You Can Choose Not To Have Sex
You might not be ready to have sex if:
- you aren’t sure about it
- you feel pressured, scared or uncomfortable
- you need to get drunk or high to do it.
- your partner is not ready
- you can’t talk to your partner about safer sex, birth control or STI
- you or your partner could get pregnant but don’t want a baby and don’t use birth control
- you don’t have condoms or dental dams to protect yourself and your partner
Text box 4
STI rates are the highest among Canadians 25 years or younger. If you choose to have sex, remember to always use condoms and/or dental dams.
Health Services For Screening And Treatment Of Stis Remain Weak
People seeking screening and treatment for STIs face numerous problems. These include limited resources, stigmatization, poor quality of services and often out-of-pocket expenses.
In many settings, STI services in low- and middle-income countries are often neglected and underfunded. These problems lead to difficulties in providing screening for asymptomatic infections, insufficient number of trained personnel, limited laboratory capacity and inadequate supplies of appropriate medicines.
Read Also: How To Heal Kidney Infection Naturally
Sexually Transmitted Infections In Hiv/aids
King-Man HO
Sexually transmitted infections can broadly be defined as infections that are transmissible through sexual contact. Many enteric infections may also be grouped under this category because of their faecal oral route of transmission sometimes associated with sexual activities. For simplicity of discussion, STI in this chapter refers to infections that are predominantly transmitted through sexual contact. Common viral STI include anogenital herpes, anogenital human papilloma virus infection. Common bacterial STI include syphilis, gonorrhoea, and Chlamydia trachomatis . Other common STI agents include Trichomonas vaginalis, and Phthirus pubis.
Also Check: Yeast Infection Resistant To Monistat
Stis And Hiv In The Female Genital Tract
There are a large series of reports of detection of HIV virus in the female genital tract with a wide variety of STIs -. Graham and colleagues sought to understand how genital ulceration impacted cervical and vaginal shedding of HIV-1 in women receiving ART in Kenya . Among 145 women who initiated ART, 36 developed a genital ulcer after at least two months of ART ten women had detectable HIV-1 RNA in their genital secretions. King and colleagues followed 1114 women initiating ART to determine factors that influence viral shedding. During 5.8% of patient visits , HIV-1 RNA was detected in genital secretions but not blood plasma. The median concentration of HIV-1 RNA in genital secretions was between 1000 and 5000 copies/mL. As time on ART increased, the proportion of women with detectable genital HIV-1 RNA decreased. Correlates of detectable HIV-1 RNA in the genital tract in women with undetectable HIV in blood included more advanced WHO stage of disease, the presence of an ulcerative STI, cervical tenderness and the antiretroviral combination employed. The latter observation emphasizes differences in the pharmacology of ART in the male and female genital tract that can influence the suppression of replication of HIV , -.
Will Treating Stds Prevent Me From Getting Hiv
No. Its not enough.
If you get treated for an STD, this will help to prevent its complications, and prevent spreading STDs to your sex partners. Treatment for an STD other than HIV does not prevent the spread of HIV.
If you are diagnosed with an STD, talk to your doctor about ways to protect yourself and your partner from getting reinfected with the same STD, or getting HIV.
Dont Miss: Is Zpack Good For Tooth Infection
Recommended Reading: I Need Antibiotics For Sinus Infection
What To Expect During Testing
The health care provider will ask you questions about your sexual activity. This will help them decide what kinds of testing, physical examination and treatment you need. They may ask about:
- type of sex you’re having
- this will determine where on your body may have been exposed to STI
Each test is different, and will depend on:
- the STI that you’re being tested for
- the health care provider’s assessment
Your health care provider may collect a urine sample to test for:
Your health care provider may recommend other tests depending on the situation.
Tell your health care provider if you want a support person in the room during your examination.
You may see the terms STI and STBBI when reading about getting tested. STBBI stands for sexually transmitted and blood-borne infections. The term takes into account that some infections can be transmitted through the blood in a non-sexual context, like HIV and hepatitis C.
What Is Consent And What Is Sexual Assault
Consent is when you and your partner feel informed and freely agree to participate in any sexual activity. Your body is yours alone and only you can give your consent.
If one of you is drunk, on drugs, or feels forced, consent has not actually been given. And even if you originally said “yes”, you can still change your mind. Saying “no” at any time still means “no.” Any type of sexual activity without your consent or your partner’s consent is sexual assault.
You may feel pressured to have sex
Pressure to engage in sexual activity can come from many sources, including someone you know well, such as a classmate, friend or partner, someone who has been bullying you , or someone you have chatted with or ‘met’ on a dating site or hookup app.
Sexting is considered a risky sexual activity, even though it isn’t physical and won’t cause an STI. Sexting usually involves sending sexually explicit pictures and/or texts online. Once those images or words are sent, you have no control over whether or not they will be shared with other people.
Text box 5
Visit Sex & U for more information on consent, sexual assault and online safety.
If you think you’ve been sexually assaulted, it’s not your fault. Don’t hesitate to seek help. Find a sexual assault crisis centre near you.
Read Also: How Soon After Hiv Infection Can You Infect Others
Age And Sex Distribution
In 2018, more than three quarters of reported chlamydia cases were among people less than 30 years of age. This is similar to what is seen in gonorrhea, but in contrast to infectious syphilis, in which the same age groups accounted for only 37.8%. People between the ages of 15 to 24 accounted for more than half of the reported chlamydia cases in 2018.
Overwhelmingly, females accounted for the majority of cases in the younger age groups. Females less than 30 years of age accounted for 48.9% of all cases in 2018, whereas males of the same age group accounted for 27.1% of all cases. Nearly one-quarter of all cases occurred in females between the ages of 20 and 24 years. Among cases 30 years of age and older, males accounted for the majority of cases.
The highest rates of reported chlamydia cases were among the 20 to 24 year age group , followed by the 15 to 19 and 25 to 29 year age groups .
Figure 3. Rates of reported chlamydia cases in Canada, by age group and year, 2009-2018*
*2018 data does not include British Columbia.
This graph presents the overall rates of reported chlamydia cases by age group, between 2009 and 2018, in Canada. The horizontal axis shows the calendar years from 2009 to 2018. The vertical axis shows the rate of reported chlamydia cases per 100,000 population for age groups from under 15 years old to 60 years old and over.
| Year |
|---|
| 8.0 |
*2018 data does not include British Columbia.
*2018 data does not include British Columbia.
| Age groups |
|---|
| 3.6 |
| Year |
|---|
| 12.9 |
| Year |
|---|
| 3.6 |
Illustrations Of Sexually Transmitted Diseases And Hiv/aids Pdf
For students of all the branches of medicine and surgery and health professionals that aspire to be greater and better at their procedures and medications. A renowned book by those who have read it and learnt from it. Many have already ordered it and is on the way to their home. Whether you work in the USA, Canada, UK or anywhere around the world. If you are working as a health professional then this is a must read.. The most reviewed on book Sexually Transmitted Diseases and HIV/AIDS PDF is available for grabs now here on our website free. Whatever books, mainly textbooks we have in professional courses specially Medicine and surgery is a compendium in itself so understand one book you need to refer another 2-10 books. Beside this there are various other text material which needs to be mastered!! Only reference books are partially read but all other books have to be read, commanded and in fact read multiple times.
The Writers
Prof. Vinod Kumar Sharma Professor of Dermatology, Venerology and Leprology, Director HIV Clinical Research Programme, Human Health Care and Research Foundation, India
Proportions of Sexually Transmitted Diseases and HIV/AIDS PDF
- Publisher : Viva Books 2nd edition
- Language : English
- Dimensions : 7.87 x 5.51 x 1.57 inches
Read Also: Common Urinary Tract Infection Antibiotics
How Long Does It Take For An Std To Show Up
This question is often difficult to answer. There are more than 20 types of sexually transmitted diseases , and many do not cause noticeable symptoms. In other cases, symptoms may not develop until several months or even years after exposure.
Instead of asking how long it takes for STD symptoms to show up, the better question may be how long does it take for antibodies to develop? When you are exposed to germs, such as the various viruses and bacteria that cause STDs, your bodys immune system produces special antibodies to fight off the specific invader. In fact, many forms of STD testing screen for certain antibodies, not the virus or bacterium itself.
The time between exposure and when a measurable amount of antibodies or symptoms are present is known as an incubation period. The incubation periods for STDs vary significantly here are just a few examples of STD incubation periods:
- Gonorrhea One to 28 days
- Genital and oral herpes Two to 12 days
- Trichomoniasis Five to 28 days
- Chlamydia One to three weeks
- HIV Two to four weeks
- Hepatitis B Eight to 22 weeks
- HPV One month to 10 years
- Syphilis Three weeks to 20 years
How Long After Sex Do Sti Symptoms Appear
25 October 2021
Realising you have contracted an STI is a shock for anyone but heading immediately to a private health clinic isnt always the correct solution and may result in a wasted trip.
In this blog we will discuss how long after sex you will begin to experience STI symptoms, how soon you should get a private STI test, and whether some STI symtoms can be mistaken for a UTI.
Recommended Reading: Have Uti Symptoms But No Infection
How Common Are Stds
STDs are common, especially among young people. There were 26 million new sexually transmitted infections in 2018 in the United States. About half of these infections are in people between the ages of 15 and 24. Young people are at greater risk of getting an STD for several reasons:
- Young womens bodies are biologically more prone to STDs.
- Some young people do not get the recommended STD tests.
- Many young people are hesitant to talk openly and honestly with a doctor or nurse about their sex lives.
- Not having insurance or transportation can make it more difficult for young people to access STD testing.
- Some young people have more than one sex partner.
What If Youve Never Been Screened For Stis Before Where Do You Start
If youve never been screened before and want to, congratulations on deciding to take your sexual health into your own hands. Seriously, the importance of this step cant be overstated!
Start by finding a testing center near you by checking out this STI testing center guide. Before you head to the testing spot, make sure they test for all the STIs youre interested in getting tested for. Some clinics only test for HIV, for example.
Most testing centers only test for genital gonorrhea, genital chlamydia, HIV, and syphilis unless asked otherwise, Gersh notes.
Don’t Miss: Prescribed Medicine For Yeast Infection
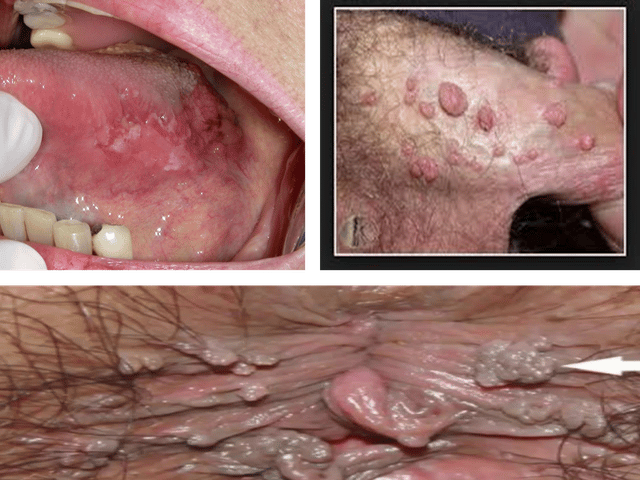
What Is Syphilis
Syphilis is classified as a sexually transmitted infection and is typically passed from one person to another via sexual activity. Contrary to popular belief, though, you can get syphilis non-sexually. In fact, there are a few ways you can contract this infection even if you dont engage in any kind of sex.
This STI is diagnosed when a certain kind of bacteria, treponema pallidum, proliferates on male or female sex organs. Generally speaking, its passed on by skin-on-skin contact. There are different stages of syphilis, and it is most contagious during the stage where sores or rashes are found on the skin.
Once you contract syphilis, you might not know you have it for a few days or even a few months. The early symptoms of syphilis are subtle, but if youre able to catch this infection early on, you have a much better chance of treating it. If it is left untreated for an extended period of time, you could experience brain damage, heart disease, or even death.
How To Stay Safe
So, what can you do to stay safe?
When used correctly, condoms offer one of the most effective methods of protection against STIs, including HIV. Female condoms are also effective and safe.
We are often not aware that they may have an STI.
Any sexually active person can catch an STI, those who change partners frequently or do not use condoms are at higher risk. Previous successful treatment for an STI doesn’t make you immune to catching the infection again.
An outreach worker discusses health issues with young people in Cambodia.Juan Daniel Torres, Courtesy of Photoshare
Read Also: Cvs Brand Yeast Infection Treatment
What Happens If I Dont Treat An Std
Some curable STDs can be dangerous if they arent treated. For example, if left untreated, chlamydia and gonorrhea can make it difficultor even impossiblefor a woman to get pregnant. You also increase your chances of getting HIV if you have an untreated STD. Some STDs, like HIV, can be fatal if left untreated.
Chances Of Getting An Std: Separating Myths From Facts
Sexually transmitted diseases are diseases that result from sexually transmitted infections . The terms are often used interchangeably, but technically speaking, the virus or condition that is spread from person to person is typically an STI. If the infection leads to symptoms, which doesnt always happen, it becomes an STD.
Although STIs are fairly common and widely discussed, theres also a lot of misinformation out there. Because of that, it can be hard to get the real facts about STIs. This article provides clear answers about the chances of getting an STD from different types of sexual encounters.
Recommended Reading: How Do I Know If Eczema Is Infected
Etymology And Other Terms
The term condom first appears in the early 18th century: early forms include condum , condon and cundum . The words etymology is unknown. In popular tradition, the invention and naming of the condom came to be attributed to an associate of Englands , one Dr. Condom or Earl of Condom. There is however no evidence of the existence of such a person, and condoms had been used for over one hundred years before King Charles II ascended to the throne.:54,68
A variety of unproven Latin etymologies have been proposed, including condon ,condamina , and cumdum .:701 It has also been speculated to be from the Italian word guantone, derived from guanto, meaning glove. William E. Kruck wrote an article in 1981 concluding that, As for the word condom, I need state only that its origin remains completely unknown, and there ends this search for an etymology. Modern dictionaries may also list the etymology as unknown.
Other terms are also commonly used to describe condoms. In North America condoms are also commonly known as , or rubbers. In Britain they may be called French letters or rubber johnnies. Additionally, condoms may be referred to using the manufacturers name.
Read Also: Do You Get Medicine For A Sinus Infection
Learning Objective Performance Indicators
- Describe the recommendations for sexually transmitted infection screening in persons with HIV
- List the CDC recommended treatments for the most common sexually transmitted infections in persons with HIV
- Summarize different stages of syphilis and recommended treatments at each stage
- Discuss laboratory-based methods for diagnosing syphilis
DisclosuresAley G. Kalapila, MD, PhDDisclosures
Recommended Reading: 8 Hour Infection Control Course For Dental Assistants
How Can You Protect Yourself From Hiv And Stds
- Avoid or put off having sex. If you do have sex, use a male latex or female condom every time.
- Latex male condoms and female condoms, when used the right way every time, are very effective in preventing HIV and many other STDs. Condoms may prevent the spread of other STDs like HPV or genital herpes, only when the condom covers the infected areas or sores.
- Talk with your partner about HIV and STDs.
- Dont share drug works
- Get STD and HIV counseling and testing.
To find out if you might have an STD, visit your doctor or clinic as soon as you can.