During Hiv Infection Cd4 T Cells In Lymphoid Tissues Initiate A Highly Inflammatory Form Of Cell Death That Helps Cripple The Immune System
HIV-infected T cellFLICKR, NIAIDHIV leads to AIDS primarily because the virus destroys essential immune cells called CD4 T cells, but precisely how these cells are killed has not been clear. Two papers published simultaneously today in Nature and Science reveal the molecular mechanisms that cause the death of most CD4 T cells in lymphoid tissues, the main reservoir for such cells, during infection.
Two research teams led by Warner Greene at the Gladstone Institutes in San Francisco have demonstrated that the vast majority of CD4 T cells in lymphoid tissues, despite their ability to resist full infection by HIV, respond to the presence of viral DNA by sacrificing themselves via pyroptosisa highly inflammatory form of cell death that lures more CD4 T cells to the area, thereby creating a vicious cycle that ultimately wreaks havoc on the immune system.
Its really elegant science, said Anthony Fauci
Richard Koup, who leads the immunology lab at the Vaccine Research Center at the NIH, agreed: For years weve just said HIV infects the cells and kills them, but its clearly more complicated than that. These papers start to delineate the multiple different mechanisms that HIV might have to kill CD4 T cells.
G. Doitsh et al., Cell death by pyroptosis drives CD4 T-cell depletion in HIV-1 infection, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature12940, 2013.
How Do I Know If I Have Hiv
The only way to know for sure if you have HIV is to get tested. Testing is relatively simple. You can ask your health care provider for an HIV test. Many medical clinics, substance abuse programs, community health centers, and hospitals offer them too.
To find an HIV testing location near you, use the HIV Services Locator.
HIV self-testing is also an option. Self-testing allows people to take an HIV test and find out their result in their own home or other private location. You can buy a self-test kit at a pharmacy or online. Some health departments or community-based organizations also provide self-test kits for a reduced cost or for free.
Learn more about HIV self-testing and which test might be right for you.
The COVID-19 pandemic has made it more difficult for some people to access traditional places where HIV testing is provided. Self-testing allows people to get tested for HIV while still following social distancing practices. Ask your local health department or HIV service organization if they offer self-testing kits.
What Else Do I Need To Know About Taking Hiv/aids Medicines
It’s important to take your medicines every day, according to the instructions from your health care provider. If you miss doses or don’t follow a regular schedule, your treatment may not work, and the HIV virus may become resistant to the medicines.
HIV medicines can cause side effects. Most of these side effects are manageable, but a few can be serious. Tell your health care provider about any side effects that you are having. Don’t stop taking your medicine without first talking to your provider. He or she may give you tips on how to deal with the side effects. In some cases, your provider may decide to change your medicines.
Don’t Miss: Does Urgent Care Test For Yeast Infections
If You Already Have Hiv
If you are infected with HIV, you can greatly lower the risk of spreading the infection to your sex partner by starting treatment when your immune system is still healthy.
Experts recommend starting treatment as soon as you know you are infected.footnote 20
Studies have shown that early treatment greatly lowers the risk of spreading HIV to an uninfected partner.footnote 21, footnote 22
Your partner may also be able to take medicine to prevent getting infected.footnote 16 This is called pre-exposure prophylaxis .
Steps to prevent spreading HIV
If you are HIV-positive or have engaged in sex or needle-sharing with someone who could be infected with HIV, take precautions to prevent spreading the infection to others.
- Take antiretroviral medicines. Getting treated for HIV can help prevent the spread of HIV to people who are not infected.
- Tell your sex partner or partners about your behavior and whether you are HIV-positive.
- Follow safer sex practices, such as using condoms.
Bodily Fluids Spread Disease
HIV is a virus that targets the protein CD4 type T-cells of the bodys immune system. The T-cells are responsible for triggering an immune response to infections. HIV destroys the CD4 T-cells, reducing their overall number and ultimately limiting the bodys ability to fight off infections and certain types of cancers.
You May Like: What Antibiotic Good For Ear Infection
How Does Hiv Transmit In The Body
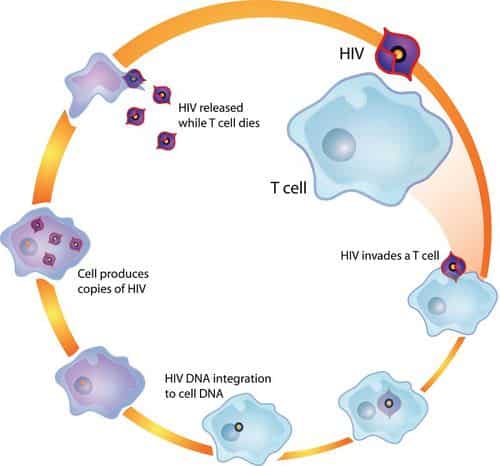
Since the virus targets the bodys immune system, its first victim or host cell would be the T-helper cells . It attaches and invades these white blood cells and takes control of the cell overall. Once the virus manages to infiltrate the DNA of the CD4 cells, it can now replicate and make copies of the infected CD4 cells, spreading it all over the body via your bloodstream.
The CD4 cells are then destroyed, and the HIV that rides on the host cell then takes over the duplication and spread of the virus. If left untreated, your CD4 cell count goes down to severely low levels, indicating the advancement of your HIV infection to AIDS.
One can categorize HIV infection into 3 acute, chronic, and the advanced stage called AIDS.
Key Role For Human Lymphoid Cultures In Discovering Hiv Death Pathway
In contrast to the productive infection and direct killing observed with activated blood CD4 T cells and CD4 T cell lines, studies of HIV infection employing primary lymphoid tissue highlighted a key role of death occurring within the bystander cell population . We have explored HIV-associated CD4 T cell death using an ex vivo human lymphoid aggregate culture system formed with fresh human tonsil or spleen tissues . This system recapitulates many of the conditions encountered by HIV in vivo and, thus, offers a biologically relevant approach for modeling the molecular and cellular events that occur during HIV infection in vivo. Importantly, HLACs can be infected with a low number of viral particles in the absence of artificial mitogens or cytokine activation, allowing analysis of CD4 T cell death in a natural and preserved lymphoid environment. Infection of HLACs with HIV-1 resulted in the near complete depletion of CD4 T cell population without changes in the CD8 T cell and B cells compartments. However, only approximately 5% of these CD4 T cells became productively infected with the virus. Conversely, 95% of the dying CD4 T cells were resting, nonpermissive CD4 T cells. A key question was how HIV promotes the death of these frequently bystander cells.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat A Bacterial Throat Infection
How Is Hiv Spread
The spread of HIV from person to person is called HIV transmission. HIV is spread only through certain body fluids from a person who has HIV. These body fluids include:
HIV transmission is only possible through contact with HIV-infected body fluids. In the United States, HIV is spread mainly by:
- Sharing injection drug equipment , such as needles or syringes, with someone who has HIV
The spread of HIV from a woman with HIV to her child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding is called perinatal transmission of HIV. For more information, read the HIVinfo fact sheet on Preventing Perinatal Transmission of HIV.
You cannot get HIV by shaking hands or hugging a person who has HIV. You also cannot get HIV from contact with objects, such as dishes, toilet seats, or doorknobs, used by a person with HIV. HIV is not spread through the air or water or by mosquitoes, ticks, or other blood-sucking insects. Use the HIVinfo You Can Safely ShareWith Someone With HIV infographic to spread this message.
Stage : Chronic Hiv Infection
After the acute stage has ended and if the person has not received treatment the virus remains active, reproducing at very low levels but continuing to damage immune cells.
At this stage, there are usually no symptoms or very mild ones. This is why doctors sometimes call stage 2 asymptomatic HIV infection or clinical latency. The virus can still pass to others during this stage, even if it causes no symptoms.
Without treatment, this stage can last for 10 years or more before the person develops stage 3 HIV.
However, modern antiretroviral medications can stop the infection from progressing. These drugs greatly reduce the amount of HIV in the body, the viral load, to very low levels.
When the viral load is so low that tests cannot detect it, HIV can no longer damage the immune system or transmit to other people. Some people refer to this as undetectable equals untransmittable or U=U.
A person with stage 2 HIV who takes effective antiretroviral therapy may never develop stage 3 HIV.
For more in-depth information and resources on HIV and AIDS, visit our dedicated hub.
You May Like: Yeast Infection Won T Heal
Hiv Effects On The Skin
Many people get a skin rash in the first stage of an HIV infection. It usually goes away without treatment in days or weeks. Over time, a number of things might cause more rashes. Itâs always important to let your doctor know about a rash, because it might be a sign of a serious problem, or an HIV medication could be causing it.
People who have HIV are more likely to get viral infections. Herpes zoster, herpes simplex, and Molluscum contagiosum can cause rashes or blisters.
Kaposiâs sarcoma causes lesions, patches, or nodules that are a different color from your skin. Sometimes, you can also get lesions on your internal organs. These may be life-threatening.
Screening And Diagnostic Tests
If doctors suspect exposure to HIV infection, they do a screening test for HIV. Doctors also recommend that all adults and adolescents, particularly pregnant women, have a screening test regardless of what their risk appears to be. Anyone who is concerned about being infected with HIV can request to be tested. Such testing is confidential and often free of charge.
The current combination screening test tests for two things that suggest HIV infection:
Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system to help defend the body against a particular attack, such as that by HIV. Antigens are foreign substances that can trigger an immune response.
The body takes several weeks to produce enough antibodies to be detected by the test, so results of the antibody test are negative during the first few weeks after the virus enters the body . However, results of the p24 antigen test can be positive as early as 2 weeks after the initial infection. The combination tests can be done quickly by a laboratory. Also, a version of these tests can be done in a doctor’s office or clinic . If results are positive, doctors do a test to distinguish HIV-1 from HIV-2 and a test to detect the amount of HIV RNA in the blood .
The newer combination screening test is quicker and less complex than older screening tests, which use enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect HIV antibodies and then confirm positive results using a separate, more accurate, specific test such as the Western blot test.
Also Check: Heal Bladder Infection Without Antibiotics
Can Hiv Be Prevented
To reduce the risk of getting HIV, people who are sexually active should:
- use a latex condom every time they have sex
- get tested for HIV and make sure all partners do too
- reduce their number of sexual partners
- get tested and treated for STDs having an STD increases the risk of getting infected with HIV. To find a testing site, visit the CDC’s National HIV and STD Testing Resources.
- consider taking a medicine every day if they are at very high risk of getting infected
For everyone:
- Do not inject drugs or share any kind of needle.
- Do not share razors or other personal objects that may touch blood.
- Do not touch anyone else’s blood from a cut or sore.
What Impact Does Hiv Have On The Body

HIV weakens the bodys natural defences, and over time it damages the immune system.
The impact of HIV on the body depends on a persons general health, such as:
-
how quickly they are diagnosed
-
how quickly they start antiretroviral treatment
-
how consistently they take their treatment
The HIV lifecycle is made up of four stages. Each of these involve a number of processes which happen in and around a human CD4 cell.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Sick From A Tooth Infection
Contributors To Cd4+ T
CD4+ T-cells are known to be the central facilitators for both cellular and humoral immune responses against exogenous antigens and are kept constant in the human body by homeostatic mechanisms .HIV binds to the CD4 molecule on the surface of helper T-cells and replicates within them. This results in destruction of CD4+ T-cells and leads to a steady decline in this population of T-cells. The definition of progressive and slow loss of CD4+ T-cells is not clear. In order to understand the correlation between CD4+ T-cell depletion and immunopathogenesis, and its relationship with disease progression, a number of dynamic models have been put forward. Two of the most acknowledged mechanisms are discussed in detail in this review. These include direct virus attack leading to cytolytic effect and chronic immune activation resulting in apoptosis.
Hiv Takes Control Of T Cells
Once inside the cell, the capsid dissolves, liberating the viral RNA and the reverse transcriptase. Now, in order to infect the cell, the viral RNA needs to travel into the T cells nucleus . However, for that to happen, an important transformation needs to take place.
Normally, the T cells nucleus communicates with the rest of the cell by transforming DNA into RNA and sending it out of the nucleus. The genetic materials passport to leave the nucleus is to be transformed into single-stranded RNA. In the same fashion, the passport to enter the nucleus is to be transformed into double-stranded DNA.
Viral RNA needs to become DNA in order to start the replication process. Reverse transcriptase allows the RNA to borrow material from the cell and to write backwards a chain of viral DNA.
HIV is considered a retrovirus because of its capacity to transform RNA into DNA, reversing the natural process that takes place in cells. This is accomplished by the reverse transcriptase. Retroviruses are a special family of viruses to which only a few known viruses belong .
Read Also: Mesh Infection And Hernia Repair A Review
Pathophysiology Of Cd4+ T
- Division of HIV/AIDS, Department of Clinical Research, National Institute for Research in Tuberculosis , Chennai, India
The hall mark of human immunodeficiency virus infection is a gradual loss of CD4+ T-cells and imbalance in CD4+ T-cell homeostasis, with progressive impairment of immunity that leads ultimately to death. HIV infection in humans is caused by two related yet distinct viruses: HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV-2 is typically less virulent than HIV-1 and permits the host to mount a more effective and sustained T-cell immunity. Although both infections manifest the same clinical spectrum, the much lower rate of CD4+ T-cell decline and slower progression of disease in HIV-2 infected individuals have grabbed the attention of several researchers. Here, we review the most recent findings on the differential rate of decline of CD4+ T-cell in HIV-1 and HIV-2 infections and provide plausible reasons for the observed differences between the two groups.
If I Have Hiv How Can I Keep From Spreading It To Others
The best ways to keep from spreading HIV to others are many of the same ways you use to protect yourself:
- Let sexual partners and anyone you inject drugs with know that you have HIV.
- Follow your treatment plan and dont miss medications. If you have an undetectable viral load, you greatly reduce the risk of transmitting HIV through sex.
- Talk to your sexual partner about taking PrEP.
- Dont share needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
- Limit the number of sexual partners you have.
- If youre pregnant and have HIV, following your treatment plan, including ART medications, can reduce your risk of transmitting the virus to your child.
You May Like: Get Antibiotics For Sinus Infection Online
What Is The Connection Between The Hiv Life Cycle And Hiv Medicines
Antiretroviral therapy is the use of a combination of HIV medicines to treat HIV infection. People on ART take a combination of HIV medicines every day. HIV medicines protect the immune system by blocking HIV at different stages of the HIV life cycle. HIV medicines are grouped into different drug classes according to how they fight HIV. Each class of drugs is designed to target a specific step in the HIV life cycle.
Because an HIV treatment regimen includes HIV medicines from at least two different HIV drug classes, ART is very effective at preventing HIV from multiplying. Having less HIV in the body protects the immune system and prevents HIV from advancing to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome .
ART cannot cure HIV, but HIV medicines help people with HIV live longer, healthier lives. HIV medicines also reduce the risk of HIV transmission .
Cars Blaring Boss Nagging Take A Deep Breath Now Another
A subpopulation of the immune cells targeted by HIV may play an important role in controlling viral loads after initial infection, potentially helping to determine how quickly infection will progress. In the Feb. 29 issue of Science Translational Medicine, a team of researchers from the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard describe finding a population of HIV-specific CD4 T cells cells traditionally thought to direct and support activities of other immune cells that can directly kill HIV-infected cells.
We observed the emergence of CD4 T cells able to kill HIV-infected cells in those patients who are able to control viral replication soon after acute infection, says Harvard Medical School Assistant Professor of Medicine Hendrik Streeck, a Ragon Institute faculty member and senior author of the report. These cells appear very early in HIV infection, and we believe they may set the stage for the course of the disease.
The primary role of CD4 T cells is to assist other cells of the immune system and their importance is illustrated by how completely the immune response collapses after the cells, the main cellular targets of HIV, are destroyed. Ironically, CD4 cells that are specifically targeted against HIV are preferentially infected and depleted by the virus.
The lead author of the Science Translational Medicine report is Damien Soghoian of the Ragon Institute.
Also Check: Best Treatment For A Urinary Tract Infection