Overview Of Kidney And Bladder Infections
The primary function of the kidneys within the human body is to clean the blood of water and waste products by turning them into urine. The urine is kept in the bladder, from where it is transferred to the urinary tract and urethra, and then transported out of the body.
Kidneys can be affected by a number of different problems, including a bacterial infection called pyelonephritis. In most cases the bacteria only colonize one of the two kidneys, either acutely or chronically.
An acute kidney infection is more commonly observed, and its symptoms are similar to many other disorders, so the diagnosis may take a little time.
One of the most prominent signs of a bacterial kidney infection is a very high body temperature of 38°C or over. Shivers usually accompany such fever.
Also, infected kidneys tend to hurt and the individual is likely to feel strong pain in the lower back, as well as possibly their sides and abdomen. The combination of severe pain and high fever usually results in feeling sick to the stomach and vomiting. The pain associated with kidney infections is strong and will often stop you from performing daily tasks.
Kidney infections produced by bacteria are often preceded by inflammation of the urinary tract and bladder infection. The signs of problems in those areas are relatively easy to spot, with the most prominent symptom of a urinary tract infection being a burning sensation on bladder voiding .
Home Remedies And Treatments For Kidney Infections
Some people prefer to treat medical conditions with home remedies or complementary remedies.
Because of how serious kidney infections are, its important that you dont rely on home remedies. Instead, take the prescription antibiotics a doctor gives you and use home remedies to help ease symptoms or pain.
You can also use home remedies to avoid UTIs and improve kidney function.
Recommended Reading: Can Kidney Stones Look Like Sand
Upec Systemic Colonization Persists Longer Than A Commensal E Coli Strain
To determine whether systemic dissemination by UPEC is a pathogen-specific process or simply represents the natural course of bacterial clearance from the bloodstream, nonpathogenic E. coli K-12 strain MG1655 was tested in the bacteremia model. At 24 hpi, the spleen and liver contained significantly lower levels of MG1655 than CFT073 . Mice infected with MG1655 also had lower levels of cecal colonization, although this difference was not significant at 24 hpi. To examine the persistence dynamics of these strains, cecal colonization was examined at up to 7 dpi. Because pGEN-lux is only stably maintained in CFT073 for 48 h in the absence of antibiotic selection , isogenic lacZ mutants of CFT073 and MG1655 were used to allow differentiation from the cecal microbiota. Thus, while it is important to note that this represents a method of bacterial quantification different from that shown previously that does not depend on the presence of pGEN-lux, cecal colonization by CFT073 did not differ from that by CFT073 lacZ at 24 hpi . While CFT073 colonization persisted in the cecum at 72 hpi at nearly 104 CFU/g, E. coli MG1655 was cleared by this time point from 9 of 10 mice . By 7 dpi, CFT073 had been cleared from the ceca of 7 of 10 mice. These data indicate that nonpathogenic E. coli is not capable of persisting systemically during bacteremia in this model and suggest that UPEC dissemination and persistence represent pathogenic mechanisms.
Read Also: Can Dehydration Cause Bladder Infection
Kidney Infection Caused By E Coli
The kidneys are key organs that filter the blood and eliminate waste products, while keeping essential minerals and substances to distribute to the rest of the body. All the waste from the blood leaves the body via urine. Both kidneys or one kidney may get infected with a variety of harmful bacteria, causing pyelonephritis the medical name for a bacterial kidney infection). Very often, E. coli is responsible.
- One is acute pyelonephritis clinically identified by flank pain and fever and generally perceived as being a kidney infection.
- The second is cystitis, characterized by dysuria and increased frequency and urgency of urination, which is generally perceived to be a bladder infection and accounts for 95% of all visits to physicians for UTIs.
Tissue Perfusion Does Not Eliminate Bacterial Infiltration
One possible explanation for widespread dissemination and organ colonization is that UPEC remains in the bloodstream after inoculation and that the dissemination observed was simply due to bacteria present in organ-associated blood vessels and did not represent colonization of specific tissues. To test this hypothesis, intravenously inoculated mice were perfused immediately after euthanasia at 24 hpi with 40 ml sterile saline before organ excision and processing. Gross organ blanching was used as an indication that blood was depleted from the body and perfusion was complete , although complete blanching of the spleen was not observed. Bacterial levels in the liver, cecum, kidneys, and brain were not significantly different between nonperfused and perfused animals . In contrast, perfusion significantly reduced bacterial levels in the lungs , with undetectable levels in five of six perfused mice, indicating that nearly all of the bacteria recovered from the lungs were due to circulating UPEC. Perfused mice also had lower levels of bacteria in their spleens , although the median bacterial load was still greater than 104 CFU/g, indicating that both circulating and tissue-associated bacteria contributed to splenic infiltration. Overall, these data show that most of the bacterial infiltration observed was indeed due to tissue colonization and not merely the presence of circulating blood.
Also Check: Can Bladder Infections Heal On Their Own
Treatment Of Kidney Infection
Most kidney infections need prompt treatment with antibiotics to stop the infection damaging the kidneys or spreading to the bloodstream.
You may also need painkillers.
If you’re especially vulnerable to the effects of an infection , you may be admitted to hospital and treated with antibiotics through a drip.
Most people who are diagnosed and treated promptly with antibiotics feel completely better after about 2 weeks.
People who are older or have underlying conditions may take longer to recover.
Treatment Of Kidney Infections
One of the most common kinds of treatment that anyone who has ever had a urinary tract or kidney infection knows about is to drink as much fluids as possible, especially water. If the patient has high fever over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen, paracetamol, and Aspirin are often helpful. In order to get rid of the bacteria the health care provider will prescribe antibiotics for a few weeks. The full course of treatment has to be taken to make sure all bacteria are gone even when the symptoms have disappeared.
Recommended Reading: Will A Bladder Infection Go Away On Its Own
What To Do If You Think You Have A Kidney Infection
It is extremely important to seek medical attention as soon as possible when you know or strongly suspect that you have a kidney infection. Not only are the symptoms unlikely to get better on their own, they could very easily become much worse. To treat a serious bacterial infection, which a kidney infection definitely is, you absolutely require antibiotic treatment. Only a doctor can prescribe that.
Alongside obligatory antibiotics, do everything you can to prevent dehydration. This is even more important for pregnant women and elderly patients. Fever, discomfort and pain may be resolved using some OTC pain killer drugs, such as Aspirin, paracetamol or ibuprofen. In most cases people feel better after day or two, after starting antibiotics. However, it is crucial to complete your entire course as your doctor has prescribed it.
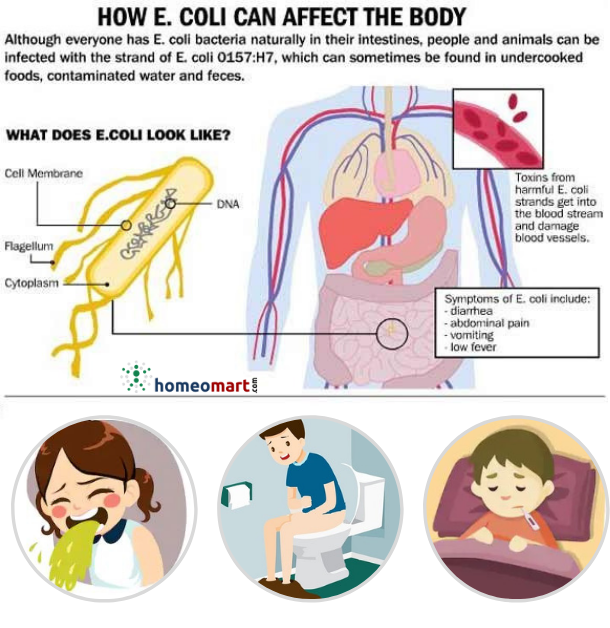
How Does E Coli Make You Sick
The most familiar strains of E. coli that make you sick do so by producing a toxin called Shiga. This toxin damages the lining of your small intestine and causes your diarrhea. These strains of E. coli are also called Shiga toxin-producing E. coli . The STEC that is most well-known in North America and most often referred to is E. coli O157:H7, or just E. coli O157
There are other types of STEC that are called non-O157 STEC. These strains cause similar illness to the O157 strain but are less likely to lead to serious complications.
Read Also: Can A Chipped Tooth Get Infected
What Tests Should I Request To Confirm My Clinical Dx In Addition What Follow
Gross hematuria occurs infrequently with pyelonephritis being more common with lower urinary tract infections, such as hemorrhagic cystitis.
Pyuria, which is defined as more than 5-10 white blood cells per high-power field, is present in almost all patients with pyelonephritis. Usually, there are more than 20 WBCs/high power field in acute cases, with lower numbers in subacute cases.
The dipstick leukocyte esterase test is useful in screening for pyuria and is aided by the nitrite production test . Combined, they have a sensitivity of 79% and specificity of 81%.
The urine microscopic examination may show hematuria, but hematuria is nonspecific. White cell casts are suggestive of pyelonephritis.
Proteinuria is expected up to 2 grams/day. If proteinuria exceeds 3 grams/day, one should suspect glomerulonephritis. The presence of bacteria on microscopic examination is suggestive but may be present in lower urinary tract infections.
Urine culture is indicated in any patient with pyelonephritis, especially to screen for antibiotic resistance.
Blood cultures are indicated in any patient who had been or is in the process of being admitted. Approximately 12-20% of blood cultures are positive in acute glomerulonephritis.
Table 1
Intestinal E Coli Infections
Escherichia coli are bacteria that are all around you. You can find E. coli everywhere in your environment, including on your skin and in your intestines. Most strains of E. coli are harmless but some strains can make you very sick and can cause sepsis.
Sometimes incorrectly called blood poisoning, sepsis is the bodys life-threatening response to infection. Like strokes or heart attacks, sepsis is a medical emergency that requires rapid diagnosis and treatment.
Sepsis and septic shock can result from an infection anywhere in the body, such as pneumonia, influenza, or urinary tract infections. Worldwide, one-third of people who develop sepsis die. Many who do survive are left with life-changing effects, such as post-traumatic stress disorder , chronic pain and fatigue, organ dysfunction , and/or amputations.
Recommended Reading: Can Ear Infections Go Away
Things You Can Do Yourself
To help ease pain:
- takeparacetamolup to 4 times a day to reduce pain and a high temperature for people with a UTI, paracetamol is usually recommended over NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or aspirin
- you can give childrenliquid paracetamol
- rest and drink enough fluids so you pass pale urine regularly during the day, especially during hot weather
Its important to follow the instructions on the packet so you know how much paracetamol you or your child can take, and how often.
It may also help to avoid having sex until you feel better.
You cannot pass a UTI on to your partner, but sex may be uncomfortable.
Taking cystitis sachets or cranberry products has not been shown to help ease symptoms of UTIs.
Editorial Sources And Fact
References
You May Like: How Long Should I Take Antibiotics For Tooth Infection
What Are The Causes Of Kidney Infections
Normally, bacteria are flushed out by the flow of urine. However, several problems can increase the risk of a kidney infection. These problems can include:
- Structural abnormalities blocking urine flow.
- An enlarged prostate gland compressing the urethra.
- Backflow of urine from the bladder to the kidneys.
- If your immune system is affected .
- Pregnancy, during which time the enlarging uterus can squeeze the ureters and reduce the flow of urine, allowing the bacteria to migrate to the kidneys.
- Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus.
What Is E Coli
Escherichia coli is a bacteria that normally lives in the intestines of both healthy people and animals. In most cases, this bacteria is harmless. It helps digest the food you eat. However, certain strains of E. coli can cause symptoms including diarrhea, stomach pain and cramps and low-grade fever. Some E. coli infections can be dangerous.
Also Check: Whats The Best Antibiotic For Ear Infection
What Are The Symptoms Of Kidney Infections
Symptoms of kidney infections vary by age. Symptoms may include
- cloudy, dark, bloody, or foul-smelling urine
- frequent, painful urination
A child younger than 2 years old with a kidney infection may only have a high fever.
An adult older than age 65 with a kidney infection may have none of the typical symptoms. An older person may only have problems with thinking, such as
Symptoms Of Kidney Infection
Symptoms of pyelonephritis often begin suddenly with chills, fever, pain in the lower part of the back on either side, nausea, and vomiting.
, including frequent, painful urination. One or both kidneys may be enlarged and painful, and doctors may find tenderness in the small of the back on the affected side. Sometimes the muscles of the abdomen are tightly contracted. Irritation from the infection or the passing of a kidney stone can cause spasms of the ureters. If the ureters go into spasms, people may experience episodes of intense pain . In children, symptoms of a kidney infection Urinary Tract Infection in Children A urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection of the urinary bladder , the kidneys , or both. Urinary tract infections are caused by bacteria. Infants and younger… read more often are slight and more difficult to recognize. In older people, pyelonephritis may not cause any symptoms that seem to indicate a problem in the urinary tract. Instead, older people may have a decrease in mental function , fever, or an infection of the bloodstream .
In chronic pyelonephritis, the pain may be vague, and fever may come and go or not occur at all.
Also Check: What Otc Medicine Is Best For Yeast Infections
What Steps Are Involved In Getting A Stool Sample To My Healthcare Provider
Some general instructions for collecting a stool sample at home include:
- First, wash your hands with soap and water.
- If its possible to urinate before setting up for the stool collection, do so. You dont want to get urine in your stool sample if you can help it.
- To collect diarrhea, tape a plastic bag to the toilet seat. You only need to collect a small amount a couple tablespoons.
- Place the plastic bag into a clean plastic container and seal with lid.
- Wash your hands with soap and water.
- Write your name and date on the container, place within another bag, wash your hands again and deliver to your healthcare provider on the same day you collect your sample. If you cant deliver your sample immediately, you can store it in your refrigerator for up to 24 hours.
- Do not collect the sample from the toilet bowl. Do not mix in toilet paper, soap or water.
Pyelonephritis Diagnosis And Treatment
There are a slew of tests which a doctor can perform in order to properly diagnose a kidney infection including:
- X-ray imaging of the bladder and urethra when full and when urinating
- Digital rectal examination
- Dimercaptosuccinic acid scintigraphy
Kidney infections are commonly treated with antibiotics over the course of several weeks. Antibiotic treatment may first target common forms of bacteria but once urine culture comes back from the lab your doctor can prescribe more specific antibiotics based on the bacteria which is causing the infection.
If patients are severely ill intravenous fluids and hospital stays may be recommended along with antibiotic treatment in order to speed up recovery.
Emily Lunardo studied medical sociology at York University with a strong focus on the social determinants of health and mental illness. She is a registered Zumba instructor, as well as a Canfit Pro trainer, who teaches fitness classes on a weekly basis. Emily practices healthy habits in her own life as well as helps others with their own personal health goals. Emily joined Bel Marra Health as a health writer in 2013.
Five-Star Guarantee of Satisfaction
Science-Backed IngredientsQuality GuaranteeSafe Manufacturing PracticesBel Marra Health AssuranceSatisfaction Guaranee
You May Like: How To Get Antibiotics For Sinus Infection
What Causes A Kidney Infection
Kidney infections are caused by bacteria or viruses.
Scientists believe that most kidney infections start as a bladder infection that moves upstream to infect one or both of your kidneys. Most often, the infection is caused by bacteria that normally live in your bowel. The urinary tract has several ways to prevent infection from moving up the urinary tract. For example, urination most often flushes out bacteria before it reaches the bladder. Sometimes your body cant fight the bacteria and the bacteria cause a UTI. If you dont get medical treatment to stop the infection, the bacteria may infect your kidneys.
In some cases, your blood can carry bacteria or viruses from another part of your body to your kidneys.
Other Ways To Prevent Recurring Utis
If you have more than 3 UTIs in 1 year, or 2 UTIs in 6 months, there are other things that may help prevent UTIs.
There is some evidence that women under 65 years old who keep getting UTIs may find it helpful to take:
- a supplement called D-mannose this is not recommended for pregnant women
- cranberry products, such as juice or tablets
Speak to your doctor before taking any of these during pregnancy.
Be aware that D-mannose and cranberry products can contain a lot of sugar.
Page last reviewed: 18 November 2020 Next review due: 18 November 2023
You May Like: Best Way To Get Rid Of Yeast Infection Fast
Also Check: How To Cure A Bacterial Sinus Infection