What Are Protease Inhibitors And How Do They Work
Protease inhibitors are antiviral drugs used for treating human immunodeficiency virus infections and hepatitis C virus infections.
During infection with HIV or hepatitis C, the HIV or HCV multiply within the body’s cells. Viruses are released from the cells and spread throughout the body where they infect other cells. In this manner, HIV and hepatitis C infection is perpetuated among new cells that the body produces continually. During the production of the viruses, new proteins are made. Some of the proteins are structural proteins that form the body of the virus. Other proteins are enzymes that manufacture DNA and other components for the new viruses. Protease is an enzyme that is used in the formation of new structural proteins and enzymes. Protease inhibitors block the activity of protease and this results in the formation of defective viruses that are unable to infect the body’s cells. As a result, the number of HIV or hepatitis C viruses in the body decreases.
Mechanism Based Strategy For Drug Design
| Fig. 10 FDA approved HIV-1 . |
In the commercially available and some of the that are currently being tested clinically, a nonhydrolyzable hydroxyethylene or hydroxyethylamine moiety is used as the basic core for the development of these . Other noncleavable transition state isosteres have also been used, including statine, norstatine, phosphinate, reduced , dihydroxyethylene,38α-keto amide39 and more recently silicon-based 40. Basically, the core is a good isostere replacement at the scissile bond that is believed to mimic the tetrahedral transition state of the proteolytic reaction. More than 2000 have been developed and most of the effective contain a core structure to mimic the transition state of the protease catalysis. In the crystal structures of HIV-1 PR complexed with these , the central hydroxy group of the core is located between Asp-25 and Asp-25â² and makes favorable electrostatic contacts. It has been shown that the interaction between the two catalytic aspartates and the is worth more than 4 kcal molâ1.41 A review that discusses in detail the various interactions of the different with the binding site has been published.42
| Fig. 11 Noncleavable transition-state isostere developed for the synthesis of HIV PR . |
| Fig. 12 General structure of cyclic urea. Structure of the DMP4550. Schematic interaction of a cyclic urea based with HIV PR. |
Guidelines For Hiv During Pregnancy
Guidelines on management of HIV in pregnancy and postpartum were released on March 14, 2019, by the British HIV Association .
Screening
Pregnant women living with HIV should be offered peer support if it is available.
Evaluation of antenatal and postnatal depression should be made at booking, 4-6 weeks postpartum, and 3-4 months postpartum.
Pregnant women diagnosed with HIV should be screened for sexual health.
Complete HIV drug resistance testing before treatment is initiated except in women presenting after 28 weeks.
Perform a CD4 cell count at the initiation of combination antiretroviral therapy and an additional CD4 count at delivery.
For women who begin cART during pregnancy, perform an HIV viral load 2-4 weeks after starting, at least once every trimester, at 36 weeks, and at the time of delivery.
Perform liver function tests in women who begin cART during pregnancy and again with each routine blood test.
If a patient has started cART during pregnancy and has not suppressed plasma viral load to < 50 HIV RNA copies/mL, recommend an adherence review, resistance testing, therapeutic drug monitoring, regimen optimization, and treatment intensification.
Antiretroviral Therapy During Pregnancy
Continue cART treatment for patients who are conceiving and on an effective cART regimen.
Start ART during pregnancy and advise to continue lifelong treatment for all pregnant women including elite controllers.
All women should have started cART by the 24th week of pregnancy.
Also Check: Oregano Oil For Tooth Infection
How Do Protease Inhibitors Work In Antiretroviral Therapy For Hiv Infection
Once the HIV enters and integrates its genome with the host cells DNA, it makes long chains of HIV proteins. At this stage the virus is immature and noninfectious to other T-cells. The viral DNA then releases an enzyme known as protease, which is essential in breaking up the protein chains to make new functional virus particles.
Protease inhibitors bind to the protease enzyme and inhibit its activity, and prevent the break-up of the protein chains. Formation of new infectious virus particles is then prevented or inhibited.
HIV may eventually mutate and develop resistance to the drugs. Many second-generation protease inhibitors continue to be effective until multiple mutations take place.
Safety And Adverse Events
Common adverse events with the protease inhibitors include fever, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, rash, fatigue, and headache 19 however, AEs vary among agents. In addition to these common effects, several metabolic changes may occur.
In a recent analysis of combined rates and reasons for switching to ARV because of intolerance or toxicity, PIs were identified as being as responsible as NNRTIs for necessitating therapy changes.70 Regimens were changed for 14% of 3,333 patients treated in the Chelsea and Westminster HIV cohort receiving HAART, with most switches occurring after six months of initial therapy. Toxicity was the reason for the switches in 61% of these patients. Further, the observed toxicity switch rate per 1,000 patient-years between PI-based regimens and NNRTI-based regimens did not differ statistically or clinically. The switch rate for patients receiving PIs was 26.4% . The switch rate for patients receiving NNRTIs was 22.2% .
Within the PI class, no statistical or clinically significant differences were noted with respect to the observed toxicity switch rate CIs associated with this rate for all agents overlapped:70
- fosamprenavir, 89.5% 95% CI, 10.8323.5
- saquinavir, 81.2% 95% CI, 37.1154
- lopinavir, 46.9% 95% CI, 22.586.2
- atazanavir, 27% 95% CI, 11.753.2
Notable metabolic changes associated with PIs are discussed in further detail next.
Don’t Miss: Can Urgent Care Treat Urinary Tract Infection
Types Of Protease Inhibitors
Of the 26 drugs approved by the FDA for treatment of HIV, 10 are protease inhibitors.Protease inhibitors usually end in -avir. There are two classes of protease inhibitors: first-generation and second-generation inhibitors. The first-generation protease inhibitors include:
- Indinavir
- Nelfinavir
- Saquinavir
The HIV virus developed mutations to avoid the action of these protease inhibitors prompting scientists to create a new class of drug that could treat HIV-resistant cases.
These second-generation protease inhibitorsthat are now widely and more commonly used in combination AVR therapyinclude:
- Atazanavir, which may be marketed under the name Reyataz, or Evotaz if it is prescribed in a combination tablet.
- Darunavir, which may be marketed under the name Prezista, or Rezolsta and Symtuza if it is prescribed in a combination tablet.
- Lopinavir, which is only available in the combination tablet Kaletra.
The complete list of the ten FDA approved protease inhibitors are:
Qsar Properties Of Carbon Nanotubes And Fullerenes
The modified structure of carbon fullerene suggested to act as HIV-1 protease inhibitor , where the X atom is either O, S or Se. QSAR is useful for expressing the biological activities of the compounds and the outcome of this study concluded that the interaction with oxygen molecule has lowest optimization energy, which makes interaction more stable . Fullerene and its derivatives were investigated by protein-ligand docking and QSAR methods. This revealed that these approaches are able to predict the binding affinities and interactions with HIV-1 protease and it concluded that they showed better interaction with HIV-1 protease, compared to other nanomaterials . The chemical and physical properties of CNTs and carbon fullerene are illustrated in Tables 1.2 and 1.3.
Table 1.2. The Physiochemical Properties of Fullerene C60 That Contribute Probable Drug Like Nature to This Nanolead
| Chemical and Physical Properties |
|---|
| Thickness | 50150 nm |
Don’t Miss: Natural Remedy For Infection In Urinary Tract
Other Sexually Transmitted Disease Testing
Screening for other maternal sexually transmitted diseases is recommended in pregnancy. For example, screening for maternal syphilis is important not only for the prevention of congenital syphilis but also because maternal syphilis has been associated with an increased risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
Vaginal speculum examination should be performed to obtain cervical cytology smear and assays for gonorrhea and chlamydia, as vaginal swabs are preferred over testing other sites in HIV-infected individuals. All sexually transmitted diseases should be treated promptly. Genital warts and vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia are more common among HIV-seropositive than HIV-seronegative women, but wart regression is as common in women with HIV as those without and cancer is infrequent. Women infected with HIV have a higher incidence of cervical dysplasia.
D Printed Physical Model Of Hiv Protease
Shown below are 3D printed physical models of HIV Protease. Both versions are shown in alpha carbon format, with select side chains shown colored by element, with carbon gray, nitrogen blue, oxygen red and sulfur yellow. Both models have been designed with precisely embedded magnets that allow the two chains to pull apart into individual pieces.
The MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling
The MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling uses 3D printing technology to create physical models of protein and molecular structures, making the invisible molecular world more tangible and comprehensible. To view more protein structure models, visit our Model Gallery.
Read Also: Cure Yeast Infection Without Medication
Lipid Profile And Ultrasonography
Other laboratory studies should include a lipid profile, which is not usually obtained in pregnancy. Although cholesterol normally increases in pregnancy, baseline values are required, as certain medications have been associated with increased triglyceride and cholesterol levels.
Initial obstetric ultrasonography for viability and dating is important for determining treatment and planning delivery. Potential teratogenicity is highest during the first trimester, and some patients may consider delaying treatment until after the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. In women who are severely ill, the risks and benefits of this delay must be weighed. Targeted ultrasonography may be warranted depending on medication exposure.
Effects Of Hiv Pis On Apoptosis In Vivo In Non
Most studies that evaluate changes in apoptosis in response to antiretroviral therapies are confounded by at least two factors. First, the majority of these studies evaluate apoptosis changes that occur in patients receiving multiple anti-HIV drugs, commonly one or two PIs in addition to one or two reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Secondly, most of these studies evaluate changes in apoptosis that occur in HIV-infected patients, in whom a decrease in viral replication occurs almost universally, although the magnitude of these viral reductions is highly variable. Since reduced viral burden is likely to impact apoptosis, one cannot confidently ascribe reduced apoptosis solely either to direct drug effect or to reduced virus burden.
Figure 3
Female ND4 mice were anesthetized, the cecum externalized, punctured , and replaced into the peritoneum. Mice received control vehicle gavage, or PI either before or after the CLP as indicated. Mice were followed for 48h, and survival monitored. In separate mice, 12h following CLP, thymus was harvested and analyzed by TUNEL for apoptosis. Reprinted with permission. This research was originally published in Weaver et al. Improved survival in experimental sepsis with an orally administered inhibitor of apoptosis. The FASEB Journal 2004 18:11851191
Recommended Reading: How Does Infection Cause Sickle Cell Crisis
Blood Counts And Viral Load
For pregnant women infected with HIV, in addition to the standard prenatal assessment, continued assessment of HIV status is important. A complete blood cell count to assess anemia and white blood cell count as well as renal and liver function tests should be included. Initial evaluation includes CD4+ counts, which help determine the degree of immunodeficiency.
Viral load, determined by plasma HIV RNA copy number assesses the risk of disease progression. The viral load is important in decisions regarding maternal treatment and delivery management however, because perinatal HIV transmission can occur even at low or undetectable HIV RNA copy numbers, the viral load is not used to decide whether to start antiretroviral medications. Moreover, newer guidelines now recommend initiation of ART for all HIV-infected individuals, regardless of CD4+ count, to reduce the morbidity and mortality associated with HIV infection and the risk of all modes of transmission.
Fighting Drug Resistance: Hiv Protease
HIV protease, an aspartyl protease, is the target of several important antiHIV drugs however, drug-resistant mutants of the protease have emerged. Mutational analysis of clinical isolates has uncovered some of the mechanisms of induced drug resistance. In several cases, HIV protease has incorporated active-site mutations that weaken its binding to the inhibitor. A commonly found active-site mutation, valine 82 to alanine , results in â¼10-fold reduced binding of three marketed drugs. In addition to active-site mutations, many clinical isolates contain mutations distant from the active site. These mutations can effect drug resistance by reducing drug binding, increasing enzyme activity, or acting synergistically with active-site mutations. One example of a synergistic mutation is leucine 63 to phenylalanine, which partially restores the function of the handicapped active-site mutant V82F/I84V. X-ray crystallographic studies are beginning to provide details about the structural consequences of such drug-resistant mutations. Eventually, structureâfunction studies of HIV protease may speed discovery of new therapies by suggesting ways to circumvent mutationally induced drug resistance.
Biswa Ranjan Meher, Seema Patel, in, 2013
Also Check: How Do Doctors Treat Sinus Infections
Role Of Protease In Hiv
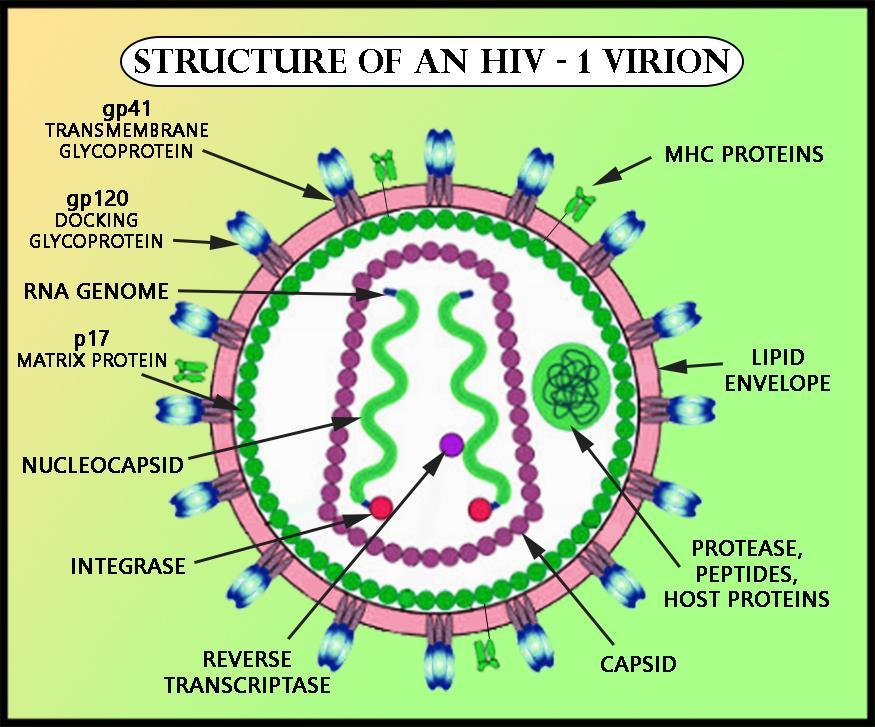
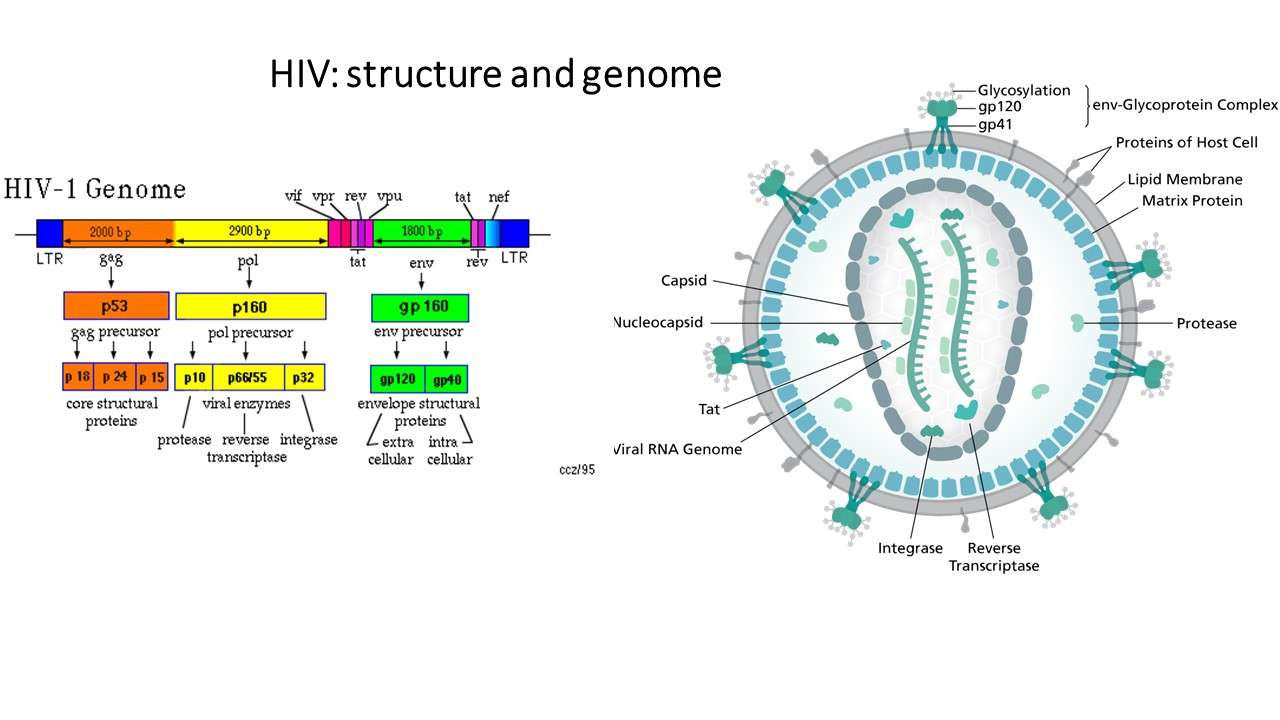
Since viruses are so small they must make maximum use of the minimalgenetic information that they have. HIV does this by making a long polypeptidechains that contains many proteins. These protein precurser, Gag and GagPol must be cleaved by protease at 9 specific points in order to producefunctional proteins. The gag precurser will eventually give rise to structuralproteins and pol precurser will give rise to enzymes such as reverse transcriptase,integrase, and protease. Thus, an HIV specific protease is necessary forthe the HIV to make more functional viruses. The HIV protease is not foundin mammalian cells. The HIV protease is unique in that it can cleave betweena phenylalanine and tyrosine or proline. To look at the reaction click Thisis a very important fact because no human enzyme can cleave between eithertyrosine or phenyalanine and proline. For more information on the geneticsof HIV click here.The HIV Protease is an enzyme with two symmetrical subunits. The activesite is located where the two subunits meet. HIV proteases are asparticacid proteases and thus, aspartate 25 plays a key role in binding the substrate.
How Effective Are Protease Inhibitors Against Hiv
Protease inhibitors arenât used on their own to treat HIV theyâre used together with other treatments.
A method called HAART is an effective and widely accepted treatment method for HIV and AIDS. The effectiveness of the HAART method is based on the use of three or more medications simultaneously to treat HIV. The medications it relies on most heavily are protease inhibitors, along with other therapies.
Although the HAART method for treating HIV is aggressive in nature, it has a proven track record in the prevention of HIV-related deaths. It has even worked to reduce HIV viral loads to undetectable levels.
âWhat does this mean for HIV patients? If you had HIV, then having an undetectable viral load would not mean that you are cured. It would mean, however, that a standard blood test wouldnât trace the HIV in your system.
Thatâs good news, because having undetectable levels of HIV in your system is a sign that you cannot pass HIV on to sexual partners. You may even have a reduced risk of passing HIV on to a child during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
Read Also: My Tooth Is Infected And My Face Is Swollen
Side Effects And Resistance Of Protease Inhibitors
Though the HIV-pr-based therapeutic strategies have achieved considerable success, they are plagued by the challenges of serious side effects and resistance. Conventional protease inhibitors cause side effects such as dyslipidemia, characterized by increased plasma levels of triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and total cholesterol. The abnormal lipid profile predisposes the patients to coronary diseases . Also, certain inhibitors result in insulin resistance, the metabolic dysfunction contributing to cognitive impairment . The administration of several drugs has put selective pressure on HIV leading to frequent mutations and subsequent evolution of resistant forms . Multidrug-resistant HIV has emerged as a cause of treatment failure, morbidity, and mortality. U.S. Food and Drug Administration -approved HIV-pr inhibitor drugs face various degrees of resistance . There have been a large number of computer simulation studies to understand the HIV-pr dynamics and drug resistance behavior primarily using molecular dynamics simulations . The affinity of amprenavir to HIV-pr variants V32I, I50V, I54V, I54M, I84V, and L90M decreased 3- to 30-fold compared to the wild type . The mutation V82T greatly enhances drug resistance of HIV-pr toward darunavir and tipranavir, by altering the hydrophobicity of the binding pocket .
Figure 8.3. Inhibitors of HIV-1 protease that are approved by FDA to treat AIDS and AIDS-related malignancies ).
Treatment Of Patients Whose Initial Pi Therapy Fails
PIs are clearly an important component of effective salvage therapy for patients who have not responded to nucleoside analogue therapy. Indinavir in combination with lamivudine and zidovudine has been shown to be highly effective for patients who have had extensive zidovudine treatment and for patients who have had experience with multiple nucleoside analogues, as long as they are lamivudine-naive . The combination of PI with NNRTIs and nucleosides has also been used successfully as salvage therapy for patients who have had extensive NRTI treatment .
For patients who have persistent or recurrent evidence of HIV replication during therapy with NNRTIs in combination with nucleoside analogues, the use of a combination including a PI also seems to be effective as salvage therapy, although studies have had only short follow-up periods . A good response to PI-based therapy after therapy directed only at the reverse transcriptase enzyme is theoretically plausible.
Initial resistance to nelfinavir may result predominantly from a single-point mutation that conveys limited cross-resistance to other PIs . Ritonavir plus saquinavir-based regimens appear to be less successful after initial failure of an indinavir- or ritonavir-including regimen, in part because of the occurrence of resistance at the time of the switch . However, changing from the initial therapy early after the detection of HIV-1 RNA in plasma may enhance the response to subsequent dual-PI regimens.
Recommended Reading: Swollen Chin From Tooth Infection