Its Not Just A Mans Disease
Approximately one-quarter of people with HIV in the United States are female, the CDC reports, and most were exposed to the virus through heterosexual sex. A woman who is pregnant and has HIV/AIDS can pass HIV to her unborn children during pregnancy she can also transmit the virus during childbirth and when breast-feeding, the CDC says.
Tests For Hiv And Aids
Blood tests are the most common way to diagnose the human immunodeficiency virus , the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome . These tests look for antibodies to the virus that are present in the blood of infected individuals. People exposed to the virus should get tested immediately.
Early testing is crucial with HIV. If you test positive for the virus, you and your doctor can develop a treatment plan to help fight HIV and ward off complications. Early testing also can alert you to avoid high-risk behavior that could spread the virus to others.
Because it can take from six weeks to six months to develop antibodies to the virus, follow-up tests may be needed. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history and risk factors and perform a physical examination.
The primary tests for diagnosing HIV and AIDs include:
UCSF Health medical specialists have reviewed this information. It is for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace the advice of your doctor or other health care provider. We encourage you to discuss any questions or concerns you may have with your provider.
Is Hiv/aids Different In Older Adults
A growing number of older people are living with HIV/AIDS. One reason is because improved treatments are helping people with the disease live longer. Nearly half of people living with HIV in the United States are age 50 and older. Many of them were diagnosed with HIV in their younger years. However, thousands of older people get HIV every year.
Older people are less likely than younger people to get tested, so they may not know they have HIV. Signs of HIV/AIDS can be mistaken for the aches and pains of normal aging. Older adults might be coping with other diseases and the aches and pains of normal aging, which can mask the signs of HIV/AIDS.
Some older people may feel ashamed or afraid of being tested. Plus, doctors do not always think to test older people for HIV. Some people may not have access to high-quality health facilities and services, which can limit their treatment options. By the time the older person is diagnosed, the virus may be in the late stages and more likely to progress to AIDS.
Remember, if you are at risk, get tested regularly for HIV.
For people who have HIV, it is important to start treatment as soon as possible after diagnosis. Treatment can help reduce the level of HIV in the blood to undetectable levels. When treatment makes HIV undetectable, the possibility of spreading the virus to a sexual partner becomes very low. This is known as treatment as prevention .
Also Check: I Think I Have A Kidney Infection
Everyone Should Know Their Hiv Status
Thats why its so important for everyone to know their HIV status. The only way to know for sure whether you have HIV is to get tested.
CDC recommends that everyone between the ages of 13 and 64 get tested for HIV at least once as part of routine health care. If your behavior puts you at risk after you are tested, you should think about being tested again. Some people who remain at higher risk should get tested more often.
Hiv Is An Infection That Can Lead To Aids
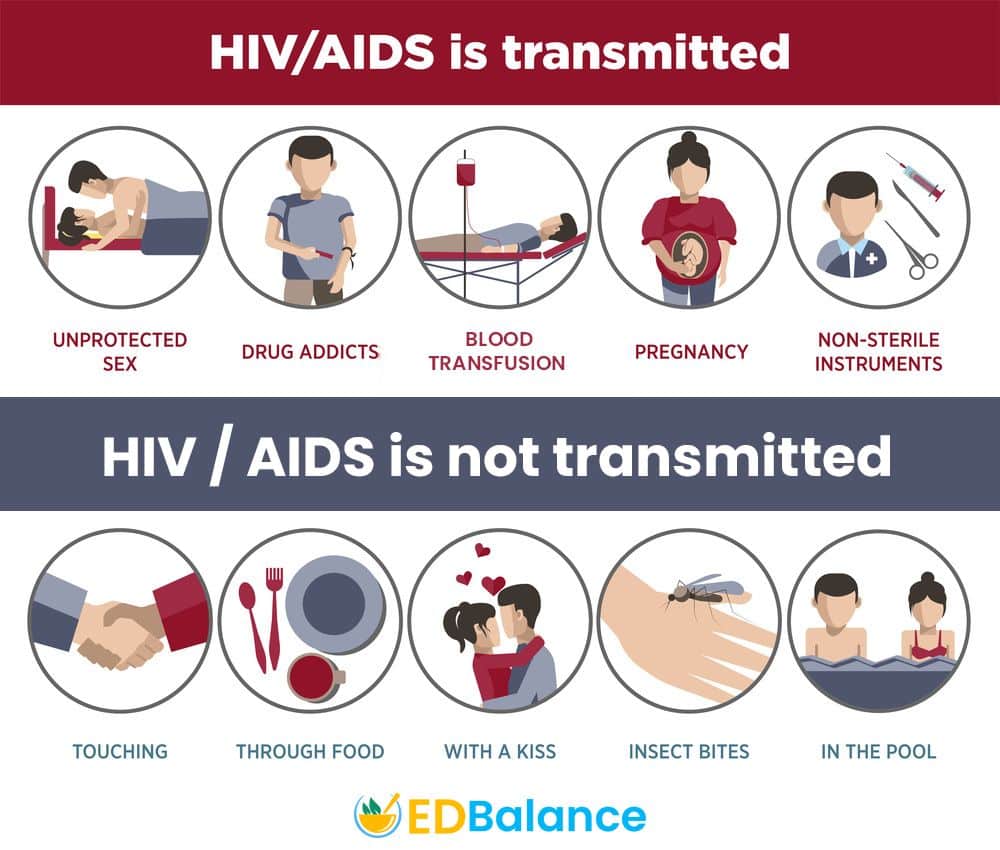
When HIV is left untreated, it can wreak havoc on a persons immune system. As this happens, the body is less able to fight off infections. AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome, which means the immune system has been made less effective by HIV. When this happens, a person is considered to have an acquired immune deficiency or AIDS.
Its important to note that you cannot have AIDS without being infected with HIV. But people can, and do, live long lives with HIV and never develop AIDS.Once you have HIV, the virus stays in your body for life. Theres no cure for HIV, but medicines can help you stay healthy. HIV medicine lowers or even stops your chances of spreading the virus to other people. When your viral load is undetectable or you can no longer detect the virus in your body, you cant pass HIV to your partner.
Thats why treatment is so necessary. With the proper care and medication, people with HIV can live long and healthy lives. Find a provider near you today.
You May Like: Describe The Relationship Between An Hiv Infection And Aids
New Hope For Stopping Hiv
Testing and Medical Care Save Lives
About 1.2 million people in the US are living with HIV.
1 in 5
Nearly 1 in 5 people with HIV dont know they are infected, dont get HIV medical care, and can pass the virus on to others without knowing it.
1 in 4
Only 28% of people with HIV are taking HIV medicine regularly and have their virus under control.
Too many people dont know they have HIV . About 1.2 million people are living with HIV in the US but about 240,000 dont know they are infected. Each year, about 50,000 people get infected with HIV in the US. Getting an HIV test is the first step to finding out if you have HIV and getting medical care. Without medical care, HIV leads to AIDS and early death.
Theres new hope today for stopping HIV in the US. Medicines can lower the level of virus in the body. ART helps people with HIV live longer, healthier lives and also lowers the chances of passing HIV on to others. However, only 28% are getting the care they need to manage the disease and keep the virus under control. To help stop HIV, get tested. If you have HIV, get medical care and work with your health care provider to control the virus and not pass it on to others.
Many people dont know they have HIV or take all the actions to control it.
Testing: More people need to be tested for HIV.
Treating: Many people with HIV do not receive the medical care they need.
HIV care in the United States
1.2 million people are living with HIV
A Sexually Transmitted Infection
Katie Salerno/Flickr Creative Commons
If you have a sexually transmitted infection , there is a chance you may have HIV as well.
Some STIs like syphilis and herpes cause open sores that make it easier for HIV to get inside the body.
STIs like gonorrhea and chlamydia cause inflammation in the genitals that attract the immune cells that HIV likes to target and infect.
Having syphilis can increase your risk of HIV by as much as 500%. Other STIs can also raise your risk for HIV. You should be tested for HIV if you test positive for any STI.
Also Check: Does Amoxicillin Help With Bladder Infection
What Is Hiv What Is Aids
HIV is a virus that damages and weakens the body’s immune system the system your body uses to fight off infection and disease. Having HIV puts a person in danger of experiencing other life-threatening infections and certain cancers.
When the body cannot fight off infections and some other diseases anymore, HIV can lead to a serious illness called AIDS. When someone has AIDS, they are more likely to get infections, and more vulnerable to unusual forms of cancers and other serious diseases. But, with early and uninterrupted treatment, it is possible that a person with HIV will never develop AIDS.
If you think you may have HIV, you should get tested. Everyone age 13 to 64 should be tested at least once for HIV. If you are over 64 and are at risk for HIV, talk with your doctor. Your doctor can help determine how often you should be tested and help find ways to reduce your risk.
There are drugs that, when taken consistently, can help suppress the amount of HIV in your blood to undetectable levels, improving your health overall and making it harder to pass HIV on to your sexual partners. To get the best results, it is important to start treatment as soon as possible. If you are unsure about your HIV status, get tested. Always protect yourself and your partners when having sex or using needles.
Can Medications Prevent Hiv
There are medications that can help prevent HIV in people who have been exposed or are at high risk for exposure. These include pre-exposure prophylaxis and post-exposure prophylaxis .
Pre-exposure prophylaxis
PrEP is a pill you take every day if you dont have HIV but are at high risk of getting infected.
- You have a sexual partner with HIV.
- You havent consistently used a condom.
- In the past six months, youve been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease .
PrEP is also recommended if you dont have HIV, you inject drugs and at least one of the following is true:
- You inject drugs with a partner who has HIV.
- You share needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
PrEP is not a replacement for other preventative measures. You should still use condoms and avoid sharing needles to inject drugs while taking PrEP.
Post-exposure prophylaxis
PEP uses HIV medicines to try to prevent an HIV infection soon after you are exposed. PEP is for those who dont have HIV or dont know if they have HIV and think theyve been exposed through consensual sex, sexual assault, shared needles , or work.
You must start PEP within 72 hours of exposure and take it every day for 28 days. PEP is only for emergency use and does not replace other precautions, like condom use.
You May Like: Can Antiviral Medication Cause Yeast Infections
What Is The Treatment For Hiv
Individuals who are HIV positive will likely need to see a specialist. As with many other conditions, early detection offers more options for treatment. Today, there are medical treatments that can slow down the rate at which HIV weakens the immune system. However, there are other treatments that can prevent or cure the conditions associated with HIV. Anti-retroviral drug therapy may be given to a pregnant woman, which has proven to greatly reduce the chance of an infant developing HIV. A cesarean section may be recommended to reduce infant transmission from the birth canal. In the U.S., where other feeding options are available, an infected mother should be discouraged from breastfeeding her infant. Consult your child’s doctor for more information regarding various drug therapies.
Side Effects Of Hiv Treatment
People on current HIV treatments may experience mild side effects including:
- tiredness and fatigue
If you are on treatment, see your doctor every 3 to 6 months.
Regular blood tests are necessary to make sure your treatment is working and not causing serious side effects. It is recommended that you also get tested for STIs and talk to your doctor about your sexual health and overall wellbeing. Ensure you are having routine screening for cancers and keeping your vaccinations up to date.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Yeast Infection Without Antibiotics
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can live and long and healthy life and will not transmit HIV to your HIV-negative partners through sex.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Its important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
Was Able To Identify The Time He Seroconverted Because He And His Partner Tested Together And His
Some people experienced a ‘seroconversion illness’ with lack of energy, tiredness, sweats, joint pains, flu-like symptoms, gum infections, weight loss, glandular fever like symptoms and rashes. One man said he had lost a stone in weight and, not suspecting the cause, had been rather pleased. During a seroconversion illness people may take a few months to become HIV positive. One man’s doctor told him, ‘Even though your tests are negative, I am convinced you are HIV positive.’ Many other people did not recall having a seroconversion illness either because it was too mild or they did not experience any symptoms. Other people did not want to know if the symptoms they had were due to HIV because of fear. One man who had a seroconversion illness said he, ‘Could not afford to think about it.’
People sometimes got an HIV diagnosis at the time of seroconversion particularly if they were very ill and needed to be hospitalised. Some gay men knew about seroconversion illness and strongly suspected what was happening to them when they had symptoms. Others said they or their health professionals sometimes mistook their seroconversion illness for allergies, a bad flu, glandular fever or even syphilis. After seroconversion people usually become well and it can be many years before they develop any HIV-related illnesses or AIDS if at all.
When and how infection happenedPeople believed they were infected in a wide range of ways including:
You May Like: Yeast Infection Make You Pee A Lot
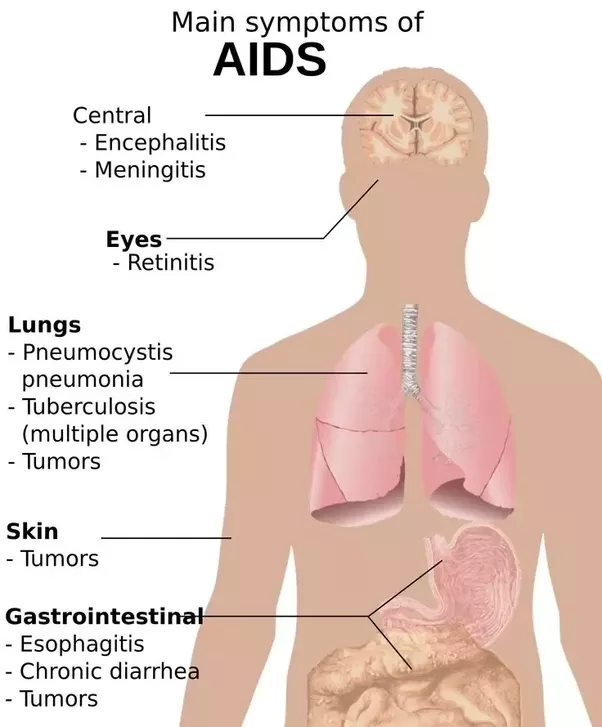
Many People Have No Symptoms But Watch For These
Unexplained rash, swollen lymph nodes, oral thrush, night sweats, and sudden and unexplained weight loss are all possible signs of HIV. Having a sexually transmitted infection isn’t a physical sign of HIV, but it does indicate a greater risk of having HIV as well.
The signs or symptoms of human immunodeficiency virus are not always obvious, though. And in fact, most people who have HIV do not exhibit any of them. Signs of HIV can also depend on whether a person is in the new or persistent stage of infection.
Only an HIV test can tell you for sure if you have the virus. Still, it is important to know about these six common signs and symptoms of HIV, especially if you are someone who is considered to be at higher risk for infection. This article explains each of them.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
U.S. National Library of Medicine / National Institutes of Health
A rash is often the first sign of HIV, but it only appears in 2 of every 5 newly infected people.
An HIV rash looks a certain way: large areas of flat, reddened skin peppered with tiny bumps.
The rash can be itchy or painful. Once a person gets the rash, flu-like symptoms are also common.
The HIV rash usually starts two to six weeks after exposure to the virus and will go away within one to two weeks. The rash is widespread and mainly affects the trunk and face, but can also be on the arms, legs, hands, and feet.
Hiv Among Youth In The Us
Protecting a Generation
1 in 4 new HIV infections occurs in youth ages 13 to 24 years
12,000
About 12,000 youth in 2010, or about 1,000 per month, were infected with HIV.
About 60% of all youth, with HIV do not know they are infected, are not getting treated, and can unknowingly pass the virus on to others.
About 50,000 people are infected with HIV each year, and 1 in 4 is 13 to 24 years old. Youth make up 7% of the more than 1 million people in the US living with HIV. About 12,000 youth were infected with HIV in 2010. The greatest number of infections occurred among gay and bisexual youth. Nearly half of all new infections among youth occur in African American males.
The risk for HIV for most youth begins when they start having sex or start injecting drugs. HIV causes a serious infection that, without treatment, leads to AIDS and early death. All youth should know how HIV is transmitted and prevented, understand what puts them at risk for HIV, and be tested if they are at risk.
Many people get infected with HIV as a teen or young adult
New HIV infections in youth in 2010
Most youth are not getting tested for HIV
Many factors put youth at risk
Preventing risky behaviors in youth
Youth can
Parents and families can
Health care providers can
Everyone can
Don’t Miss: Sphenoid Sinus Infection Neck Pain
Second Stage: Clinical Latency Symptoms
After your immune system loses the battle with HIV, the flu-like symptoms will go away. But thereâs a lot going on inside your body. Doctors call this the asymptomatic period or chronic HIV infection.
In your body, cells called CD4 T cells coordinate your immune systemâs response. During this stage, untreated HIV will kill CD4 cells and destroy your immune system. Your doctor can check how many of these cells you have with blood tests. Without treatment, the number of CD4 cells will drop, and youâll be more likely to get other infections.
Most people don’t have symptoms they can see or feel. You may not realize that you’re infected and can pass HIV on to others.
If youâre taking ART, you might stay in this phase for decades. You can pass the virus on to other people, but itâs extremely rare if you take your medicines.
How Is Hiv Not Spread
HIV is not spread by:
- Mosquitoes, ticks, or other insects
- Saliva, tears, sweat, feces, or urine that is not mixed with the blood of a person with HIV
- Shaking hands hugging sharing toilets sharing dishes, silverware, or drinking glasses or engaging in closed-mouth or social kissing with a person with HIV
- Drinking fountains
- Other sexual activities that dont involve the exchange of body fluids .
Read Also: Keflex For Tooth Infection Dosage