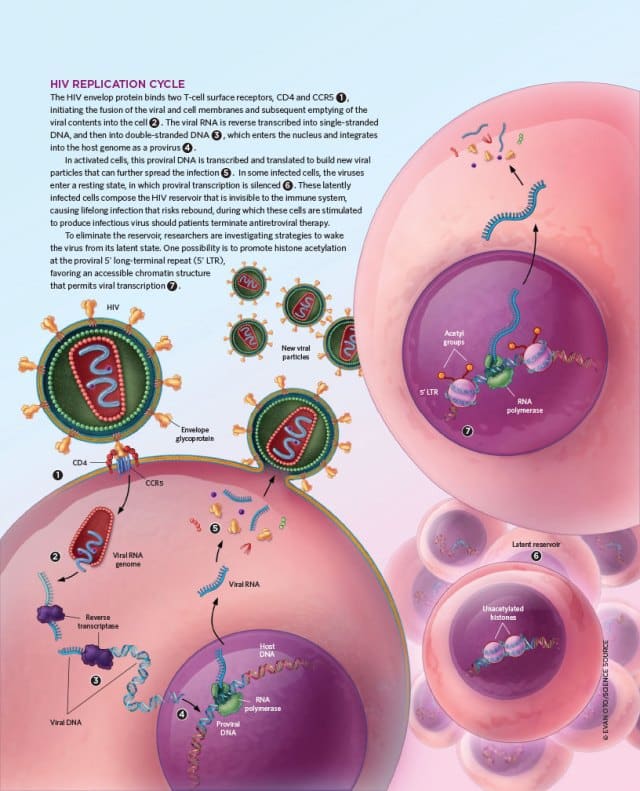
What Is The Hiv Life Cycle
HIV attacks and destroys the CD4 cells of the immune system. CD4 cells are a type of white blood cell that play a major role in protecting the body from infection. HIV uses the machinery of the CD4 cells to multiply and spread throughout the body. This process, which is carried out in seven steps or stages, is called the HIV life cycle.
What Is The Difference Between Hiv And Aids
The term AIDS refers to the most advanced stages of HIV infection. Most of the conditions affecting people with AIDS are opportunistic infections that generally do not affect healthy people. In people with AIDS, these infections are often severe and sometimes fatal because the immune system is so ravaged by HIV that the body cannot fight off the infection. Symptoms of opportunistic infections common in people with AIDS include:
- coughing and shortness of breath
- seizures and lack of coordination
- difficult or painful swallowing
- severe headaches
People with AIDS also are particularly prone to developing various cancers. These cancers are usually more aggressive and difficult to treat in people with AIDS.
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can live and long and healthy life and will not transmit HIV to your HIV-negative partners through sex.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Its important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
Also Check: Can Amoxicillin Give You A Yeast Infection
The Fourth Stage: Full
Over the years, the diagnostic elements of this end-stage of HIV infection have undergone various changes under different classification systems. The advent of AIDS marks an important milestone in the course of the infection. Although very few people try to, and successfully do, bounce back by following a strict treatment plan, AIDS is still referred to as an irreversible diagnosis.
Recovery from individual opportunistic infections may occur, including a state of remission for cancerous tumours. Recurrence, however, can be both more frequent and intense. AIDS becomes more and more difficult to treat until finally, the infected person succumbs. This happens 18-24 months after the onset of AIDS.
Essentially, the components of AIDS consist of the direct consequences of damage by HIV, as well as the indirect consequences of immunosuppression.
What Are The Symptoms Of Chronic Hiv Infection
The first possible symptoms of HIV infection may develop within 2-4 weeks after youâre exposed to the virus. You might notice flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, and rashes. Or you could have no symptoms at all.
In this first stage of HIV/AIDS the virus reproduces itself very quickly and spreads all over your body. This makes the virus especially easy to transmit to others through sexual contact. The virus starts to destroy infection-fighting cells in your immune system called CD4 T cells, or sometimes just âT cells.â
Once you reach the second stage of HIV/AIDS chronic HIV infection the virus has started to reproduce at a far slower pace. Even without treatment, many people in this stage donât notice any HIV-related symptoms for 10 years or more. Thatâs why some doctors also call it âasymptomatic HIV infectionâ or âclinical latency.â
Still, in some cases, you might get mild infections with symptoms like:
- Oral yeast infection
Whether you have symptoms or not, without treatment, HIV continues to take a relentless toll on your immune system. Your HIV levels go slowly up and your CD4 levels go slowly down until the illness progresses to the most serious stage: AIDS.
Treatment during these early stages of the illness can have huge health benefits, especially with an approach known as antiretroviral therapy, or ART.
Read Also: Antibiotic For Yeast Infection And Uti
What Are Symptoms Of Hiv
The first symptoms of HIV are called primary or acute HIV infection. These early symptoms usually occur two to four weeks after a person is infected with the virus.
Acute HIV infection symptoms last about 2 weeks and are usually mild. People often dont realize they have HIV at this point. Early symptoms may include:
You May Like: What Is The Hiv Aids Rate In The United States
Where Can Someone Get Tested For Hiv
Your health care provider can give you an HIV test. HIV testing is also available at many hospitals, medical clinics, substance use programs, and community health centers. Use CDC’s GetTested treatment locator to find an HIV testing location near you. Getting tested through a professional health care provider is recommended however, there are HIV self-testing kits available. Rapid self-test and mail-in self-test are the two types of HIV self-tests, but state laws regarding self-testing may limit their availability in a location.
A rapid self-test is an oral fluid test done entirely at home or in private. There is currently one U.S. Food and Drug Administration -approved rapid self-test called OraQuick In-Home HIV test. A mail-in self-test requires a person to provide a blood sample from a fingerstick, which is then sent to a lab for testing.
Don’t Miss: Best Antibiotic For Ear Piercing Infection
The Asymptomatic Stage Of Hiv
Once seroconversion is over, most people feel fine and dont experience any symptoms. This is often called the asymptomatic stage and it can last for several years.
Though you might feel well at this stage, the virus is active, infecting new cells, making copies of itself and damaging your immune systems ability to fight illness.
Clinical Latency Stage Of Hiv Infection
The symptoms during ARS may last for a few weeks, according to the National Institutes of Health.
After this point, the infection progresses to the clinical latency stage, a period during which the virus reproduces at very low levels, but it is still active.
Also known as asymptomatic HIV infection or chronic HIV infection, the clinical latency stage typically causes no HIV-related symptoms.
For people who are not taking any anti-retroviral medication for their infection, the clinical latency stage lasts for 10 years, on average, but it may progress quicker.
ART, though, can keep the virus from growing and multiplying, prolonging the clinical latency state for several decades.
Its important to note that people living with HIV in the clinical latency stage are contagious and can still transmit the virus to other people. But, as the CDC notes, people who take ART exactly as prescribed and maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their HIV negative-partner through sex.
Don’t Miss: How Long Should I Take Antibiotics For Tooth Infection
Is Hiv Testing Confidential
HIV testing can be confidential or anonymous.
Confidential testing means that your HIV test results will include your name and other identifying information, and the results will be included in your medical record. HIV-positive test results will be reported to local or state health departments to be counted in statistical reports. Health departments remove all personal information from HIV test results before sharing the information with CDC. CDC uses this information for reporting purposes and does not share this information with any other organizations, including insurance companies.
Anonymous testing means you do not have to give your name when you take an HIV test. When you take the test, you receive a number. To get your HIV test results, you give the number instead of your name.
Who Should Get Tested For Hiv
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that everyone 13 to 64 years of age get tested for HIV at least once as part of routine health care. As a general rule, people at higher risk for HIV should get tested each year. Sexually active gay and bisexual men may benefit from getting tested more often, such as every 3 to 6 months. If you are over 64 years of age and at risk, your health care provider may recommend HIV testing.
Factors that increase the risk of HIV include:
- Injecting drugs and sharing needles, syringes, or other drug equipment with others
- Exchanging sex for money or drugs
- Having a sexually transmitted disease , such as syphilis
- Having sex with anyone who has any of the HIV risk factors listed above
Talk to your health care provider about your risk for HIV and how often you should get tested for HIV.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get A Wax With A Yeast Infection
Second Stage: Clinical Latency Symptoms
After your immune system loses the battle with HIV, the flu-like symptoms will go away. But thereâs a lot going on inside your body. Doctors call this the asymptomatic period or chronic HIV infection.
In your body, cells called CD4 T cells coordinate your immune systemâs response. During this stage, untreated HIV will kill CD4 cells and destroy your immune system. Your doctor can check how many of these cells you have with blood tests. Without treatment, the number of CD4 cells will drop, and youâll be more likely to get other infections.
Most people don’t have symptoms they can see or feel. You may not realize that you’re infected and can pass HIV on to others.
If youâre taking ART, you might stay in this phase for decades. You can pass the virus on to other people, but itâs extremely rare if you take your medicines.
What Factors Affect The Progression Of Hiv Into Aids
There are a number of factors which influence the progression of HIV for every infected person. These include:
- Nature of transmission
- Incubation period of the virus in the bloodstream.
- The number of viral particles transferred from the HIV-positive person to the other.
- Any simultaneous viral or bacterial infection.
- The strain of virus being transmitted.
- Biochemical abnormalities, .
- Heredity and genetic make-up.
- Immunosuppressive behaviour .
- Access and commitment to, and discipline over, ARVs and/or a prescribed HIV treatment plan.
Also Check: Can You Get Over The Counter Medication For Yeast Infection
What Infections Are Associated With Hiv/aids
HIV and AIDS are conditions or states, that affect people who test positive for HIV, the viral organism. Both conditions, HIV and AIDS, may enable the exact same opportunistic infections to set in, but it will be more likely that an AIDS patient will present more intense symptoms than an HIV patient. Some of the AIDS-defining infections include:
- Kaposis sarcoma
- Meningitis/encephalitis due to cryptococcal or toxoplasmosis infection
- Pulmonary, miliary or extrapulmonary tuberculosis
- Dementia for no other reason
- Cancers such as lymphoma .
Early Symptoms In Primary Hiv
The first noticeable stage is primary HIV infection. This stage is also called acute retroviral syndrome , or acute HIV infection.
It usually causes flu-like symptoms, so its possible for someone in this stage to think they have severe flu or another viral illness rather than HIV. Fever is the most common symptom.
Other symptoms include:
Read Also: Can You Have Hiv Symptoms And Test Negative
You May Like: Best At Home Yeast Infection Treatment
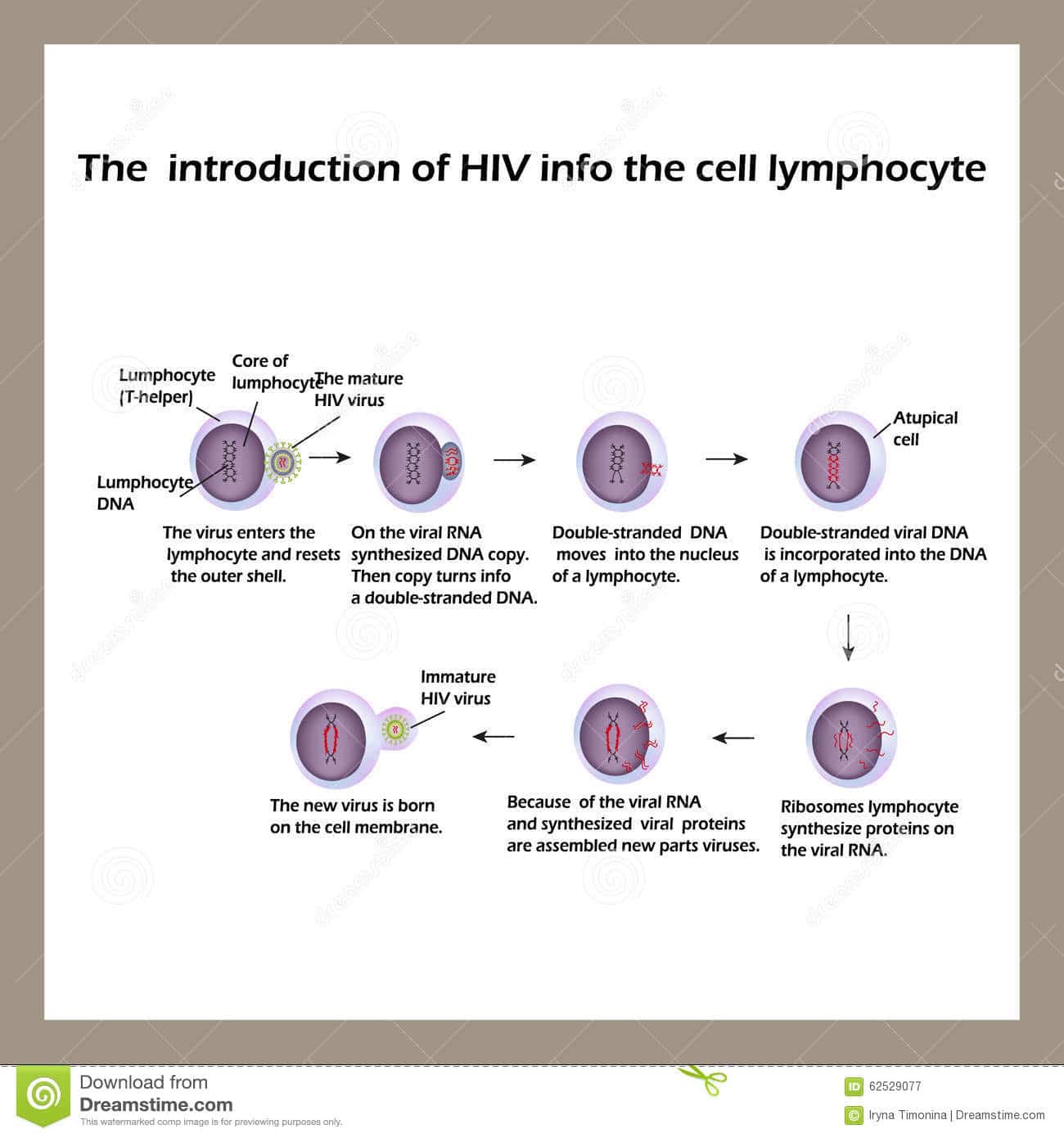
How Hiv Infects The Body
HIV is a virus that can cause an HIV infection if it gets into our blood stream.
It then goes on to infect our immune system â the part of our body that keeps you healthy.
It does this by entering T-helper cells so that our immune system canât find and destroy it. Then it makes copies of itself so it can go on to infect other cells.
This is called the HIV lifecycle and it is how the virus multiplies in our body.
Taking antiretroviral drugs is the only way to interrupt the HIV lifecycle and stay healthy.
Cdc Stages Of Hiv Infection
- Acute retroviral syndrome: This is an illness with symptoms like mononucleosis. It often develops within a few days of infection with HIV, but it also may occur several weeks after the person is infected. The symptoms can range from mild to severe and usually disappear on their own after 2 to 3 weeks. But many people do not have symptoms or they have such mild symptoms that they dont notice them.
- Stage 1 : There are no AIDS-related conditions AND the CD4+ cell count is at least 500 cells per microlitre or the percent of CD4+ cells is at least 29% of all lymphocytes.
- Stage 2 : There are no AIDS-related conditions AND the CD4+ cell count is 200 to 499 or the percent of CD4+ cells is 14% to 28% of all lymphocytes.
- Stage 3 : The CD4+ cell count is lower than 200, the percent of CD4+ cells is less than 14% of all lymphocytes, or an AIDS-related condition is present.
In general, the higher the CD4+ count, the less likely it is that opportunistic diseases will occur. Most people who have untreated HIV experience a gradual drop in the number of CD4+ cells. Each person responds uniquely to this decline.
Read Also: Urgent Care For Infected Tattoo
Pronounced Fatigue And Weakness
The weakened state of the immune system and the lack of nutrients can often make people feel extremely tired and weak. They may need frequent breaks when trying to complete daily tasks, and they might not be able to walk for very long before taking another break. This can often be frustrating, particularly for active people who previously enjoyed a greater sense of independence and also the ability to undertake more physical activities.
Why Is Hiv Testing Important
Knowing your HIV status can help keep youand otherssafe.
If you are HIV negative:
A negative HIV test result shows that you do not have HIV. Continue taking steps to avoid getting HIV, such as using condoms during sex and, if you are at high risk of getting HIV, taking medicines to prevent HIV . For more information, read the HIVinfo fact sheet on The Basics of HIV Prevention.
If you are HIV positive:
A positive HIV test result shows that you have HIV, but you can still take steps to protect your health. Begin by talking to your health care provider about antiretroviral therapy . People on ART take a combination of HIV medicines every day to treat HIV infection. ART is recommended for everyone who has HIV, and people with HIV should start ART as soon as possible. ART cannot cure HIV, but HIV medicines help people with HIV live longer, healthier lives.
A main goal of ART is to reduce a persons viral load to an undetectable level. An undetectable viral load means that the level of HIV in the blood is too low to be detected by a viral load test. People with HIV who maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partner through sex.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If Your Yeast Infection Is Gone
What Is Hiv And Aids
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus, which is the virus that causes HIV infection. The abbreviation HIV can refer to the virus or to HIV infection.
AIDS stands for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. AIDS is the most advanced stage of HIV infection.
HIV attacks and destroys the infection-fighting CD4 cells of the immune system. The loss of CD4 cells makes it difficult for the body to fight off infections and certain cancers. Without treatment, HIV can gradually destroy the immune system and HIV infection advances to AIDS.
Also Check: Can You Live With Someone With Hiv
What Is The Connection Between The Hiv Life Cycle And Hiv Medicines
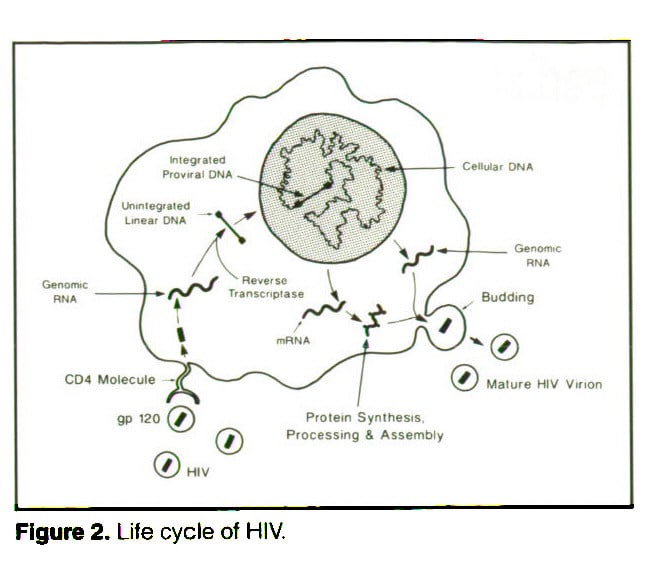
Antiretroviral therapy is the use of a combination of HIV medicines to treat HIV infection. People on ART take a combination of HIV medicines every day. HIV medicines protect the immune system by blocking HIV at different stages of the HIV life cycle. HIV medicines are grouped into different drug classes according to how they fight HIV. Each class of drugs is designed to target a specific step in the HIV life cycle.
Because an HIV treatment regimen includes HIV medicines from at least two different HIV drug classes, ART is very effective at preventing HIV from multiplying. Having less HIV in the body protects the immune system and prevents HIV from advancing to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome .
ART cannot cure HIV, but HIV medicines help people with HIV live longer, healthier lives. HIV medicines also reduce the risk of HIV transmission .
Recommended Reading: What Is A Tooth Infection Called
The Second Stage Of Hiv: The Asymptomatic Silent Phase
Following infection, there is a period of intense, unchecked viral replication. This happens 2 to 4 weeks after infection, and the replication activity lasts 1 to 2 weeks. Its after this process that the infected person recovers and is henceforth referred to as seropositive for HIV antibodies.
Though HIV replication is massive, most patients only experience moderate flu-like symptoms at this stage. Typically, the illness is sudden in onset and is characterised by fever, swelling of the lymph glands, a measles-like rash all over the body, ulcers in the mouth and sometimes on the genitalia.
Disease of the gastrointestinal tract is often involved, manifesting as nausea, vomiting and/or diarrhoea. Infected persons may also present inflammation of the pharynx and dysphasia, meningitis or encephalitis.
This acute HIV syndrome does not occur in all individuals infected with the virus, and many individuals who are HIV-positive, do not recall ever having experienced the illness. It has been estimated that approximately 5070% of individuals who are HIV-positive experience acute HIV illness. This syndrome is rarely seen in children.