Hepatitis B Virus Infection Status
The patients hepatitis B virus infection status should be tested upon entry into care, including measurement of hepatitis B surface antigen , hepatitis B surface antibody , and antibody to hepatitis B total core antigen . If HBsAg is positive, HBV viral load should be obtained. Those who are susceptible to infection should be vaccinated against HBV.
General Signs And Symptoms:
The general signs of vestibular dysfunction are vertigo and unsteadiness. These symptoms are not entirely specific to the inner ear, and may also be caused by a variety of other processes that are prevalent in the HIV population as well as the normal population, such as migraine, low blood pressure, anxiety, and peripheral neuropathy.
Has The Introduction Of Antiretroviral Therapy Changed The Cancer Risk Of People Infected With Hiv
The introduction of highly active antiretroviral therapy , also called combination antiretroviral therapy , starting in the mid-1990s greatly reduced the incidence of certain cancers in HIV-infected patients, especially Kaposi sarcoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma . The likely explanation for this reduced incidence is that cART lowers the amount of HIV circulating in the blood, thereby allowing partial restoration of immune system function to fight the viruses that cause many of these cancers.
Although the risk of these AIDS-defining cancers among people infected with HIV is lower than in the past, it is still much higher than among people in the general population . This persistently high risk may reflect the fact that cART does not completely restore immune system functioning. Also, many people infected with HIV are not aware they are infected, have had difficulty in accessing medical care, or for other reasons are not receiving adequate antiretroviral therapy.
The introduction of cART has not reduced the incidence of all HIV-related cancers, and in fact AIDS-defining cancers. For example, the incidence of liver and may be increasing among HIV-infected individuals .
Read Also: How To Treat Ear Infection Over The Counter
Hiv: A Brief Overview
HIV, or human immunodeficiency virus, is a sexually transmitted virus that spreads through exposure to certain body fluidsâlike genital secretions or blood. HIV transmission can also occur from a mother to a child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
HIV attacks and impairs the bodyâs immune cells, which weakens the immune system and can eventually progress to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome if it isnât treated. AIDS can be a life-threatening condition, particularly if HIV treatment is not initiated promptly, which is why HIV testing is crucial for protecting your health.
What Are The Symptoms Of An Ear Infection
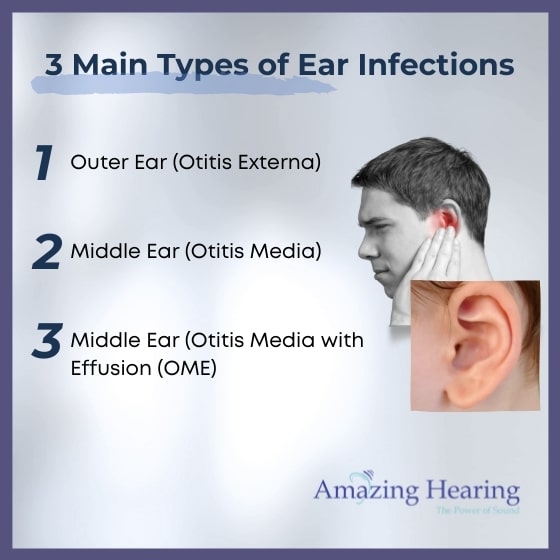
Ear infections can be uncomfortable and painful. If you have pain and pressure in your ear, you might suspect that you have one.
But babies and toddlers usually dont have the words yet to tell you that they have ear pain. So, how do you know if your child has an ear infection?
Common signs that may be an indication of an ear infection in young children include:
- Body language. Watch out for your baby or toddler pulling on their ear. This could be an indication of ear pain.
- Fever. A fever is a sign that the body is trying to fight off an infection.
- Fussiness or irritability. Is your child cranky and irritable for no other reason? Are they crying more than usual, too?
- Ear drainage. Pus or fluid draining out the ear is a common sign of an ear infection. The fluid may be yellow or bloody, which signifies a ruptured eardrum.
- Trouble hearing. When fluid builds up in the middle ear, it can create temporary hearing loss.
- Unsteadiness. The fluid in the ear can also upset your childs sense of balance, leading to unsteadiness or even dizziness.
- Inability to lie down comfortably. Lying down can cause an uncomfortable shift in pressure within the middle ear.
- Diarrhea. A child with an ear infection may sometimes experience some diarrhea or vomiting.
Many of these symptoms are also signs of an ear infection in older children and adults.
In general, the most common causes of hearing loss include:
Some people are also born with hearing loss, which is known as congenital hearing loss.
Recommended Reading: Is Amoxicillin Good For Tooth Infection
Is Hearing Loss Simply An Issue Of Age
Given the design of the MACS and WIHS research, some might conclude that HIV simply “adds” to the natural hearing loss seen in aging adults. Certainly, it is acknowledged that the persistent, long-term inflammation associated with HIV can cause premature senescence in a number of organ systems, including the heart and brain. Might it be reasonable to suggest that the same might happen with a person’s hearing?
A number of researchers are not so sure. One study from the Taipei Medical Center in Taiwan aimed to assess hearing loss in a cohort of 8,760 patients with HIV and 43,800 patients without HIV. Hearing loss was evaluated based on medical records over a five-year period from January 1, 2001, to December 31, 2006.
According to the research, sudden hearing loss occurred almost twice as frequently in HIV patients aged 18 to 35 but not in those 36 years of age or older.
While the investigators were unable to conclude that HIV was the principal cause for such lossparticularly since factors like noise exposure and smoking were excluded from the analysisthe scale of the study does suggest that HIV may, in some part, be a contributing factor.
Similarly, a 2012 study from the National Institutes of Health research network suggested that children infected with HIV in utero are two to three times more likely to have hearing loss by the age of 16 than their non-infected counterparts.
Transmission Of Hiv Infection
HIV is most commonly transmitted to children by
-
An infected mother before birth or during birth
-
After birth through the mother’s milk
In young children, HIV infection is nearly always acquired from the mother. More than 95% of HIV-infected children in the United States acquired the infection from their mother, either before or around the time of birth . Most of the remaining children now living with AIDS acquired the infection from sexual activity, including, rarely, sexual abuse. Because of improved safety measures regarding screening of blood and blood products, in recent years almost no infections have resulted from the use of blood and blood products in the United States, Canada, or Western Europe.
Experts are not sure how many HIV-infected women give birth each year in the United States, but the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate is about 5,000. Without preventive measures, 25 to 33% of them would transmit the infection to their baby. Transmission often takes place during labor and delivery.
The risk of transmission is highest among mothers who
-
Acquire HIV infection during pregnancy or while breastfeeding
-
Are severely ill
-
Have more virus in their body
However, transmission has declined significantly in the United States from about 25% in 1991 to less than 1% in 2018. Mother-to-child transmission has been reduced because of an intensive effort to test and treat infected pregnant women during both pregnancy and delivery.
You May Like: Yeast Infection Medicine Side Effects
People Living With Hiv/aids
As a person living with HIV/AIDS, you have many opportunities for a healthy and full life. You may also have some health challenges. One of those challenges is avoiding infections.
Many fungal infections are called opportunistic infections, which means that they usually affect people with weak immune systems. Because HIV weakens the immune system, you have a greater chance of getting some types of fungal infections, like cryptococcosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and pneumocystis pneumonia .
Children Under 18 Months Of Age
For children under 18 months of age, standard adult blood tests for HIV antibodies or antigens are not helpful, because the blood of an infant born to an HIV-infected mother almost always contains HIV antibodies passed through the placenta even if the infant is not infected. So, to definitively diagnose HIV infection in children under 18 months of age, special blood tests called nucleic acid amplification tests are done. These tests detect genetic material using polymerase chain reaction Polymerase chain reaction Genetic diagnostic technologies are scientific methods that are used to understand and evaluate an organisms genes. Genes are segments of deoxyribonucleic read more tests. The diagnosis of HIV infection is confirmed if the NATs detect genetic material from HIV in the childs blood.
Testing using NATs should be done at frequent intervals, typically in the first 2 weeks of life, at about 1 month of age, and between 4 months and 6 months of age. Such frequent testing identifies most HIV-infected infants by 6 months of age. Some infants who have a very high risk of developing HIV may be tested more frequently.
All infants should be tested if they are born to mothers who
-
Have HIV infection
-
Are at risk of HIV infection
Recommended Reading: Is Bactrim Good For Tooth Infection
Hiv/aids And Skin Conditions
Skin conditions are common in people with HIV/AIDS. Many, including Kaposi sarcoma, thrush, and herpes, are caused by germs that take advantage of a weakened immune system. That’s why they are called “opportunistic” infections. Others, like photodermatitis, may be linked to inflammation caused by an overactive immune system as it revives during antiretroviral drug therapy or due to the drugs themselves.
Here are some of the more common skin conditions related to HIV/AIDS.
Chronic Viral Infection/ Opportunistic Infections
In some cases, HIV infection is initially diagnosed when the patient presents with an AIDS-defining illness. These include the following :
- Bacterial infections, multiple or recurrent
- Herpes simplex virus – Chronic ulcers or bronchitis, pneumonitis, or esophagitis
- Histoplasmosis, disseminated or extrapulmonary
- Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia or pulmonary lymphoid hyperplasia complex
- Lymphoma –Burkitt , immunoblastic , or primary
- Mycobacterium avium complex or Mycobacterium kansasii, disseminated or extrapulmonary
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis of any site, pulmonary, disseminated, or extrapulmonary
- Mycobacterium, other species or unidentified species, disseminated or extrapulmonary
- Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
- Wasting syndrome attributed to HIV
Also Check: Will Amoxicillin Help Kidney Infection
Main Aspects Of Peripheral And Central Hearing System Involvement In Unexplained Hiv
- Department of OtolaryngologyHead and Neck Surgery, Hadassah Hebrew-University Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel
Objective: Hearing abnormalities frequently occur in Human Immunodeficiency Virus infected individuals. Both conductive and uni- or bilateral sensorineural hearing loss have been described along with other audiological and vestibular symptoms such as tinnitus, vertigo and balance disturbances. While frequent middle ear infections may explain impairment of peripheral hearing abilities, the exact etiology of cochlear, and central auditory processing deficits still remains unclear. Direct effects of HIV, opportunistic infections, ototoxic side effects of antiretroviral therapy , and immunologic responses to the central nervous system involving the auditory pathway have been proposed. We aim to review the audiological profile in HIV infected adults related to the effects of HIV and HAART on the inner ear structures.
Methods: We present a review of the literature on cases of HIV related SNHL in adult patients and studies conducted to investigate audiometric changes in such patients. Data on presentation, diagnosis and pathophysiology were reviewed.
Results: Sensorineural hearing loss in the higher frequencies is a common form of hearing loss in HIV infected individuals throughout disease progression, along with decreased otoacoustic emission responses, increased PTA hearing thresholds and prolonged latencies for auditory brainstem responses .
Could Antiretroviral Drugs Be A Cause

Linking hearing loss to antiretroviral therapy has become an even more contentious issue than linking loss to HIV itself. Since the mid- to late-1990s, a number of small studies had suggested ART, as an independent factor, was associated with an increased risk of hearing loss. Most of these studies have since been questioned given that individual drug agents had never evaluated and factors like disease stage, ART initiation and adherence were never included.
A small, 2011 study from South Africa did seek to investigate the impact of stavudine, lamivudine, and efavirenz on hearing. And while the data did show slightly elevated rates of impairment among HIV-positive patients on ART, the investigator fell short of linking those losses to the drugs themselves.
Despite the paucity of evidence, there are concerns that not enough attention is being paid to the ontological effects of antiretroviral drugs, including drug-related mitochondrial toxicities that can potentially enhance or exacerbate HIV-associated disorders, particularly those affecting the neurological system.
As more and more focus is being placed on both quality of life and the avoidance of aging-related disorders in long-term infection, greater strides may need to be taken in order to provide definitive answers to the question of hearing loss in the HIV-infected population.
Don’t Miss: Will Antibiotics Stop Tooth Infection
What Can Effective Hiv Treatment Do
HIV medication keeps you healthy so you can live a normal lifespan.
Treatment can also reduce your viral load to undetectable levels so that you wont be able to pass on HIV to anyone else. It can take up to six months from starting treatment to become undetectable, so its important to test and start treatment on time.
Comparison Of Acute Hiv Symptoms To Similar
In this chapter you will find a comparison of early HIV symptoms to other common medical conditions. It will help you to know the most important differences between them from the doctorâs viewpoint.
Often, different conditions have similar symptoms and signs. Any experienced doctor keeps in mind other conditions that look and present similarly. It is called making a differential diagnosis.
The differences between similar conditions can be very subtle, so all signs and symptoms should be analyzed carefully:
- Timing of the symptoms
In this section, we will help you to distinguish early HIV symptoms from symptoms of other conditions.
Since early HIV symptoms can be very nonspecific, we will make these two comparisons:
- General symptoms of early HIV to mononucleosis
- Early HIV to flu
We will put practical comparative information in tables side by side so it will be easier to see the similarities and differences between those conditions and early HIV.
The tables will be followed by frequently asked questions that are answered by an expert doctor to clarify some practical points.
Letâs proceed!
Read Also: Hair Follicle Infection Antibiotic Treatment
Evaluation Of Central Auditory Pathways
The Central Auditory Pathway is a complex system that can be tested objectively through auditory brainstem evoked responses , EcoG, middle, and late latency evoked responses , P300 wave measurement and other specific tests. With our search criteria we found two articles looking at central auditory processing through ABR or gap detection thresholds . Matas et al. compared controls with HIV infected subjects and AIDS patients . ABR measurements were done for clicks to measure latencies and interpeak intervals. MLR measurements were performed to determine contra- and ipsilateral amplitudes. ABR latencies were prolonged for the HIV seropositive subjects and AIDS patients compared to controls, as well as the I-V interpeak latency . MLR in HIV infected subjects showed prolonged latencies and decreased amplitudes when the electrode was placed at C3 compared to seronegative controls. The difference was most obvious for AIDS patients. P300 is an electric wave in the electric encephalogram that occurs at 300 ms after stimulus and is often measured at the posterior aspect of the skull. Matas et al. found also here significantly prolonged latencies for HIV infected and AIDS diseased participants . The Gap detection threshold was evaluated in HIV infected subjects with or without ART . Measured at 65 dB, a slight increase in gap detection threshold was found among HIV infected participants compared to seronegative controls.
You May Like: Can Cefuroxime Treat Yeast Infection
Sudden Unexplained Weight Loss
National Human Genome Research Institute
Weight loss is common in people living with HIV during the advanced stages of the disease.
This type of weight loss is more than just a few poundsit’s a sudden, unexplained weight loss of 10% or more of a person’s body weight, in which both fat mass and lean muscle are lost.
The condition is also called HIV wasting syndrome. It’s not as common today as it once was because antiretroviral drugs keep the virus suppressed and allow the immune system to rebuild itself. Wasting is mainly seen in people who have not been treated for HIV.
The exact cause of HIV wasting is unknown, but it is thought that the constant inflammation caused by HIV makes the body burn energy faster and reduces testosterone levels .
Other causes of wasting include malnutrition, chronic diarrhea, tuberculosis, and cancerall of which require urgent diagnosis and treatment.
Also Check: Can You Give Yourself A Yeast Infection
How Are These Disorders Treated
No single treatment can cure the neurological complications of HIV/AIDS. Some disorders require aggressive therapy while others are treated as symptoms arise.
Neuropathic painchronic pain caused by damage to the nervous systemis often difficult to control. Medicines range from over-the-counter pain killers to anticonvulsant drugs, opiates, and some classes of antidepressants. Inflamed tissue caused by autoimmune or other conditions can press on nerves, causing pain. Such illnesses may be treated with corticosteroids or procedures such as plasma exchange, formally known as plasmapheresis, that clear the blood of harmful substances that cause inflammation.
Treatment options for AIDS- and HIV-related neuropsychiatric or psychotic disorders include antidepressants and anticonvulsants. Psychostimulants may also improve depression and reduce fatigue. Drugs such as cholinesterase inhibitors, which can temporarily improve or stabilize memory and thinking skills in people with dementia, may relieve confusion and slow mental decline. Benzodiazepines may be prescribed to treat anxiety. Psychotherapy may also help some individuals.
Other treatments may include physical therapy and rehabilitation, radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy to shrink cancerous brain tumors that may be related to HIV, antifungal or antimalarial drugs to combat certain bacterial infections associated with the disorder, and penicillin to treat neurosyphilis.