Coverage And Cost Comparison Of Amoxicillin Vs Augmentin
Amoxicillin is a generic antibiotic that is covered by Medicare and insurance plans. As a generic drug, it can often be purchased at low costs depending on the prescription. The average retail cost is around $24. A SingleCare amoxicillin coupon may help lower the cost of an amoxicillin prescription.
Augmentin is a brand-name antibiotic that is also available as a generic version. The generic version is usually covered by Medicare and insurance plans. The average retail cost of Augmentin is around $167 depending on the prescription. An may help lower the cash price of generic Augmentin.
| Amoxicillin |
| Yes | 1% |
Frequency is not based on data from a head-to-head trial. This may not be a complete list of adverse effects that can occur. Please refer to your doctor or healthcare provider to learn more.
If You Forget To Take It
If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s nearly time for your next dose. In this case, just leave out the missed dose and take your next dose at the usual time.
Never take 2 doses at the same time. Never take an extra dose to make up for a forgotten one.
If you forget doses often, it may help to set an alarm to remind you. You could also ask your pharmacist for advice on other ways to remember your medicines.
Antibiotics For Ear Infections: The Best Treatment Options
Ear infections are incredibly common in children, and they can also affect adults. Oftentimes ear infections go away in a few days without any treatment. When an ear infection is severe or doesnt resolve on its own, antibiotics may be a necessary and effective treatment.
In this article, Ill describe the different types of ear infections that affect children and adults. Then Ill discuss the antibiotics used to treat ear infections and their possible side effects.
Finally, Ill explain other treatment options, how best to prevent ear infections, and when you should speak with your doctor or pediatrician.
Recommended Reading: Antibiotics For Infected Cartilage Piercing
Symptoms Of Ear Infections
- The main symptom is an earache.
- Younger children will cry, act fussy or have trouble sleeping because of pain.
- About 50% of children with an ear infection will have a fever.
- Complication: In 5% to 10% of children, the eardrum will develop a small tear. This is from the pressure in the middle ear. The ear then drains cloudy fluid or pus. This small hole most often heals over in 2 or 3 days.
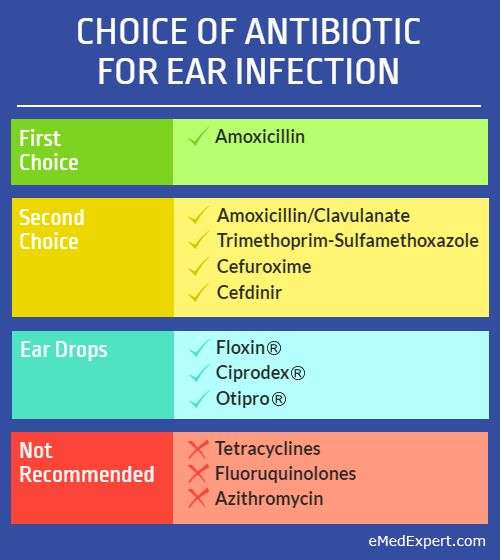
Amoxicillin Clavulanate In Treatment Of Acute Otitis Media
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| Verified February 2009 by University of Turku. Recruitment status was: Active, not recruitingFirst Posted : March 6, 2006Last Update Posted : February 11, 2009 |
| Study Type : | |
| Quadruple | |
| Primary Purpose: | Treatment |
| Official Title: | Phase 4 Efficacy Study of Antimicrobials in the Treatment of Acute Otitis Media in Young Children |
| Study Start Date : |
| Reconstituted amoxicillin-clavulanate at 40/5.7 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses for 7 days. | Drug: amoxicillin-clavulanateAmoxicillin clavulanate 40 mg/kg/day divided into two daily doses for 7 days. Capsules will be produced by pulverizing amoxicillin clavulanate tablets and mixing that with lactose monohydrate. Each capsule will contain Augmentin tablet powder 68 mg and lactose monohydrate 572 mg. This means amoxicillin 40 mg and clavulanate 5,7 mg respecting the dose per 2 kg. |
| Placebo Comparator: 2Reconstituted placebo in 2 divided doses for 7 days. | Drug: PlaceboPlacebo twice a day for 7 days. Placebo capsules contain lactose monohydrate 640 mg. |
Don’t Miss: Three Stages Of Hiv Infection
The Natural History Of Aom
Surprisingly, clinical outcome of antibiotic therapy for AOM correlates poorly with in vitro antibiotic sensitivity of the causative organism. Most experimental evidence demonstrates that clinical outcome is determined chiefly by host and pathogen factors and that antibiotic therapy plays a smaller role. In general, antibiotic therapy has little effect on long-term outcome of AOM, such as clearance of effusion. The high rate of spontaneous resolution and the frequent occurrence of recalcitrant AOM have made it almost impossible to demonstrate any significant difference between different antibiotic therapies in clinical trials.
Chlamydia pneumoniae is an atypical pathogen commonly associated with upper respiratory infections in children. It differs from the otitis pathogens just described in that it is relatively insensitive to b-lactams but, for now at least, remains sensitive to macrolides. In fact, C pneumoniae has been recently detected by culture or polymerase chain reaction in up to 8% of middle ear specimens.19 However, it is also commonly found in nasopharyngeal specimens from well preschoolers.20 In the few cases of C pneumoniae associated AOM studied, most infected patients improved without macrolide therapy. Clearly, this area needs further study. For now, we do not believe that the theoretical benefit of action against atypical organisms justifies the use of macrolide antibiotics as routine second-line therapy for amoxicillin-unresponsive AOM.
What Are Symptoms Of Ear Infections
Symptoms of ear infections include:
Additional signs of ear infections in young children and infants may also include:
- Pulling on the ear/rubbing the ear
Middle ear infection is usually caused by:
- Bacteria the most common bacterial causes include:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Haemophilus influenzae
Infections of the ear canal are usually caused by water that remains in the outer ear canal for an extended period of time, which, when combined with the earwax and debris already present in the ear canal, provided a moist environment for bacteria or yeast to grow and cause infection. While its commonly called swimmers ear, diving or bathing and showering can also permit just enough water into the ear to create a fertile breeding ground for infection.
Don’t Miss: Strongest Antibiotic For Tooth Infection
Interpreting The Recommendations Of The Cdc Working Group
According to the CDC report, amoxicillin remains the initial drug of choice for the treatment of acute otitis media. Higher dosages of amoxicillin are recommended to address the issue of penicillin-resistant pneumococci.25 The increased dosage produces higher levels of amoxicillin in middle ear fluid.26 However, regardless of the dosage, amoxicillin will not eradicate beta-lactamaseproducing H. influenzae or M. catarrhalis. For this reason, alternatives to amoxicillin should ideally be effective against these beta-lactamaseproducing pathogens.
The CDC recommendations include the possibility of performing tympanocentesis in selected cases to guide management of refractory acute otitis media. Few family physicians, however, perform this procedure. Otolaryngologists are infrequently available to accommodate a same-day referral for the procedure, and still fewer have done it without the benefit of general anesthesia.
Who Should Use Antibiotic Eardrops
Antibiotic eardrops can be more effective and safer for:
- People with Swimmers Ear, an infection caused by water in the ear.
- Children who have tubes in their ears. The tubes prevent most infections behind the eardruman area known as the middle ear. If there is an infection, antibiotic eardrops can be given right through the tube.
Also Check: Airborne Infection Isolation Room Requirements
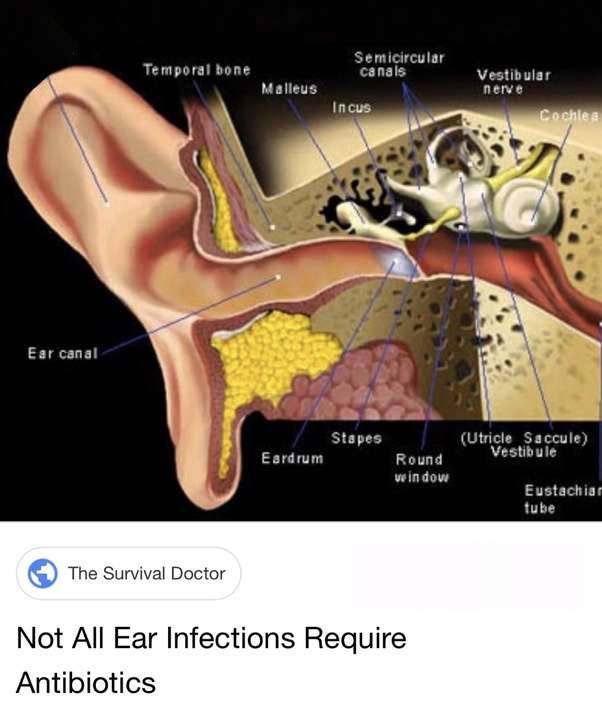
Treating Middle Ear Infections
The middle ear is internal. It starts behind the eardrum and goes to the oval window . It contains three tiny bones, called the ossicles, that are necessary for hearing function.
The auditory tube runs from the middle ear to the throat. Its function is to ventilate and equalize pressure in the middle ear. Fluid from the middle ear space drains into the throat and is usually swallowed.
What Is Amoxicillin What Is Augmentin How Do They Work
Amoxicillin belongs to a class of antibiotics called penicillins. Other members of this class include ampicillin , piperacillin , ticarcillin , and several others. Amoxicillin is used to treat infections due to bacteria that are susceptible to the effects of amoxicillin. Common bacterial infections that amoxicillin is used for include infections of the middle ear, tonsils, throat, larynx , bronchi , lungs , urinary tract, and skin. Amoxicillin also is used to treat gonorrhea.
Augmentin is a combination antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections including sinusitis, pneumonia, ear infections, bronchitis, urinary tract infections, and infections of the skin. Amoxicillin belongs to the penicillin drug class.
Read Also: Is An Infected Wisdom Tooth An Emergency
Ear Piercing Infection Effects
If the infection is in the acute early stages, catching it right away can help stop the situation from becoming chronic. Seek medical advice if you were recently diagnosed with an acute ear infection, but the treatment advised by your doctor has been ineffective, or your symptoms are increasing. If you are exhibiting signs of a recurring infection, you need to get in to see the doctor at once.
These regimen of antibiotics shall soon eradicate the infection. Antibiotic ear drops may also help to reduce any pain you experience. For severe, chronic diseases, the doctor may advise surgery if you do not experience any improvement after receiving treatment or your hearing is being affected. For children who have their ears pierces on their younger years, particularly hearing problems can cause speech and language impediments during a formative period, so the issue must be dealt with summarily.
Read Also: Safe Yeast Infection Treatment While Pregnant
But Will It Still Work
In most cases, yes! Thats why the guidelines for treating ear infections changed in 2013.However, each childs situation is unique, and your familys medical provider is the best personto decide how long your child should take an antibiotic for an ear infection. On the other hand, ifyour child is over the age of two and has a non-severe ear infection, it makes sense to ask yourprovider about the possibility of a shorter course of treatment.
As always, talk to your doctor if you have other questions or concerns, and always follow thedirections on your childs medication.
You can read the full AAP clinical practice guideline for treating ear infections here.
If you are a medical provider, please consider taking our 5-minute survey.
Recommended Reading: Chicago Fire Infection Part 2
Amoxicillin & Clavulanate Potassium Compound
beta-lactam antibiotic drugClavamox chewable tablets soft tissue infectionsFDA approved veterinary antibacterial drug62mg, 125mg, 250mg, and 375mgThe recommended dose of amoxicillin trihydrate and clavulanate potassium for ear infections in dogs is6.25mg per pound125mg per day125mg/day doses in two divided doses like 62.5mg in the morning and 62.5mg in the evening
Pretx Pediatric Research In Emergency Therapeutics
Child Health Update is produced by the Pediatric Research in Emergency Therapeutics program at the BC Childrens Hospital in Vancouver, BC. Dr Sakulchit is a member and Dr Goldman is Director of the PRETx program. The mission of the PRETx program is to promote child health through evidence-based research in therapeutics in pediatric emergency medicine.
Do you have questions about the effects of drugs, chemicals, radiation, or infections in children? We invite you to submit them to the PRETx program by fax at 604 875-2414 they will be addressed in future Child Health Updates. Published Child Health Updates are available on the Canadian Family Physician website .
Don’t Miss: Tooth Infection And Hip Replacement
Combatting The Myth Of Amoxicillin Immunity
A major complication of amoxicillin failure is that it convinces many parents that “amoxicillin doesn’t work for my child anymore.” Once a patient has failed to respond to amoxicillin therapy, it is tempting to label that patient “amoxicillin unresponsive” and to exclude amoxicillin from the armamentarium available for future episodes of AOM. However, as reviewed above, it is inappropriate to attribute all episodes of amoxicillin-unresponsive AOM to resistance. In most cases, the bacteria isolated from these patients are sensitive to amoxicillin. The impact of initial antibiotic choice on outcome is minimal. One population-based study found a 12% to 13% rate of antibiotic failure as measured by a prescription for a second course of antibiotics within three weeks.35 The failure rate was similar regardless of the agent first prescribed, but the cost of the prescription was five- to 20-fold higher for the second-line agent. So, despite occasional failure, amoxicillin should remain the first choice for pediatric patients with AOM.
Patients with recurrent AOM might benefit from influenza and pneumococcal immunization, and their parents may respond to a discussion of risk factors such as cigarette smoke, pacifiers, and group day care. Most parents are more willing to accept a watchful approach to AOM therapy once they understand the risks that “antibiotic roulette” poses to a child in day care.
What Causes Ear Infections
The ear is organized into three structures, the outer, middle, and inner ear. The outer ear contains the outer structure, the auditory canal and the tympanic membrane .
The inner ear is an air-filled space that contains three small bones responsible for transferring vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. The inner ear is within the temporal bone and contains membranes and a solution which is responsible for sound transmission.
There are three types of ear infections:
- Acute otitis media: an infection of the middle ear
- Otitis media with effusion: an infection of the middle ear when fluid builds up causing an infection
- Swimmers ear: infection of the outer ear canal
Bacteria or viruses cause ear infections. The most common bacteria for ear infections include streptococcus pneumoniae and haemophilus influenzae. Viruses that cause the common cold can cause ear infections.
Symptoms include:
You May Like: Does Bactrim Help With Tooth Infection
Common Questions About Amoxicillin
There’s no evidence to suggest that taking amoxicillin reduces fertility in either men or women.
If you or your child take amoxicillin as a liquid medicine, it can stain your teeth. This does not last and should go after brushing your teeth well.
Amoxicillin capsules do not stain teeth.
Yes. Amoxicillin should not affect you being able to drive or cycle.
You can eat and drink normally while taking amoxicillin.
Yes, you can drink alcohol with amoxicillin.
What Drugs Interact With Zithromax
Zithromax may interact with arsenic trioxide, cyclosporine, pimozide, tacrolimus, theophylline, warfarin, other antibiotics, antidepressants, anti-malaria medications, cholesterol-lowering medicines, ergot medicines, heart or blood pressure medications, heart rhythm medicines, HIV medicines, medicine to prevent or treat nausea and vomiting, medicines to treat psychiatric disorders, migraine headache medicines, narcotics, sedatives, tranquilizers, or seizure medicines. Tell your doctor all medications and supplements you use.
Don’t Miss: Can Your Jaw Hurt From A Sinus Infection
Oral Antibiotics Have Risks
- Oral antibiotics are more likely to cause resistant bacteria outside the ear. When that happens, these medicines will not work as well in the future. Illnesses will be harder to cure and more costly to treat.
- Antibiotic eardrops kill the bacteria faster and more completely than oral antibiotics. Drops dont go into the bloodstream, so more medicine reaches the infection.
Early Antibiotics Help Ear Infections In Young Children

Study Leaders Predict Changes in the Current Watch-and-Wait Approach
Jan. 12, 2011 — Young children with ear infections recover faster and more completely if doctors give antibiotics right away rather than waiting to see if the kids get better on their own.
The findings come from two clinical trials, one in the U.S. and one in Finland. For young children with middle ear infections — otitis media — both studies found immediate antibiotic treatment far superior to watchful waiting.
Current treatment recommendations in the U.S., Canada, and Europe allow for a watch-and-wait approach to suspected middle ear infections in young children. Change is coming, predicts study leader Alejandro Hoberman, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh.
“The real issue for children with acute otitis media is that the circumstances for when to give antibiotic treatment are unclear,” Hoberman tells WebMD. “I truly believe, based on our results, that once they are diagnosed properly, more young children will recover more quickly when treated with antibiotics.”
Infectious disease expert Jerome Klein, MD, of Boston University School of Medicine, notes that U.S. pediatricians wait and watch only when the diagnosis of otitis media is uncertain. In Canada and many European nations, doctors are more likely to wait.
“It was very clear that the duration of symptoms were clearly better in the kids who took antibiotics,” Fauci tells WebMD. Fauci was not involved in either study.
Don’t Miss: How Can I Treat A Kidney Infection At Home
Other Ear Infection Treatment Options
Most middle ear infections go away without any treatment within 2-3 days, while inner ear infections take a few weeks to resolve on their own.
No matter the type of ear infection, your healthcare provider may recommend treatments in addition to or in place of antibiotics to help clear the infection:
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Culture and gram stain of purulent drainage of skin infections can help aid in the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections, but this is not a requirement . Alternatively, it is not recommended to perform a swab, biopsy, or blood culture from a cellulitis infection . For abscesses, incision and drainage is the recommended treatment . For infections involved with penetrating trauma, as could be the case with a recent body piercing, treatment with antimicrobials directed against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species are recommended . Recommended treatment duration is five days, but therapy extension is advisable if not improved during that treatment period .
Recommended Reading: Urgent Care For Infected Piercing