Hiv Life Expectancy: How Long Can You Live With Hiv Or Aids
The most frequently asked question for HIV-positive patients is how long can you live with HIV? Fortunately, the answer is far more promising than it was 20 years ago. Join Flo as we discuss how advancements in medical technology have altered the prognosis for those living with HIV or AIDS.
A national database containing statistics from 25 states shows that the average HIV life expectancy has more than doubled between 1996 and 2005. The bump from 10.5 to 22.5 years after diagnosis can be attributed to vast improvements in drug therapy and related approaches. However, experts still say this is only an average, and plenty of other circumstances must be taken into account regarding HIV life expectancy.
How Long Does It Take For Hiv To Progress To Aids
How long does it take for HIV to progress to AIDS? In all but a few rare cases, if left untreated, HIV will progress to a stage of infection called AIDS. This is when the immune defenses have been compromised, and the body is less able to defend itself against potentially life-threatening infections.
How Long Can Stds Live On Clothing
The short answer to the question How long can STDs live on clothing? is: Not very long at all. STDs have adapted to live within warm, moist environments and rely on a host to survive. While the germs that transmit the flu or the common cold can survive for some time on surfaces, the same is not true for most STD viruses.
Youre highly unlikely to contract an STD from trying on a piece of clothing, but the chance is still greater than zero. Lets look at how STDs can might possibly infect someone through clothing, how long STD viruses can live outside the body, and ways to prevent infection.
You May Like: Hiv Test After 4 Weeks Accuracy
Don’t Miss: How To Avoid Bladder Infections After Intercourse
How Long Can Hiv Survive On Clothes
How Long Does HIV Survive Outside the Body? In general, the virus doesnt live long once its outside of a human body. Studies show that HIV grown in the lab, when placed on a surface, loses most of its ability to infect 90% to 99% within several hours.
Can HIV blood survive on clothes?
Getting HIV infected blood on your skin or clothes etc is not a risk. It needs to get into your body (through a cut, tear in the skin or through a mucous membrane.
How long can HIV survive in dried blood?
Of all the body fluids that can transmit HIV, blood contains the highest concentrations of the virus. HIV may survive in dried blood for up to 56 days at room temperature. It might survive even longer inside blood that is within a syringe, as it does not have exposure to air.
Recommended Reading: Highest Aids Rate In The World
What Are The Treatments For Hiv/aids
There is no cure for HIV infection, but it can be treated with medicines. This is called antiretroviral therapy . ART can make HIV infection a manageable chronic condition. It also reduces the risk of spreading the virus to others.
Most people with HIV live long and healthy lives if they get and stay on ART. It’s also important to take care of yourself. Making sure that you have the support you need, living a healthy lifestyle, and getting regular medical care can help you enjoy a better quality of life.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get A Yeast Infection From Not Wearing Underwear
When Do Symptoms Occur
Some people have flu-like symptoms within two to four weeks after infection, but others may not feel sick or not develop symptoms at all until later.
See a healthcare provider if you have symptoms of HIV and think you may have been exposed to HIV. Getting tested for HIV is the only way to know for sure.
You can prevent HIV by using condoms correctly every time you have sex pre-exposure prophylaxis, a prevention method in which the HIV-negative partner takes daily HIV medicine to prevent HIV and treatment as prevention, a method in which the HIV-positive partner takes daily HIV medicine to achieve and maintain an undetectable viral load.
Only antigen/antibody tests or nucleic acid tests can diagnose acute HIV infection. NATs look for actual virus in the blood, and antigen/antibody tests look for HIV antibodies and antigens. Antibodies are produced by your immune system when youre exposed to viruses like HIV, and antigens are foreign substances that cause your immune system to activate.
However, no test can detect HIV immediately after infection. NATs can usually tell if you have an HIV infection 10 to 33 days after exposure, while antigen/antibody tests can tell 18 to 45 days after exposure.
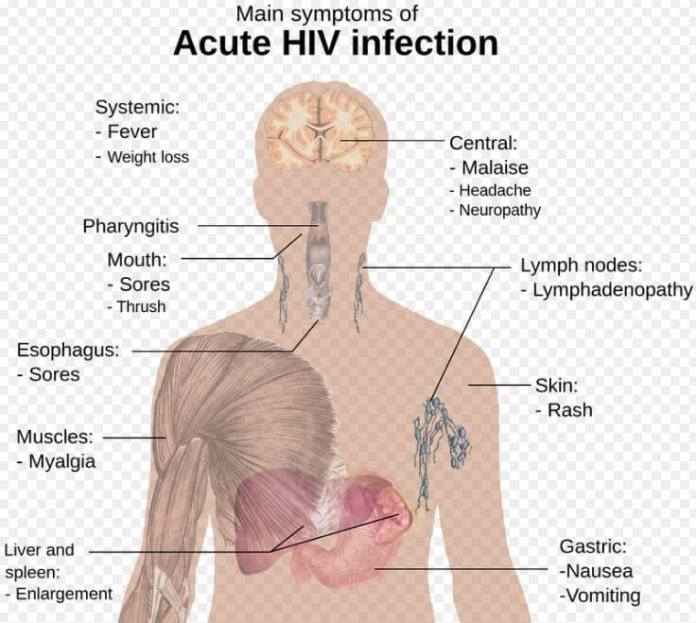
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Mouth ulcers or sores
The Asymptomatic Stage Of Hiv
Once seroconversion is over, most people feel fine and dont experience any symptoms. This is often called the asymptomatic stage and it can last for several years.
Though you might feel well at this stage, the virus is active, infecting new cells, making copies of itself and damaging your immune systems ability to fight illness.
Don’t Miss: Summer’s Eve For Yeast Infection
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Hiv
No two people with HIV will have the same symptoms, and some may not have any at all. But the infection can cause some common changes over time.
In the first few weeks: These first, flu-like symptoms happen because your body is reacting to HIV. Your immune system is trying to fight it off. The symptoms at this stage can include:
- Aches and pains in muscles and joints
Keep in mind that even if you have these symptoms, that doesnât automatically mean you are HIV-positive. Many different illnesses can cause these problems. Talk to a doctor or an HIV testing facility if you think you might be infected.
At this early stage of HIV infection, itâs important to know that you may not get accurate results from an HIV test. It can take 3-12 weeks for enough signs of the virus to show up on routine tests for the infection, which measure antibodies against HIV. A new kind of screening, called a nucleic acid test, can detect the virus itself during this early stage, but itâs expensive and not usually used for routine HIV testing.
Let the testing site or your doctor know if you think you might be recently infected. Also, be sure to use a condom every time you have sex, and take other steps to prevent spreading the virus.
After years with untreated HIV, youâre likely to get infections caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi that your body is no longer strong enough to fight off. They can be a sign that your infection has gone from HIV to AIDS. You might have:
Show Sources
Putting A Number On It: The Risk From An Exposure To Hiv
This information was provided by CATIE . For more information, contact CATIE at 1-800-263-1638.
Author: James Wilton
Service providers working in HIV prevention are often asked by their patients and clients about the risk of HIV transmission from an exposure to HIV through sex. What do the latest studies tell us about this risk? And how should we interpret and communicate the results?
Read Also: Will Keflex Treat A Bladder Infection
What Are The Stages Of Hiv
HIV has three stages:
Stage 1: Acute HIV
Some people get flu-like symptoms a month or two after theyve been infected with HIV. These symptoms often go away within a week to a month.
Stage 2: Chronic stage/clinical latency
After the acute stage, you can have HIV for many years without feeling sick. It’s important to know that you can still spread HIV to others even if you feel well.
Stage 3: AIDS
AIDS is the most serious stage of HIV infection. In this stage, HIV has severely weakened your immune system and opportunistic infections are much more likely to make you sick.
Opportunistic infections are ones that someone with a healthy immune system could typically fight off. When HIV has advanced to AIDS, these illnesses take advantage of your weakened immune system.
Youre more likely to get certain cancers when you have AIDS. These cancers and opportunistic infections together are called AIDS-defining illnesses.
To be diagnosed with AIDS, you must be infected with HIV and have at least one of the following:
- Fewer than 200 CD4 cells per cubic millimeter of blood .
- An AIDS-defining illness.
Heres Evidence From Investigated Outbreaks
Investigations of HIV outbreaks from unsafe health care provide other evidence about patients risks to get HIV from skin-piercing instruments. In Elista, Russia, in 1988-89, for example, hospitals spread HIV from 1 to more than 260 children within 15 months . For HIV to go from 1 to 260 children in 15 months, the number of infections had to double 6 times doubling on average every 2.5 months. To get to 260 infections in 15 months, each HIV-infected child had to, on average, infect another every 2.5 months. If the risk to transmit HIV through contaminated equipment was 0.3%, an HIV-positive patient would have to have, on average, more than 300 skin-piercing procedures after which equipment was reused without sterilization for HIV to go from him or her to another patient. That would take years, not just several months. Similarly, in Roka Cambodia, HIV went from 1 to 198 patients in an estimated 15 months .
Clearly, in these investigated outbreaks the risk to transmit HIV through reused and unsterilized instruments was much greater than 0.3%. If an HIV-positive person in Russia got an average of 10-50 skin-piercing procedures before HIV reached and infected someone else, then the risk to transmit would be 2% to 10% . These are crude estimates but certainly more realistic that the widely reported 0.3%.
Table: Risk to get HIV from HIV-contaminated skin-piercing instruments
| Skin-piercing procedures with unsterilized instruments | Estimated risk |
Recommended Reading: Can Bactrim Treat Bladder Infection
What Is The Treatment For Hiv
Individuals who are HIV positive will likely need to see a specialist. As with many other conditions, early detection offers more options for treatment. Today, there are medical treatments that can slow down the rate at which HIV weakens the immune system. However, there are other treatments that can prevent or cure the conditions associated with HIV. Anti-retroviral drug therapy may be given to a pregnant woman, which has proven to greatly reduce the chance of an infant developing HIV. A cesarean section may be recommended to reduce infant transmission from the birth canal. In the U.S., where other feeding options are available, an infected mother should be discouraged from breastfeeding her infant. Consult your child’s doctor for more information regarding various drug therapies.
If I Have Hiv How Can I Keep From Spreading It To Others
The best ways to keep from spreading HIV to others are many of the same ways you use to protect yourself:
- Let sexual partners and anyone you inject drugs with know that you have HIV.
- Follow your treatment plan and dont miss medications. If you have an undetectable viral load, you greatly reduce the risk of transmitting HIV through sex.
- Talk to your sexual partner about taking PrEP.
- Dont share needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
- Limit the number of sexual partners you have.
- If youre pregnant and have HIV, following your treatment plan, including ART medications, can reduce your risk of transmitting the virus to your child.
Also Check: Yeast Infection Worse After Monistat
Human Tissue Explant Models
An extensive body of literature describes human tissue explant models and their application to the analysis of HIV-1 and SIV transmission. Much of this has been summarized in recent reviews . Although increasing attention in recent years has been paid to penile and gastrointestinal explant models, most information , can be correlated with in situ studies of primate infection by SIV . in a cervicovaginal explant model also observed that CCR5+ CD4+ T cells with the effector memory phenotype are a primary target for infection. Human cervicovaginal tissue ex vivo was found to preferentially support productive infection by R5 HIV-1 rather than by X4 HIV-1 despite ample expression of CXCR4. Productive infection by R5 HIV-1 occurred preferentially in activated CD38+ CD4+ T cells in association with activation of HIV-1uninfected CD4+ T cells that may amplify viral infection. That CXCR4-tropic HIV-1 replicated only in the few tissues that were enriched in CD27+ CD28+ effector memory CD4+ T cells, if translatable to tissue in vivo, could in part explain the selection of R5 viruses during transmission. Still other human cervical explant studies were conducted by Shattock and colleagues . This work characterized cellular factors involved in HIV-1 entry and identified potential therapeutic agents that block infection . In this model, blockade of CD4 or CCR5/CXCR4 prevented localized mucosal infection and trafficking by dendritic cells.
When To Contact A Doctor
Anyone who is showing symptoms of HIV should contact a doctor as soon as possible. This is especially important if the individual has recently had sexual contact with someone else or shared a needle with someone else.
HIV can remain asymptomatic for a long time. For this reason, anyone who has recently had unprotected sex and is concerned about exposure to HIV should contact a doctor as soon as they can, even if they do not have any symptoms. The same goes for anyone who has recently shared a needle.
It can be difficult to discuss the possibility of having HIV. However, without proper treatment, HIV can be life threatening. In these situations, it is very important for people to put their long-term health first and to discuss the matter with a doctor.
Recommended Reading: Are Sinus Infections Contagious Through Kissing
Who Does Hiv Affect
Its a myth that HIV only infects certain people. Anyone can get HIV if theyre exposed to the virus. Having sex without a condom or sharing needles to inject drugs are the most common ways that HIV spreads.
Some populations are statistically more affected by HIV than others. Groups disproportionately affected by HIV include:
- People who identify as gay, bisexual and men who have sex with men .
- Certain races such as people who are Black or Hispanic.
- Those who exchange sex for money or other items are also at high risk for HIV infection.
While these arent the only populations impacted by HIV, its important to consider that they face unique barriers to accessing preventative care, getting tested, and receiving comprehensive treatment. Homophobia, racism, poverty, and social stigmas around HIV continue to drive inequities and keep people from accessing high-quality healthcare.
Heres Evidence From Needlestick Accidents
A summary of 23 studies reported 3 in 1,000 healthcare workers exposed to HIV through needlesticks got HIV. From such data, many people including health experts who should know better say the risk to get HIV after an injection with a contaminated syringe or needle is 0.3%. A closer look at needlestick accidents shows a much greater risk to transmit HIV through accidents that are similar to injections and other skin-piercing medical procedures.
Specifically: a 1997 study of healthcare workers who did and did not get HIV after needlestick accidents found that most accidents were shallow scratches. Only 7% were deep injuries, deep enough for the hole of the needle to be within the skin, as in an injection. The risk to get HIV after deep needlesticks was 15 times greater than for all needlesticks.
Thus, from needlestick accidents, a first approximation of the risk to transmit HIV through injections all of which fit the definition of a deep injury is 4.5% . The same study found other factors could raise or lower that risk for example, risks could be even greater if the source patient was very sick with a lot of virus, or if there was blood visible on the instrument.
Also Check: Is It Possible To Transmit Hiv When Undetectable
Don’t Miss: Can A Tooth Infection Give You An Ear Infection
Some Practices Dont Reduce Your Risk Of Hiv
Some people use unreliable methods to reduce their risk of HIV. These include:
- Serosorting choosing your sexual partner based upon them having the same HIV status as you.
- Strategic positioning where an HIV-negative partner penetrates an HIV-positive partner.
- Withdrawal when the insertive partner pulls out before ejaculating .
None of these strategies are reliable, so you are at risk of HIV transmission.Having sex only with people who have the same HIV status can be very risky. For example, a person may think they are HIV-negative, but may have been exposed to HIV since their last test, or may never have been tested at all.
Using a combination of proven, reliable strategies like condoms, PrEP, and undetectable viral load is the best way to prevent HIV transmission.
Can You Get Hiv From Having Sex With Someone Who Has Aids
If you have sex with someone who has AIDS, not HIV, can you still get HIV? Sarah*
Yes. People who have AIDS are infected with the HIV virus. This means they can pass HIV on to others.
AIDS happens after someone has had HIV for many years. In AIDS, the immune system is severely weakened. When someone gets HIV, that person can spread the infection to other people immediately. And if HIV develops into AIDS, the virus can spread to others.
HIV/AIDS spreads when infected blood or body fluids enter the body. This can happen:
- through sharing needles for injecting drugs or tattooing
HIV/AIDS also can pass from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
To reduce your risk of getting HIV/AIDS if you are sexually active:
- Use a condom every time you have sex .
- Get tested for HIV and make sure all partners do too.
- Have fewer sexual partners.
- Get tested and treated for STDs having an STD increases the risk of HIV infection.
- Consider taking a medicine every day if you are at very high risk of getting infected .
It’s also important to:
- not inject drugs or share any kind of needle
- not share razors or other personal objects that may touch blood
- not touch anyone else’s blood from a cut or sore
*Names have been changed to protect user privacy.
Don’t Miss: Does Urgent Care Do Yeast Infections