Stages Of Hiv Infection
Stages of Infection
There are four stages of HIV and as with all illnesses, how it progresses, how long it takes and the affect it has on the individual depends on a number of factors for example, general health, lifestyle, diet etc.
Stage 1: Infection
HIV quickly replicates in the body after infection. Some people develop short lived flu-like symptoms for example, headaches, fever, sore throat and a rash within days to weeks after infection. During this time the immune system reacts to the virus by developing antibodies this is referred to as sero-conversion.
Stage 2:Asymptomatic
As the name suggests, this stage of HIV infection does not cause outward signs or symptoms. A person may look and feel well but HIV is continuing to weaken their immune system. This stage may last several years and without a HIV test many people do not know they are infected.
Stage 3:Symptomatic
Over time the immune system becomes damaged and weakened by HIV and symptoms develop. Initially they can be mild but they do worsen, symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, mouth ulcers, thrush and severe diarrhoea. The symptoms are caused by the emergence of opportunistic infections they are referred to as opportunistic infections because they take advantage of a persons weakened immune system. Some examples of opportunistic infections are PCP, toxoplasmosis, TB and kaposi sarcoma.
Stage 4:AIDS/Progression of HIV to AIDS
Early Symptoms In Primary Hiv
The first noticeable stage is primary HIV infection. This stage is also called acute retroviral syndrome , or acute HIV infection. Because HIV infection at this stage usually causes flu-like symptoms, its possible for someone in this stage to think their symptoms are due to a severe flu rather than HIV. Fever is the most common symptom.
Other symptoms include:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , primary HIV symptoms may show up two to four weeks after initial exposure. Symptoms can continue for up to several weeks. However, some people may exhibit the symptoms only for a few days.
People with early HIV sometimes dont show any symptoms, yet they can still transmit the virus to others. This is attributed to the fast, unrestrained viral replication that occurs in the early weeks after contracting the virus.
Read Also: If Tooth Hurts Is It Infected
Sudden Unexplained Weight Loss
National Human Genome Research Institute
Weight loss is common in people living with HIV during the advanced stages of the disease.
This type of weight loss is more than just a few poundsit’s a sudden, unexplained weight loss of 10% or more of a person’s body weight, in which both fat mass and lean muscle are lost.
The condition is also called HIV wasting syndrome. It’s not as common today as it once was because antiretroviral drugs keep the virus suppressed and allow the immune system to rebuild itself. Wasting is mainly seen in people who have not been treated for HIV.
The exact cause of HIV wasting is unknown, but it is thought that the constant inflammation caused by HIV makes the body burn energy faster and reduces testosterone levels .
Other causes of wasting include malnutrition, chronic diarrhea, tuberculosis, and cancerall of which require urgent diagnosis and treatment.
Recommended Reading: Have Uti Symptoms But No Infection
Stage : Chronic Infection
Also known as the asymptomatic stage, chronic HIV infection is the point where the virus remains at low levels inside the body.
Some people have no symptoms at all during this period despite the virus still replicating and this can last for several years.
Others may have more severe symptoms than they experienced during the acute stage. These can range from coughing and fatigue to weight loss and diarrhea. A high fever is also possible.
What Is The Difference Between Hiv And Aids
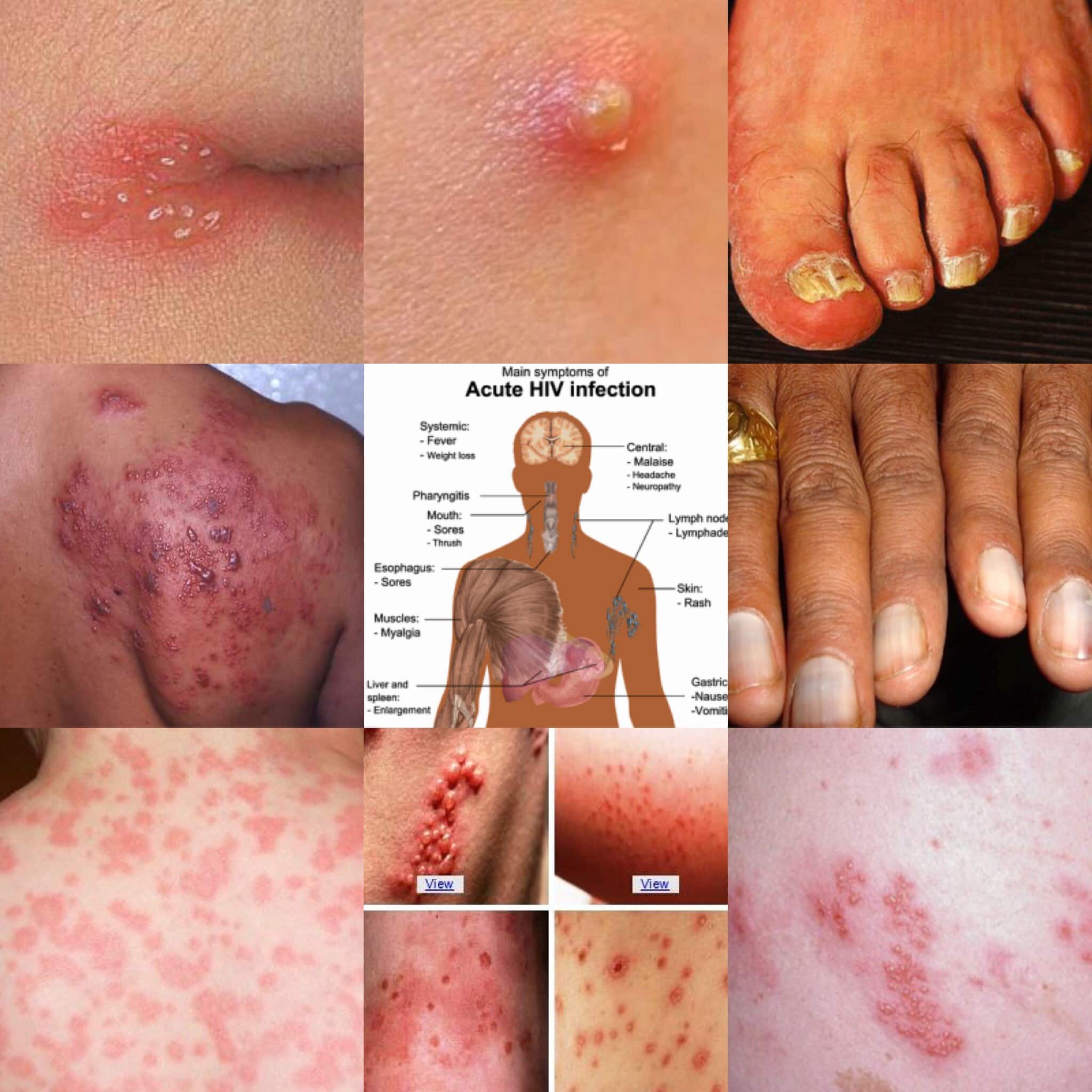
The term AIDS refers to the most advanced stages of HIV infection. Most of the conditions affecting people with AIDS are opportunistic infections that generally do not affect healthy people. In people with AIDS, these infections are often severe and sometimes fatal because the immune system is so ravaged by HIV that the body cannot fight off the infection. Symptoms of opportunistic infections common in people with AIDS include:
- coughing and shortness of breath
- seizures and lack of coordination
- difficult or painful swallowing
- severe headaches
People with AIDS also are particularly prone to developing various cancers. These cancers are usually more aggressive and difficult to treat in people with AIDS.
Recommended Reading: Antibiotic Cream For Ear Infection
Chronic Hiv Infection With Antiretroviral Treatment
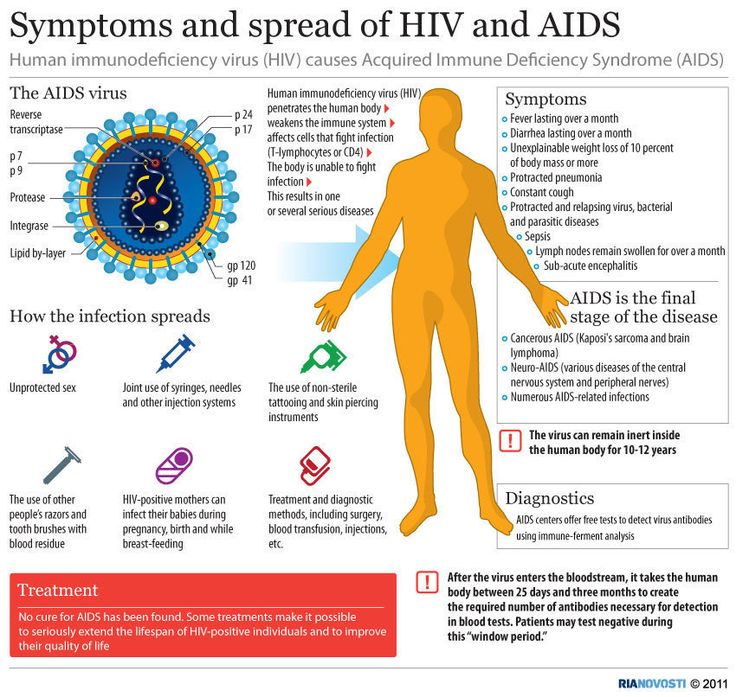
If you take effective HIV treatment, you can live with HIV as a chronic, manageable condition. A chronic health condition is one which continues for a long period of time.
This stage is not included in most descriptions of the stages of infection, which only describe disease progression in the absence of treatment.
However, most people living with HIV who have access to good healthcare are living with HIV as a chronic condition and will continue to do so for the rest of their lives. They are unlikely to fall ill or die as a direct result of HIV.
In order to reach this stage and to remain in it, you need to take HIV treatment and continue to take it, on an ongoing basis. These medications reduce levels of HIV in your body and strengthen the immune system. This usually prevents the symptoms and opportunistic infections described above from occurring.
One of the benefits of effective HIV treatment is that is stops HIV from being passed on. Treatment drastically reduces the amount of HIV in body fluids to the point where there is not enough HIV to transmit the virus to sexual partners.
The chronic infection phase can last for decades. People who start HIV treatment as soon as possible, are able to stick with it and have access to good healthcare are likely to have a similar life expectancy to their peers who dont have HIV.
What Are The Four Stages Of Hiv
The World Health Organization classifies human immunodeficiency virus into four stages
- Stage 1 : The CD4+ cell count is at least 500 cells per microliter.
- Stage 2 : The CD4+ cell count is 350 to 499.
- Stage 3 : The CD4+ cell count is 200 to 349.
- Stage 4 : The CD4+ cell count is less than 200.
The normal CD4+ cell count should be between 500 and 1600 cells per microliter. The higher the CD4+ cell count, the lower the chances of opportunistic diseases.
Read Also: Homeopathic Remedy For Bladder Infection
Whats The Difference Between Hiv And Aids
The difference between HIV and AIDS is that HIV is a virus that weakens your immune system. AIDS is a condition that can happen as a result of an HIV infection when your immune system is severely weakened.
You cant get AIDS if you arent infected with HIV. Thanks to treatment that slows down the effects of the virus, not everyone with HIV progresses to AIDS. But without treatment, almost all people living with HIV will advance to AIDS.
How Can I Know If I Have Hiv
You cant tell if someone has HIV just by looking at them, and you may not have any symptoms if youre infected by HIV. The only way to know if you have HIV is to take an HIV test.
Since nearly 1 out of 7 people with HIV dont know it, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control & Prevention recommends screening people between the ages of 13 to 64 at least once as part of routine healthcare. This test is voluntary and confidential.
Also Check: Herbal Medicine For Tooth Infection
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can live and long and healthy life and will not transmit HIV to your HIV-negative partners through sex.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Its important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Aids
Having an infection with the HIV virus does not automatically mean that the patient has AIDS. As the HIV virus infects more and more CD4 cells and makes more copies of itself, the patients immune system gets overwhelmed and begins to falter. When the immune system breaks down due to HIV infection, opportunistic infections like fungal infections, pneumonias, and cancers can occur. When this level of HIV infection occurs, it is called AIDS .
Some of the signs and symptoms of progression of HIV to AIDS are:
Read Also: Oral Drugs For Yeast Infection
The Asymptomatic Stage Of Hiv
Once seroconversion is over, most people feel fine and dont experience any symptoms. This is often called the asymptomatic stage and it can last for several years.
Though you might feel well at this stage, the virus is active, infecting new cells, making copies of itself and damaging your immune systems ability to fight illness.
How Do I Take Care Of Myself With Hiv
The best way to take care of yourself while living with HIV is to follow your treatment plan.
- Make sure to take your medications as prescribed and on time.
- Show up to all appointments so your healthcare team can monitor how youre feeling and know if theres a need to adjust your treatment.
- Follow your healthcare providers recommendations on how to avoid additional illnesses.
Read Also: Will Macrobid Treat Yeast Infection
Does Hiv Go Away
HIV doesnt go away on its own. It inserts itself into your DNA so your cells think that its a part of you. There can be many years without symptoms after initial infection, but HIV can still be damaging your immune system even if you dont feel sick.
There may be periods while on medication where the virus is not detectable by an HIV test. In these cases, HIV can be hiding in your body, undetected. It can wake up and start destroying your cells again in the future.
This is why continuing to take HIV medication, even if you dont feel sick or the virus is undetectable, is extremely important. Without treatment, HIV will weaken your immune system until you cant fight off other serious illnesses.
How Is Hiv Treated
HIV is treated with a combination of medicines taken by mouth every day. This combination of pills is called antiretroviral therapy .
Taking a combination of types of pills, rather than just one, is the most effective way to keep HIV from multiplying and destroying your cells. There are also combination pills that have several medications in a single pill. Your healthcare provider will carefully select a combination specifically for you.
The goal of ART is to reduce HIV in the blood to an amount thats not detectable by an HIV test and to slow HIVs weakening of your immune system.
Medications used to treat HIV
Each type of pill used in ART has a different way of keeping HIV from making more copies of itself or from infecting your cells. There can be many different brand names of the same type of ART drug.
Types of ART medications include:
- Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors .
- Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors .
- Protease inhibitors .
- Combination of HIV medicines.
You May Like: How To Heal Sinus Infection At Home
First Stage: Acute Hiv Infection Symptoms
Most people don’t know right away when they’ve been infected with HIV. But they may have symptoms within 2 to 6 weeks after theyâve gotten the virus. This is when your body’s immune system puts up a fight. It’s called acute retroviral syndrome or primary HIV infection.
The symptoms are similar to those of other viral illnesses, and they’re often compared to the flu. They typically last a week or two and then go away. Early signs of HIV include:
- Headache and other neurological symptoms
If you have symptoms like these and might have come into contact with someone with HIV in the past 2 to 6 weeks, go to a doctor and ask that you get an HIV test. If you donât have symptoms but still think you might have come into contact with the virus, get tested.
Early testing is important for two reasons. First, at this stage, levels of HIV in your blood and bodily fluids are very high. This makes it especially contagious. Second, starting treatment as soon as possible might help boost your immune system and ease your symptoms.
A combination of medications can help fight HIV, keep your immune system healthy, and keep you from spreading the virus. If you take these medications and have healthy habits, your HIV infection probably wonât get worse.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
- Am I at high risk for HIV?
- What can I do to reduce my risk of HIV?
- How can I make sure I take my medications correctly?
- What can I do to protect myself from other illnesses?
- How can prevent the spread of HIV?
- What do my test results mean?
- What do my blood counts mean?
- What vaccinations should I get?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Treatments have come a long way since the height of the AIDS epidemic. You have the best chance of living a long life if youre diagnosed early and are able to get on and stick with ART medications. People living with HIV today are able to work, have active social lives and families, and pursue fulfilling relationships. In fact, this can have a positive impact on your well-being.
While weve come a long way with treatments, unfortunately, social stigmas around HIV still persist. In addition to the feelings of fear and uncertainty a new diagnosis can bring, you may wonder how those around you will respond. If youre hesitant to get tested or get treatment, or if you just arent sure what your next steps are, you can reach out to a community organization that specializes in HIV. Remember that you are deserving of support, compassion and high-quality healthcare.
Also Check: Difference In Kidney Infection And Uti
Seroconversion And Acute Hiv Infection
In the first few weeks after infection with HIV, some people have a short flu-like illness that is called a seroconversion illness. This coincides with the period during which the body first produces antibodies to HIV. The most commonly experienced symptoms are fever, swollen glands, muscle aches and tiredness.
The severity of symptoms at this stage can vary considerably between people they can be so mild as to go unnoticed, or so severe that admission to hospital is needed. They usually go away within two to three weeks.
This early stage of HIV infection is called acute HIV infection. The US public health agency the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention describes it as stage 0.
During acute infection, there are very high levels of HIV in the body , which means that the risk of passing HIV on is higher than at other times.
You can start HIV treatment during acute infection. HIV treatment lowers the amount of virus in the body, which allows the immune system to strengthen and helps prevent illnesses from occurring. Starting HIV treatment in this early phase may have particular benefits in terms of preserving the immune system.
People who start HIV treatment go straight to the chronic stage of infection, described towards the end of the page.
Symptom : Night Sweats
Night sweats are repeated episodes of extreme sweating, causing bedding and any nightclothes to become soaked. Many people will get night sweats during the early stages of HIV. These can be even more common later in infection and arent related to exercise or the temperature of the room.Get tested if symptoms of HIV appear
With such a vast array of symptoms, HIV testing is vital to ensure a proper diagnosis. If you think youve been exposed to HIV, or have an active sex life with casual sex partners, regardless of whether you are showing symptoms of HIV or not, its important to get tested as soon as possible.
If youre in Sydney, you can get a rapid HIV test and STI check-up at a. If youre not in Sydney, you can still get a rapid HIV test and STI check-up using our where to get tested tool here.
You May Like: Can Ear Infections Heal On Their Own
You May Like: Metronidazole For Tooth Infection Dosage
Treatment Initiation According To Cd4 Count
In 2008, a subset analysis of the Strategic Management of Antiretroviral Therapy study found that although deferring treatment until the CD4+ T-cell count dropped below 200 cells/µL had been the standard of care, initiation of combined antiretroviral therapy at higher CD4 counts was associated with decreased morbidity and mortality in HIV disease.
Similarly, the National Institutes of Health Comprehensive International Program of Research on AIDS HT 001 clinical study showed that starting antiretroviral therapy at CD4 T-cell counts between 200-350 cells/µL improves survival compared with deferring treatment until the CD4 T-cell count drops below 200 cells/µL, which was the standard of care at the time.
Interim analysis of CIPRA HT 001 showed that of 816 HIV-infected adults with early HIV disease, 6 of those who began antiretroviral therapy within 2 weeks of enrollment died, whereas 23 participants in the standard-of-care group died. Among participants who began the study without tuberculosis infection, 18 individuals in the early treatment group developed tuberculosis, whereas 36 people in the standard-of-care group developed tuberculosis.
These interim results were statistically significant and led to ending the trial early to offer antiretroviral therapy to all participants in the standard-of-care group with a CD4+ T-cell count of less than 350 cells/µL.