before Taking This Medicine
You should not use amoxicillin if you are allergic to any penicillin antibiotic, such as ampicillin, dicloxacillin, oxacillin, penicillin, or ticarcillin.
To make sure this medicine is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have:
-
kidney disease
-
diarrhea caused by taking antibiotics or
-
food or drug allergies .
It is not known whether this medicine will harm an unborn baby. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
Amoxicillin can make birth control pills less effective. Ask your doctor about using a non-hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy.
It may not be safe to breastfeed while using this medicine. Ask your doctor about any risk.
How To Take Oral Antibiotics
Its important to always take your antibiotics as prescribed. It may be tempting to combine the doses, but they will not be as effective and could lead to adverse side effects, such as stomach upset.
Even if you begin to feel better, you should continue to take the antibiotics until you finish your medication to prevent the infection from returning. You should avoid alcohol while taking antibiotics.
While antibiotics are good for clearing a bacterial infection, they can also rid the body of helpful “good” bacteria at the same time. Because of this, you may want to consider taking a probiotic supplement while you are on antibiotics.
Probiotics are living organisms that can help to prevent the imbalance of bacteria within your gut that often comes from taking antibiotics. Studies have shown that taking probiotics while taking antibiotics can lower the chances of side effects from a bacterial imbalance, such as gastrointestinal upset and diarrhea.
Don’t Miss: Natural Medicine For Kidney Infection
Will I Need Any Tests For A Fungal Ear Infection
Your doctor will probably treat your ear first and take an ear swab if the condition doesn’t get better. Taking an ear swab is a fairly simple procedure and involves the doctor putting a swab that looks very similar to a cotton bud in your ear and swishing it around. This shouldn’t be painful unless your ear is very tender and inflamed from the infection. Even then, gentle swabbing should only cause mild discomfort.
What Happens If My Child Keeps Getting Ear Infections
To keep a middle ear infection from coming back, it helps to limit some of the factors that might put your child at risk, such as not being around people who smoke and not going to bed with a bottle. In spite of these precautions, some children may continue to have middle ear infections, sometimes as many as five or six a year. Your doctor may want to wait for several months to see if things get better on their own but, if the infections keep coming back and antibiotics arent helping, many doctors will recommend a surgical procedure that places a small ventilation tube in the eardrum to improve air flow and prevent fluid backup in the middle ear. The most commonly used tubes stay in place for six to nine months and require follow-up visits until they fall out.
If placement of the tubes still doesnt prevent infections, a doctor may consider removing the adenoids to prevent infection from spreading to the eustachian tubes.
You May Like: Is It A Uti Or Kidney Infection
About Dr Cathy Barnette Dvm
Dr. Barnette is a veterinarian and freelance writer based in Florida. Her 14 years of experience in small animal clinical practice have allowed her to witness firsthand the communication gaps that often exist between pet owners and members of the veterinary team. Her goal is to create engaging content that educates owners, empowering them to make the best possible decisions for their pets. Dr. Barnette has two cats of her own, in addition to a dog and a pet dove.
How Can I Tell If My Child Has An Ear Infection
Most ear infections happen to children before theyve learned how to talk. If your child isnt old enough to say My ear hurts, here are a few things to look for:
- Tugging or pulling at the ear
- Fussiness and crying
- Fluid draining from the ear
- Clumsiness or problems with balance
- Trouble hearing or responding to quiet sounds
Don’t Miss: Can A Uti Feel Like A Yeast Infection
How K Health Can Help
Did you know you can access online urgent care with K Health?
Check your symptoms, explore conditions and treatments, and if needed, text with a healthcare provider in minutes.
K Healths AI-powered app is HIPAA compliant and is based on 20 years of clinical data.
K Health has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references.
What Is The Treatment For Ear Infections
Medications used to treat ear infections include:
- Pseudoephedrine to ease ear pressure
- Antibiotic ear drops for infections of the ear canal
- Steroid ear drops for infections of the ear canal
- Oral antibiotics for infections of the middle ear , and severe infections of the outer ear
For mild cases of ear infection, doctors often recommend watching and waiting before starting use of antibiotics, as many cases will go away on their own. Consult your childs pediatrician before giving any over-the-counter medications to your child.
Home remedies to relieve symptoms include:
- Warm compresses applied to the area to help soothe pain
- Over-the-counter pain eardrops
Read Also: Can A Bladder Infection Stop Your Period