Treatment Strategies For Recurrent Utis
Recurrent urinary tract infections, defined as three or more UTIs within 12 months, or two or more occurrences within six months, is very common among women these but arent treated exactly the same as standalone UTIs. One of the reasons: Continued intermittent courses of antibiotics are associated with allergic reactions, organ toxicities, future infection with resistant organisms, and more.
Because of this, its strongly recommended that you receive both a urinalysis and urine culture from your healthcare provider prior to initiating treatment. Once the results are in, the American Urological Association suggests that healthcare professionals do the following:
- Use first-line treatments. Nitrofurantoin, TMP-SMX, and fosfomycin are the initial go-tos. However, specific drug recommendations should be dependent on the local antibiogram. An antibiogram is a periodic summary of antimicrobial susceptibilities that helps track drug resistance trends.
- Repeat testing. If UTI symptoms persist after antimicrobial therapy, clinicians should repeat the urinalysis, urine culture, and antibiotic susceptibility testing to help guide further management.
- Try vaginal estrogen. For peri- and post-menopausal women with recurrent UTIs, vaginal estrogen therapy is recommended to reduce risk of future UTIs.
RELATED: The Link Between UTIs and Sex: Causes and How to Prevent Them
Drink Plenty Of Water
Although urinating can be painful when you have a UTI, its important to drink as many fluids as possible particularly water. Most adults should aim to drink between six and eight 8-ounce glasses of water per day.
The more you drink, the more youll urinate, which can help flush harmful bacteria from the urinary tract.
Ongoing Management Of Uti
Dr N: So, shes going to come in next week and give a urine sample. Well see if the E coli has been cleared and then try to figure out what the next step will be.
Urine testing should be in response to symptoms as outlined in the . Repeated urine testing as a test of cure is not warranted among older patients. Among patients with recurrent symptomatic UTI , use of chronic suppressive antibiotics for 6 to 12 months are effective at reducing UTI episodes and should be considered. Nitrofurantoin given at 50 mg daily is used in older patients with minimal adverse effects and no growth of nitrofurantoin-resistant fecal flora after 1 year of treatment. Six months of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole , trimethoprim , and nitrofurantoin are also effective, but trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole resistant E coli fecal isolates were more common in patients treated with trimethoprim-based regimens.
Donât Miss: How Do You Fix Overactive Bladder
Don’t Miss: Can Wisdom Teeth Get Infected
How To Use Ciprofloxacin Tablet
Read the Medication Guide and, if available, the Patient Information Leaflet provided by your pharmacist before you start taking ciprofloxacin and each time you get a refill. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
This medication may be taken with or without food as directed by your doctor, usually twice a day in the morning and evening.
Shake the container well for 15 seconds before pouring each dose. Carefully measure the dose using a special measuring device/spoon. Do not use a household spoon because you may not get the correct dose. Do not chew the contents of the suspension.
Do not use the suspension with feeding tubes because the suspension may clog the tube.
The dosage and length of treatment is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. Drink plenty of fluids while taking this medication unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
Take this medication at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after taking other products that may bind to it, decreasing its effectiveness. Ask your pharmacist about the other products you take. Some examples include: quinapril, sevelamer, sucralfate, vitamins/minerals , and products containing magnesium, aluminum, or calcium .
Ask your doctor or pharmacist about safely using nutritional supplements/replacements with this medication.
For the best effect, take this antibiotic at evenly spaced times. To help you remember, take this medication at the same time every day.
Key Points About Urinary Tract Infections
- Urinary tract infections are a common health problem that affects millions of people each year. These infections can affect any part of the urinary tract.
- Most UTIs are caused by E. coli bacteria, which normally live in the colon.
- The most common symptoms of UTIs include changes in urination such as frequency, pain, or burning urine looks dark, cloudy, or red and smells bad back or side pain nausea/vomiting and fever.
- Antibiotics are used to treat UTIs. Other treatments may include pain relievers, and drinking plenty of water to help wash bacteria out of the urinary tract.
- Other things that can be done may help reduce the likelihood of developing UTIs.
Don’t Miss: Bv And Yeast Infection Medication
Intracellular Bacteria Localization By Laser Confocal Microscopy
Although all the evaluated UPECs were able to enter the eukaryotic cells, confirmation and localization of intracellular bacteria was performed by confocal laser scanning microscopy . Four strains were tested, two of which were negative for the presence of IBC in urine desquamated cells .
After image acquisition and their subsequent analysis, all the strains were observed in small groups, rather than dispersed in the cytoplasm .
Figure 4E. coli invasion assay in T24 cells. The images represent the xyz stacks obtained with CLSM. Maximum intensity z-projections are shown in the central panel, upper and left are zx and zy, respectively. In red actin staining , in blue DNA , and in green UPEC . UPEC 7, the intracellular bacteria are observed in groups inside the eukaryotic cell resembling IBC. UPEC 144, intracellular bacteria are observed in big groups in a perinuclear localization. UPEC 172, in this case the intracellular bacteria are dispersed in the cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell. Severe damage is observed as the cells had their membrane damaged and the presence of philopodia this is in agreement with cytotoxicity assay as UPEC 172 had one of the highest values. UPEC 174, disperse intracellular bacteria is observed.
Can Doctors Treat Utis Via Telemedicine
Telemedicine is an increasingly popular method of treating UTIs. In addition to being convenient, its also discreet and frequently more affordable than an in-office visit.
Since doctors cant collect a urine specimen via telemedicine, they will typically make their diagnosis using a series of questions that identify and analyze your symptoms. Your telehealth provider will also want to know if you have a history of UTIs, as well as if there are any other factors that may complicate your UTI, such as pregnancy or a chronic health condition.
Ultimately, the fact that UTIs are extremely common assists physicians in their ability to accurately diagnose and treat UTIs online. In the event that your UTI symptoms present themselves as more severe or as something else entirely, your telemedicine professional will instruct you to visit another physician in the office for a follow-up or to perform a urinalysis. Most of the time, however, your telehealth provider can diagnose your infection and prescribe antibiotics via video alone. Certain telehealth providers may be able to fill your prescription as well, which can save you the expense of going through a pharmacy.
Recommended Reading: Diff Between Uti And Yeast Infection
Ear Infection And Uti At Same Time: Causes Symptoms & Treatment
Although its quite possible for you to have an ear infection and UTI at the same time, chances are that you wont be able to pass either one out through your cough, sneeze, or other nasal symptoms.
If you are experiencing severe ear pain,or if you have a fever and chills, and you think it could be the onset of an ear infection, then its important to see your doctor as quickly as possible.
He or she can order tests to see if you have an ear infection.
Your ear pain might be caused by irritation, such as when you get a foreign object stuck in your ear.
Recommended Reading: How To Reduce Bladder Pain
When To Get Medical Advice
Itâs a good idea to see your GP if you think you might have a UTI, particularly if:
- you have symptoms of an upper UTI
- the symptoms are severe or getting worse
- the symptoms havenât started to improve after a few days
- you get UTIs frequently
Your GP can rule out other possible causes of your symptoms by testing a sample of your urine and can prescribe antibiotics if you do have an infection.
Antibiotics are usually recommended because untreated UTIs can potentially cause serious problems if theyâre allowed to spread.
Read Also: How To Heal Urinary Tract Infection Naturally
Don’t Miss: How To Get Ear Infection To Drain
What Are The Best Antibiotics For Utis
A urinary tract infection is an infection of the urinary system. It is often associated with painful symptoms, which are typically treated with antibiotics. The best antibiotics for treating a UTI depend on the type of UTI and the severity of the symptoms. Nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim, and cephalexin are common antibiotics prescribed to treat UTIs.
Without insurance, prescriptions can be expensive, but Mira can help you out. For only $45 a month, Mira members get access to up to 80% off different medications, affordable lab testing, and virtual and urgent care visits. Ease your pain, for Mira today.
Otc Uti Treatment: Key Takeaway
Women are prone to contracting a urinary tract infection at least once in their life. Certain UTIs do not need treatment if they are diagnosed on time and if the symptoms are cared for, however, some UTIs require medical intervention in the form of antibiotics.
While antibiotics are the standard treatment for UTIs, researchers are looking for better OTC treatment options for UTI symptoms that might eliminate their need. Several OTC UTI treatment drugs help prevent and manage UTI symptoms but should never be considered a replacement to prescribed antibiotics. The only clinically proven cure for a UTI is a prescribed antibiotic and nothing else as of yet.
If you think you have a UTI, you may visit Family Medicine Austin and consult our healthcare experts. It is always advised to avoid self-treatment and seek medical help.
I am Jeannette, the medical writing specialist here at Family Medicine Austin. I have over five years of experience working with a range of medical and healthcare across the U.S.
Complete The Form Below And Well Get Back To You Immediately.
You May Like: Who To Go To For Eye Infection
What Is The Urinary Tract
The urinary tract makes and stores urine, one of the body’s liquid waste products. The urinary tract includes the following parts:
- Kidneys: These small organs are located on back of your body, just above the hips. They are the filters of your body removing waste and water from your blood. This waste becomes urine.
- Ureters: The ureters are thin tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to your bladder.
- Bladder: A sac-like container, the bladder stores your urine before it leaves the body.
- Urethra: This tube carries the urine from your bladder to the outside of the body.
Uncomplicated Cystitis In Nonpregnant Patients
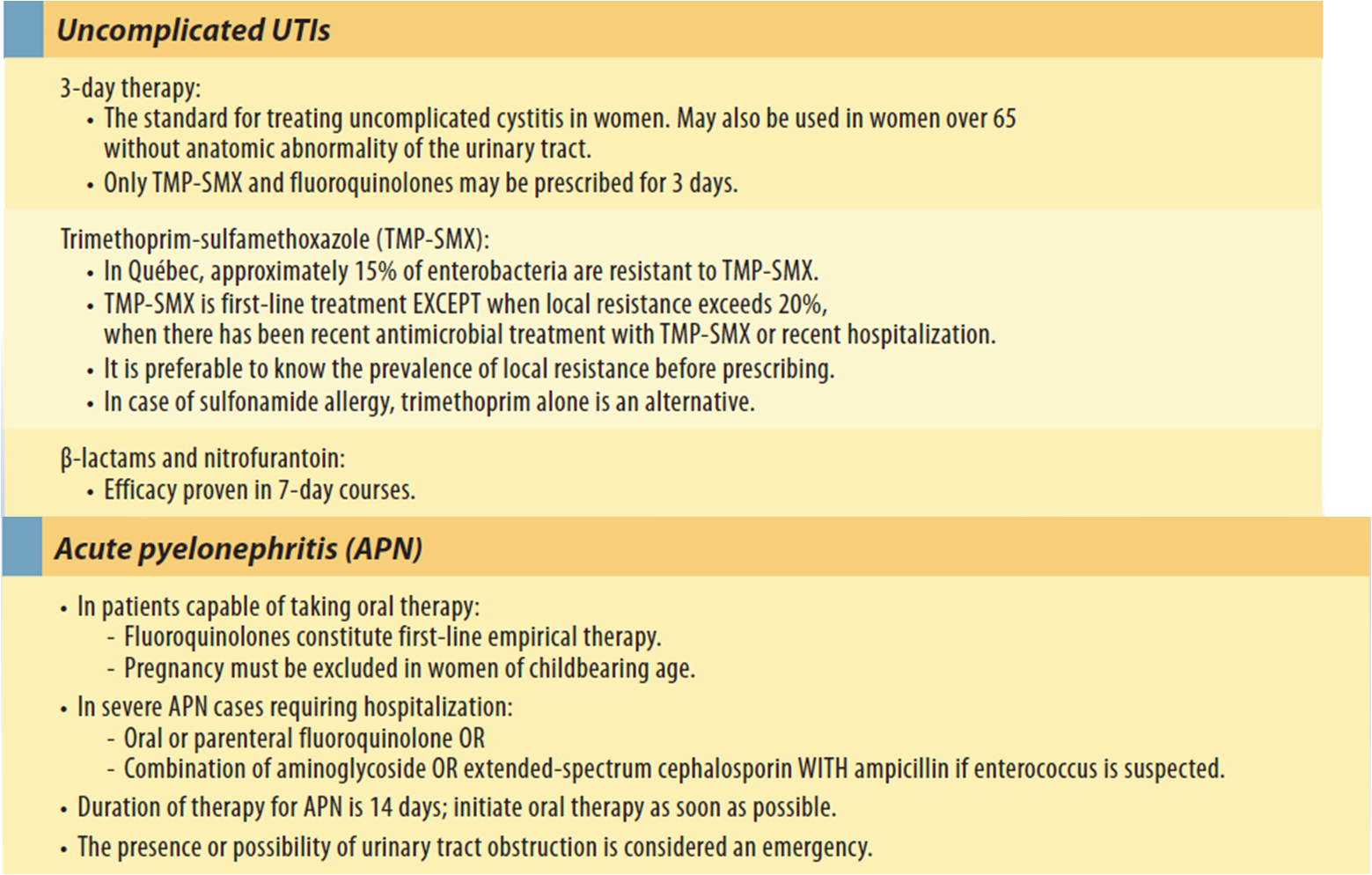
Uncomplicated cystitis occurs in patients who have a normal, unobstructed genitourinary tract who have no history of recent instrumentation and whose symptoms are confined to the lower urinary tract. Uncomplicated cystitis is most common in young, sexually active women. Patients usually present with dysuria, urinary frequency, urinary urgency, and/or suprapubic pain. Treatment regimens for uncomplicated cystitis in nonpregnant women are provided in Table 1, below.
References
Gupta K, Hooton TM, Naber KG, et al. International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2011 Mar. 52:e103-20. . .
Wagenlehner FM, Schmiemann G, Hoyme U, Fünfstück R, Hummers-Pradier E, Kaase M, et al. . Urologe A. 2011 Feb. 50:153-69. . .
Abrahamian FM, Moran GJ, Talan DA. Urinary tract infections in the emergency department. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2008 Mar. 22:73-87, vi. .
Little P, Turner S, Rumsby K, Warner G, Moore M, Lowes JA, et al. Dipsticks and diagnostic algorithms in urinary tract infection: development and validation, randomised trial, economic analysis, observational cohort and qualitative study. Health Technol Assess. 2009 Mar. 13:iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-73. .
Foxman B. The epidemiology of urinary tract infection. Nat Rev Urol. 2010 Dec. 7:653-60. .
You May Like: Natural Antibiotics For Dental Infection
When To See Your Doctor
If you see blood or what may be blood in your urine, you should see your provider as soon as possible to figure out the cause.
And if you also experience any of the below symptoms, it is particularly important that you seek medical attention right away. This may mean a visit to your local emergency room, if you are unable to see your regular provider on short notice.
These symptoms include:
-
Large amounts of bright-red blood in the urine, especially if you are on blood-thinning medications
-
Peeing a lot more or a lot less than usual
-
Not peeing for more than 24 hours
-
Inability to empty your bladder
Ranking The Best Antibiotics For Uti Of 2021
Antibiotics for UTI alleviate the pain and discomfort of urinary tract infections quickly and reliably.
Every year more than six million Americans visit their doctors seeking treatment of UTIs. The overwhelming majority are women, who are 30 times more likely to suffer UTIs than men.
In nearly all confirmed UTI cases, antibiotics are prescribed and start providing relief within 24 hours. Typically, within a few days, most or all symptoms have been eliminated.
There are more than 100 different antibiotics, but not all are useful in treating a UTI. The following are the best antibiotics for UTI of 2021. Speak to your doctor to determine which one is right for you.
Recommended Reading: Male Urinary Tract Infection Treatments
Can Men Get A Uti
Because women have shorter urethras, UTIs are much more common for them. However, men are not immune to UTIs and do get them occasionally, especially if they are not circumcised.
According to Melissa Ernst, a FastMed Family Nurse Practitioner in North Carolina, Men can get UTIs in fact, approximately 12% of all UTIs occur in males.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Urinary Tract Infection Male
What Are The Symptoms Of A Uti
Symptoms of a UTI can differ depending on what part of the urinary tract is infected.
A bladder infection usually causes symptoms that include the following:
- Burning when urinating
- The feeling that you need to pee frequently, but when you go to the toilet very little urine comes out
- Pain in the pelvic area just above the pubic bone.
Bladder infections are usually considered a simple UTI and treatment is usually with antibiotics for three to five days. Symptoms usually resolve in a couple of days.
People with an infection of the urethra may experience symptoms similar to a bladder infection in addition to itching or irritation at the end of the urethra where the pee comes out.
Symptoms of a kidney infection are usually more widespread and more severe than those of a bladder infection and may include:
- Fever or chills
- Pink or red-tinged urine
- Burning when urinating
- The feeling that you need to pee frequently, but when you go to the toilet very little urine comes out
- Pain in the pelvic area just above the pubic bone
- Moderate to severe lower back pain
- Nausea or vomiting.
You May Like: How To Stop An Ear Infection From Getting Worse
Usual Adult Dose For Otitis Media
250 to 333 mg orally every 6 hours OR 500 mg orally every 12 hours-Maximum dose: 4 g per day-Duration of therapy: 7 to 14 daysUse: Treatment of otitis media caused by susceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Moraxella catarrhalis
Whats The Difference Between A Urinary Tract Infection And Bladder Infection
A urinary tract infection is a more general type of infection. There are many parts of your urinary tract. A UTI is a term for an infection that takes place throughout the urinary tract. A bladder infection, also called cystitis, is a specific infection. In this infection, bacteria makes its way into the bladder and causes inflammation.
Not all urinary tract infections become bladder infections. Preventing the spread of the infection is one of the most important reasons to treat a UTI quickly when you have symptoms. The infection can spread not only to the bladder, but also into your kidneys, which is a more complicated type of infection than a UTI.
You May Like: Causes Of Weak Bladder Control
Also Check: Z Pack To Treat Sinus Infection
How Long To Take Antibiotics For A Uti
Very severe or complicated UTI cases may need up to 14 days of medication, but most patients with uncomplicated UTIs only require 3-7 days of treatment to fully eradicate their infection.
The exact number of doses needed depends on which antibiotic you are taking.
You should always make sure to take the full course of antibiotics that your healthcare provider prescribes to you to avoid antibiotic resistance in the future, even if symptoms improve before youre done.
What About Cranberry Juice For Uti

Its a long-held belief that consuming cranberry juice may help prevent and treat urinary tract infections. While its true that cranberries contain an active ingredient that can prevent adherence of bacteria to the urinary tract, there is still no evidence that cranberry products can treat a UTI.
One of the reasons: Products like cranberry juice or cranberry capsules are not explicitly formulated with the same amount of PACs that have shown potential in lab studies. Moreover, a 2019 report in the Journal of Urology noted that the availability of such products to the public is a severe limitation to the use of cranberries for UTI prophylaxis outside the research setting.
In all, theres actually very little high-quality research on the topic of prevention. For instance, a 2016 study in The Journal of the American Medical Association, found that among female nursing home residents, daily consumption of cranberry capsules resulted in no significant prevention of UTIs.
While consuming cranberry juice or supplements is not considered a first-line treatment of urinary tract infections, in most cases, it cant hurt. After all, drinking plenty of liquids does dilute your urine and help spur more frequent urination, which flushes bacteria from the urinary tract. The exception: Those who are taking blood-thinning medication, such as warfarin, should not consume cranberry juice. And those with diabetes should be mindful of the high-sugar content of fruit juices.
Recommended Reading: What Antibiotic For Ear Infection In Adults