Recommended Regimens For Primary Prophylaxis
The Adult and Adolescent Opportunistic Infection Guidelines provide recommendations for preferred and alternative agents for Pneumocystis pneumonia primary prophylaxis .
- Preferred Therapy: Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is the preferred agent for Pneumocystis pneumonia prophylaxis in individuals with HIV and studies have shown that either a double-strength tablet or a single-strength tablet taken daily is effective in preventing Pneumocystis pneumonia.
- Alternative Therapy: If a patient cannot tolerate daily dosing of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, there are several alternative regimens:
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole .
- Dapsone once daily: Prior to starting dapsone, it is necessary to check a glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase level since dapsone may trigger hemolytic anemia in patients who have G6PD deficiency.
- Atovaquone once daily: Although atovaquone has efficacy similar to dapsone for Pneumocystis pneumonia prophylaxis, it is considerably more expensive and available only as a liquid formulation.
- Inhaled pentamidine: Aerosolized inhaled pentamidine is conveniently dosed once monthly, but it is contraindicated for use in persons with underlying reactive airways or pulmonary disease, penetrates poorly to the peripheral regions of the lung, lacks of systemic protection against P. jirovecii, and must be administered in a clinic or hospital setting using a special Respirgard II nebulizer.
What Is An Opportunistic Infection
In a healthy and normal functioning immune system, these pathogens do not usually cause infection, or they may cause very mild disease. Apart from advanced HIV infection, Opportunistic Infections may affect people who are on chemotherapy for cancer, immunosuppression for autoimmune diseases or post-organ transplant, among other conditions. In HIV, many of these Opportunistic Infections are what we also term as AIDS-defining illnesses that is, if these infections are found in someone who has HIV, we would classify them as having AIDS . Many of the symptoms and signs of late-stage HIV infection are due to these Opportunistic Infections rather than directly from the virus itself.
What is HIV Treatment?
HIV treatment and management consists of taking a set of correct HIV medicines to delay the control HIV, monitoring for and treating any opportunistic infections, and taking care of the patients general health and well being.
Determination Of Hiv And Cd4t Cells
HIV was determined following the method of . The presence of HIV-1 antibodies in the serum was determined using rapid HIV-1 diagnostic test kits following the manufacturersâ instructions. The sera were first tested with Determine HIV-1/2. Negative results were further tested with Capillus HIV-1/2. If the result of Capillus was found negative, then the serum was considered as negative for HIV antibodies. HIV positive cases showed two red lines/band and HIV negative cases showed one red band. FACS count microbead-based system is a microbead-based single-platform instrument that was used to count CD4T cells and other helper cells in the whole blood. The blood sample was put in a twin-tube reagent tubes, fluorochrome-labeled antibodies in the reagents binded specifically to lymphocyte surface antigens. A fixation solution was added, the sample was run on the instrument. The calculation of absolute CD3, CD4 and CD8 T-cells was determined automatically by using built-in Attractors software programme.
Overview
Advances in antiretroviral therapy have made it possible for people with HIV to live longer and healthier lives. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , 1.1 million Americans were living with HIV at the end of 2015.
Read Also: Bladder Infection Every Time I Have Intercourse
What Can People With Hiv Do To Prevent Getting An Oi
For people with HIV, the best protection against OIs is to take HIV medicines every day.
People living with HIV can also take the following steps to reduce their risk of getting an OI.
Avoid contact with the germs that can cause OIs.
The germs that can cause OIs can spread in a variety of ways, including in body fluids or in feces. To avoid sexually transmitted diseases or infections, use condoms every time you have sex. If you inject drugs, do not share drug injection equipment. After any contact with human or animal feces, wash your hands thoroughly with warm, soapy water.
Ask your health care provider about other ways to avoid the germs that can cause OIs.
Be careful about what you eat and drink.
Food and water can be contaminated with OI-causing germs. To be safe, do not eat certain foods, including undercooked eggs, unpasteurized dairy products or fruit juices, or raw seed sprouts.
In addition, do not drink water directly from a lake or river. For more information, read the HIV and Nutrition and Food Safety fact sheet from HIVinfo.
Travel safely.
If you are visiting a country outside the United States, avoid eating food and drinking water that could make you sick. Before you travel, read the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention fact sheet on Traveling with HIV.
Get vaccinated.
Talk to your health care provider about which vaccines you need. To learn more, read the HIVinfo fact sheet on HIV and Immunizations.
What Are Some Of The Most Common Opportunistic Infections
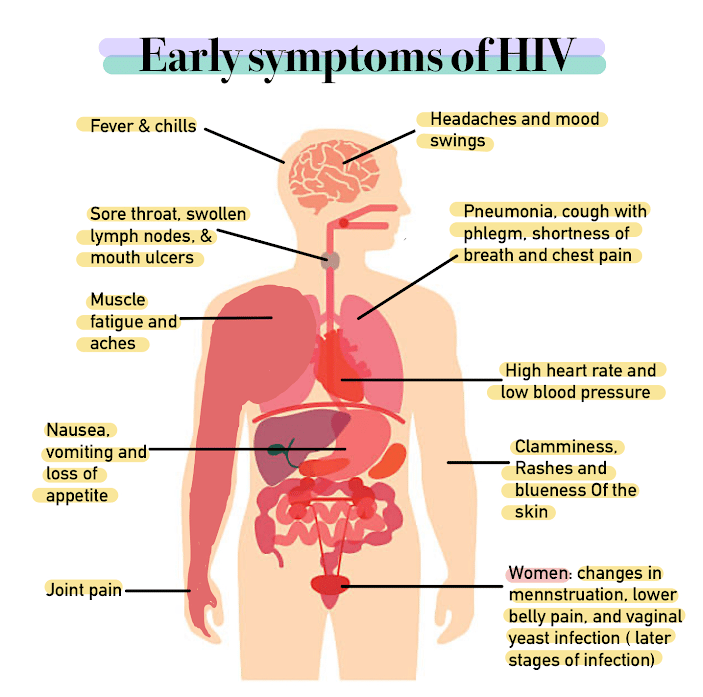
Some of the most common OIs in people living with HIV in the U.S. are:
- Herpes simplex virus 1 infectiona viral infection that can cause sores on the lips and mouth
- Salmonella infectiona bacterial infection that affects the intestines
- Toxoplasmosisa parasitic infection that can affect the brain
Visit CDC for a detailed list.
Read Also: Meds Good For Sinus Infection
Hiv And Opportunistic Infections
When someone with HIV has a weakened immune system , they are at risk of opportunistic infections. These are illnesses that are more common among those with weak immune systems. If your immune system is strong, it can normally stop you from getting these infections.
Common opportunistic infections associated with HIV include:
- cryptococcal meningitis
- oesophageal candidiasis
- certain cancers, including Kaposis sarcoma.
If you have a low CD4 count, there are medicines available that can prevent opportunistic infections. However, being on effective ART and keeping your CD4 count up is the best way to avoid opportunistic infections.
Head Eyes Ears Nose And Throat Findings
Parotid enlargement is observed in 30% of children with category C disease and in 15% of children with disease in other categories.
Tonsillar hypertrophy may be observed. Aphthous ulcers may be observed.
Thrush in the oral cavity and posterior pharynx is observed in approximately 30% of HIV-infected children. In children with AIDS, the prevalence of thrush is correlated with a low CD4+ count. Thrush in the posterior pharynx may signify candidal esophagitis, especially in patients with feeding difficulties or retrosternal pain.
CMV retinitis occurs in 3.4% of children with CD4+ counts of less than 50/mL.
Don’t Miss: How To Get An Ear Infection
Limitation Of The Study
Since the nature of the data collection was retrospective, the study relied on the available information for the number and types of diseases reported during follow-up. Therefore some data might be missed. Some of the diagnoses were not clinical as there was limited capacity to make definitive diagnoses.
The Magnitude Of Opportunistic Infections And Associated Factors In Hiv
Teklay Zeru Weldearegawi, Hadgu Gerensea, Hagos Berihu, Gebreamlak Gidey, Mebrahtom Zeru Welearegay
Corresponding author: Teklay Zeru Weldearegawi, Department of Nursing, College of Health Sciences, Aksum University, Aksum, Ethiopia
Received: 05 Dec 2018 – Accepted: 04 Mar 2020 – 17 Apr 2020
Domain: Palliative care
Keywords: AIDS, opportunistic infections, WHO clinical stage, CD4 count, southern zone Tigray
©Teklay Zeru Weldearegawi et al. Pan African Medical Journal . This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Teklay Zeru Weldearegawi et al. The magnitude of opportunistic infections and associated factors in HIV-infected adults on antiretroviral therapy in southern zone Tigray, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. Pan African Medical Journal. 2020 35:126.
Available online at:
Research
You May Like: What Antibiotics For A Urinary Tract Infection
Primary Prophylaxis And Preemptive Therapy Not Recommended
The most important way to prevent CMV end-organ disease in persons with HIV is to use antiretroviral therapy to restore and optimize immune system function in those with severe immunosuppression. In the pre-antiretroviral era, one study that evaluated oral ganciclovir for primary prophylaxis showed a reduction in CMV disease, but use of ganciclovir for prophylaxis was not recommended due to toxicity and cost. Another more recent trial evaluated preemptive valganciclovir therapy for patients with a CD4 count less than 100 cell/mm3 and CMV viremia, but this strategy of preemptive therapy was not protective. Thus, in the modern antiretroviral therapy era, the Adult and Adolescent Opportunistic Infection Guidelines do not recommend prophylactic or preemptive therapy as a strategy to prevent CMV disease.
Operational Definition Of Variables
In this study, an event was considered when HIV-infected child developed any form of OIs after ART initiation during the follow-up period.
Censored was recorded when HIV-infected children dropped or transfer out to other health institutions or are still on active ART follow-up, but did not develop any OIs by the end of the study.
ART adherence was classified as good, fair, or poor, according to the percentage of drug dosage calculated from the total monthly dose of ART drugs. Good was reported with compliance equal to or greater than 95% or3 missed doses per month fair reflected 8594% compliance and between 4 and 8 missing doses per month) and poor reflected less than 85% compliance or9 missed dose per month) .
Child developmental status was classified as appropriate , delayed and regression .
Children with weight/age Z-score< 2 SD, height/age Z-score< 2 SD, and weight/height Z-score< 2 SD were considered to be underweight, stunted, and wasted respectively .
CD4 counts or percentage below the threshold was considered if the child had CD4 cell counts < 1500/mm3 or 25% for age< 12months, CD4 cell counts < 750/mm3 or< 20% for age 1235months, CD4 cell counts < 350/mm3 or< 15% for age 3659months, and CD4 cell counts < 200/mm3 or< 15% for age60months .
You May Like: Emergency Antibiotics For Tooth Infection
Opportunistic Infections In Hiv
Overview
Advances in antiretroviral therapy have made it possible for people with HIV to live longer and healthier lives. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , 1.1 million Americans were living with HIV at the end of 2015.
However incredible the advances in care, people who are HIV-positive still have an important role to play in safeguarding their health. They should work closely with their healthcare providers and stay on top of their antiretroviral therapy. They also need to protect themselves from opportunistic infections, which are a serious threat to anyone living with HIV.
Opportunistic Infections Free Survival Time Of Predictor Variable
The result of this study showed the OI-free survival time of patients classified as bedridden functional status was less when compared to patients classified as working active status. Additionally, adult patients with poor ART drug adherence had less OI free survival time than patients with good ART drug adherence.
|
Figure 3 KaplanMeier survival curves to compare the OIs-free survival time of PLWHIV on ART with different categories of functional status at Dessie Comprehensive Specialized Hospital from January 2015 to December 2020. |
|
Figure 4 KaplanMeier curves of OI-free survival proportion based on adherence to ART drugs at Dessie Comprehensive Specialized Hospital from January 2015 to December 2020. |
You May Like: Prednisone Prescribed For Sinus Infection
Data Collection Procedures And Quality Assurance
The data extraction form was based on The Federal Ministry of Healths HIV-care/ART follow-up and intake records which are currently used in Ethiopian ART clinics. The data extraction form included the following variables: socio-demographic characteristics, ART and other medication, clinical and laboratory-related information. Data was collected over three weeks in April, 2021 by three BSc well prepared nurses in the ART clinic of DCSH. To ensure data quality, a well-adapted data extraction form from a standardized ART intake and follow-up form was used, and data collectors took one day training. All the filled variables were double-checked for completeness by taking some randomly selected cards and the supervisor carefully monitored the entire data collection process. The predictor variables were recorded at the baseline and occurrences of OI were registered during follow up period based on the health professionals reporting on the patient chart. Before data entry, data were checked for completeness and consistency.
Opportunistic Infections You Need To Know About
The CDC has made a list of more than 20 serious diseases that can become OIs if you have HIV/AIDS. You might have one of these diseases and be healthy enough to fight it off normally, but if it is hard to get rid of and lasts too long, it is considered an OI.
If you have one or more of the diseases on the CDC’s list, you could be considered to have AIDS that’s why the CDC calls them AIDS-defining conditions. Here are the most common OIs:
- Cytomegalovirus, a viral infection that can cause blindness
- Herpes simplex virus, which can cause a serious outbreak of cold sores
- Mycobacterium avium complex, a bacterium that causes fever, digestive problems, and weight loss
- Pneumocystis, a fungal infection that can cause a severe type of pneumonia
- Toxoplasmosis, a protozoal infection that can cause brain damage
- Tuberculosis, a bacterium that can infect both your lungs and your brain
- Kaposi’s sarcoma, a cancer often marked by red, purple, brown, or black skin blotches or nodules
Other OIs include lymphoma, encephalopathy , and wasting syndrome, often marked by weight loss, ongoing fever, diarrhea, and malnutrition.
Read Also: How To Avoid Bladder Infections After Intercourse
Why Do People With Hiv Get Ois
Once a person has HIV, the virus begins to multiply and damages the immune system. A weakened immune system makes it harder for the body to fight off OIs.
HIV medicines prevent HIV from damaging the immune system. But without treatment with HIV medicines, HIV can gradually destroy the immune system and advance to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome . Many OIs, for example, certain forms of pneumonia and TB, are considered AIDS-defining conditions, which are infections and cancers that are life-threatening in people with HIV.
Patient Education And Screening Examinations
Recognizing early signs of CMV-related disease and implementing appropriate therapy will diminish the severity of disease. Individuals with HIV and advanced immunosuppression should be educated about the warning signs of active CMV retinitis, including floaters, flashing lights, or any decrease in vision. In addition, since some individuals may be asymptomatic early on in CMV retinitis, most experts recommend a formal ophthalmologic examination for any person with HIV with a CD4 count less than 50 cells/mm3 to rule out evidence of retinitis in the era prior to the use of modern antiretroviral therapy, some experts recommended performing ophthalmologic examinations every 3 to 4 months in these patients. The screening ophthalmologic examination is particularly important for patients anticipating starting antiretroviral therapy, since patients with untreated or unrecognized CMV retinitis are at significant risk of developing CMV immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome following initiation of antiretroviral therapy.
Recommended Reading: What Do Doctors Prescribe For Yeast Infections
You May Like: How To Know A Tooth Is Infected
Talking To Your Healthcare Professional About Hiv And Other Health Conditions
If youre managing another health condition alongside HIV, its important to make sure your healthcare professionals communicate well. Often, youll see one healthcare professional for HIV and another for the other condition.
In some cases, drugs for another condition can interact with your HIV treatment, making one or both of them less effective or unsafe, so its important that your healthcare professionals know about the drugs youre taking.
Ideally, your healthcare professionals should talk to each other directly, but this isnt always possible. The more you learn and understand about your health, the more you can help the flow of information between those supporting you.
It can be helpful to take some notes with you to each appointment such as the names of any drugs you are taking, and any symptoms you want to talk about.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Management of HIV patients is best accomplished with the help of an interprofessional team of healthcare professionals that includes the infectious disease specialist, pharmacist, internist, infection control specialty nurses, and other specialists depending on the organ infected. This approach demonstrates the best chances for optimal patient care and therapeutic success.
The pharmacist has to emphasize medication compliance and regular follow up of HIV seropositive individuals. Education on the importance of checking serial CD4+ counts and its implications in initiating chemoprophylaxis to prevent opportunistic infections must be emphasized at every clinic visit. Safe sex practices, needle disposal education in intravenous drug users are highly encouraged to reduce the spread of HIV infection.
Recommended Reading: Activated Charcoal For Tooth Infection
Why Opportunistic Infections Occur
Opportunistic infections are the result of a weakened immune system. In the case of HIV, the virus targets the immune system by depleting CD4 T lymphocytes . CD4 cells are lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell that is vital to helping the body fight off infections by coordinating the immune response.
When an HIV infection occurs, CD4 cells are progressively depleted, leading to immunosuppression and an immunocompromised state. This is why people with HIV are more prone to opportunistic infections and why cases of OIs are more severe in those with HIV.A normal CD4 cell count is between 500 and 1,500. When immunosuppression occurs, CD4 counts fall below 500. A CD4 count lower than 200 is considered to be AIDS.
How Is Pcp Treated
For many years, antibiotics were used to prevent PCP in cancer patients with weakened immune systems. It was not until 1985 that a small study showed that these drugs would also prevent PCP in people with AIDS.
The success in preventing and treating PCP is dramatic. Percentages have been cut by about half for PCP as the first AIDS-defining diagnosis, and for PCP as the cause of death of people with AIDS.
Unfortunately, PCP is still common in people who are infected with HIV for a long time before getting treatment. In fact, 30% to 40% of people with HIV develop PCP if they wait to get treatment until their CD4 cell counts are around 50.
A new anti-PCP drug, DB289, is being studied in a Phase II trial. Early clinical trials showed very good results.
The drugs now used to treat PCP include TMP/SMX, dapsone, pentamidine, and atovaquone.
- TMP/SMX is the most effective anti-PCP drug. Its a combination of two antibiotics: trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole .
- Dapsone is similar to TMP/SMX. Dapsone seems to be almost as effective as TMP/SMX against PCP.
- Pentamidine is a drug that is usually inhaled in an aerosol form to prevent PCP. Pentamidine is also used intravenously to treat active PCP.
- Atovaquone is a drug used in people with mild or moderate cases of PCP who can not take TMP/SMX or pentamidine.
Read Also: Is A Uti The Same Thing As A Bladder Infection