How Do Doctors Diagnose Inner Ear Infection
An instrument called a pneumatic otoscope is often the only specialized tool a doctor needs to diagnose an ear infection. This instrument enables the doctor to look in the ear and judge whether there is fluid behind the eardrum. With the pneumatic otoscope, the doctor gently puffs air against the eardrum.
How Should Augmentin Be Taken
For Adults:
- The usual adult dose is one 500-mg tablet of Augmentin every 12 hours or one 250-mg tablet of Augmentin every 8 hours. For more severe infections and infections of the respiratory tract, the dose should be one 875-mg tablet of Augmentin every 12 hours or one 500-mg tablet of Augmentin every 8 hours. Adults who have difficulty swallowing may be given the 125 mg/5 mL or 250 mg/5 mL suspension in place of the 500-mg tablet. The 200 mg/5 mL suspension or the 400 mg/5 mL suspension may be used in place of the 875-mg tablet.
- Two 250-mg tablets of Augmentin should not be substituted for one 500-mg tablet of Augmentin. Since both the 250-mg and 500-mg tablets of Augmentin contain the same amount of clavulanic acid , two 250-mg tablets are not equivalent to one 500-mg tablet of Augmentin.
- The 250-mg tablet of Augmentin and the 250-mg chewable tablet should not be substituted for each other, as they are not interchangeable. The 250-mg tablet of Augmentin and the 250-mg chewable tablet do not contain the same amount of clavulanic acid . The 250-mg tablet of Augmentin contains 125 mg of clavulanic acid, whereas the 250-mg chewable tablet contains 62.5 mg of clavulanic acid.
What Are The Signs That An Antibiotic Is Not Working For A Urinary Tract Infection
Usually people start to feel better within 1-2 days of starting an antibiotic to treat a bladder infection. If your symptoms dont improve or you start to feel worse then your antibiotic may not be working.
The symptoms of an uncomplicated bladder infection typically include:
- Pain or a burning sensation when you urinate or pee
- Needing to pee frequently
- Feeling like you need to pee within minutes of going
- Blood stained pee
- Feeling pressure or cramping in your lower abdomen
If your antibiotic is not working then these symptoms will likely continue and you may even develop symptoms of a more serious kidney infection including:
- Fever
- Pain in your lower back or side
- Nausea and vomiting
Left untreated, kidney infections can permanently damage the kidneys and can sometimes become life-threatening.
Kidney infections are usually treated with a longer 7-14 day course of antibiotics and in more severe or complicated cases may require treatment with intravenous antibiotics and admission to hospital. If you have a kidney infection it may take you a few more days to feel better after you start antibiotics.
You May Like: Over The Counter Yeast Infection Meds
Dangers Of An Unresolved Dental Abscesses
Leaving an abscess untreated will lead to serious medical complications in addition to severe pain. The infection will spread to other parts of your body, including your brain and nearby organs.
A dental abscess infection that travels to the brain is very difficult to treat because of the blood-brain barrier. Its also common for infections to spread into the sinuses.
An infection in your teeth or gums might indicate that you have heart health problems. Researchers believe gum disease is linked to heart disease and heart attack risk.
The infection can also spread to the surrounding bones. Facial bones are especially intolerant to infection. There is a high risk that bone removal will be needed to stop the further spread of the infection.
Even if you have a mild abscess, it can spread and weaken the bones, which creates problems in the future for your teeth.
An untreated abscess also poses a risk for tooth loss. Usually, a root canal and crown are enough to save the affected tooth. However, left untreated, theres a high likelihood your dentist will need to pull the tooth.
One of the most serious issues linked to untreated dental abscesses is . This is an infection in the bloodstream and it puts your entire body at risk.
If the abscess is not treated in time and it ruptures, the infection can spill into your blood and circulate throughout your body. and requires IV antibiotic treatment and long-term hospitalization.
Summary
Can Amoxicillin Not Working For Ear Infection

Likely causes of amoxicillin-unresponsive AOM include infection caused by amoxicillin-resistant bacteria, inadequate dosing or absorption of amoxicillin, poor penetration of amoxicillin into the middle ear space, reinfection with a second organism, and AOM caused by viral infection or viral and bacterial co-infection.
Read Also: Can Strep Cause An Ear Infection
Do You Need Antibiotics
Your physician may recommend a watch-and-see approach rather than prescribing antibiotics right away. Typically, you will keep an eye on symptoms for three days to see if they improve. This approach usually is used for children whose ear infections cannot be definitively diagnosed or who are under the age of 2.
If the infection does not clear up, you will need antibiotics. In some cases, a doctor will write you a prescription just in case the infection does not clear up.
If the ear infection is caused by a virus, antibiotics will not be prescribed because they do not work against viruses. Relieving symptoms while keeping an eye on the progression of the infection is the best course of treatment for a viral ear infection.
Types Of Ear Infections
The most common type of ear infection is called acute otitis media .
AOM infections
AOM is more common in children because they have smaller eustachian tubes. Located between the middle ear and upper throat, these tubes are responsible for fluid drainage.
If this fluid doesnt drain, a buildup and infection may occur. Fluid trapped in the middle ear behind your eardrum may also cause:
Other common infections
Other common types of ear infections include:
- Otitis media with effusion . The infection has cleared up, but fluid may still be stuck in the middle ear.
- Chronic otitis media with effusion . Fluid continues to build up on a recurring basis despite the lack of infection. This chronic condition can lead to serious side effects, such as hearing loss .
- Swimmers ear : occurs in the outer ear when water becomes trapped and promotes bacterial growth in the ear canal.
Don’t Miss: Natural Remedies For Tooth Infection Swelling
The Link To Hearing Loss
Middle ear infections can affect your child’s hearing. This can be unsettling, but it’s almost always temporary and doesn’t result in any permanent hearing loss. Still, any hearing loss should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Addressing hearing loss is important because infants and toddlers who suffer from chronic ear infections experience stretches of mild hearing loss during a crucial learning period for speech and language.
What Are The Complications
The most serious complications secondary to ear infections are mastoiditis and meningitis . Both are extremely rare.
Chronic draining ears and chronic perforations are uncommon, but occur more frequently as a result of resistant pneumococcus. However, these complications are commonly seen in developing countries where antibiotics are not readily available. Permanent hearing loss from very severe recurrent infections is a major concern, but is still rarely observed with effective antibiotic therapy. Children with an ear infection suffer only some temporary, low grade hearing loss. As the fluid resolves, which may take months, the hearing returns to baseline levels.
Your child’s doctor may work with an ear-nose-and-throat doctor to help treat the more severely afflicted child, or one who has suspected chronic hearing loss. Children with chronic fluid persisting for more than four months, or with more than five or six ear infections in a year, may require the insertion of “tubes.” This is most important during the first two years of life when hearing is critical for speech and language development. Chronic ear infections may aggravate learning and later school problems, but cause and effect on this issue remains speculative.
You May Like: I Have A Urinary Tract Infection And Im Bleeding
Whats The Difference Between Antibiotic Solutions And Suspensions
Solutions are liquids where the active ingredients are dissolved. Suspensions are liquids in which the particles are suspended, or scattered throughout the liquid, and not quite dissolved. Some medications are stable as a suspension but not as a solution.
The main difference between the two is how irritating they might be. Antibiotic solutions are generally more irritating than suspensions because solutions have a more acidic pH of 3-4, whereas suspensions have a less acidic pH of 5.
Solutions may also contain alcohol to help kill bacteria, but the alcohol can be extremely irritating when these solutions are applied.
What Happens If An Antibiotic Doesn’t Work For A Urinary Tract Infection
Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for urinary tract infections , most of which are caused by a bacteria called Escherichia Coli . Infections of the lower urinary tract, which includes bladder infections , are the most common type of UTI and are usually treated with a 3-5 day course of antibiotics. Sometimes, however, the antibiotic prescribed to treat a bladder infection doesnt work.
If you suspect your antibiotic isnt working you should promptly contact your healthcare provider. Left untreated a UTI may become more serious and in rare cases cause permanent or life-threatening complications.
Read Also: Amoxicillin Vs Penicillin For Tooth Infection
Cautions With Other Medicines
There are some medicines that do not mix well with amoxicillin.
Tell your doctor if you’re taking any of these medicines before you start taking amoxicillin:
- methotrexate, used to treat arthritis and psoriasis
- warfarin, a medicine to prevent blood clots
- gout medicines called probenecid or allopurinol
- other antibiotics
Tell your doctor if you’ve recently had, or are due to have, an oral typhoid vaccine. Amoxicillin can make it less effective.
What Should I Do If My Antibiotic Doesnt Work For My Urinary Tract Infection
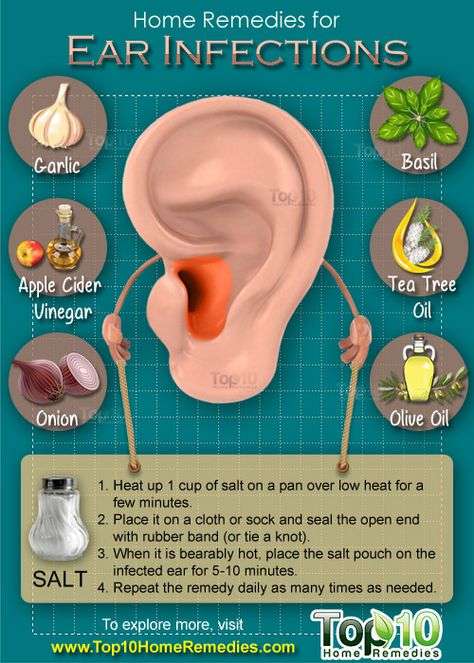
If your symptoms dont improve within a couple of days or get worse after starting an antibiotic you should contact your healthcare provider. A different antibiotic, a longer course of antibiotics or another treatment may be required. A physical exam or urine sample may be required.
When you have a UTI its important to:
- Only take an antibiotic that has been prescribed for you
- Take the antibiotic exactly as instructed by your healthcare provider and finish the full course of treatment even if you feel better
- Drink plenty of water and other fluids
- Urinate or pee regularly
You May Like: Can Hiv Cause Ear Infection
All About Ear Infections
Ear infection: The diagnosis strikes fear in the hearts of parents, who want to do what’s best for their child but tend to get conflicting medical advice. What makes ear infections so troubling is not only the damage that repeated infections can cause, but also the danger of over-treating the infection: antibiotic resistance. What’s a concerned parent to do? Here’s what the experts know.
How Common Is Acute Otitis Media
Acute otitis media is predominantly an infection of young children, primarily occurring in the first three years of life. Children in the 1990s experience 30% more episodes of acute otitis media as compared with children in the 1970s, probably as a consequence of high rates of day care. Currently, acute otitis media accounts for one-fourth of all pediatric office visits in the first three years.
Nearly 94% of children will experience at least one ear infection in the first three years of life, with an average of about three episodes in the first and second years, and one and one-half episodes in the third year. As many as 5% to 8% of children will undergo the placement of ventilating tubes in their first 24 months of life. Much of this is related to the high rate of daycare attendance in the United States, with increased exposure to infectious agents.
Don’t Miss: Will Bactrim Treat Tooth Infection
When To Seek Medical Advice
Most cases of otitis media pass within a few days, so there’s usually no need to see your GP.
However, see your GP if you or your child have:
- symptoms showing no sign of improvement after two or three days
- a lot of pain
- a discharge of pus or fluid from the ear some people develop a persistent and painless ear discharge that lasts for many months, known as chronic suppurative otitis media
- an underlying health condition, such as cystic fibrosis or congenital heart disease, which could make complications more likely
Read more about diagnosing middle ear infections
Joy Victory Managing Editor Healthy Hearing
Joy Victory has extensive experience editing consumer health information. Her training in particular has focused on how to best communicate evidence-based medical guidelines and clinical trial results to the public. She strives to make health content accurate, accessible and engaging to the public.Read more about Joy.
You May Like: Is A Uti And Yeast Infection The Same Thing
Diagnosis Of Ear Infections
Your physician will look into your ear with an otoscope, a medical instrument with a light on one end designed to get a better view inside the ear. Your doctor will look for the visual signs of ear infection, such as redness and inflammation.
To check for fluid buildup, a pneumatic otoscope, which blows air at the eardrum, will be used. If there is excessive fluid behind the eardrum, it will not move as it should when the air hits it.
In some cases, hearing tests may also be performed to assess any damage to the ear from the infection.
Different types of ear infections present with different symptoms, which can include:
- Inner ear infections: Hearing loss, ringing in the ears , dizziness, loss of balance, nausea and vomiting, and ear pain
- Middle ear infections: Fluid in the ear, ear pain, fever, a feeling of general illness, pressure in the ears, and hearing loss
- Outer ear infections: Inflammation of the ear canal, itching in the ear, ear pain, swelling of the ear canal, redness, and fluid draining from the ear
Ear Infection Doctor Discussion Guide
Children with ear infections, especially toddlers or infants, may not be able to describe their symptoms, but an ear infection will often present with the following signs:
- Tugging or pulling at their ears
- Fussing or crying
- Being clumsy and having balance issues
- Trouble hearing or responding to quiet noises
Who Shouldn’t Use Ear Drops
Ear drops can be helpful when treating an ear infection, but there are times when you shouldnât use them. For example, if you or your child has a perforated eardrum, you should avoid the use of certain ototoxic ear drops because fluid from the drops can get deep into the ear and cause more problems.
Also Check: How To Reduce Tooth Infection Without Antibiotics
How Is An Ear Infection Treated
The intense ear pain of acute otitis media can be partially relieved by adequate doses of ibuprofen or acetaminophen. For more severe earaches, some doctors may prescribe codeine. Numbing eardrops provide minimal relief, and only for a short time. A warm washcloth or sweet oil directly instilled in the ear canal may temporarily distract from the child’s ear pain.
Nearly all doctors in the United States believe that acute otitis media should be treated with antibiotics by mouth, particularly if the child has symptoms. Antibiotics generally provide prompt and dramatic relief of the ear pain. Oral antibiotics for acute otitis media are safe and effective, with exceedingly rare serious side effects.
In a few European countries, ear infections are not treated in children older than two years, unless symptoms persist for more than 48 hours. A few U.S. physicians recommend this same tactic.
Amoxicillin is the drug of choice for initial ear infections, except in the penicillin allergic child. In an attempt to enhance the effectiveness of this inexpensive and safe antibiotic, many doctors are now prescribing amoxicillin twice a day and in double the daily standard dose. Effectiveness for initial therapy with most antibiotics approaches 70% to 80%. There are other antibiotics to treat children who do not respond to amoxicillin or who never seem to respond to initial amoxicillin therapy.
Tympanocentesis:
How Do You Know When Your Child Has An Ear Infection
The most common symptom of an ear infection is ear pain. While an older child can tell you that his ear hurts, a younger child may simply act irritable and cry more than usual. Lying down, feeding, and sucking cause painful pressure changes in the middle ear, so the child may eat less than the normal amount or have trouble sleeping. Other symptoms are fever, loss of balance, difficulty hearing, and yellow or blood-spotted drainage from the child’s ear. If your child tugs at her ear, it may not be due to an ear infection. Ear pain or irritability can also be caused by a sore throat, teething, or swimmer’s ear.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get A Wax With A Yeast Infection
Research May Reveal Why Some Ear Infections Refuse To Go Away
— Unfortunately for kids with painful ear infections, whatever doesn’t kill the bacteria invading their middle ears will only make them stronger.
New laboratory research suggests that antibiotics commonly used to treat ear infections can stimulate certain strains to form “mats,” called biofilms, which protect the bacteria from antibiotics. The results may explain why some earaches return, even after multiple rounds of antibiotics.
People come into contact with biofilms all the time. They are the gunk on your teeth after eating candy and the red scum on your unscrubbed tub. But when infectious bacteria form biofilms in the body, they can be especially hard to remove.
Biofilms help bacteria to evade antibiotics by shielding live cells with layers upon layers of dead bacterial cells, which are held together by sticky sugars, proteins, and even long strands of DNA released from the dead microbes. This glue-like mix of materials sticks the cells to one another and to surfaces in the body.
In the lab, the researchers exposed different strains of NTHi to three antibiotics commonly prescribed to treat ear infections. Though the bacteria can form biofilms on their own, when exposed to lower, sub-lethal levels of antibiotics, many made bigger, thicker films. This could happen in the body when a person misses a dose, stops treatment early or when inflammation prevents the drugs from reaching the ear fluid.
But many parents still want an immediate prescription, just to be safe.