The Chance Of Hiv Transmission Through One
This table shows the chance of contracting HIV through one-time unprotected rectal sex with a partner who is HIV-positive. As you can see, the chance of the âbottomâ person contracting the disease from an HIV-positive âtopâ is much greater than the other way around.
| Receptive person | Inserter | |
|---|---|---|
| Per exposure | 1 transmission per 72 exposures | 1 transmission per 909 exposures |
How Many Cases Of Hiv Have Resulted From Occupational Needlestick Injuries
In the US, there were a total of 58 cases of confirmed occupational transmission of HIV to healthcare workers up to 2013, with only one since 1999. In the UK, there have only ever been five definite cases of HIV infection following a needlestick injury in a healthcare setting, and none reported in the past 20 years. The number of cases of HIV acquisition following an accidental needlestick injury globally is thought to be around 100 people in total.
Between 2004 and 2013, a total of 1478 healthcare workers were reported as having been exposed to patient blood containing HIV in the UK. Three-quarters of these took PEP, and almost all did so within 24 hours, with no HIV infections as a result.
How Safe Is Oral Sex
Giving oral sex to a woman is also considered relatively low risk. Transmission could take place if infected sexual fluids from a woman got into the mouth of her partner. The likelihood of infection might be increased if there is menstrual blood involved or if the woman is infected with another sexually transmitted disease.
The likelihood of either a man or a woman becoming infected with HIV as a result of receiving oral sex is extremely low, as saliva does not contain infectious quantities of HIV.
Recommended Reading: Does Nitrofurantoin Treat Kidney Infection
What We Know About Injecting Silicone
Silicone injections can be done safely by a health care provider, but sometimes people inject silicone with friends or acquaintances at parties. Theres a chance that someone can get or transmit HIV if an HIV-negative person uses needles, syringes, and other injection equipment after someone with HIV has used them. This is because the needle, syringe, or other injection equipment may have blood in them, and blood can carry HIV. Likewise, youre at risk for getting or transmitting hepatitis B and C if you share needles, syringes, or other injection equipment because these infections are also transmitted through blood.
More information:More information:
More information: Hepatitis B and C are viruses that infect the liver. Many people with hepatitis B or C dont know they have it because they dont feel sick. Even if you dont feel sick, you can transmit the virus to others. The only way to know for sure if you have hepatitis B or C is to get tested. Your health care provider will recommend a hepatitis B or C test if you have risk factors for these infections, such as injection drug use. If you dont have a health care provider, click here to find contact information for your local health department.
If a person with HIV takes their HIV medicine as prescribed and gets and keeps an undetectable viral load , their chance of transmitting HIV through sharing needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment is reduced.
More information
Explore other resources from CDC:
Can I Transmit Hiv To My Baby During Pregnancy Or Breastfeeding
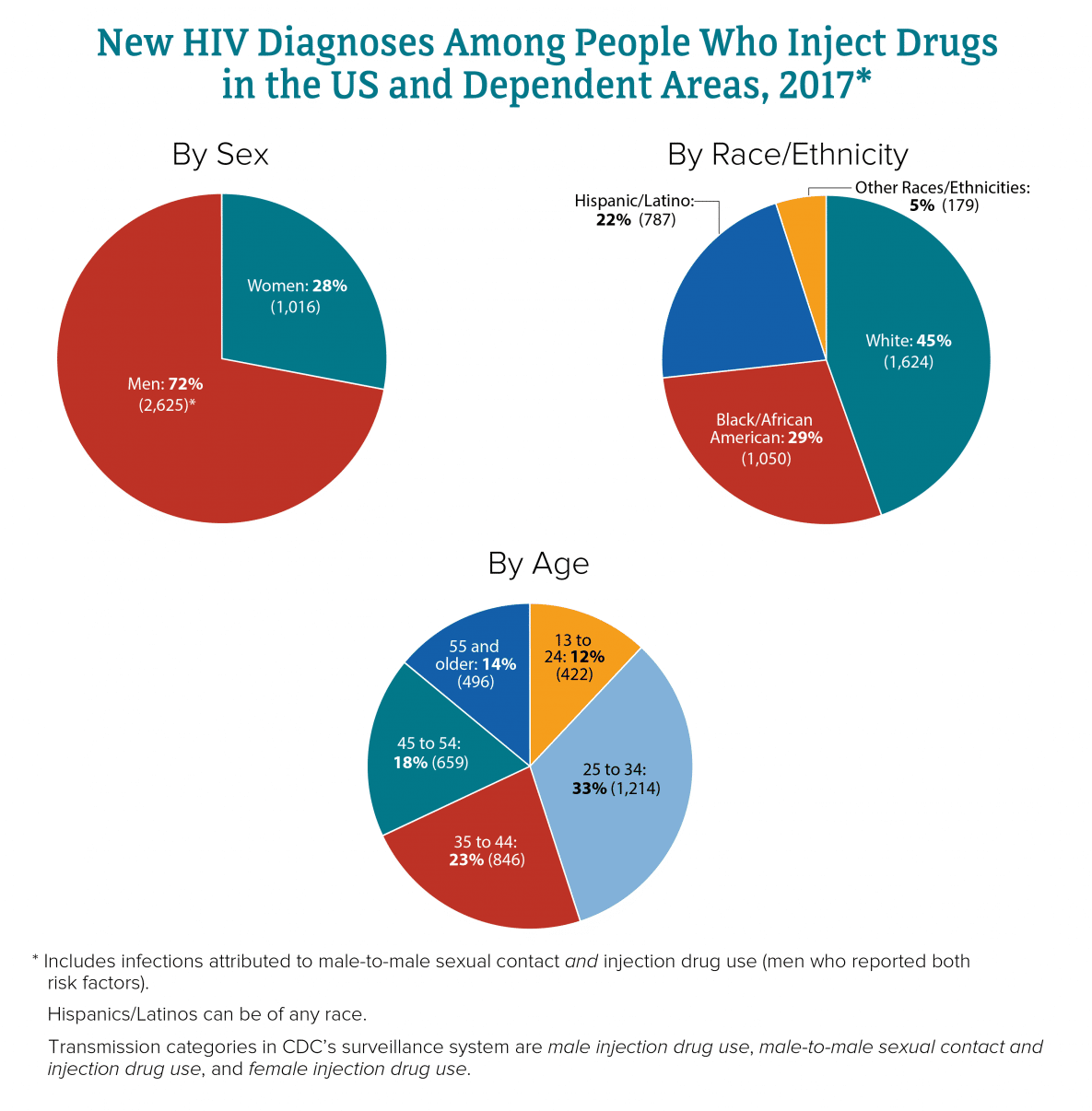
An HIV-infected pregnant woman can pass the virus on to her unborn baby either before or during birth. HIV can also be passed on during breastfeeding. If a woman knows that she is infected with HIV, there are drugs she can take to greatly reduce the chances of her child becoming infected. Other ways to lower the risk include choosing to have a caesarean section delivery and not breastfeeding.
Also Check: Online Antibiotic For Tooth Infection
Is There Risk Of Hiv Transmission When Having A Tattoo Body Piercing Or Getting A Hair Cut Or Shave
There is a risk of HIV transmission if instruments contaminated with blood are not sterilized between clients. However, people who carry out body piercing or tattooing should follow procedures called ‘universal precautions’, which are designed to prevent the transmission of blood borne infections such as HIV and Hepatitis B.
When having a hair cut there is no risk of infection unless the skin is cut and infected blood gets into the wound. Traditional ‘cut-throat’ razors used by barbers now have disposable blades, which should only be used once, thus eliminating the risk from blood-borne infections such as Hepatitis and HIV.
The Chance Of Hiv Transmission With Protection
The likelihood of HIV transmission goes down by 70% when condoms are used. This table summarizes the chance of contracting HIV through one-time contact when protection is used.
| Protected receptive vaginal | Protected insertive vaginal | Protected receptive rectal | Protected insertive rectal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per exposure | 1 transmission per 4,167 exposures | 1 transmission per 8,334 exposures | 1 transmission per 241 exposures | 1 transmission per 3,030 exposures |
The numbers in this table are calculated based on the chance of transmission without protection and the 70% reduction in HIV transmission with condom use.
Recommended Reading: Penicillin Vs Amoxicillin For Tooth Infection
Diseases Spread By Needles
- Varicella zoster virus, which causes chickenpox and shingles
- Epstein-Barr, a type of herpes virus
When it comes to HIV, your chances of getting it goes up if the needle:
- Has blood on it
- Was first stuck in someoneâs artery or vein
- Was used for a very deep injury
- Was used on someone who dies within 2 months of the needle stick injury
Will I Need Any Treatment
If your healthcare professional thinks you’re at low risk of infection, you may not need any treatment.
If there’s a higher risk of infection, you may need:
- antibiotic treatment for example, if you have cellulitis
- vaccination against hepatitis B
- treatment to prevent HIV
If there’s a high risk of infection with HIV, your healthcare professional may consider treatment called post-exposure prophylaxis .
You May Like: Chapter 13 Sexually Transmitted Infections And Hiv Aids
Hiv Infection In Health Professionals
Health professionals are not considered at high risk for HIV infection, because they use protection when dealing with blood or body fluids.
- The chances of becoming infected after being stuck or cut with an instrument that is contaminated with HIV-infected blood are about 1 out of 300.footnote 1
- The chances of becoming infected if HIV-infected blood is splashed in the eye, nose, or mouth are about 1 out of 1,000.footnote 1
There probably isn’t much risk of getting HIV if contaminated blood comes into contact with intact skin. But the risk may be higher if contaminated blood touches cut, scraped, or broken skin.
The degree of risk depends on:
- How much blood the person is exposed to.
- The amount of HIV present in the blood. People who have symptoms of early HIV infection and those who are very sick with AIDS tend to have greater amounts of HIV in their blood.
Health care workers who are at risk for HIV because of an accidental needle stick or other exposure to body fluids should get medicine to prevent infection.footnote 2 Treatment works best when it is started as soon as possible after exposure and no later than 72 hours after exposure.
Protect yourself from accidental exposure by disposing of sharp objects properly and wearing protective gloves, gowns, and eye and face protection. It is likely that work guidelines are available that will tell you what to do if you are exposed to HIV. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends the following precautions:
The Chance Of Hiv Transmission Through Needles: With Blood Transfusion Needle Sharing And Needle Prick
This table shows the chance of contracting HIV by means other than sex. Please note the much higher likelihood of getting HIV through needle sharing.
| Blood transfusion | |
|---|---|
| 1 transmission per 500 exposures | 1 transmission per 160 exposures |
Get treated and/or tested for HIV
Same day treatment and testing
You May Like: Amoxicillin Dosage For Ear Infection
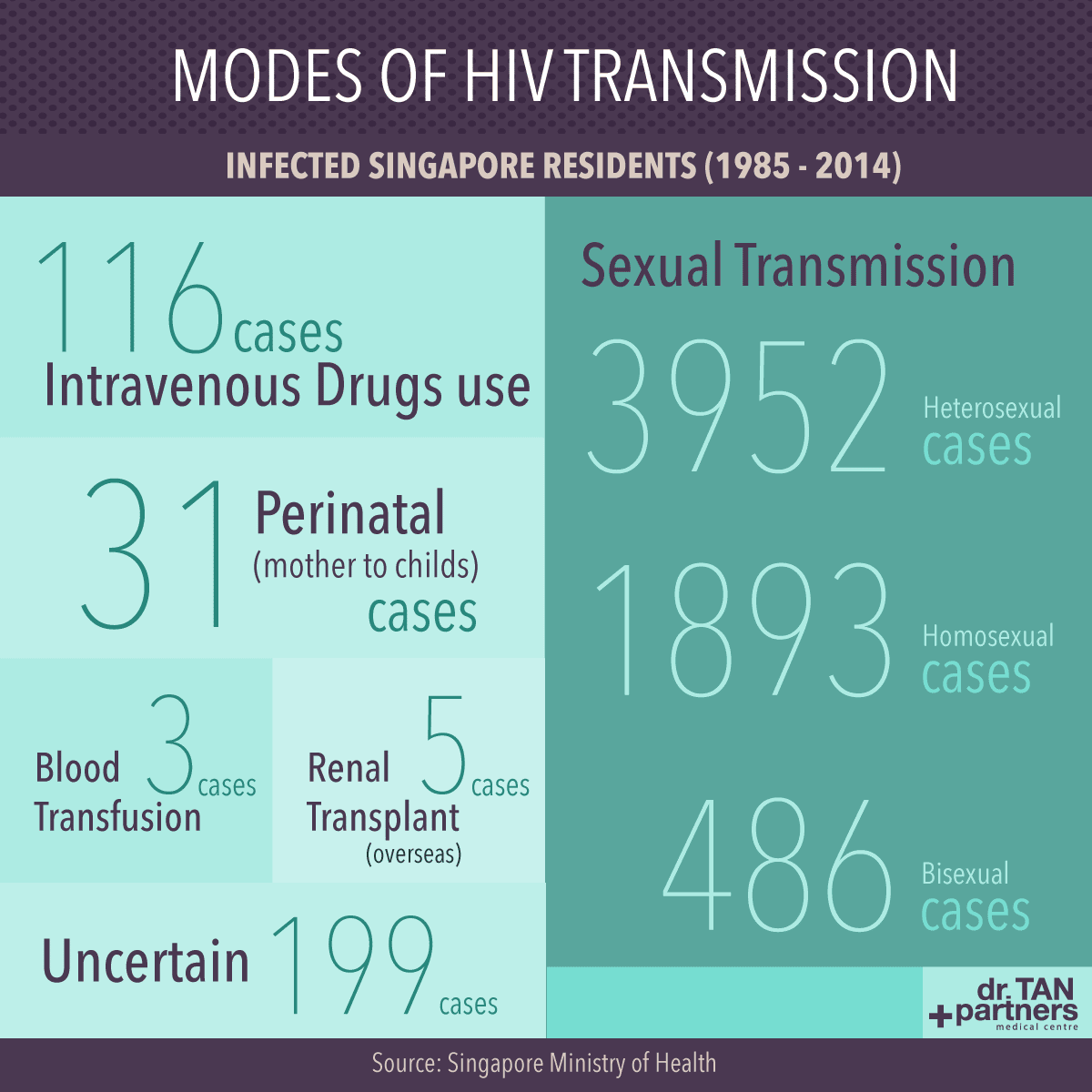
How Is Hiv Transmitted Through Needles
HIV isnt transmitted only through sexual contact. Sharing needles also puts a person at higher risk of contracting HIV.
When a needle is injected into a persons body, it breaks the skin barrier. If the needle has already been injected into another person, it can carry traces of their blood, along with any infections they have. The contaminated needle can introduce these infections into the second persons body.
Researchers dont know if having an undetectable viral load reduces the risk of HIV transmission through shared needles, but its reasonable to assume it may provide some risk reduction.
HIV can affect anyone. Whatever their age, gender, sexuality, ethnicity, or race, everyone should take steps to protect themselves. But due to socioeconomic factors, some demographic groups have higher HIV transmission rates and generally are more affected by HIV.
According to the CDC , the general demographic traits most affected by HIV are:
Transgender women are also highly impacted by HIV transmissions as a population, reports the CDC .
These groups are disproportionately affected by HIV, but they arent inherently at greater risk of contracting HIV. An individuals personal risk depends on their behaviors, not on their age, gender, sexuality, ethnicity, race, or any other demographic factor.
What We Know About Injecting Drugs
The risk for getting or transmitting HIV is very high if an HIV-negative person uses needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment after someone with HIV has used them. This is because the needles, syringes, or other injection equipment may have blood in them, and blood can carry HIV. Likewise, youre at risk for getting or transmitting hepatitis B and C if you share needles, syringes, or other injection equipment because these infections are also transmitted through blood.
More Information
In 2017, 6% of new HIV diagnoses in the United States were attributed to injection drug use and 3% were attributed to injection drug use and male-to-male sexual contact . On average, an HIV-negative person has about a 1 in 160 chance of getting HIV every time they share needles, syringes, or other injection equipment with a person who has HIV.
More Information There may be extremely tiny amounts of blood in syringes or works that you may not be able to see, but could still carry HIV. Be aware that HIV can survive in a used syringe for up to 42 days depending on temperature and other factors.
There are medicines to treat hepatitis B. If youve never had hepatitis B, theres a vaccine to prevent it. There are medicines to treat hepatitis C, but they arent right for everyone. Theres no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. Talk to your health care provider to learn more about hepatitis B and C.
You May Like: Signs Of Hernia Mesh Infection
Implications For Hiv Prevention Messaging
Although there is excitement surrounding new HIV prevention strategies, safer sex messaging and prevention counselling need to emphasize that the correct and consistent use of condoms remains the most effective method of preventing the sexual transmission of HIV .
When answering questions about the effectiveness of condoms, its important to emphasize that they have several advantages over other options. Key messages include the following:
Despite the advantages of condoms, we cant ignore the important role that other prevention strategies may play in helping someone reduce their risk of HIV transmission. Condoms are not without their disadvantages and these can make it difficult for people to use them consistently and correctly. For example, condom use can be difficult to negotiate, condoms can decrease sexual pleasure and intimacy, they need to be available at the time of intercourse, they may be difficult to use when under the influence of alcohol or drugs, and they do not allow a woman to conceive. For these reasons, some people may choose to reduce their risk of HIV transmission in other ways.
You May Like: Order Antibiotics For Sinus Infection
Cdc Examines Confirmed And Suspected Cases
In the January 9, 2015 issue of Morbidity and Mortality Weekly, CDC officials identified 58 confirmed and 150 possible cases of occupationally acquired HIV between the years 1985 and 2013.
Confirmed cases were those in which the healthcare worker was established to be HIV-negative while the source patient was shown to be HIV-positive. By contrast, possible cases were those in which the HIV status of the source patient was unknown or no documented link was established between the healthcare worker and source patient.
Of the 58 confirmed cases, all but four occurred between the years 1985 and 1995, just prior to the advent of antiretroviral therapy and the release of the first U.S. guidelines for the use of post-exposure prophylaxis in cases of accidental HIV exposure.
Since 1999, only one confirmed case of occupationally-acquired HIV has ever been reported to the CDC.
While the CDC report in no way lessens the importance of PEP in cases of needlestick and other percutaneous injuries, it does suggests that, in the words of the researchers, “more widespread and earlier treatment to reduce patient viral loads” has contributed to the almost complete mitigation of HIV risk insofar as occupational exposure is concerned.
You May Like: Sinus Infection Post Nasal Drip
Is It True That Gay Men Are More At Risk For Hiv Than Other People
Although anyone can be at risk for HIV, some people can be more at risk depending upon the types of sexual practices and drug use they are engaging in. Being gay does not necessarily mean you are at higher risk, but certain activities gay men sometimes participate in might put them at greater risk. Overall, the gay male population in Canada has higher rates of HIV infection than some other populations. Stigma and homophobia can affect a person’s ability to access information about safer sex specifically for gay men.
How Do You Get Hiv From Injecting Drugs
During an injection, some blood goes into the needle and syringe. A needle and syringe that someone living with HIV has used can contain blood with the virus in it after the injection. If you then use the same injecting equipment, you are likely to inject HIV-infected blood directly into your bloodstream.
Recommended Reading: How To Drain Fluid From Ear Infection
Condoms Are Made From Different Materials
Its possible to purchase condoms made from a variety of different materials, including latex and synthetic materials, like polyurethane and polyisoprene.
Lambskin condoms are more porous than other types of condoms. This allows germs, particularly viruses, to pass through the condom. Because of this, theyre not effective at preventing HIV and many other STIs.
Its estimated that about of the worldwide population is allergic to latex. People with a latex allergy can use condoms made of synthetic material to prevent having an allergic reaction while protecting against HIV transmission.
How To Prevent The Spread Of Hiv
People living with HIV can use the following to prevent transmitting it to others:
- Preexposure prophylaxis : This daily pill contains two antivirals: Tenofovir and emtricitabine. When a person takes it daily, PrEP can reduce the risk of acquiring HIV through sex by 99%. PrEP is for those who do not have HIV but are at a high risk of contracting it.
- Postexposure prophylaxis : ART drugs that can prevent HIV infection after potential exposure. The CDC recommend starting PEP within of a recent potential HIV exposure.
You May Like: Oregano Oil Capsules For Sinus Infection
Can Analingus Result In Hiv Transmission
For this answer, we turn back to Bob Frascino, M.D.:
Although there have been no documented cases of acquiring HIV from rimming or being rimmed, there are a number of other significant STIs that can easily be transmitted through rimming, including hepatitis A, herpes, and intestinal parasites. You can decrease the risk by using a dental dam barrier .
As for whether to rim or not, only you can decide what level of risk you are willing to take. At least now you have the facts.
Also Check: Can You Treat A Kidney Infection At Home
Can I Become Infected With Hiv If I Inject Drugs And Share The Needles With Someone Else Without Sterilizing The Needles

We strongly recommend that you use new equipment every time you inject. You can get new equipment from Counterpoint Needle & Syringe Program at Regional HIV/AIDS Connection.
There is a possibility of becoming infected with HIV if you share injecting equipment with someone who has the virus. If HIV infected blood remains inside the needle or in the syringe and someone else then uses it to inject themselves, that blood can be flushed into the bloodstream. Sharing needles, syringes, spoons, filters or water can pass on the virus. Disinfecting equipment between uses can reduce the likelihood of transmission, but does not eliminate it.
Read Also: Swelling Mouth From Tooth Infection
Do Birth Control Methods Other Than Condoms Reduce The Risk Of Stds Including Hiv
No. Only condoms reduce the risk of pregnancy, STDs and HIV. Birth control pills, the birth control patch, contraceptive injections such as Depo-Provera, intrauterine devices , diaphragms, and any birth control methods other than condoms do not provide protection against STDs and HIV. You should use a latex male condom or a female condom for STD and HIV prevention along with any other method you use to prevent pregnancy. Condoms can prevent the spread of other STDs, like HPV or genital herpes, only when the condom covers all of the infected area or sores.
Read Also: Why Does Farxiga Cause Yeast Infections