Hiv Effects On The Immune System
Your immune system has many types of white blood cells that fight infection. HIV gets inside a kind called CD4 cells and makes copies of itself. The virus kills the cell, and the new viruses go off to find more.
Your body responds by making more CD4 cells, but after a while, it canât keep up with the virus. This makes your immune system weak. Youâre more likely to get sick, even from common germs. Infections last longer, are more severe, and might come back more often.
If you follow your doctorâs directions with ART, it knocks out HIV, stopping it from infecting more CD4 cells and from weakening your immune system.
Hiv Effects On The Circulatory System
Several things make your chances of heart-related problems go up. Because HIV affects your immune system, your body will be inflamed as it tries to fight the infection, like itâs on a constant simmer. This kind of inflammation has been linked to heart disease.
Some drugs you take for HIV can also make heart disease more likely. They can cause insulin resistance, which makes you more likely to get diabetes, and problems breaking down fats. Diabetes, in turn, raises your risk of heart disease. You might need medicines to control your blood sugar and cholesterol.
If you smoke, quit. Eat a variety of vegetables and fruits, plenty of whole grains, and foods with omega-3 fatty acids. Choose lean cuts of meat and low-fat dairy products. Exercise, like taking a brisk walk, for 20 to 30 minutes most days of the week.
If you’re carrying extra weight, losing as little as 5 or 10 pounds could make a big difference.
How Is Hiv Diagnosed
A doctor may suspect HIV if symptoms last and no other cause can be found.
If you have been exposed to HIV, your immune system will make antibodies to try to destroy the virus. Doctors use tests to find these HIV antibodies or antigens in urine, saliva, or blood.
If a test on urine or saliva shows that you are infected with HIV, you will probably have a blood test to confirm the results.
Most doctors use a blood test to diagnose HIV infection. If the test is positive , a test to detect HIV DNA or RNA will be done to be sure.
HIV antibodies or antigens usually show up in the blood within 3 months. If you think you have been exposed to HIV but you test negative for it:
- Get tested again. A repeat test may be done after a few weeks to be sure you are not infected.
- Meanwhile, take steps to prevent the spread of the virus, in case you do have it.
You can get HIV testing in most doctors’ offices, public health clinics, hospitals, and Planned Parenthood clinics. You can also buy a home HIV test kit in a drugstore or by mail order. Make sure it’s one that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration . If a home test is positive, see a doctor to have the result confirmed and to find out what to do next.
You May Like: Does Vitamin C Help With Yeast Infections
Hiv Rashes Caused By Medication
Drugs that treat HIV and related infections can trigger rashes. These often go away several days or weeks after you stop taking the drug. Talk with your doctor before stopping any medication.
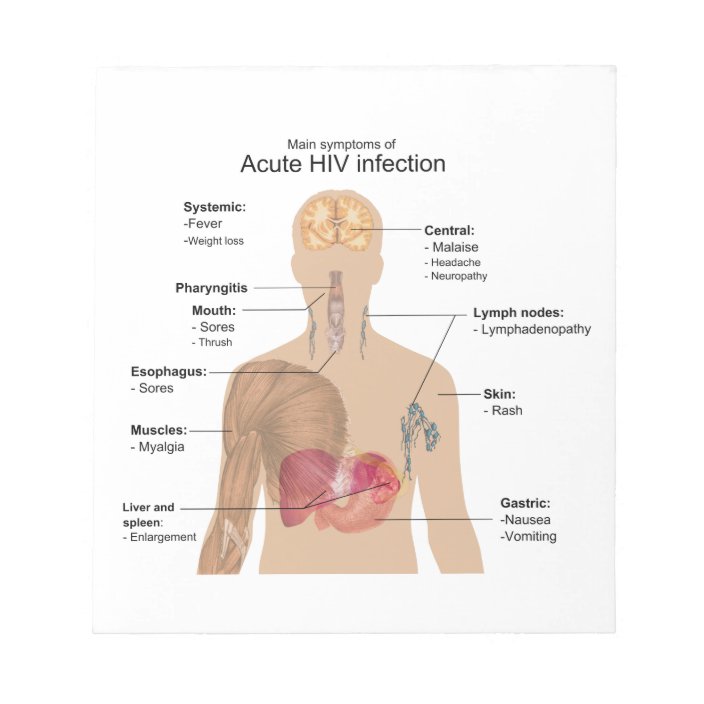
If you have a rash along with fever, fatigue, headache, muscle pains, upset stomach, vomiting, and belly pain, you might have a âhypersensitivity reaction,â which can happen with several HIV medications, including:
- Abacavir and medications that have abacavir in them
Get medical help right away if you have those symptoms or if you have:
- Painful red or purplish rash
- Blisters that spread on your skin and around your mouth, nose, and eyes
These could be signs of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a severe form of hypersensitivity reaction. Itâs rare but can be life-threatening.
You May Like:
Testing Positive For Hiv
If you test positive, your doctor will complete a medical history and physical exam.
He or she may order several lab tests to check your overall health, including:
- A complete blood count , to identify the numbers and types of cells in your blood.
- A chemistry screen, to measure the blood levels of certain substances and to see how well your liver and kidneys are working.
Other tests may be done to check for current or past infections that may become worse because of HIV. You may be tested for:
You May Like: Can I Go To Urgent Care For A Yeast Infection
What Are The Factors That Affect Disease Progression
The most important factor affecting HIV progression is the ability to achieve viral suppression. Taking antiretroviral therapy regularly helps many people slow the progression of HIV and reach viral suppression.
However, a variety of factors affect HIV progression, and some people progress through the phases of HIV more quickly than others.
Factors that affect HIV progression can include:
- Ability to achieve viral suppression. Whether someone can take their antiretroviral medications and achieve viral suppression is the most important factor by far.
- Age when symptoms start. Being older can result in faster progression of HIV.
- Health before treatment. If a person had other diseases, such as tuberculosis, hepatitis C, or other sexually transmitted diseases , it can affect their overall health.
- Timing of diagnosis. Another important factor is how soon a person was diagnosed after they contracted HIV. The longer between their diagnosis and treatment, the more time the disease has to progress unchecked.
- Lifestyle. Practicing an unhealthy lifestyle, such as having a poor diet and experiencing severe stress, can cause HIV to progress more quickly.
- Genetic history. Some people seem to progress more quickly through their disease given their genetic makeup.
Some factors can delay or slow the progression of HIV. These include:
Living a healthy lifestyle and seeing a healthcare provider regularly can make a big difference in a persons overall health.
What Is The Connection Between The Hiv Life Cycle And Hiv Medicines
Antiretroviral therapy is the use of a combination of HIV medicines to treat HIV infection. People on ART take a combination of HIV medicines every day. HIV medicines protect the immune system by blocking HIV at different stages of the HIV life cycle. HIV medicines are grouped into different drug classes according to how they fight HIV. Each class of drugs is designed to target a specific step in the HIV life cycle.
Because an HIV treatment regimen includes HIV medicines from at least two different HIV drug classes, ART is very effective at preventing HIV from multiplying. Having less HIV in the body protects the immune system and prevents HIV from advancing to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome .
ART cannot cure HIV, but HIV medicines help people with HIV live longer, healthier lives. HIV medicines also reduce the risk of HIV transmission .
Read Also: How Long Can A Bladder Infection Last
Hiv Infection: How Hiv Infects The Body
HIV-infected H9 T cell | NIAID
HIV on Bridges Between Infected Immune Cell and Uninfected Brain Cell | NIH Image Gallery
Robert is a senior partner of Webber Wentzel, a major South African law firm. Robert specialises in mergers and acquisitions, project related and other transactional work, in the main in the health and technology arenas. Robert has worked in, and is expert in a number of African jurisdictions including Angola, Botswana, Ghana, Ethiopia, Djibouti, Mozambique, Kenya, Namibia and others.
Robert was lead attorney for Business Unity South Africa and Business 4 South Africa during the COVID-19 pandemic and he was and remains led attorney to the South African National Department of Health in relation to COVID-19 vaccines.
Robert was previously Honorary Business Representative for the Middle East and Africa Group for International Enterprise Singapore the government agency driving Singapores external economy. He has also been recognized in several International journals as an expert several legal fields. Robert has BA and LLB degrees from the University of the Witwatersrand.
Robert is the co-author of two books, namely Public Offers of Company Securities and of Business Rescue and Compromise Offers.
Your application form was sent successfully. Candidates who are selected for interviews will be requested to furnish additional certified information that may be required to make a final selection.
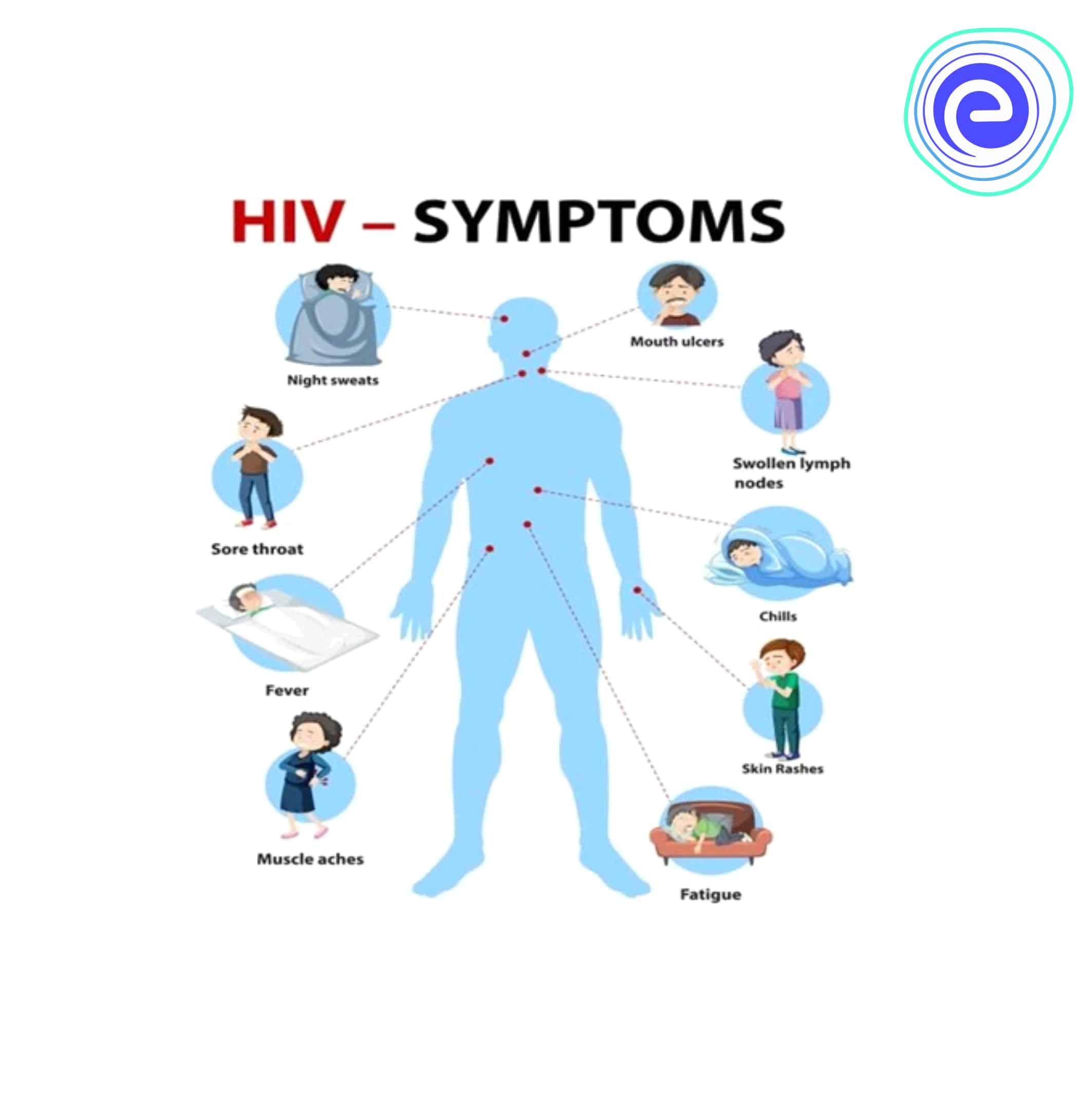
How To Manage Hiv Symptoms
Antiretroviral medications are the first-line treatment for human immunodeficiency virus . Patients should be compliant with the medications to reduce the amount of virus in the body.
The various symptoms and their treatments are as follows
- Weight loss: In addition to the HIV medications , patients should eat a well-balanced diet and high-protein supplements and perform exercises to build muscle mass. The physician may prescribe medications such as Megace and to treat wasting syndrome commonly seen in HIV patients.
- Skin problems: Skin infections or dry itchy skin are usually treated with antifungal or antibacterial cream. Oral medicines may also be required.
- Herpes: Shingles can cause a painful, blisteringrash. Antiviral medications, pain relievers and calamine lotions are mainly used to treat rashes.
- Fever: Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and applying cold compresses may bring down the temperature.
- Nagging cough: Dry cough can be due to an infection known as pneumocystis pneumonia. The physician may prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection. Medicines to thin the mucus may also help.
- Diarrhea: Doctors may prescribe antidiarrheals to control diarrhea. Patients need to drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Ear Infection To Drain
Stage : The Asymptomatic Stage
Once a person has been through the acute primary infection stage and seroconversion process, they can often start to feel better. In fact, HIV may not cause any other symptoms for up to 10 or even 15 years .
However, the virus will still be active, infecting new cells and making copies of itself. HIV can still be passed on during this stage. If left untreated, over time, HIV infection will cause severe damage to the immune system.
Dont Miss: What Percentage Of Americans Have Hiv
Treatment To Prevent Hiv Infection
Health care workers who are at risk for HIV because of an accidental needlestick or other exposure to body fluids should get medicine to prevent infection.footnote 11
Also, medicine may prevent HIV infection in a person who has been raped or was accidentally exposed to the body fluids of a person who may have HIV.footnote 12 This type of treatment is usually started within 72 hours of the exposure.
And studies have shown that if you are not infected with HIV, taking antiretroviral medicines can protect you against HIV.footnote 13, footnote 14, footnote 15 But to keep your risk low, you still need to use safer sex practices.
Don’t Miss: Sinus Infection Not Responding To Antibiotics
What Are The Seven Stages Of The Hiv Life Cycle
The seven stages of the HIV life cycle are: 1) binding, 2) fusion, 3) reverse transcription, 4) integration, 5) replication, 6) assembly, and 7) budding.
To understand each stage in the HIV life cycle, it helps to first imagine what HIV looks like.
Now, follow each stage in the HIV life cycle as HIV attacks a CD4 cell and uses the machinery of the cell to multiply.
Prevention Of Hiv Infection
At present, there is no effective HIV vaccine to prevent HIV infection or slow the progression of AIDS in people who are already infected. However, treating people who have HIV infection reduces the risk of their transmitting the infection to other people.
Transmission of HIV through its most common routessexual contact or sharing of needlesis almost completely preventable. However, the measures required for preventionsexual abstinence or consistent condom use Prevention Sexually transmitted diseases are infections that are typically, but not exclusively, passed from person to person through sexual contact. Sexually transmitted infections may be caused… read more and access to clean needlesare sometimes personally or socially unpopular. Many people have difficulty changing their addictive or sexual behaviors, so they continue to put themselves at risk of HIV infection. Also, safe sex practices are not foolproof. For example, condoms can leak or break.
Also Check: Can You Get Yeast Infection In Your Bum
Hiv And Aids Cases Are Reportable
HIV cases became reportable to the U.S. Department of Health in the fall of 1999. AIDS cases have been reportable to the CDC since 1984, when the existence of the syndrome that follows HIV infection was clearly established.
AIDS and symptomatic HIV infections have been reportable to the Washington State Department of Health since 1984 and 1993, respectively. HIV cases became reportable to the Washington State Department of Health in fall 1999.
Can Medications Prevent Hiv
There are medications that can help prevent HIV in people who have been exposed or are at high risk for exposure. These include pre-exposure prophylaxis and post-exposure prophylaxis .
Pre-exposure prophylaxis
PrEP is a pill you take every day if you dont have HIV but are at high risk of getting infected.
- You have a sexual partner with HIV.
- You havent consistently used a condom.
- In the past six months, youve been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease .
PrEP is also recommended if you dont have HIV, you inject drugs and at least one of the following is true:
- You inject drugs with a partner who has HIV.
- You share needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
PrEP is not a replacement for other preventative measures. You should still use condoms and avoid sharing needles to inject drugs while taking PrEP.
Post-exposure prophylaxis
PEP uses HIV medicines to try to prevent an HIV infection soon after you are exposed. PEP is for those who dont have HIV or dont know if they have HIV and think theyve been exposed through consensual sex, sexual assault, shared needles , or work.
You must start PEP within 72 hours of exposure and take it every day for 28 days. PEP is only for emergency use and does not replace other precautions, like condom use.
Recommended Reading: Over The Counter Yeast Infection Relief
Increased Cervical Cancer Risk
Women with HIV are at higher risk for cervical cancer, a cancer that begins in the cervix. This is because human papillomavirus is the most common cause of the cancer, and women with HIV are more likely to have the cancer-causing types of HPV .
Because of this increased risk, it is recommended that women with HIV discuss the ideal Pap smear screening schedule with a healthcare provider. For example, some guidance recommends having two pap smears in the first year after diagnosis with one Pap smear done every year after if the first two screenings were normal .
Entry And Reverse Transcription
Like other viruses, HIV infects host cells with the goal of producing more viruses. HIV targets cells of the immune system, and in particular, T-cells, which are a type of white blood cell. During the first stage of the HIV life cycle, a virus enters the body and then identifies a host T-cell through interactions between receptor proteins on the T-cell surface and viral envelope proteins on the surface of the viral membrane. A second T-cell surface protein, called a coreceptor , also binds to Env proteins, triggering major shape changes in Env and leading to the fusion of the viral and host cell membranes. Subsequently, the conical HIV capsid, which contains two copies of the viral genome as single-stranded RNAs, is deposited into the host cell. Soon after the HIV capsid enters, the viral RNA genome begins to be copied into double-stranded DNA, a process known as reverse transcription. Reverse transcription is carried out by a viral protein called reverse transcriptase , using host tRNAs to help prime the reaction and dNTPs to build new DNA strands. Meanwhile, the HIV capsid is transported to the nucleus through interactions with microtubule-based motor proteins.
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection Antibiotics Metronidazole
Whatpart Of The Body Does Hiv Infect
HIV infects our immune system. This is the part of our body that stops us getting sick. HIV infects a type of white blood cell in our immune system called a T-helper cell . These cells keep us healthy by fighting off infections and diseases. However, HIV hides inside these cells, tricking the body so that the immune system cant find and destroy it.
How Is Hiv Treated
HIV medications, known as antiretroviral therapy , slow the progression of the disease in your body by lowering the amount of HIV in your blood. This keeps the immune system strong enough to fight off other infections. ART involves taking a combination of HIV medications every day regardless of how long someone has had the virus or how healthy they are. You can also visit HIV.gov to learn more about treatment options.
Read Also: Ears Pop When Blowing Nose Sinus Infection
Associations Between Symptom Clusters
There was a strong correlation between Symptom Cluster 1 and Symptom Cluster 2 . Fatigue and muscle pain/joint aches loaded on both factors and were reported among the most prevalent and most bothersome symptoms. The high prevalence of fatigue and muscle pain/joint aches persisted in subjects with both clusters with HIV-1 viremia or aviremia . There were no statistical differences in clusters based on gender or race.
In symptom clusters in patients with HIV-1 viral loads > 500 copies/mL, symptom clusters did not have any overlap. The first cluster accounted for 42% of the variability in reported symptoms, with rash added to the symptoms listed in comparison to the full population model. The second cluster loaded symptoms with an inverse correlation between weight variables and appetite, and accounted for 8% of the variability of symptoms reported .