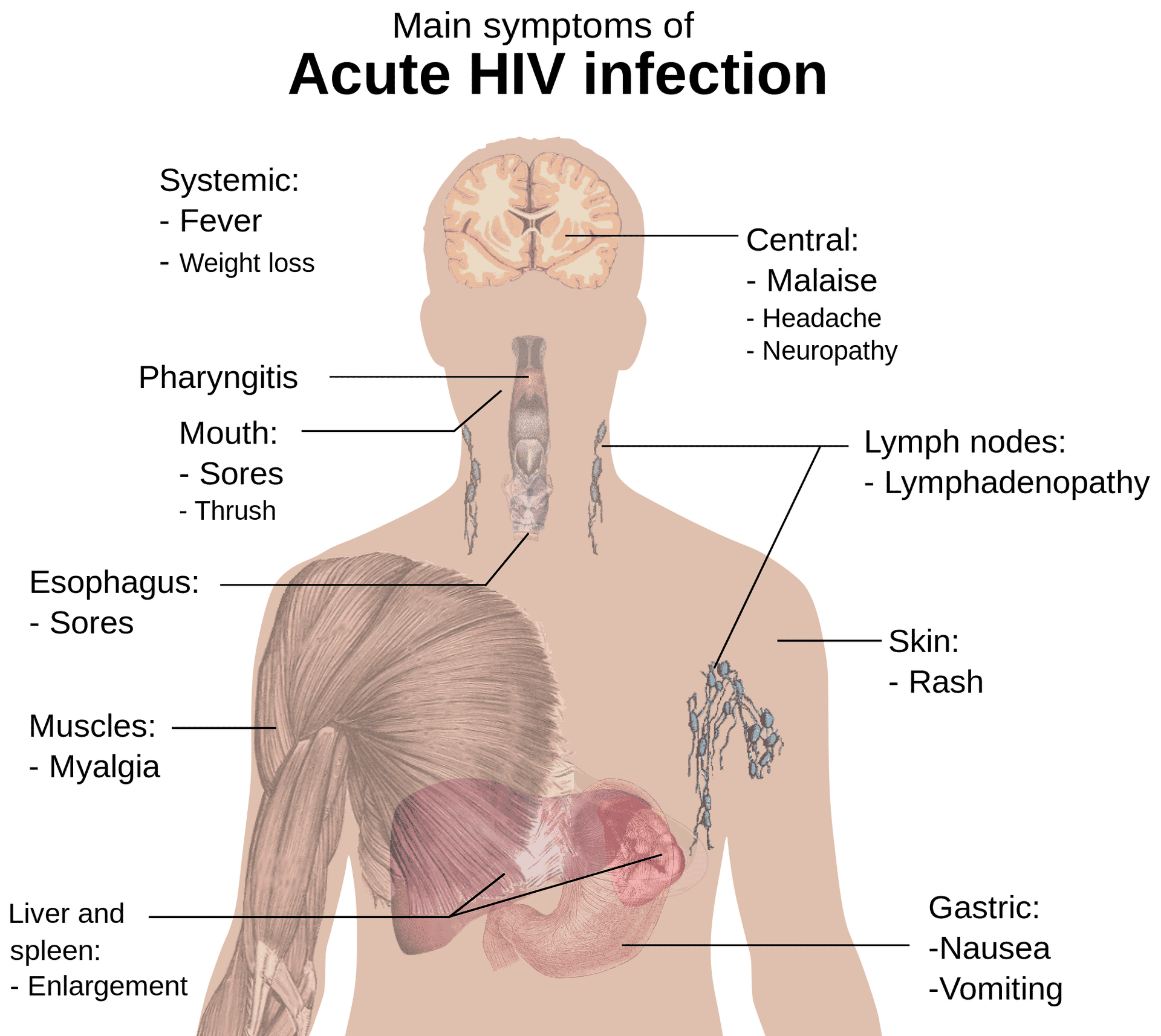
First Stage: Acute Hiv Infection Symptoms
Most people dont know right away when theyve been infected with HIV. But they may have symptoms within 2 to 6 weeks after theyâve gotten the virus. This is when your bodys immune system puts up a fight. Its called acute retroviral syndrome or primary HIV infection.
The symptoms are similar to those of other viral illnesses, and theyre often compared to the flu. They typically last a week or two and then go away. Early signs of HIV include:
- Headache and other neurological symptoms
If you have symptoms like these and might have come into contact with someone with HIV in the past 2 to 6 weeks, go to a doctor and ask that you get an HIV test. If you donât have symptoms but still think you might have come into contact with the virus, get tested.
Early testing is important for two reasons. First, at this stage, levels of HIV in your blood and bodily fluids are very high. This makes it especially contagious. Second, starting treatment as soon as possible might help boost your immune system and ease your symptoms.
A combination of medications can help fight HIV, keep your immune system healthy, and keep you from spreading the virus. If you take these medications and have healthy habits, your HIV infection probably wonât get worse.
Recommended Reading: How Long After Contracting Hiv Do You Get Symptoms
Clinical Latency Stage Of Hiv Infection
The symptoms during ARS may last for a few weeks, according to the National Institutes of Health.
After this point, the infection progresses to the clinical latency stage, a period during which the virus reproduces at very low levels, but it is still active.
Also known as asymptomatic HIV infection or chronic HIV infection, the clinical latency stage typically causes no HIV-related symptoms.
For people who are not taking any anti-retroviral medication for their infection, the clinical latency stage lasts for 10 years, on average, but it may progress quicker.
ART, though, can keep the virus from growing and multiplying, prolonging the clinical latency state for several decades.
Its important to note that people living with HIV in the clinical latency stage are contagious and can still transmit the virus to other people. But, as the CDC notes, people who take ART exactly as prescribed and maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their HIV negative-partner through sex.
What Comes First Hiv Or Aids
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome is the most severe stage of the infection caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus . People always develop an HIV infection first. If left untreated, the virus damages your immune system, and you develop AIDS.
Two measurements help determine the severity of your HIV infection: your viral load the amount of virus in your blood and your level of CD4 immune cells. These cells help your body fight off infections and are targeted by the virus.
The higher your viral load and the lower your CD4 count, the closer you progress from the early stages of HIV infection to AIDS.
Recommended Reading: Chances Of Being Infected With Hiv Without Condom
Barriers To Hiv Prevention
Some people living with HIV or at risk for HIV may have less access to preventive care, testing and treatment regimens. They may also live in an environment that makes it difficult to talk about HIV infection. Specific factors include:
- Lack of financial resources
- Lack of convenient, affordable health care
- Fear of violent reactions from partners, particularly for those abusive relationships
- Less access to transportation
- Homelessness, making it difficult to stick with treatment regimens, store medications and eat consistently healthy meals
- Lack of emotional or physical support
- Added responsibility of caring for others, especially children, that can make it difficult to care for themselves and take their medicines
- Fear of telling their family about their HIV
Fortunately, there are resources available for people who are diagnosed with HIV to help them overcome many of these challenges.
Stages Of Hiv Infection
Stages of Infection
There are four stages of HIV and as with all illnesses, how it progresses, how long it takes and the affect it has on the individual depends on a number of factors for example, general health, lifestyle, diet etc.
Stage 1: Infection
HIV quickly replicates in the body after infection. Some people develop short lived flu-like symptoms for example, headaches, fever, sore throat and a rash within days to weeks after infection. During this time the immune system reacts to the virus by developing antibodies this is referred to as sero-conversion.
Stage 2:Asymptomatic
As the name suggests, this stage of HIV infection does not cause outward signs or symptoms. A person may look and feel well but HIV is continuing to weaken their immune system. This stage may last several years and without a HIV test many people do not know they are infected.
Stage 3:Symptomatic
Over time the immune system becomes damaged and weakened by HIV and symptoms develop. Initially they can be mild but they do worsen, symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, mouth ulcers, thrush and severe diarrhoea. The symptoms are caused by the emergence of opportunistic infections they are referred to as opportunistic infections because they take advantage of a persons weakened immune system. Some examples of opportunistic infections are PCP, toxoplasmosis, TB and kaposi sarcoma.
Stage 4:AIDS/Progression of HIV to AIDS
You May Like: Does Youngboy Really Have Herpes
Recommended Reading: Why Are Diabetics At Risk For Infection
What Are The Symptoms Of Chronic Hiv Infection
The first possible symptoms of HIV infection may develop within 2-4 weeks after youâre exposed to the virus. You might notice flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, and rashes. Or you could have no symptoms at all.
In this first stage of HIV/AIDS the virus reproduces itself very quickly and spreads all over your body. This makes the virus especially easy to transmit to others through sexual contact. The virus starts to destroy infection-fighting cells in your immune system called CD4 T cells, or sometimes just âT cells.â
Once you reach the second stage of HIV/AIDS — chronic HIV infection — the virus has started to reproduce at a far slower pace. Even without treatment, many people in this stage donât notice any HIV-related symptoms for 10 years or more. Thatâs why some doctors also call it âasymptomatic HIV infectionâ or âclinical latency.â
Still, in some cases, you might get mild infections with symptoms like:
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Oral yeast infection
Whether you have symptoms or not, without treatment, HIV continues to take a relentless toll on your immune system. Your HIV levels go slowly up and your CD4 levels go slowly down until the illness progresses to the most serious stage: AIDS.
Treatment during these early stages of the illness can have huge health benefits, especially with an approach known as antiretroviral therapy, or ART.
Understanding The Timeline Of Hiv Symptoms
An HIV infection progresses in three stages. Here is a snapshot of the symptoms you are likely to experience at each of the three stages:
Stage 1 Acute HIV Infection: This stage is the first stage of HIV infection in which the early symptoms start appearing within 2 to 4 weeks after infection. This stage has flu-like symptoms such as:
Some people do not experience any signs at this stage also. In this case, it is known as a latent infection. This asymptomatic stage can last up to nearly ten years or even more in some cases.
Stage 3 AIDS: By stage three of the infection, the infection has advanced to become AIDS. This is the final stage of HIV infection, and by this time, the levels of CD4 cells have fallen below 200 cells per cubic millimeter of blood , indicating that there is widespread damage to your immune system. Common symptoms of this stage include:
- Regular coughing
- Breathing problems
The first noticeable stage of symptoms is known as primary HIV infection or acute retroviral syndrome . It is also commonly just referred to as acute HIV infection. Symptoms at this stage resemble flu-like symptoms, and naturally, many people just end up assuming that they have severe flu instead of HIV infection.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that the first HIV symptoms become apparent around two to four weeks after exposure to the virus.
Also Check: Common Treatment For Sinus Infection
How Long After A Possible Exposure Should I Be Tested For Hiv
It takes the human body three to six months to seroconvert, or recognize the HIV virus in such a way that it would appear positive in a blood test. The amount of time between transmission and seroconversion is called the window period. For the most accurate results, it is best to wait until the three-to-six month window period has passed to get tested.
Getting Tested For Hiv
HIV testing is important. Someone living with HIV who isnt getting treatment can still transmit the virus, even if they have no symptoms. Others may pass the virus to others through an exchange of bodily fluids. But todays treatment can effectively eliminate the risk of transmitting the virus to a persons HIV-negative sexual partners.
According to the CDC , antiretroviral therapy can lead to viral suppression. When someone with HIV can maintain an undetectable viral load, they cant transmit HIV to others. The CDC defines an undetectable viral load as fewer than 200 copies per milliliter of blood.
Taking an HIV test is the only way to determine whether the virus is in the body. There are known risk factors that increase a persons chance of contracting HIV. For example, people whove had sex without a condom or shared needles may want to consider seeing their healthcare professional about getting tested.
Also Check: Eye Infection Not Pink Eye
Signs And Symptoms Of Hiv
Within two to four weeks after infection, its possible for people with HIV to experience flu-like symptoms. Symptoms may include fever, chills, rash, night sweats, and sore throat. This is the first stage of HIV and is referred to as acute HIV infection.
Some of the other symptoms of HIV infection may include:
- Swollen lymph nodes
Symptoms can vary from person to person. Its also possible for people to not feel sick at all after getting infected. The longer someone goes untreated, the higher the likelihood the infection will progress to a later stage.
How Hiv Infects The Body
HIV is a virus that can cause an HIV infection if it gets into our blood stream.
It then goes on to infect our immune system the part of our body that keeps you healthy.
It does this by entering T-helper cells so that our immune system cant find and destroy it. Then it makes copies of itself so it can go on to infect other cells.
This is called the HIV lifecycle and it is how the virus multiplies in our body.
Taking antiretroviral drugs is the only way to interrupt the HIV lifecycle and stay healthy.
Recommended Reading: How To Heal Sinus Infection At Home
Timeline Of Hiv Symptoms
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus is a virus most commonly associated with causing AIDS. This virus attacks the immune system, targeting the bodys natural defense system that protects us against diseases. When you contract HIV, the symptoms start becoming apparent within a few weeks. Flu-like symptoms are the first to appear, which include fever, a tickle at the back of your throat, sore throat, and fatigue. After this stage, the disease tends to remain in an asymptomatic stage until it progresses to AIDS. Left untreated, HIV infection will keep progressing in stages, getting worse over time, and ultimately developing into AIDS. There are three stages of HIV infection, and the symptoms of each of these steps are different from person to person. We take a look at the various symptoms associated with the various stages in this timeline of HIV symptoms.
Symptom : Night Sweats
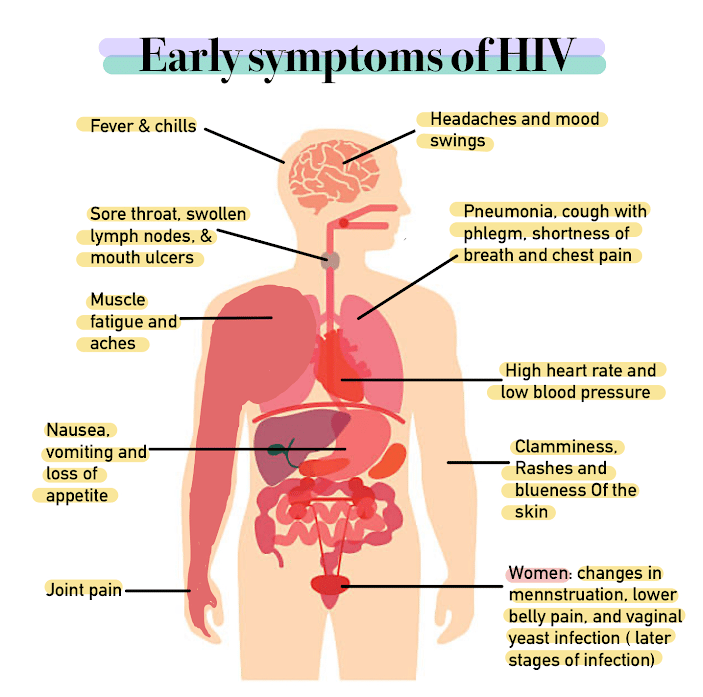
Night sweats are repeated episodes of extreme sweating, causing bedding and any nightclothes to become soaked. Many people will get night sweats during the early stages of HIV. These can be even more common later in infection and arent related to exercise or the temperature of the room.Get tested if symptoms of HIV appear
With such a vast array of symptoms, HIV testing is vital to ensure a proper diagnosis. If you think youve been exposed to HIV, or have an active sex life with casual sex partners, regardless of whether you are showing symptoms of HIV or not, its important to get tested as soon as possible.
If youre in Sydney, you can get a rapid HIV test and STI check-up at a. If youre not in Sydney, you can still get a rapid HIV test and STI check-up using our where to get tested tool here.
You May Like: Signs Your Tooth Is Infected
How Does Chronic Hiv Infection Affect Other Conditions
As more and more people with HIV live into old age, doctors have found that chronic HIV infection might raise your risk for other illnesses like heart disease, high blood pressure, and peripheral neuropathy.
The increases arenât generally huge and scientists arenât yet sure why they happen. But research continues to provide information to help us get to the bottom of these issues.
Show Sources
American Heart Association: âAs HIV patients live longer, heart disease might be their next challenge,â âWhat’s the connection between high blood pressure and HIV?â
Hypertension: âHypertension in HIV-Infected Adults.â
Johns Hopkins Medicine: âHIV Neuropathy.â
Mayo Clinic: âHIV/AIDS.â
Antigen Or Antibody Testing
Antigens are external substances, like virus particles, that enter the body and activate the immune system. Antibodies are the particles the immune system produces to fight infections. This form of testing detects both antigens and antibodies.
Antigen and antibody tests use a finger prick to find signs that a person has HIV. These tests can detect HIV about 1890 days after initial exposure.
Read Also: Best Relief For Tooth Infection
Second Stage: Clinical Latency Symptoms
After your immune system loses the battle with HIV, the flu-like symptoms will go away. But thereâs a lot going on inside your body. Doctors call this the asymptomatic period or chronic HIV infection.
In your body, cells called CD4 T cells coordinate your immune systemâs response. During this stage, untreated HIV will kill CD4 cells and destroy your immune system. Your doctor can check how many of these cells you have with blood tests. Without treatment, the number of CD4 cells will drop, and youâll be more likely to get other infections.
Most people don’t have symptoms they can see or feel. You may not realize that you’re infected and can pass HIV on to others.
If youâre taking ART, you might stay in this phase for decades. You can pass the virus on to other people, but itâs extremely rare if you take your medicines.
What Happens If You Do Treat Chronic Hiv Infection
Itâs important to keep in mind that there is no cure for HIV/AIDS. Once you have the virus, youâll need treatment to keep its worst effects at bay. That said, treatment of chronic HIV infection works very well, especially if you start it early.
Treatment involves antiretroviral therapy, or ART. This is a combination of medicines that helps stop HIV from making copies of itself. That gives your body a chance to raise the levels of CD4 cells that help fight off opportunistic infections.
Properly followed, the right prescription of antiretroviral therapy can bring your HIV viral load down so low that it canât be detected by current blood tests. This not only makes you healthier, it also makes you less likely to pass the virus on to a sexual partner. Someone with an undetectable viral load has almost no chance of passing the virus to a partner.
This undetectable viral load is the goal of ART. Maintain it, and you and your doctors may be able to keep AIDS at bay for decades. This effectively keeps you in this second stage of HIV/AIDS, chronic HIV infection, almost indefinitely.
In fact, most people in the U.S. with HIV who get ART treatment will never develop AIDS.
Also Check: Yeast Infection Medicine For Guys
Latency Causes A Break In Symptoms
After initial exposure and possible primary infection, HIV may transition into a stage called clinically latent infection. Its also referred to as asymptomatic HIV infection due to a noticeable lack of symptoms. This lack of symptoms includes possible chronic symptoms.
According to HIV.gov, latency in HIV infection can last for 10 or 15 years. This doesnt mean that HIV is gone, nor does it mean that the virus cant be transmitted to others. Clinically latent infection may progress to the third and final stage of HIV, also referred to as AIDS.
The risk for progression is higher if a person with HIV isnt receiving treatment, such as antiretroviral therapy. Its important to take prescribed medications during all stages of HIV even if there arent any noticeable symptoms. There are several medications used for HIV treatment.
Is Stage 3 Of Hiv Considered Aids
Once your CD4 cells drop below 200, the HIV has progressed to stage 3, also known as acquired immune deficiency syndrome . During this phase, those who go untreated usually live approximately three years unless they become infected with another illness. During this time, you may become ill from opportunistic infections. These are infections that happen more often due to a weakened immune system. You may experience:
- Recurring fever
- Sever chills at night
- Severe diarrhea that is long-lasting
- Purple spots on your skin
- Consistent breathing problems
- Purple spots on your skin
- Unexplained bruising
Don’t Miss: How Does A Doctor Test For Kidney Infection