What Happens If You Dont Treat Chronic Hiv Infection
If you donât treat chronic HIV infection, your illness is likely to progress to the third and final stage, AIDS. This usually happens after 10 or more years of chronic HIV infection, though it sometimes happens sooner.
At this point, serious damage to your immune system makes it harder for your body to fight off certain infections and cancers. These âopportunisticâ infections and cancers often happen in people with a weakened immune response.
This is very serious. People with AIDS who donât get treatment typically survive about 3 years. And with AIDS, youâre also more likely to have a high viral load that spreads more easily to sexual partners.
Third Stage: Aids Symptoms
AIDS is the advanced stage of HIV infection. This is usually when your CD4 T-cell number drops below 200 and your immune system is badly damaged. You might get an opportunistic infection, an illness that happens more often and is worse in people who have weakened immune systems. Some of these, such as Kaposi’s sarcoma and pneumocystis pneumonia , are also considered âAIDS-defining illnesses.â
If you didn’t know earlier that you were infected with HIV, you may realize it after you have some of these symptoms:
- Being tired all the time
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck or groin
- Fever that lasts more than 10 days
Cdc Stages Of Hiv Infection
- Acute retroviral syndrome: This is an illness with symptoms like mononucleosis. It often develops within a few days of infection with HIV, but it also may occur several weeks after the person is infected. The symptoms can range from mild to severe and usually disappear on their own after 2 to 3 weeks. But many people do not have symptoms or they have such mild symptoms that they don’t notice them.
- Stage 1 : There are no AIDS-related conditions AND the CD4+ cell count is at least 500 cells per microliter or the percent of CD4+ cells is at least 29% of all lymphocytes.
- Stage 2 : There are no AIDS-related conditions AND the CD4+ cell count is 200 to 499 or the percent of CD4+ cells is 14% to 28% of all lymphocytes.
- Stage 3 : The CD4+ cell count is lower than 200, the percent of CD4+ cells is less than 14% of all lymphocytes, or an AIDS-related condition is present.
The World Health Organization classifies HIV infection into 4 stages:footnote 1
You May Like: Will Salt Water Help A Tooth Infection
What Is The Treatment For Hiv
The treatment for human immunodeficiency virus involves a combination of medications known as antiretroviral therapy . ART cannot cure HIV however, it can increase the survival rate of patients.
ART halts the multiplication of the virus and reduces the amount of virus in the body to help the patient stay healthier.
Once the treatment has been started, the patient must remain compliant with the dosage for the medicines to be effective. Noncompliance can result in developing resistance to the medicines.
What Are The Four Stages Of Hiv
The World Health Organization classifies human immunodeficiency virus into four stages
- Stage 1 : The CD4+ cell count is at least 500 cells per microliter.
- Stage 2 : The CD4+ cell count is 350 to 499.
- Stage 3 : The CD4+ cell count is 200 to 349.
- Stage 4 : The CD4+ cell count is less than 200.
The normal CD4+ cell count should be between 500 and 1600 cells per microliter. The higher the CD4+ cell count, the lower the chances of opportunistic diseases.
You May Like: Does A Tooth Infection Cause Headaches
Who Stages Of Hiv Infection
- Stage 1 : The CD4+ cell count is at least 500 cells per microliter.
- Stage 2 : The CD4+ cell count is 350 to 499.
- Stage 3 : The CD4+ cell count is 200 to 349.
- Stage 4 : The CD4+ cell count is less than 200 or the percent of CD4+ cells is less than 15% of all lymphocytes.
In general, the higher the CD4+ count, the less likely it is that opportunistic diseases will occur. Most people who have untreated HIV experience a gradual drop in the number of CD4+ cells. Each person responds uniquely to this decline.
How Does Chronic Hiv Infection Affect Other Conditions
As more and more people with HIV live into old age, doctors have found that chronic HIV infection might raise your risk for other illnesses like heart disease, high blood pressure, and peripheral neuropathy.
The increases arenât generally huge and scientists arenât yet sure why they happen. But research continues to provide information to help us get to the bottom of these issues.
Show Sources
American Heart Association: âAs HIV patients live longer, heart disease might be their next challenge,â âWhat’s the connection between high blood pressure and HIV?â
Hypertension: âHypertension in HIV-Infected Adults.â
Johns Hopkins Medicine: âHIV Neuropathy.â
Mayo Clinic: âHIV/AIDS.â
You May Like: 3 Day Yeast Infection Treatment Vs 7 Day
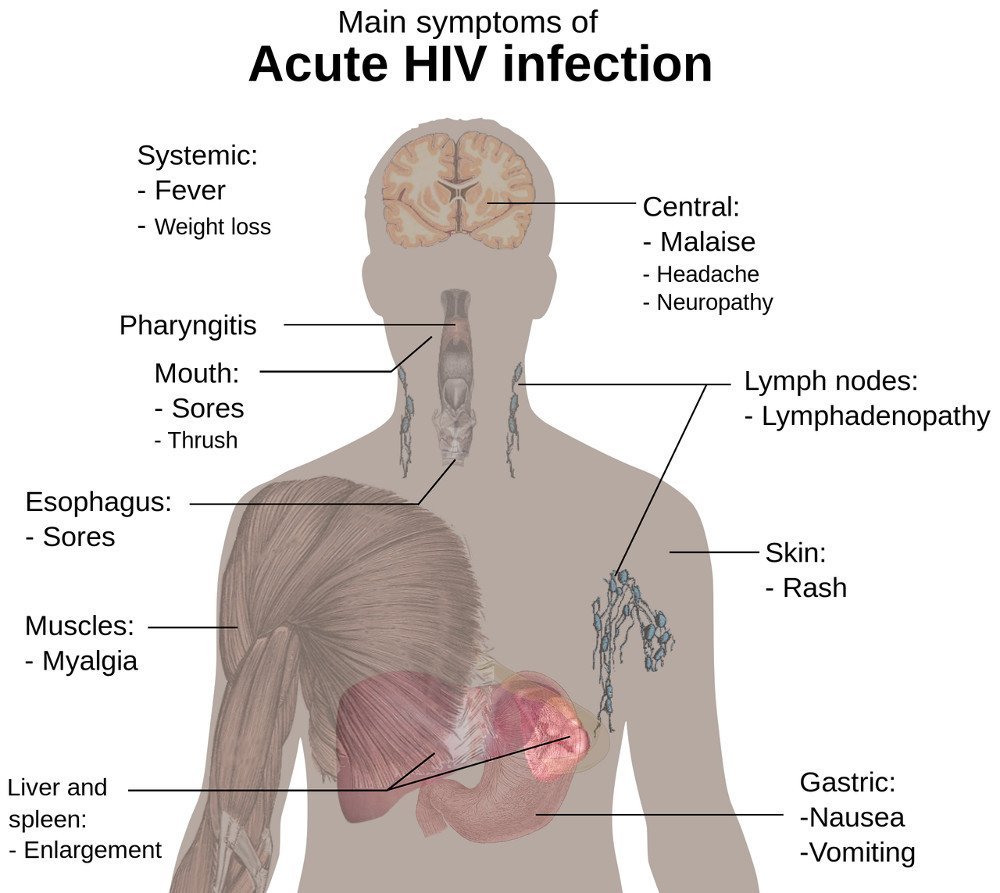
Stage : Acute Hiv Infection
This is the first stage of an HIV infection. It starts about 2 to 4 weeks after the virus enters your body and lasts about 2 weeks. Symptoms in this early stage are similar to the flu. They include:
Inside your body, the virus is making lots of copies of itself and spreading to all your cells. The virus attacks your infection-fighting immune cells called CD4 cells. Itâs this interaction between the virus and your immune system that causes the symptoms.
At this stage, you have lots of HIV in your blood. As a result, itâs easy for you to spread the virus to another person. If you find out youâve got an acute HIV infection, itâs a good idea to start treatment right away to get the infection under control.
How Can You Tell If You Have Hiv
The only way to know for sure if you have HIV is to get tested. You cant rely on symptoms to tell whether you have HIV.
Knowing your HIV status gives you powerful information so you can take steps to keep yourself and your partner healthy:
- If you test positive, you can take medicine to treat HIV. People with HIV who take HIV medicine as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load can live long and healthy lives and will not transmit HIV to their HIV-negative partners through sex. An undetectable viral load is a level of HIV in the blood so low that it cant be detected in a standard lab test.
- If you test negative, you have more HIV prevention tools available today than ever before, like pre-exposure prophylaxis , medicine people at risk for HIV take to prevent getting HIV from sex or injection drug use, and post-exposure prophylaxis , HIV medicine taken within 72 hours after a possible exposure to prevent the virus from taking hold.
- If you are pregnant, you should be tested for HIV so that you can begin treatment if you’re HIV-positive. If you have HIV and take HIV medicine as prescribed throughout your pregnancy and childbirth and give HIV medicine to your baby for 4 to 6 weeks after giving birth, your risk of transmitting HIV to your baby can be less than 1%. HIV medicine will protect your own health as well.
Use the HIV Services Locator to find an HIV testing site near you.
Also Check: Monthly Yeast Infections Before Period
What Are The Symptoms Of Hiv
Not everyone will have identical symptoms because it depends on the person and what stage of the disease they are in.
There are three stages of human immunodeficiency virus . Each stage has a unique set of symptoms. These include the following
Stage 1: Acute HIV infection
This stage starts around two to four weeks after getting HIV. The symptoms are similar to those of the flu, which last for a week or two. Symptoms include the following
How Do You Know If Chronic Hiv Has Progressed To Aids
Your doctor can tell by doing a blood test of your CD4 immune cells. A count of less than 200 cells/mm3 means you have AIDS. Certain opportunistic infections may also be enough to diagnose this third stage of the illness.
But only your doctor can tell you your stage for certain. Thatâs why itâs important to check in regularly with your medical team about your general health and treatment if you have HIV/AIDS.
Regular checkups can ensure that you get the right treatment at the right time and that you donât put your sexual partners at risk.
You May Like: Can Amoxicillin Treat Skin Infections
What Are Symptoms Of Hiv
The first symptoms of HIV are called primary or acute HIV infection. These early symptoms usually occur two to four weeks after a person is infected with the virus.
Acute HIV infection symptoms last about 2 weeks and are usually mild. People often dont realize they have HIV at this point. Early symptoms may include:
Second Stage: Clinical Latency Symptoms
After your immune system loses the battle with HIV, the flu-like symptoms will go away. But thereâs a lot going on inside your body. Doctors call this the asymptomatic period or chronic HIV infection.
In your body, cells called CD4 T cells coordinate your immune systemâs response. During this stage, untreated HIV will kill CD4 cells and destroy your immune system. Your doctor can check how many of these cells you have with blood tests. Without treatment, the number of CD4 cells will drop, and youâll be more likely to get other infections.
Most people don’t have symptoms they can see or feel. You may not realize that you’re infected and can pass HIV on to others.
If youâre taking ART, you might stay in this phase for decades. You can pass the virus on to other people, but itâs extremely rare if you take your medicines.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell Your Boyfriend You Have A Yeast Infection
First Stage: Acute Hiv Infection Symptoms
Most people don’t know right away when they’ve been infected with HIV. But they may have symptoms within 2 to 6 weeks after theyâve gotten the virus. This is when your body’s immune system puts up a fight. It’s called acute retroviral syndrome or primary HIV infection.
The symptoms are similar to those of other viral illnesses, and they’re often compared to the flu. They typically last a week or two and then go away. Early signs of HIV include:
- Headache and other neurological symptoms
If you have symptoms like these and might have come into contact with someone with HIV in the past 2 to 6 weeks, go to a doctor and ask that you get an HIV test. If you donât have symptoms but still think you might have come into contact with the virus, get tested.
Early testing is important for two reasons. First, at this stage, levels of HIV in your blood and bodily fluids are very high. This makes it especially contagious. Second, starting treatment as soon as possible might help boost your immune system and ease your symptoms.
A combination of medications can help fight HIV, keep your immune system healthy, and keep you from spreading the virus. If you take these medications and have healthy habits, your HIV infection probably wonât get worse.
How To Prevent Hiv From Progressing
The most effective way is to take antiretroviral medication as soon as possible and to do so consistently as prescribed.
Antiretroviral therapy keeps the immune system healthy and reduces the risk of transmitting the virus to virtually zero.
The sooner a person receives a diagnosis, the sooner they can begin treatment. Early treatment can improve the persons outlook and lower the risk of the virus passing on to others.
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Doctor Treats Yeast Infection
Stage : Chronic Hiv Infection
Other names for this stage are the asymptomatic stage or clinical latency. At this stage, you still have the virus in your body but at low levels. Itâs possible you wonât notice any symptoms. But as long as the virus is at detectable levels, you can pass the infection to another person.
Without treatment, this stage can last 10 years or longer. Some people will get worse and progress to the next stage faster than others. If you take medicine, this stage can last for a long time. You may never move to the next stage.
Chronic Hiv Infection With Antiretroviral Treatment
If you take effective HIV treatment, you can live with HIV as a chronic, manageable condition. A chronic health condition is one which continues for a long period of time.
This stage is not included in most descriptions of the stages of infection, which only describe disease progression in the absence of treatment.
However, most people living with HIV who have access to good healthcare are living with HIV as a chronic condition and will continue to do so for the rest of their lives. They are unlikely to fall ill or die as a direct result of HIV.
In order to reach this stage and to remain in it, you need to take HIV treatment and continue to take it, on an ongoing basis. These medications reduce levels of HIV in your body and strengthen the immune system. This usually prevents the symptoms and opportunistic infections described above from occurring.
One of the benefits of effective HIV treatment is that is stops HIV from being passed on. Treatment drastically reduces the amount of HIV in body fluids to the point where there is not enough HIV to transmit the virus to sexual partners.
The chronic infection phase can last for decades. People who start HIV treatment as soon as possible, are able to stick with it and have access to good healthcare are likely to have a similar life expectancy to their peers who dont have HIV.
Read Also: Taking Diflucan Without A Yeast Infection
Seroconversion And Acute Hiv Infection
In the first few weeks after infection with HIV, some people have a short flu-like illness that is called a seroconversion illness. This coincides with the period during which the body first produces antibodies to HIV. The most commonly experienced symptoms are fever, swollen glands, muscle aches and tiredness.
The severity of symptoms at this stage can vary considerably between people they can be so mild as to go unnoticed, or so severe that admission to hospital is needed. They usually go away within two to three weeks.
This early stage of HIV infection is called acute HIV infection. The US public health agency the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention describes it as stage 0.
During acute infection, there are very high levels of HIV in the body , which means that the risk of passing HIV on is higher than at other times.
You can start HIV treatment during acute infection. HIV treatment lowers the amount of virus in the body, which allows the immune system to strengthen and helps prevent illnesses from occurring. Starting HIV treatment in this early phase may have particular benefits in terms of preserving the immune system.
People who start HIV treatment go straight to the chronic stage of infection, described towards the end of the page.
The Asymptomatic Stage Of Hiv
Once seroconversion is over, most people feel fine and dont experience any symptoms. This is often called the asymptomatic stage and it can last for several years.
Though you might feel well at this stage, the virus is active, infecting new cells, making copies of itself and damaging your immune systems ability to fight illness.
Read Also: What’s The Best Antibiotic For Tooth Infection
What Are The Types Of Hiv Tests
There are three types of human immunodeficiency virus tests used to diagnose HIV infections, which are
- Antibody tests: These tests check for HIV antibodies in the blood or oral fluid.
- Antigen/antibody tests: These help to detect both HIV antibodies and antigens in the blood.
- Nucleic acid tests: These look for HIV in the blood.
How Is Hiv Transmitted
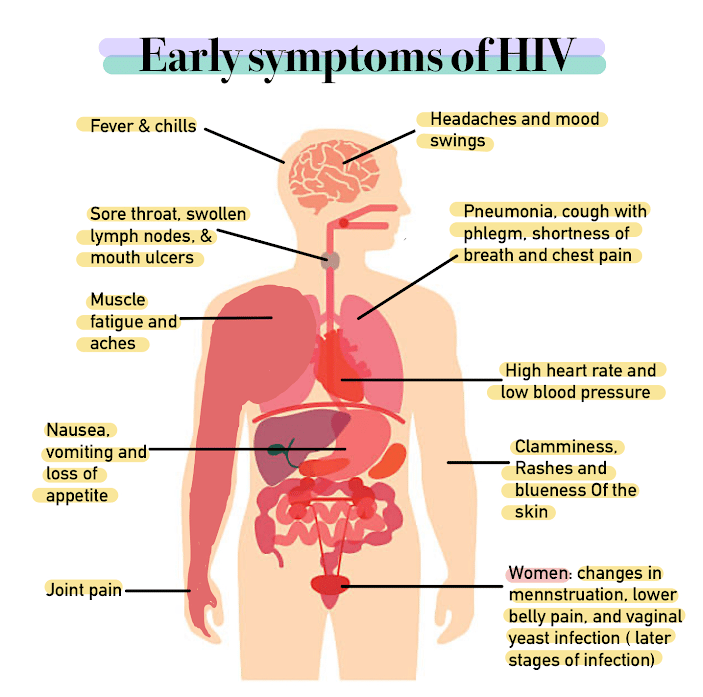
Human immunodeficiency virus is transmitted by coming in direct contact with certain body fluids of the person infected with HIV. These fluids are as follows
- Receiving blood products that are contaminated with HIV
- Getting stuck with an HIV-contaminated needle
Hence, taking precautions either while having sex or sharing a needle is the best way to prevent HIV.
Read Also: How Do You Know If Your Yeast Infection Is Gone
What Happens If You Do Treat Chronic Hiv Infection
Itâs important to keep in mind that there is no cure for HIV/AIDS. Once you have the virus, youâll need treatment to keep its worst effects at bay. That said, treatment of chronic HIV infection works very well, especially if you start it early.
Treatment involves antiretroviral therapy, or ART. This is a combination of medicines that helps stop HIV from making copies of itself. That gives your body a chance to raise the levels of CD4 cells that help fight off opportunistic infections.
Properly followed, the right prescription of antiretroviral therapy can bring your HIV viral load down so low that it canât be detected by current blood tests. This not only makes you healthier, it also makes you less likely to pass the virus on to a sexual partner. Someone with an undetectable viral load has almost no chance of passing the virus to a partner.
This undetectable viral load is the goal of ART. Maintain it, and you and your doctors may be able to keep AIDS at bay for decades. This effectively keeps you in this second stage of HIV/AIDS, chronic HIV infection, almost indefinitely.
In fact, most people in the U.S. with HIV who get ART treatment will never develop AIDS.
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can live and long and healthy life and will not transmit HIV to your HIV-negative partners through sex.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Its important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
Recommended Reading: Can Boric Acid Cause A Yeast Infection