How To Drain Ear Fluid
This article was medically reviewed by Luba Lee, FNP-BC, MS. Luba Lee, FNP-BC is a board certified Family Nurse Practitioner and educator in Tennessee with over a decade of clinical experience. Luba has certifications in Pediatric Advanced Life Support , Emergency Medicine, Advanced Cardiac Life Support , Team Building, and Critical Care Nursing. She received her Master of Science in Nursing from the University of Tennessee in 2006.There are 15 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 713,581 times.
Reasons To Have A Myringotomy
A myringotomy may be done:
- To restore hearing loss caused by chronic fluid build-up and to prevent delayed speech development caused by hearing loss in children
- To place tympanostomy tubes these tubes help to equalize pressure. It may also help prevent recurring ear infections and the accumulation of fluid behind the ear drum.
- To help treat an ear infection that is not responding to medical treatment
- To take sample fluid from the middle ear to examine in the lab for the presence of bacteria or other infections
After the procedure, pain and/or pressure in the ear due to fluid build-up should be alleviated. Hearing loss due to fluid build-up should improve as well.
How Long Will It Take My Child To Get Better
Your child should start feeling better within a few days after visiting the doctor. If its been several days and your child still seems sick, call your doctor. Your child might need a different antibiotic. Once the infection clears, fluid may still remain in the middle ear but usually disappears within three to six weeks.
Also Check: Infected Gum Around One Tooth
What Should I Expect If I Or My Child Has An Ear Infection
Ear infections are common in children. Adults can get them too. Most ear infections are not serious. Your healthcare provider will recommend over-the-counter medications to relieve pain and fever. Pain relief may begin as soon as a few hours after taking the drug.
Your healthcare provider may wait a few days before prescribing an antibiotic. Many infections go away on their own without the need for antibiotics. If you or your child receives an antibiotic, you should start to see improvement within two to three days.
If you or your child has ongoing or frequent infections, or if fluid remains in the middle ear and puts hearing at risk, ear tubes may be surgically implanted in the eardrum to keep fluid draining from the eustachian tube as it normally should.
Never hesitate to contact your healthcare provider if you have any concerns or questions.
Can Ear Infections Affect Hearing
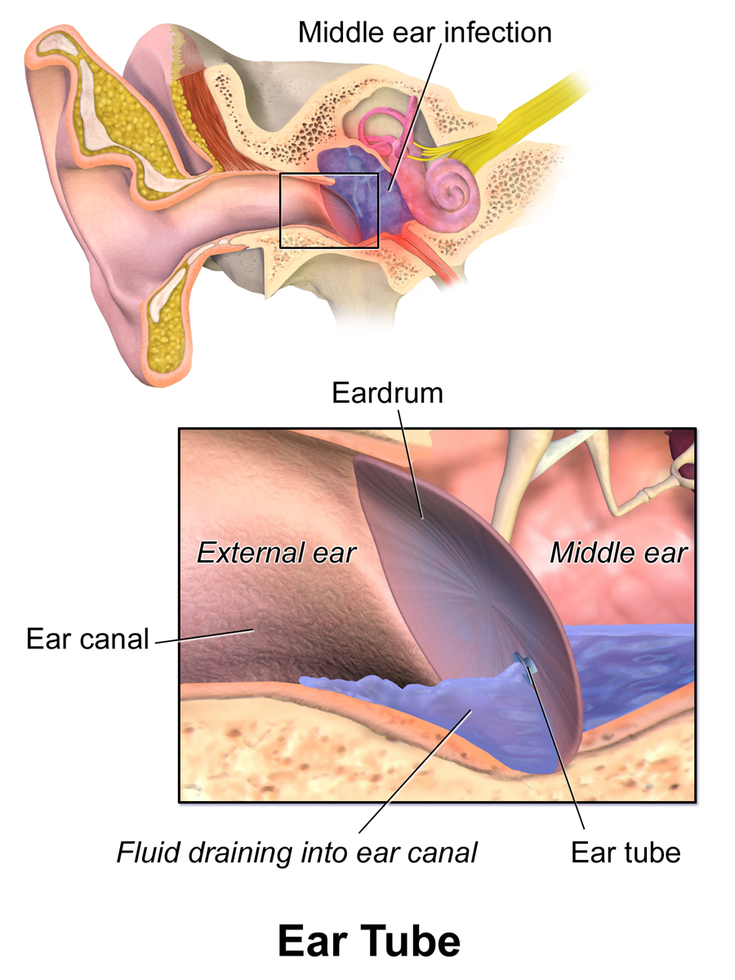
Fluid buildup in the middle ear also blocks sound, which can lead to temporary hearing problems. Kids having a problem might:
- not respond to soft sounds
- need to turn up the TV or radio
- talk louder
- seem inattentive at school
In kids who have otitis media with effusion, the fluid behind the eardrum can block sound, so mild temporary hearing loss can happen, but might not be obvious.
A child whose eardrum has ruptured might have ringing or buzzing in the ear and not hear as well as usual.
You May Like: Over The Counter Yeast Infection Meds
Sweet Oil For Ear Infection
This is one of the most effective remedies to get rid of ear infection. One of the main reasons behind ear infection is the earwax. The Eustachian tubes are blocked by the earwax. This can lead to ear pain. Sweet oil dissolves the earwax that is responsible for the blockage. Follow the steps given below to get rid of ear infection and pain.
- Warm up a bowl of sweet oil.
- Lie down in a comfortable position. You ear should face the upward direction.
- Use a dropper to put 3 to 4 drops of sweet oil in the infected ear.
- Stay in this same position for the next 20 minutes.
- Use sterilized cotton to clean out the wax and dirt from the ear.
- Repeat this method after every few hours to get rid of ear infection and prevent pain.
How Is Sudden Hearing Loss Treated
There are many treatments for SSNHL. Treatment is most successful the earlier it is given. Treatment can include oral steroids or steroids injected directly into the ear . If the first treatments do not work, your otolaryngologist should discuss âsalvage therapy.â The benefits of treatment may include more quick and complete recovery of hearing, but there are also side effects of steroids that must be considered when choosing from the available options. Side effects of steroids may include sleep problems, anxiety, depression, or mood swings, increased appetite with possible weight gain, dizziness, jitteriness, high blood sugar, and/or high blood pressure. With intratympanic steroids risks include pain, dizziness, residual hole in the ear drum, and infection. In head-to-head comparisons, intratympanic injection of steroids causes much fewer side effects than oral steroids.
Watchful waiting may be recommended. This is because half of patients may get back hearing on their ownâthese are usually patients with mild to moderate degrees of hearing loss, but healthcare providers do not currently have a way to predict who will get better without treatment.
Recommended Reading: Medicine To Treat Kidney Infection
What Can I Do About My Symptoms
- Donât move too quickly you might lose your balance.
- Remove tripping hazards like area rugs and electrical cords. Put non-slip mats in your bath and shower.
- If you start to feel dizzy, lie down right away. People with vertigo often feel better if they lie down in a quiet, darkened room with their eyes closed.
- Drink lots of fluids and eat well. Avoid caffeine, alcohol, salt, and tobacco.
- If you think your meds are making you feel dizzy, talk to your doctor. They may change your dose, have you stop using them, or try something else.
- Donât drive if you have dizzy spells.
When Should I Call The Doctor About An Ear Infection
- You or your child develops a stiff neck.
- Your child acts sluggish, looks or acts very sick, or does not stop crying despite all efforts.
- Your childs walk is not steady he or she is physically very weak.
- You or your childs ear pain is severe.
- You or your child has a fever over 104° F .
- Your child is showing signs of weakness in their face .
- You see bloody or pus-filled fluid draining from the ear.
- The fever remains or comes back more than 48 hours after starting an antibiotic.
- Ear pain is not better after three days of taking an antibiotic.
- Ear pain is severe.
- You have any questions or concerns.
You May Like: Does Nuvaring Cause Yeast Infections
What Are The Causes Of Labyrinthitis
Viral infectionsâViral infections of the inner ear or activation of a virus that is has hibernated within nerve endings are thought to be the most common cause of labyrinthitis. The specific virus that causes this is usually unknown in most cases. A unique type of labyrinthitis may be caused by reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus , called Ramsay Hunt syndrome, or herpes zoster oticus. Patients may experience ear pain, facial weakness, and blisters around the ear, ear canal, and/or eardrum in addition to hearing loss and dizziness.
Bacterial infectionâA bacterial infection of the middle ear can spread to the inner ear and cause bacterial labyrinthitis. Children with inner ear deformities are at a higher risk for bacterial labyrinthitis either from a middle ear infection or from the spread of bacterial meningitis to the inner ear. Severe bacterial labyrinthitis can occur with ear pain, ear infection, drainage of pus from the ear, fevers, or chills. Patients may require hospitalization. This type of infection has a higher risk for permanent hearing loss and may also lead to labyrinthitis ossificans, where there is bone formation in the inner ear after the infection.
AutoimmuneâAutoimmune labyrinthitis is a rare cause of labyrinthitis and may come and go. It is often associated with other autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus, inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, or other autoimmune disorders.
What Are The Symptoms Of Otitis Externa
- Itching inside the ear
- Pain inside the ear that gets worse when you tug on the outer ear
- Sensation that the ear is blocked or full
- Drainage from the ear
- Redness or swelling of the skin around the ear
Recurring ear infections are also possible. Without treatment, infections can continue to occur or persist.
Bone and cartilage damage are also possible due to untreated swimmerâs ear. If left untreated, ear infections can spread to the base of your skull, brain, or cranial nerves. Diabetics, older adults, and those with conditions that weaken the immune system are at higher risk for such dangerous complications.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Tonsil Infection
Symptoms Of A Middle Ear Infection
In most cases, the symptoms of a middle ear infection develop quickly and resolve in a few days. This is known as acute otitis media. The main symptoms include:
- a lack of energy
- slight hearing loss – if the middle ear becomes filled with fluid
In some cases, a hole may develop in the eardrum and pus may run out of the ear. The earache, which is caused by the build-up of fluid stretching the eardrum, then resolves.
Managing Middle Ear Fluid
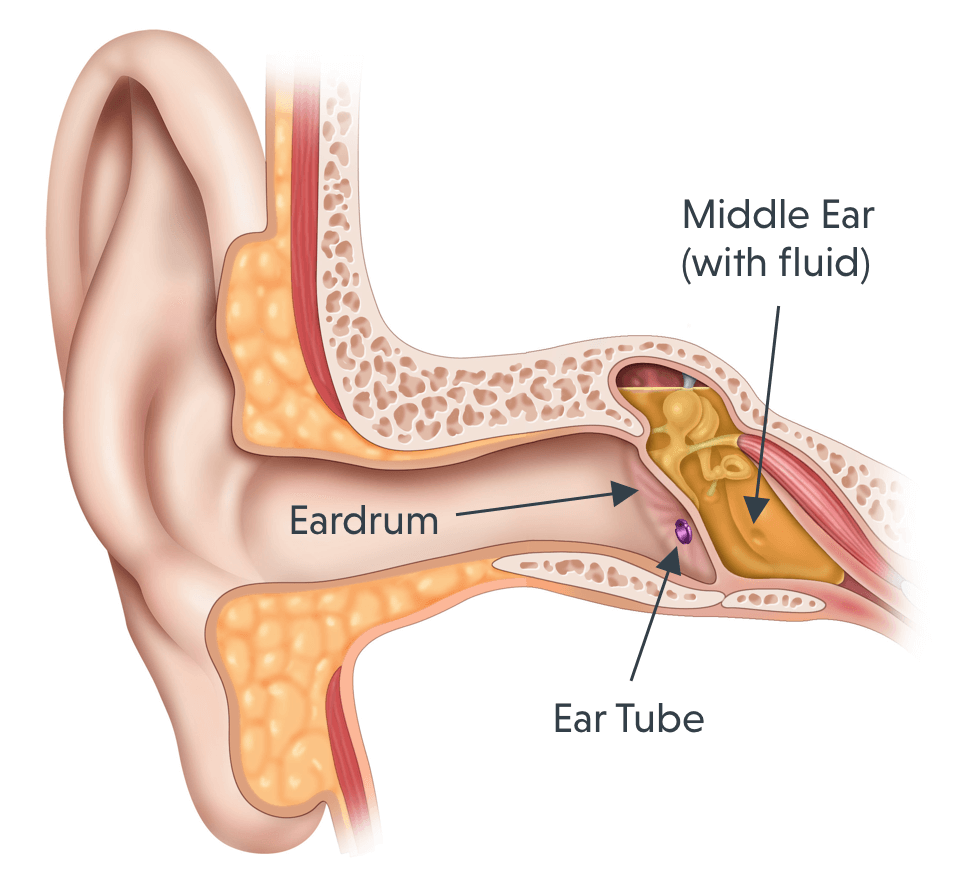
Most people are aware that middle ear infections are very common in young children. Many pediatrician visits result in treatment for otitis media, which, in children, often presents as glue ear and may be accompanied by pain, fever and reduced hearing. Children are known to be more prone to this condition due to their more horizontal Eustachian tubes and propensity for harvesting infections in general. Pain may increase until the eardrum ruptures from fluid pressure. Over 5 million cases of acute Otitis Media are reported annually in the US.
Adults can find themselves with middle ear fluid as well. This may or may not be associated with an infection. Patients often report their primary physician suspected fluid in the ears. Often the fluid trapped behind adults eardrums is serous and is typically painless. This may be the result of Eustachian tube dysfunction, in which the middle ear space cannot drain to the throat adequately, often due to congestion in the tube itself. The tympanic membrane is drawn backwards from negative pressure, and yellow watery fluid may be present, having been drawn from the tissues lining the middle ear cavity.
Symptoms most seen in adults include drainage, ear pain, recent decrease in hearing, ear fullness sensations, recent dizziness or balance difficulty, fever , and even pain, especially in children. It should be correctly diagnosed and treated swiftly.
You May Like: Best Over The Counter Tooth Infection Medicine
How To Keep Water Out
Sometimes the best offense is a good defense. To stop moisture from building up in your ears to begin with, try these tips.
- Remove earbuds if youâre sweaty.
- Coat a cotton ball with petroleum jelly and slip it into your outer ears during a bath.
- Block your ears with cotton balls when you use hair spray or hair dye.
- Use earplugs and a swim cap when you go into the water.
- Have your doctor remove earwax if you think you have a problem with wax buildup. Yes, it protects your ears, but too much can trap water in the canal. Always check with your doctor. Never try to get it out yourself.
- Use hydrogen peroxide with your doctorâs approval. If you have wax buildup, they may suggest you clean your ears with a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution. But you canât do this if you have tubes in your ears. Put about half of an ear dropper full in your ear. Let it bubble up. Then turn your head to the side, gently pull on the top of your ear, and let it drain.
What To Do For Acute Otitis Media
Some ear infections will clear up on their own without treatment. Pain management may be all thats needed to let the body fight the infection. Applying a warm cloth to the infected ear and using over-the-counter pain relievers may be enough to help manage the pain until the infection clears up. You can buy anesthetic ear drops over the counter, but dont use these if theres a hole or tear in the eardrum. Ibuprofen and acetaminophen are appropriate relievers for kids, but never give a child aspirin due to the risk of Reyes syndrome.
However, anyone with severe ear pain or a higher than 102 degrees Fahrenheit needs to be evaluated by a doctor. The doctor may prescribe antibiotics to fight the ear infection.
If ear infections become a recurring problem, the doctor may want to put tubes in the ears. This is performed with a myringotomy, in which the surgeon creates a small hole in the eardrum to drain fluid from the middle ear. Then the doctor inserts a tiny tube into the eardrum to equalize the pressure on both sides of the eardrum.
Read Also: Can You Give Yourself A Yeast Infection
What Are The Harms Of Fluid Buildup In Your Ears Or Repeated Or Ongoing Ear Infections
Most ear infections dont cause long-term problems, but when they do happen, complications can include:
- Loss of hearing: Some mild, temporary hearing loss usually occurs during an ear infection. Ongoing infections, infections that repeatedly occur, damage to internal structures in the ear from a buildup of fluid can cause more significant hearing loss.
- Delayed speech and language development: Children need to hear to learn language and develop speech. Muffled hearing for any length of time or loss of hearing can significantly delay or hamper development.
- Tear in the eardrum: A tear can develop in the eardrum from pressure from the long-lasting presence of fluid in the middle ear. About 5% to 10% of children with an ear infection develop a small tear in their eardrum. If the tear doesnt heal on its own, surgery may be needed. If you have drainage/discharge from your ear, do not place anything into your ear canal. Doing so can be dangerous if there is an accident with the item touching the ear drum.
- Spread of the infection: Infection that doesnt go away on its own, is untreated or is not fully resolved with treatment may spread beyond the ear. Infection can damage the nearby mastoid bone . On rare occasions, infection can spread to the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord and cause meningitis.
How Is An Acute Middle Ear Infection Treated
Many doctors will prescribe an antibiotic, such as amoxicillin, to be taken over seven to 10 days. Your doctor also may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, or eardrops, to help with fever and pain.
If your doctor isnt able to make a definite diagnosis of OM and your child doesnt have severe ear pain or a fever, your doctor might ask you to wait a day or two to see if the earache goes away. The American Academy of Pediatrics issued guidelines in 2013 that encourage doctors to observe and closely follow these children with ear infections that cant be definitively diagnosed, especially those between the ages of 6 months to 2 years. If theres no improvement within 48 to 72 hours from when symptoms began, the guidelines recommend doctors start antibiotic therapy. Sometimes ear pain isnt caused by infection, and some ear infections may get better without antibiotics. Using antibiotics cautiously and with good reason helps prevent the development of bacteria that become resistant to antibiotics.
If your doctor prescribes an antibiotic, its important to make sure your child takes it exactly as prescribed and for the full amount of time. Even though your child may seem better in a few days, the infection still hasnt completely cleared from the ear. Stopping the medicine too soon could allow the infection to come back. Its also important to return for your childs follow-up visit, so that the doctor can check if the infection is gone.
You May Like: Rx Ear Drops For Ear Infection
Massage For Ear Infection And Earache
My son used to have ear infections very frequently before he had his adenoids and tonsils removed. He used to suffer from earaches a lot and we used to help him get better with pain relievers. At that time, we got help from an osteopath but no matter how much he tried, ear infection came back. The last ear infection he got was last summer because of diving into the pool too many times. The fluid must have gotten into his middle ear so quickly that he turned from a happy, active child to poor, miserable kiddo writhing in pain within half an hour.
In all honesty, I thought he was exaggerating at the time. Until I got an ear infection myself a few months later following a sinus infection. The pain in my ear was so excruciating that I, a 38-year-old woman, started to cry in bed. All I could think of was how I really wanted to apologize from my son for thinking he was acting, as soon as I got rid of the pain.
I asked my husband to look up a massage video for ear infection to drain the fluid from the middle ear and relieve the earache. I was too much in pain to even open my eyes. I was trying every possible home remedy I could think of:
Lymphatic Massage Tools
My husband came back and told me he was going to do a massage to help me with the pain. After a few strokes, I already started to feel better. After massaging for 5 minutes, the pain was dissipating. After 10 minutes, the pain was gone and I was able to fall asleep.
Below is the massage video, that I bookmarked for life.