What Are Symptoms Of Ear Infections
Symptoms of ear infections include:
Additional signs of ear infections in young children and infants may also include:
- Pulling on the ear/rubbing the ear
- Fussiness
Middle ear infection is usually caused by:
- Bacteria the most common bacterial causes include:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Flu
Infections of the ear canal are usually caused by water that remains in the outer ear canal for an extended period of time, which, when combined with the earwax and debris already present in the ear canal, provided a moist environment for bacteria or yeast to grow and cause infection. While its commonly called swimmers ear, diving or bathing and showering can also permit just enough water into the ear to create a fertile breeding ground for infection.
How Can I Prevent My Child From Getting An Ear Infection
- Wash your childs hands and your own often to reduce the chance of catching a cold.
- Breastfeed your baby.
- Avoid bottle-feeding your baby when they are lying down. Never put your baby to bed with a bottle.
- Transition your baby from a bottle to a cup by 1 year of age.
- Dont use a pacifier too often.
- Dont smoke, and keep your child away from any secondhand smoke. Exposure to smoke can increase the risk of ear infections.
- Ensure your child gets the pneumococcal vaccine .
- Ensure your child gets a flu shot every year.
Pediatricians Urged To Treat Ear Infections More Cautiously
- EmbedEmbed
Giancario Gemignani-Hernandez, 2, of Pittsburgh has his ear examined by Dr. Alejandro Hoberman. Gene J. Puskar/APhide caption
toggle caption
Giancario Gemignani-Hernandez, 2, of Pittsburgh has his ear examined by Dr. Alejandro Hoberman.
Hoping to reduce unnecessary antibiotics use, the American Academy of Pediatrics on Monday issued new guidelines for how doctors should diagnose and treat ear infections.
Every year, millions of parents take their children to the pediatrician for ear infections, and most of them end up going home with antibiotics. In fact, ear infections are one of the most common reasons kids see doctors and the leading reason kids get antibiotics.
“Parents, if their child is up all night screaming and tugging the ear, they want something to make the child feel better,” says Dr. Richard Rosenfeld of the State University of New York Downstate Medical Center, who helped write the new guidelines.
But about 70 percent of children get better on their own within two or three days, and about 80 percent are better within a week to 10 days, he says.
And he says there are some real downsides to using antibiotics when they’re not necessary: They can cause upset stomachs, allergic reactions and other problems. And they can contribute to the development of superbugs infections that are getting harder and harder to cure.
The first thing the new guidelines say is: Make sure the child really has an ear infection.
Correction Feb. 25, 2013
You May Like: What Antibiotic Is Prescribed For Ear Infection
What Are The Symptoms Of A Middle
Common symptoms of a middle-ear infection in adults are:
-
Pain in 1 or both ears
-
Drainage from the ear
-
Sore throat
You may also have a fever. Rarely, your balance can be affected.
These symptoms may be the same as for other conditions. Its important totalk with your health care provider if you think you have a middle-earinfection. If you have a high fever, severe pain behind your ear, orparalysis in your face, see your provider as soon as you can.
Who Should Use Antibiotic Eardrops

Antibiotic eardrops can be more effective and safer for:
- People with Swimmers Ear, an infection caused by water in the ear.
- Children who have tubes in their ears. The tubes prevent most infections behind the eardruman area known as the middle ear. If there is an infection, antibiotic eardrops can be given right through the tube.
Don’t Miss: Can A Bladder Infection Stop Your Period
What Are The Disadvantages Of Ototopical Antibiotics
Ototopical antibiotics have a few disadvantages as well, which include the following:
Difficulty in delivery
Direct delivery at the infection site may be difficult or impossible sometimes. The medication may fail to reach the infected area in the middle ear if the ear canal is blocked due to:
- Excessive and hardened earwax
- Block in the ear tubes inserted for fluid drainage from the middle ear
- Swollen or overgrown tissue
Steps must be first taken to clear the blocks before antibiotic administration. Irrigating the ear canal can easily clear a block caused by earwax and other secretions, but an ear tube block and granulation each may require some procedure and other medications.
Ototoxicity
Ototoxicity is toxicity to the ear from local administration. Ototoxicity can irritate and inflame the mucus membranes of the middle ear. If the antibiotic enters the inner ear, it may lead to:
- Vertigo
- Sensitivity reaction
Ototopical antibiotics can cause allergic reactions. Low-grade sensitivity reactions may cause persistent drainage that may be impossible to distinguish from drainage due to infection, making treatment difficult. Some people may also develop cross-sensitivity to related antibiotics.
Absence of systemic effect
Alteration of microenvironment
Common Ear Infections Don’t Need Antibiotics Health Watchdog Says
Children should not be routinely given antibiotics for ear infections, watchdog says, amid concerns about overuse reducing effectiveness of antibiotics
Children with common ear infections should not be given antibiotics, a health watchdog has said.
New draft guidance from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence says parents should treat the infections with paracetamol or ibuprofen instead. It comes a few days after the US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention also warned parents that antibiotics are not suitable for many common conditions.
On Facebook, it said: Antibiotics are not effective against viral infections like the common cold, flu, most sore throats, bronchitis, and many sinus and ear infections. Taking antibiotics can also have harmful side effects for you or your child.
The Nice guidance relates to acute otitis media an infection that occurs in the middle ear and is common in children and young people.
Evidence from Nice found that about 60% of children will show signs of improvement such as less pain within 24 hours, even if they have not taken antibiotics. Nice said some children may need antibiotics immediately, such as those who are very unwell or have symptoms of a more serious illness.
Children with discharge from the ear caused by a burst ear drum should be offered antibiotics immediately or given a prescription to use if symptoms do not improve, or get worse, within three days.
Also Check: Can An Ear Infection Go Away On Its Own
How Do You Prevent Ear Infections
You may be able to prevent ear some ear infections if you:
- Use earplugs when swimming or diving
- Dry ears thoroughly after swimming
- Never use cotton swabs inside the ear canal
- Wash hands properly to prevent the spread of viruses
- Use soap and warm water and wash for at least 20 seconds
Antibiotics For Yeast Infection
Christina Wedberg
Christina Wedberg
Christina has been a writer since 2010 and has an M.F.A. from The New School for Social Research. Christina specializes in writing about health issues and education.
A yeast infection, also known as vaginal candidiasis, is a vaginal infection.
In 92% of cases, the infection is caused by a type of yeast called Candida albicans. The remainder of yeast infections are caused by a fungus known as Candida. These fungi are normally present in warm and moist areas of the human body, and between 20% to 50% of all women carry this yeast without having any associated symptoms.
However, when Candida albicans multiplies out of control, it causes an infection, which can lead to inflammation, itching, discharge, and an unpleasant odor.
Recommended Reading: How To Make A Tooth Infection Stop Hurting
Do You Need Antibiotics
Your physician may recommend a watch-and-see approach rather than prescribing antibiotics right away. Typically, you will keep an eye on symptoms for three days to see if they improve. This approach usually is used for children whose ear infections cannot be definitively diagnosed or who are under the age of 2.
If the infection does not clear up, you will need antibiotics. In some cases, a doctor will write you a prescription just in case the infection does not clear up.
If the ear infection is caused by a virus, antibiotics will not be prescribed because they do not work against viruses. Relieving symptoms while keeping an eye on the progression of the infection is the best course of treatment for a viral ear infection.
Living With An Ear Infection
If your child suffers from several ear infections each year, youll want to look out for symptoms every time they have a stuffy nose or congestion.
Never stick anything in your childs ear to relieve the pain of an ear infection, to remove the tubes or remove a foreign object. See your childs doctor to have it removed.
Don’t Miss: Eye Infection In Dogs Medication
Should I Take My Piercing Out If Its Infected
When to remove a piercing
If a new piercing is infected, it is best not to remove the earring. Removing the piercing can allow the wound to close, trapping the infection within the skin. For this reason, it is advisable not to remove an earring from an infected ear unless advised by a doctor or professional piercer.
Cause Of Ear Infections
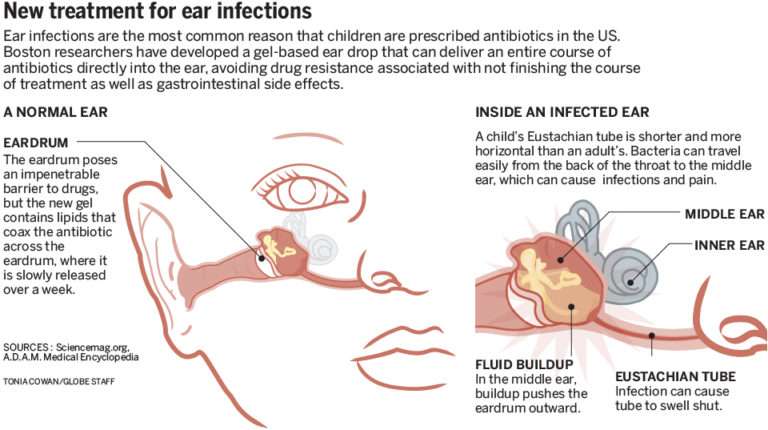
- A bacterial infection of the middle ear
- Blocked eustachian tube, usually as part of a common cold. The eustachian tube joins the middle ear to the back of the throat.
- Blockage results in middle ear fluid .
- If the fluid becomes infected , the fluid turns to pus. This causes the eardrum to bulge out and can cause a lot of pain.
- Ear infections peak at age 6 months to 2 years. They are a common problem until age 8.
- The onset of ear infections is often on day 3 of a cold.
- How often do kids get ear infections? 90% of children have at least 1 ear infection. Frequent ear infections occur in 20% of children. Ear infections are the most common bacterial infection of young children.
Read Also: Antibiotic Cream For Ear Infection
When You Need Themand When You Dont
Many children get ear infections. The infections are usually in the middle ear behind the eardrum. They may be caused by bacteria or by a virus. Doctors often treat bacterial infections with antibiotics. Antibiotics are strong medicines that kill bacteria.
Infants and some babies and children do need antibiotics.
But using antibiotics too often can be harmful. Heres why:
In most cases, antibiotics are not needed.
- They do not work for ear infections caused by viruses.
- They do not help the pain.
- Usually, viral infections and many bacterial infections go away on their own in two to three days, especially in children who are over two years old.
First, call the doctor and treat the pain.
If you suspect your child has an ear infection, you should call the doctors office and describe the symptoms. Usually, your doctor should ask you to wait a few days before bringing your child in.
The main sign of an ear infection is pain, especially on the first day. Or, a child may have a fever.
Start by giving your child an over-the-counter pain reliever, such as:
- acetaminophen .
- ibuprofen .
Antibiotics do not relieve pain in the first 24 hours. They only have a small effect on pain after that. So, pain relievers are an important treatment, and usually they are the only treatment needed.
When is treatment with antibiotics needed?If the infection is very painful and lasts more than a few days, chances are it is a bacterial infection.
02/2021
How To Use Ear Drops
Prior to using ear drops, you should always read the instructions provided to you with your prescription. You can also speak to your pharmacist or doctor for advice on using them. The following instructions will help you use ear drops correctly.
For adults:
- Lie down on a flat surface with a folded towel beneath your head and the affected ear facing the ceiling.
- Pull your earlobe up to straighten out the ear canal.
- Administer the appropriate number of drops into the ear.
- Push the ear flap gently to help ease the drops into the ear.
- Remain in this position for up to two minutes to ensure that the ear canal is fully coated with medicine.
For children:
- Have the child lie on the floor or bed with a towel beneath their head and their affected ear facing the ceiling.
- Hold their head still if they are squirming or fidgeting.
- Pull the earlobe out and down to straighten their ear canal..
- Administer the recommended number of drops
- Press on their ear flap or place a cotton ball gently into the ear and let it remain in position for several minutes to ensure that the medication coats the inside of their ear.
The process for infants is similar to children, but you can also cradle your infant while you administer the drops in an appropriate position that allows the medication to go into their ear properly.
You May Like: Gargle Salt Water For Tooth Infection
What Research Is Being Done On Middle Ear Infections
Researchers sponsored by the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders are exploring many areas to improve the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of middle ear infections. For example, finding better ways to predict which children are at higher risk of developing an ear infection could lead to successful prevention tactics.
Another area that needs exploration is why some children have more ear infections than others. For example, Native American and Hispanic children have more infections than do children in other ethnic groups. What kinds of preventive measures could be taken to lower the risks?
Doctors also are beginning to learn more about what happens in the ears of children who have recurring ear infections. They have identified colonies of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, called biofilms, that are present in the middle ears of most children with chronic ear infections. Understanding how to attack and kill these biofilms would be one way to successfully treat chronic ear infections and avoid surgery.
Understanding the impact that ear infections have on a childs speech and language development is another important area of study. Creating more accurate methods to diagnose middle ear infections would help doctors prescribe more targeted treatments. Researchers also are evaluating drugs currently being used to treat ear infections, and developing new, more effective and easier ways to administer medicines.
What Are Symptoms Of An Ear Infection
Ear infections most often occur in the middle part of the ear. Ear infections in children commonly include the following symptoms:
-
Pulling at one or both ears
-
Crying
-
solution
Your doctor will assess the type of bacteria likely causing your ear infection to determine which antibiotic to give you. Most people begin feeling relief within 24 hours of starting a course of antibiotics, and symptoms should improve significantly within 48-72 hours.
Also Check: Will Prednisone Help With Ear Infection
Should My Child See Her Pediatrician For An Ear Infection
In some cases with older babies and toddlers, mild symptoms may go away on their own. But if your child is under 6 months old, has a high fever, severe pain, drainage or swelling in the ear, its time to call your pediatrician. However, your doctor wont necessarily prescribe antibiotics right away. Ear infections are caused by both bacteria and viruses, so antibiotics arent always the solution. According to the American Academy of Family Physicians, there are several reasons why doctors dont prescribe antibiotics for every ear infection:
- Antibiotics dont work for ear infections caused by viruses.
- Antibiotics dont help the pain associated with ear infections
- Infections from both viruses and bacteria often disappear without antibiotics in a few days, especially in children over two years old.
- Physicians are keenly aware that the overprescription of antibiotics makes vital medicines less effective, so we work hard to use them only when truly necessary. In many cases, your doctor will watch the infection for a few days to see if it goes away on its own.
Preventing Ear Infections In The First Place
The AAP also recommends taking measures to reduce risk factors for ear infections, especially during infancy. These include breastfeeding for at least six months, never giving a baby a bottle while she’s lying down, and weaning from a pacifier after six months. And kids of all ages should be kept away from second-hand smoke.
Don’t Miss: Natural Antibiotics For Dental Infection
Where Is The Middle Ear
The middle ear is behind the eardrum and is also home to the delicate bones that aid in hearing. These bones are the hammer , anvil and stirrup . To provide the bigger picture, lets look at the whole structure and function of the ear:
The ear structure and function
There are three main parts of the ear: outer, middle and inner.
- The outer ear is the outside external ear flap and the ear canal .
- The middle ear is the air-filled space between the eardrum and the inner ear. The middle ear houses the delicate bones that transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. This is where ear infections occur.
- The inner ear contains the snail-shaped labyrinth that converts sound vibrations received from the middle ear to electrical signals. The auditory nerve carries these signals to the brain.
Other nearby parts
- The eustachian tube regulates air pressure within the middle ear, connecting it to the upper part of the throat.
- Adenoids are small pads of tissue above the throat and behind the nose and near the eustachian tubes. Adenoids help fight infection caused by bacteria that enters through the mouth.