Can Middle Ear Infections Be Prevented
Its not possible to prevent middle ear infections, but there are some things you can do that may reduce your childs risk of developing the condition. These include:
- make sure your child is up-to-date with their routine vaccinations particularly the pneumococcal vaccine and the DTaP/IPV/Hib vaccine
- avoid exposing your child to smoky environments
- dont give your child a dummy once theyre older than six to 12 months old
- dont feed your child while theyre lying flat on their back
- if possible, feed your baby with breast milk rather than formula milk
Avoiding contact with other children who are unwell may also help reduce your childs chances of catching an infection that could lead to a middle ear infection.
Should I Use Antibiotics For An Ear Infection
Antibiotics are a medicine prescribed by your doctor. If youre dealing with an ear infection caused by bacteria, youll likely need antibiotics. They are the best way of quickly getting rid of a bacterial infection and preventing it from spreading to other parts of the body.
The catch is that antibiotics dont work against viruses if you use antibiotics on a viral ear infection, it can actually make the infection worse. Overuse of antibiotics can lead to a condition called antibiotic resistance, which means that the medicine becomes less effective at fighting off bacteria.
Thats why doctors are careful about using antibiotics wisely and may not immediately prescribe them for ear infections.
You May Like: Chest Pain From Tooth Infection
What Causes Chronic Sinus Infection
Multiple factors acting together usually contribute to chronic sinusitis.
People with allergies are more prone to develop chronic sinusitis. About one in five people with chronic sinusitis also have asthma. This is because the linings of your nose and sinuses are in continuation with the linings of your lungs. These people are also likely to have nasal polyps .
A bacterial or viral infection can also trigger the condition. The infection is often low grade. The bacteria confine themselves in stubborn biofilms, making it difficult for your immune system or antibiotics to find and attack them.
An overlap of additional factors such as smoking, environmental pollutants, and deviated septum, further complicate the picture of chronic sinusitis.
It would be more appropriate to say that if youre already prone to allergies and nasal polyps, it becomes easier for harmful bugs, especially fungi to penetrate your sinuses. Likewise, a weak immune system makes you more susceptible to catch bacterial, viral, or fungal sinus infection.
A sinus that is inflamed and swollen can no longer sweep away the excess mucus and harmful agents due to the blockage of tiny hairs that facilitate this function.
Recommended Reading: Summer’s Eve For Yeast Infection
What’s The Difference Between The Middle Ear Infections We Get As Children Versus The Middle Ear Infections We Get As Adults
Dr. Wang: The underlying causes are usually different. They are more frequent in children because their shorter, more horizontal Eustachian tubes are more likely to get blocked. Also, their adenoids are larger compared to the rest of the throat and can interfere with the opening of the Eustachian tubes. And finally, children’s immune systems are immature and colds and viruses are often passed around day care and school.
Are Ear Infections A Symptom Of Covid
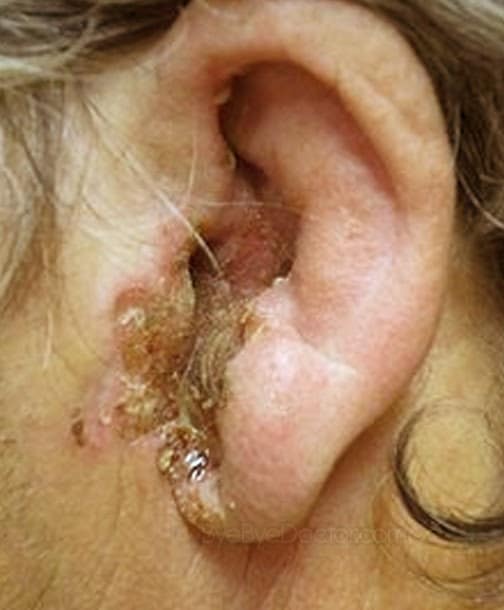
Ear infections are not typically a symptom of COVID-19. However, if you or a family member experience an earache along with other respiratory symptoms or other indicators of COVID-19, you should get tested as soon as possible. Call first before visiting a hospital, medical clinic or urgent care. Learn more about Indigos testing options.
You can also take a quick online assessment using our Coronavirus Assessment Tool, or have an e-Visit with an Indigo Online Careprovider to determine your risk and whether you need to be referred to a testing site.
Also Check: Rx693 Blue Pill For Tooth Infection
You May Like: Keep Getting Utis And Yeast Infections
What Research Is Being Done
The most important recent development to potentially reduce the frequency of ear infections is a new pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. A study from Northern California suggests that this vaccine could prevent about 7% of overall episodes of ear infections, and up to 23% of recurrent ear infections.
The new pneumococcal vaccine contains 7 of 90 types of pneumococcus, which are the most common and the most resistant bacteria. Elimination of these resistant types could have an impact on the number of antibiotic failures in children. This also could mean a reduction in the placement of tubes, possibly by one-fourth, as observed in the California study.
This vaccine is administered to infants at 2, 4, 6, and 12 months of age. Side effects have been minimal, and it has been a very safe vaccine. It uses the same technology as the universally administered HIB vaccine.
Some new antibiotics are about to undergo testing in children with acute otitis media. In preliminary testing, these drugs appear to work against the resistant pneumococcus.
About the Author
Dr. Block is a full-time practicing pediatrician in rural Bardstown, Kentucky who serves on the clinical faculties at both the University of Kentucky and the University of Louisville as an Associate Clinical Professor of Pediatrics.
His pediatric practice is one of the leading pediatric research groups in the United States and, in fact, Dr. Block was awarded the American Academy of Pediatrics 1998 Practitioner Research Award.
Surgical Treatment For Chronic Sinusitis
Although medical therapy and lifestyle tweaks are the first-line treatment for chronic rhinosinusitis, some people may fail to respond to optimal therapy. In such cases, Ear, Nose Throat and Allergy Specialist performs a surgery to widen up the blocked sinuses and remove any trapped mucus or polyps.
Other situations in which surgery could be considered include:
- When chronic sinusitis symptoms do not respond to the medical treatments listed above, and CT scan of your sinuses reveals complete blockage of one or more sinuses.
- When nasal polyps fail to shrink enough with steroids.
- When a severe deviation of the septum completely blocks your nose or hinders sinus drainage.
- When theres a suspicion of allergic fungal sinusitis. The sinuses in allergic fungal sinusitis get clogged with thick, dense mucus that is hard to remove in any way other than surgery.
Read Also: Prescription Medication For Bladder Infection
Can You Get An Outer Ear Infection From Sweating A Lot When You Work Out
Dr. Wang: It’s not common, but yes. It’s called swimmer’s ear because that is what usually causes it. But moisture can also be introduced into the ear from showering, taking a bath, rain or sweat dripping into your ear even high humidity. Outer ear infections are mostly caused by bacteria, but they can also be caused by fungus, such as the fungus that causes athlete’s foot.
When Should I Call The Doctor About An Ear Infection
- You or your child develops a stiff neck.
- Your child acts sluggish, looks or acts very sick, or does not stop crying despite all efforts.
- Your childs walk is not steady he or she is physically very weak.
- You or your childs ear pain is severe.
- You or your child has a fever over 104° F .
- Your child is showing signs of weakness in their face .
- You see bloody or pus-filled fluid draining from the ear.
- The fever remains or comes back more than 48 hours after starting an antibiotic.
- Ear pain is not better after three days of taking an antibiotic.
- Ear pain is severe.
Also Check: What Antibiotics Treat Kidney Infection
Don’t Miss: 2 Day Yeast Infection Treatment
Signs In Young Children
As babies are unable to communicate the source of their discomfort, it can be difficult to tell what’s wrong with them. Signs that a young child might have an ear infection include:
- raised temperature
- pulling, tugging or rubbing their ear
- irritability, poor feeding or restlessness at night
- coughing or a runny nose
- unresponsiveness to quiet sounds or other signs of difficulty hearing, such as inattentiveness
- loss of balance
Can Ear Infections Affect Hearing
Fluid buildup in the middle ear also blocks sound, which can lead to temporary hearing problems. Kids having a problem might:
- not respond to soft sounds
- need to turn up the TV or radio
- seem inattentive at school
In kids who have otitis media with effusion, the fluid behind the eardrum can block sound, so mild temporary hearing loss can happen, but might not be obvious.
A child whose eardrum has ruptured might have ringing or buzzing in the ear and not hear as well as usual.
Also Check: Yeast Infection From Uti Antibiotics
How Do You Know If Your Sinus Infection Is Getting Better
Lets say you do have a fever and thick, yellowish mucus. Odds are its a sinus infection. But how do you know whether or not its a bacterial sinus infection?If youre on day 3 or 4 of an infection, it will be difficult to ascertain what kind of infection you have on your own.
However, if youre somewhere between day 7 and day 11, this is what you should be on the lookout for:
- Fever is completely gone or noticeably improving
- Your congestion and discharge is obviously lessening
- You dont feel as fatigued as you did a few days ago
The theme here is obvious improvement. If your situation is improving, then you probably have a viral sinus infection and do not need antibiotics. If your situation is not improving , schedule an appointment with your doctor.
What Causes Middle Ear Infections

Most middle ear infections occur when an infection such as a cold, leads to a build-up of mucus in the middle ear and causes the Eustachian tube to become swollen or blocked.
This mean mucus can’t drain away properly, making it easier for an infection to spread into the middle ear.
An enlarged adenoid can also block the Eustachian tube. The adenoid can be removed if it causes persistent or frequent ear infections. Read more about removing adenoids.
Younger children are particularly vulnerable to middle ear infections as:
- the Eustachian tube is smaller in children than in adults
- a child’s adenoids are relatively much larger than an adults
Certain conditions can also increase the risk of middle ear infections, including:
- having a cleft palate a type of birth defect where a child has a split in the roof of their mouth
- having Down’s syndrome a genetic condition that typically causes some level of learning disability and a characteristic range of physical features
Also Check: Can Food Allergies Cause Ear Infections
Will It Happen Again And Can It Be Prevented
Most children have at least two bouts of ear infection before they are 5 years old. These are caused by common viral infections which circulate in the general population and against which your child is not immune. There is generally nothing you can do to prevent the infection from occurring. However, there is some evidence to suggest that an ear infection is less likely to develop:
- In breastfed children.
- In children who live in a smoke-free home.
- In babies and young children who do not use dummies. However, research studies have shown that the use of a dummy in young babies when getting off to sleep can reduce the risk of cot death. So, consider using a dummy in babies up to 6-12 months old at the start of each episode of sleep. But note:
- Do not force a dummy on a baby who does not want one. If the dummy falls out when a baby is asleep, just leave it out.
- Never coat a dummy with anything such as sugar.
- Clean and replace dummies regularly.
- It is best to use a dummy only to help a baby get to sleep.
- Consider stopping dummy use at around 6-12 months old.
Occasionally, some children have recurring bouts of ear infections close together. If this occurs, a specialist may advise a long course of antibiotics to prevent further bouts from occurring.
Dont Miss: I Can Smell An Infection In My Nose
What Other Types Of Ear Infections Affect Adults
Dr. Wang: A middle ear infection, or otitis media, is most frequently associated with children, but adults get them as well. This type of ear infection happens when viruses or bacteria get into the middle ear the space behind the eardrum. The middle ear fills with pus or infected fluid. The pus pushes on the eardrum, which can be very painful. Middle ear infections are caused by swelling in one or both of the Eustachian tubes. The Eustachian tubes connect the middle ear to the back of the throat and act as release valves to equalize pressure within the middle ear. When that process is interfered with, thats when infections can develop.
Read Also: Amoxicillin And Clavulanate Potassium Tooth Infection
When Else Are Antibiotics Needed
Antibiotics can be the right treatment for kids who get a lot of ear infections. Younger children or those with more severe illness may need antibiotics right from the start.
The “wait-and-see” approach also might not apply to children with other concerns, such as those who have cochlear implants, cleft palate, genetic conditions such as Down syndrome, or other illnesses such as immune system disorders.
Symptoms Of Chronic Ear Infections
Someone with a chronic ear infection does not usually have any visible symptoms. However, long-term OME can cause hearing problems and other difficulties, particularly in children. These include:
- delayed responses, or taking a long time to understand speech
- difficulties speaking or reading
- less ability to work independently
Doctors consider OME to be chronic if it lasts for or more.
According to a 2016 guideline, OME usually disappears by itself within 3 months.
They also report that 3040 percent of children experience OME more than once, and 510 percent of episodes last for 1 year or longer.
When someone has CSOM, they have a hole in their eardrum. When the eardrum bursts, it releases tension, so not everyone with CSOM will feel . However, people with AOM or recurrent AOM will likely experience pain.
The symptoms of CSOM include:
- leaking fluid from the ear
- a hole in the eardrum
People with CSOM are unlikely to have a fever.
Chronic ear infections develop from a long-lasting or recurrent acute ear infection. Preventing acute ear infections can help prevent chronic ear infection.
Acute ear infections happen when the eustachian tube, a tube that runs from the middle ear to the back of the throat, becomes clogged.
Children are more likely to be affected by ear infections because these tubes are shorter and narrower, so they become clogged more easily.
Fluid build-up in the middle ear can become infected, which will cause pain and other symptoms.
Causes of ear infections
Recommended Reading: Should I Rest With A Tooth Infection
Why Wont The Fluid In My Ear Drain
If the Eustachian tubes are blocked, fluid in the ear cannot drain normally. If bacteria grow in the middle ear fluid, an effusion can turn into a middle ear infection . This will usually increase pressure behind the eardrum and cause a lot of pain. The eardrum will become red and bulging.Aug 6, 2018
When To Seek Treatment
If you are having ear pain, you may want to wait a day or two to see if the pain will go away on its own. Often earaches will get better after a few days without any medical intervention.
Some ways to treat the pain in your own home include:
- Pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Warm compress on the infected ear
If you are still having pain after a few days, have developed a fever, or if the pain has gotten worse, then you will need to see a medical professional.
Read Also: Can You Get Better From A Sinus Infection Without Antibiotics
Ear Infections And High Fevers
Second, why do ear infections happen? The Eustachian tube that conects the middle ear to the back of the throat doesnt always work as well as wed like. It can get clogged with mucus from colds or allergies because of its small size and horizontal positioning . This predisposes to fluid collection and poor drainage from the middle ear.
Third, what about the fever and pain? If this fluid cant drain and then gets infected with germs, particularly bacteria, inflammation and pain can result in the middle ear. But each child and each ear infection is different. Some children just poke at their ears. Some get fever, low or high. Others complain of pain, pointing to the ear or throat. It may start after a few days of a cold, giving a little time for the germs to settle in and cause infection in the middle ear, or it may be found coincidentally when your child is seemingly well.
Finally, how are they treated? Your childs doctor will often prescribe an antibiotic to treat the infection. Realize that it may take up to three or four days for the pain and fever to get better. If these symptoms are not going away or your child just isnt getting better, touch base with her doctor to see if anything else is recommended.
Check If It’s An Ear Infection

The symptoms of an ear infection usually start quickly and include:
- discharge running out of the ear
- a feeling of pressure or fullness inside the ear
- itching and irritation in and around the ear
- scaly skin in and around the ear
Young children and babies with an ear infection may also:
- rub or pull their ear
- not react to some sounds
- be irritable or restless
- be off their food
- keep losing their balance
Most ear infections clear up within 3 days, although sometimes symptoms can last up to a week.
If you, or your child, have a high temperature or you do not feel well enough to do your normal activities, try to stay at home and avoid contact with other people until you feel better.
| Inner ear infection | Middle ear infection | Outer ear infection |
|---|---|---|
| Can affect both children and adults | Usually affects children | Usually affects adults aged 45 to 75 |
| Caused by viral or bacterial infections | Caused by viruses like colds and flu | Caused by something irritating the ear canal, such as eczema, water or wearing earplugs |
| Affects parts of the inner ear like the labyrinth and vestibular system, and can lead to labyrinthitis | Affects the eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of the nose | Affects the ear canal |
Don’t Miss: Warm Salt Water For Tooth Infection