How Is A Middle
Your health care provider will take a medical history and do a physicalexam. He or she will look at the outer ear and eardrum with an otoscope.The otoscope is a lighted tool that lets your provider see inside the ear.A pneumatic otoscope blows a puff of air into the ear to check how wellyour eardrum moves. If you eardrum doesnt move well, it may mean you havefluid behind it.
Your provider may also do a test called tympanometry. This test tells howwell the middle ear is working. It can find any changes in pressure in themiddle ear. Your provider may test your hearing with a tuning fork.
How Does An Ent Doctor Diagnose An Ear Infection
As soon as symptoms are present in an adult or child, consult with an New York ENT to evaluate your conditions and make an accurate diagnosis. Your doctor will use a tool called an otoscope that can see deep inside your ear with a light and magnifying glass. Doctors can often detect redness, puss, drainage, or other abnormalities in the middle ear that point to an ear infection. To determine the severity of the condition, your New York ENT may also conduct sample fluid tests, computed tomography scans, or hearing tests.
How To Tell If Your Ear Infection Is Serious Enough For Urgent Care
Have you developed an ear infection and plan on waiting until it goes away by itself? Unfortunately, its not always that easy.
The most common cause of ear infections is a blockage of the estuation tube, which controls pressure in the middle ear. Trapped bacteria results in an infection.
Although its possible for this to clear up on its own, if you ignore the problem, the infection could spread. Thats why were going over some signs that its time to visit Amory Urgent Care.
Don’t Miss: Types Of Antibiotics For Bladder Infection
Where Can I Find Additional Information About Ear Infections
The NIDCD maintains a directory of organizations that provide information on the normal and disordered processes of hearing, balance, smell, taste, voice, speech, and language.
Use the following keywords to help you search for organizations that can answer questions and provide printed or electronic information on ear infections:
Though An Ear Infection Is More Frequently Diagnosed In Children It Is Also Common In Adults Know The Type Of Infection You Have And Get Treatments Early

The ear is one of the most sensitive body parts. This sensory organ should be cared properly to avoid various problems, such as an ear infection. An ear infection is a common condition. Even though it is more frequently diagnosed in children, it is also common in adults. The ear consists of the three main parts: outer ear, middle ear and inner ear. Sound waves reach the outer ear first, then middle ear and then travel to the inner ear. A number of conditions can influence your hearing and ear infections are the most frequent.
Recommended Reading: What Medicine Is Best For A Yeast Infection
Acute Otitis Externa Or Swimmers Ear
Acute otitis externa or swimmerâs ear is caused by an infection, inflammation, or irritation of the ear canal. It can affect children and adults. This condition usually result from water getting trapped in the ear but can also be the result of eczema, excess earwax, use of hearing aids or earbuds, trauma from Q tips or other objects being inserted into the ear canals.
When Should I See A Doctor For An Ear Infection
Ear infections happen fast, so its important to understand the signs and know what to do in case you need to see a doctor. Its important to get an accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment for ear infections, especially if:
- Symptoms last for more than 24 hours
- Symptoms are present in a child less than six months of age
- Ear pain is severe
- Your infant or toddler is sleepless or irritable after an upper respiratory infection
- You see a discharge of clear fluid, pus or bloody fluid from the affected ear
If you or a loved one is experiencing one or more of these symptoms, please seek immediate medical treatment. Coastal Urgent Care of Baton Rouge is open for walk-ins 7 days a week between 9:00 a.m. and 8:00 p.m. Our team of skilled specialists has experience treating all types and severities of ear infections.
Recommended Reading: Prednisone Prescribed For Sinus Infection
What Happens If My Child Keeps Getting Ear Infections
To keep a middle ear infection from coming back, it helps to limit some of the factors that might put your child at risk, such as not being around people who smoke and not going to bed with a bottle. In spite of these precautions, some children may continue to have middle ear infections, sometimes as many as five or six a year. Your doctor may want to wait for several months to see if things get better on their own but, if the infections keep coming back and antibiotics arent helping, many doctors will recommend a surgical procedure that places a small ventilation tube in the eardrum to improve air flow and prevent fluid backup in the middle ear. The most commonly used tubes stay in place for six to nine months and require follow-up visits until they fall out.
If placement of the tubes still doesnt prevent infections, a doctor may consider removing the adenoids to prevent infection from spreading to the eustachian tubes.
What Increases Your Risk
Some things that increase your child’s risk of a middle ear infection are out of your control. These include:
- Being 3 years old or younger.
- Birth defects or other medical conditions, such as cleft palate or Down syndrome.
- A weakened immune system.
- A family history of ear infections.
- Allergies that cause long-term stuffiness in the nose and can block one or both eustachian tubes.
- Repeated colds and upper respiratory infections.
Other things can increase your child’s risk of ear infection. They include:
- Being exposed to cigarette smoke.
- Lying flat while bottle feeding.
- Using a pacifier.
- Using a bottle instead of breastfeeding.
Things that increase the risk of repeated ear infections include:
- Being in a childcare center with many other children.
- Getting the first ear infection before 6 months of age.
- Having persistent fluid behind the eardrum.
- Having an ear infection in the last 3 months, especially if it was treated with antibiotics.
You May Like: Strongest Otc Yeast Infection Medicine
Can Otitis Media With Effusion Be Prevented Or Avoided
The best ways to prevent fluid build-up in the ears are the same as preventing ear infections:
- Wash your childs hands and toys often.
- Avoid pacifiers.
- Breastfeed your baby.
- If you bottle-feed your baby, hold him or her in an upright, seated position when feeding them.
- Keep your child away from cigarette smoke.
- Make sure your childs vaccinations are up to date.
About Ear Nose And Throat
Ear, Nose, and Throat Services at UPMC Presbyterian Shadyside ranks among the best nationally on U.S. News & World Reports listings. Our team includes board-certified physicians and highly skilled speech-language pathologists and audiologists. We treat a variety of ear, nose, and throat conditions in both children and adults and provide both surgical and non-surgical options. Our doctors also take part in research and clinical trials. We have locations throughout western Pennsylvania for patient convenience.
Tags
Read Also: I Have A Urinary Tract Infection And Im Bleeding
Why Do Kids Get Ear Infections
Kids get ear infections more than adults do for several reasons:
- Their shorter, more horizontal eustachian tubes let bacteria and viruses find their way into the middle ear more easily. The tubes are also narrower, so more likely to get blocked.
- Their adenoids, gland-like structures at the back of the throat, are larger and can interfere with the opening of the eustachian tubes.
Other things that can put kids at risk include secondhand smoke, bottle-feeding, and being around other kids in childcare. Ear infections are more common in boys than girls.
Ear infections are not contagious, but the colds that sometimes cause them can be. Infections are common during winter weather, when many people get upper respiratory tract infections or colds .
Treating Outer Ear Infections
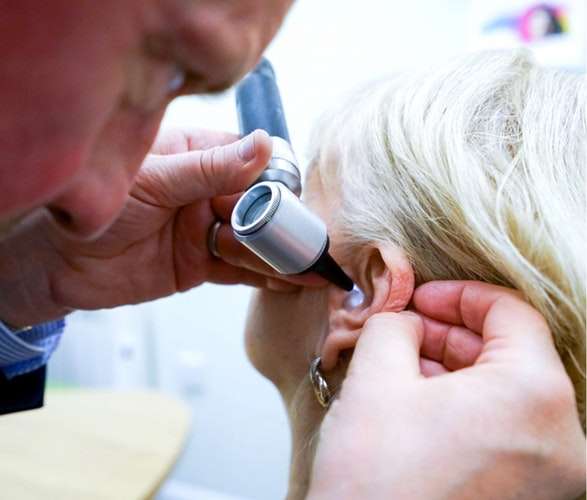
The outer ear should be carefully cleaned. That should be followed by the application of antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory medications on your ear.
Antibiotics may be prescribed if your doctor determines that the infection is bacterial.
If you have a viral infection, you may simply need to tend to the irritation on your ear and wait for the infection to resolve itself. Depending on the type of virus involved, more specialized treatment may be necessary.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Tooth Infection Pain
Ear Infections When To See A Doctor
INTRODUCTIONAn ear infection, scientifically referred to as otitis, involves inflammation of any part of the ear, as a result of infections with various microorganisms, either bacteria or viruses. Depending on where the infection is localized, ear infections are further divided into three categories, namely otitis externa, otitis media and otitis interna, with different symptoms and treatment.
PREVALENCEEar infections are very common in the general population. Otitis media, specifically, is one of the most frequently diagnosed infections during childhood it has been reported that, in the United States, almost 90% of the children will have experienced at least one incident of otitis media. Otitis externa is believed to affect 4 out of 1,000 individuals in the US each year, especially during the summer, or in areas with increased humidity and heat. Otitis interna, also known as labyrinthitis, very rarely affects children, as it is diagnosed in people older than 30 years old, approximately in 1 out of 10,000 people in the US.
TYPES OF INFECTION & PRESENTATIONOtitis ExternaOtitis externa is an infection of the auricle, the external ear canal or of both structures, due to microbes. The microorganisms that are the most common culprits are bacteria, although fungi can also cause the condition. It can assume an acute form or a chronic one if acute otitis externa is not treated properly.
What Are The Symptoms Of An Ear Infection
There are three main types of ear infections. Each has a different combination of symptoms.
- Acute otitis media is the most common ear infection. Parts of the middle ear are infected and swollen and fluid is trapped behind the eardrum. This causes pain in the earcommonly called an earache. Your child might also have a fever.
- Otitis media with effusion sometimes happens after an ear infection has run its course and fluid stays trapped behind the eardrum. A child with OME may have no symptoms, but a doctor will be able to see the fluid behind the eardrum with a special instrument.
- Chronic otitis media with effusion happens when fluid remains in the middle ear for a long time or returns over and over again, even though there is no infection. COME makes it harder for children to fight new infections and also can affect their hearing.
Don’t Miss: Best Antibiotic For Severe Sinus Infection
When To See A Doctor
Ear infections can go away on their own in many cases, so a minor earache may not be a worry.
A doctor should typically be seen if symptoms have not improved within 3 days. If new symptoms occur, such as a fever or loss of balance, a doctor should be seen immediately.
Any sign of discharge coming from the ear would also require a visit to the doctor.
What Should I Expect If I Or My Child Has An Ear Infection
Ear infections are common in children. Adults can get them too. Most ear infections are not serious. Your healthcare provider will recommend over-the-counter medications to relieve pain and fever. Pain relief may begin as soon as a few hours after taking the drug.
Your healthcare provider may wait a few days before prescribing an antibiotic. Many infections go away on their own without the need for antibiotics. If you or your child receives an antibiotic, you should start to see improvement within two to three days.
If you or your child has ongoing or frequent infections, or if fluid remains in the middle ear and puts hearing at risk, ear tubes may be surgically implanted in the eardrum to keep fluid draining from the eustachian tube as it normally should.
Never hesitate to contact your healthcare provider if you have any concerns or questions.
Dont Miss: Which Composer Experienced Severe Hearing Loss During His Lifetime
Recommended Reading: Sinus Infection Tooth Pain Antibiotics
How Is Otitis Externa Treated
Treatment for the early stages of swimmerâs ear includes careful cleaning of the ear canal and use of eardrops that stop bacterial or fungal growth and reduce inflammation. Before using any drops in the ear, it is important to be sure you do not have a perforated eardrum .
If the ear canal is swollen shut, your doctor may place a sponge or wick in the canal so the antibiotic drops will enter the swollen canal more effectively. Topical antibiotics are effective for infection limited to the ear canal. Oral antibiotics may also be prescribed if the infection goes beyond the skin of the ear canal.
Follow-up appointments are very important to monitor your condition, to clean the ear again, and to replace the ear wick as needed. Your ENT specialist has specific equipment and expertise to effectively clean the ear canal and treat swimmerâs ear. With proper treatment, most infections should clear up in seven to 10 days.
When To Call The Doctor For An Ear Infection
Some symptoms of an inner ear infection can be the same as a stroke. If you have vomiting, headache, vision changes, fever, weakness in one side of your body, slurred speech or are unable to walk, seek medical care right away.
Infections involving high fever, discharge or bleeding from the ear canal, headache, vomiting, dizziness, loss of hearing, or severe pain should be seen by a doctor. A doctor should see most people with an inner ear infection.
Also Check: Can An Ear Infection Go Away On Its Own
Living With An Ear Infection
If your child suffers from several ear infections each year, youll want to look out for symptoms every time they have a stuffy nose or congestion.
Never stick anything in your childs ear to relieve the pain of an ear infection, to remove the tubes or remove a foreign object. See your childs doctor to have it removed.
Tumors Of The Middle Ear

Polyps and Granulation Tissue of the Middle Ear: Polyps can develop in the middle ear. As such, these are not necessarily benign tumors. They look like balls of inflamed tissue which form grape-like clusters within the confines of the middle ear and mastoid. These polyps generally are reddish and bleed easily on vacuuming or any manipulation. They may be indistinguishable from more serious problems of the middle ear and mastoid. If they do not respond to medical therapy, polyps should be biopsied. In most cases of advanced polyps and inflammation of the middle ear, surgery of the middle ear and mastoid will necessary.
Cholesteatoma: These are tumors of the middle ear which are usually benign and the most common of all middle ear tumors. These are dealt with fully in a separate section, Cholesteatoma. Cholesteatoma arises from a perforation of the tympanic membrane with ingrowth of skin into the middle ear. Also, they appear congenitally from an epidermoid formation which is also described in the Recent Research section. Full information on these topics can found in this web site.
Don’t Miss: What Antibiotics Are Prescribed For Tooth Infection
How Do Ear Infections Happen
A middle ear infection usually happens because of swelling in one or both of the eustachian tubes . The tubes let mucus drain from the middle ear into the throat.
A cold, throat infection, acid reflux, or allergies can make the eustachian tubes swell. This blocks the mucus from draining. Then, or grow in the mucus and make pus, which builds up in the middle ear.
When doctors refer to an ear infection, they usually mean otitis media rather than swimmer’s ear . Otitis media with effusion is when noninfected fluid builds up in the ear. It might not cause symptoms, but in some kids, the fluid creates a sensation of ear fullness or “popping.”
Will My Hearing Come Back
Approximately half of patients with SSNHL recover at least some hearing without treatment. Patients have a 75 to 80 percent chance of recovery with steroid therapy given early. The earlier that treatment is begun, the better the chances for recovery. Patients with profound hearing loss, which is a complete or near complete loss of hearing, patients who experience dizziness with their sudden hearing loss, and individuals above age 65 have a much lower chance of getting their hearing back. In those cases, you and your healthcare provider should discuss aggressive treatments to try to bring your hearing back. Hearing can take months to return after treatment is finished.
If you do not experience full hearing recovery, you may want to talk to your otolaryngologist and audiologist about hearing aids or other devices you can use to make hearing easier.
You May Like: Best Antibiotic For Foot Infection
When Should I Call The Doctor
Very rarely, ear infections that don’t go away or severe repeated middle ear infections can lead to complications. So kids with an earache or a sense of fullness in the ear, especially when combined with fever, should be seen by their doctors if they aren’t getting better after a couple of days.
Other things can cause earaches, such as teething, a foreign object in the ear, or hard earwax. Your doctor can find the cause of your child’s discomfort and treat it.