Seek Medical Attention For Utis
It is important to seek medical attention if you think you may have a UTI particularly if you think you may have a bladder or kidney infection, both of which are very serious conditions. Early treatment of urinary infection can help to prevent infection spreading to the bladder or kidneys.
Your doctor will test your urine to check which micro-organism is present. Urinary tract infections usually respond quickly and well to antibiotics.
Uti Tests And Diagnosis
If you suspect that you have a urinary tract infection, go to the doctor. You’ll give a urine sample to test for UTI-causing bacteria.
ishonestNo.203 – Prevent Elasticity Damage
If you get frequent UTIs and your doctor suspects a problem in your urinary tract, they might take a closer look with an ultrasound, a CT scan, or an MRI scan. They might also use a long, flexible tube called a cystoscope to look inside your urethra and bladder.
A Pharmacist Can Help With Utis
You can ask a pharmacist about treatments for a UTI. A pharmacist can:
- offer advice on things that can help you get better
- suggest the best painkiller to take
- tell you if you need to see a GP about your symptoms
Some pharmacies offer a UTI management service and can prescribe antibiotics if they’re needed.
Also Check: Can Hiv Cause Ear Infection
Do I Really Need To Take Antibiotics For A Uti
In most cases, it makes sense to start antibiotics if you know you have a bacterial UTI since this is the only way to treat it.
While it is possible for a UTI to go away on its own, this doesnt always happen. Plus, youll still have to deal with uncomfortable UTI symptoms like pain during urination while waiting to see if the UTI will go away. And if it doesnt, the infection can travel up your urinary tract and cause a more serious infection in your kidneys called pyelonephritis. If youre pregnant, have underlying health conditions, or are older than 65 years old, you should not try to treat a UTI without antibiotics.
What Happens If An Antibiotic Doesn’t Work For A Urinary Tract Infection
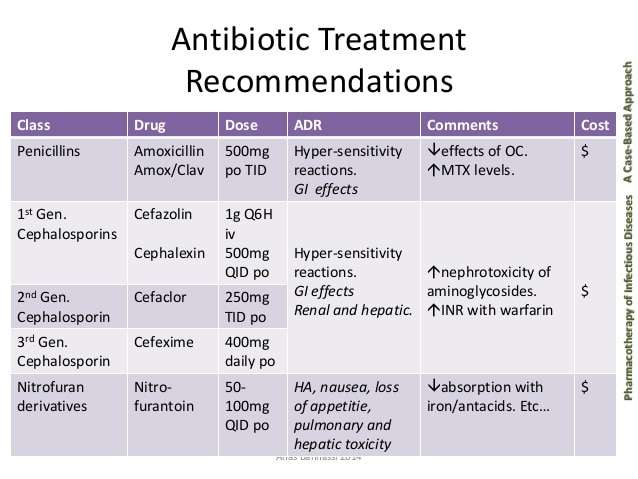
Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for urinary tract infections , most of which are caused by a bacteria called Escherichia Coli . Infections of the lower urinary tract, which includes bladder infections , are the most common type of UTI and are usually treated with a 3-5 day course of antibiotics. Sometimes, however, the antibiotic prescribed to treat a bladder infection doesnt work.
If you suspect your antibiotic isnt working you should promptly contact your healthcare provider. Left untreated a UTI may become more serious and in rare cases cause permanent or life-threatening complications.
Also Check: Dr On Demand Tooth Infection
Are There Any Over
Over-the-counter antibiotics for a UTI are not available. You should see your doctor to have your symptoms evaluated.
Your provider may recommend an OTC product called Uristat to numb your bladder and urethra to ease the burning pain during urination. Uristat can be bought without a prescription at the pharmacy. A similar phenazopyridine product called Pyridium is also available.
Take phenazopyridine for only 48 hours, and be aware it may cause your urine to turn a brown, orange or red color which may stain fabrics or contact lenses. It may be best to not wear contact lenses while being treated with phenazopyridine.
Phenazopyridine is not an antibiotic and will not cure a UTI.
See also: Ratings of Urinary Anti-Infectives
Why Do Antibiotics Sometimes Not Work For A Urinary Tract Infection
If an antibiotic doesnt work it is likely that the bacteria causing the UTI is not susceptible or is resistant to the antibiotic you are taking.
Antibiotic resistance occurs when the bacteria that is causing the infection is no longer affected by a particular antibiotic and is able to continue to grow and multiply. Inappropriate and unnecessary antibiotic use contributes to the increasing problem of antibiotic resistance.
If you felt better for a little while and then came down with the symptoms of a UTI again, it is also possible that you have a new or recurrent UTI.
Another possibility if you continue to experience symptoms of a UTI despite antibiotic treatment, is that you have another type of infection that mimics that symptoms of a UTI and you need a different antibiotic or other treatment. Sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, for example, produce symptoms that mimic a UTI. Vaginal yeast infections can also cause burning when you pee.
Don’t Miss: Natural Antibiotics For Dental Infection
Can I Become Immune To The Antibiotics Used To Treat A Uti
Your body can actually get used to the antibiotics typically used to treat a urinary tract infection . This happens in people who have very frequent infections. With each UTI and use of antibiotics to treat it, the infection adapts and becomes harder to fight. This is called an antibiotic-resistant infection. Because of this, your healthcare provider may suggest alternative treatments if you have frequent UTIs. These could include:
- Waiting: Your provider may suggest that you watch your symptoms and wait. During this time, you may be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids in an effort to flush out your system.
- Intravenous treatment: In some very complicated cases, where the UTI is resistant to antibiotics or the infection has moved to your kidneys, you may need to be treated in the hospital. The medicine will be given to you directly in your vein . Once youre home, you will be prescribed antibiotics for a period of time to fully get rid of the infection.
Which Antibiotic Will Work Best
Your doctor will take a urine sample to confirm that you have a UTI. Then the lab will grow the germs in a dish for a couple of days to find out which type of bacteria you have. This is called a culture. Itâll tell your doctor what type of germs caused your infection. Theyâll likely prescribe one of the following antibiotics to treat it before the culture comes back:
Which medication and dose you get depends on whether your infection is complicated or uncomplicated.
âUncomplicatedâ means your urinary tract is normal. âComplicatedâ means you have a disease or problem with your urinary tract. You could have a narrowing of your ureters, which are the tubes that carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder, a narrowing in the urethra which transports urine from the bladder out of the body, or, you might have a blockage like a kidney stone or an enlarged prostate . It’s also possible you have a urinary fistula or a bladder diverticulum.
To treat a complicated infection, your doctor might prescribe a higher dose of antibiotics. If your UTI is severe or the infection is in your kidneys, you might need to be treated in a hospital or doctor’s office with high-dose antibiotics you get through an IV.
Your doctor will also consider these factors when choosing an antibiotic:
- Are you over age 65?
- Are you allergic to any antibiotics?
- Have you had any side effects from antibiotics in the past?
Also Check: What If A Yeast Infection Goes Untreated
Antibiotics For Urinary Tract Infections In Older People
Antibiotics are medicines that can kill bacteria. Health care providers often use antibiotics to treat urinary tract infections .
The main symptom of a UTI is a burning feeling when you urinate.
However, many older people get UTI treatment even though they do not have these symptoms. This can do more harm than good. Heres why:
Antibiotics usually dont help when there are no UTI symptoms.
Older people often have some bacteria in their urine. This does not mean they have a UTI. But health care providers may find the bacteria in a routine test and give antibiotics anyway.
The antibiotic does not help these patients.
- It does not prevent UTIs.
- It does not help bladder control.
- It does not help memory problems or balance.
Most older people should not be tested or treated for a UTI unless they have UTI symptoms. And if you do have a UTI and get treated, you usually dont need another test to find out if you are cured. You should also not be tested just in case there is a UTI.
You should only get tested or treated if UTI symptoms come back.
Antibiotics have side effects.
Antibiotics can have side effects, such as fever, rash, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache, tendon ruptures, and nerve damage.
Antibiotics can cause future problems.
Antibiotics can kill friendly germs in the body. This can lead to vaginal yeast infections. It can also lead to other infections, severe diarrhea, hospitalization, and even death.
When should older people take antibiotics for a UTI?
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
Patients with three or more infections per year should be offered either continuous low-dose antibiotic prophylaxis, patient-initiated, or postcoital prophylaxis if the onset of infection is linked to sexual intercourse . Before a prophylactic regimen is chosen, a urine culture should be performed to determine the susceptibility of the pathogen. The duration of continuous prophylactic therapy is usually 6 months to a year. Unfortunately, within 6 months of discontinuing antibiotic prophylaxis, 40% to 60% of women develop a urinary tract infection, and prophylaxis must be resumed. Patient-initiated therapy at the onset of symptoms has been shown to be effective in young, healthy nonpregnant women. Short-course regimens have been advocated for patient-initiated therapy in compliant women with frequently recurring and symptomatic urinary tract infections. The major advantages of short-course therapy over continuous therapy are convenience and the avoidance of antibiotic toxicity symptomatic infections are not prevented, however. For postcoital prophylaxis, nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, or fluoroquinolones taken within 2 hours after sexual intercourse have been shown to significantly reduce the incidence of recurrent cystitis.,
Also Check: Sinus Infection Tooth Pain Antibiotics
How To Feel Better
If your healthcare professional prescribes you antibiotics:
- Take antibiotics exactly as your healthcare professional tells you.
- Do not share your antibiotics with others.
- Do not save antibiotics for later. Talk to your healthcare professional about safely discarding leftover antibiotics.
Drink plenty of water or other fluids. Your healthcare professional might also recommend medicine to help lessen the pain or discomfort. Talk with your healthcare professional if you have any questions about your antibiotics.
How Often Are Utis Resistant

The majority of urinary tract infections are now resistant to one or more antibiotics. The drug ampicillin, once a common treatment, has been largely abandoned because most U.T.I.s are now resistant to it.
The most important question isnt whether an infection is resistant to any drug, but whether it is resistant to the drugs that are commonly used to treat your particular infection.
When experts in the field think about resistant U.T.I.s, they say that resistance depends on the bug and the drug. What that means is that they try to figure out which particular germs are resistant to specific medications.
Don’t Miss: Best Medication For Kidney Infection
How To Use Amoxicillin Oral
Take this medication by mouth with or without food as directed by your doctor, usually every 8 or 12 hours. The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment.
Drink plenty of fluids while using this medication unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
For the best effect, take this antibiotic at evenly spaced times. To help you remember, take this medication at the same time every day.
Continue to take this medication until the full prescribed amount is finished, even if symptoms disappear after a few days. Stopping the medication too early may allow bacteria to continue to grow, which may result in a return of the infection.
Tell your doctor if your condition persists or worsens.
The Number Of Urinary Tract Infections Caused By Drug Resistant Bacteria Is Increasing New Data Shows
23 October 2017
The ‘English Surveillance Programme for Antimicrobial Utilisation and Resistance report says more than one million UTI samples were analysed in NHS laboratories across England last year , and that resistance was a common observation.
One in three of the samples analysed were found to be resistant to an antibiotic called trimethoprim, compared to 29.1% in 2015.
Trimethoprim was once the first choice treatment for UTIs before Public Health England recommended switching to a different antibiotic called nitrofurantoin. Only 3% of the UTI samples showed resistance to nitrofurantoin, the report says.
Inappropriate use of antibiotics, such as taking them for viral conditions like flu, or for mild infections that may clear-up without treatment is known to fuel resistance.
NICE recently updated its guidance for managing UTIs in children. New recommendations focus on using urine dipstick tests to identify whether antibiotic treatment is needed.
Professor Gillian Leng, deputy chief executive at NICE said:Antibiotic resistance is one of the greatest dangers to our health, which is why we must all work together to fight it.
Making sure that we use these medicines properly, only when they are really needed, is vital. And our guidance is here to help healthcare professionals navigate these sometimes difficult decisions.
Don’t Miss: Types Of Antibiotics For Bladder Infection
What Causes A Uti
Urinary tract infections occur when bacteria enters through the urethra. The bacteria may take hold in theurethra or go into the bladder. If left unchecked, this bacteria could multiply and grow into a full-blowninfection. Women are more likely to develop urinary tract infections than men because they have shorterurethras.
Other Ways To Prevent Recurring Utis
If you have more than 3 UTIs in 1 year, or 2 UTIs in 6 months, there are other things that may help prevent UTIs.
There is some evidence that women under 65 years old who keep getting UTIs may find it helpful to take:
- a supplement called D-mannose this is not recommended for pregnant women
- cranberry products, such as juice or tablets
Speak to your doctor before taking any of these during pregnancy.
Be aware that D-mannose and cranberry products can contain a lot of sugar.
Page last reviewed: 18 November 2020 Next review due: 18 November 2023
Recommended Reading: Can Azo Help Yeast Infection
What Is The Urinary Tract
The urinary tract makes and stores urine, one of the body’s liquid waste products. The urinary tract includes the following parts:
- Kidneys: These small organs are located on back of your body, just above the hips. They are the filters of your body removing waste and water from your blood. This waste becomes urine.
- Ureters: The ureters are thin tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to your bladder.
- Bladder: A sac-like container, the bladder stores your urine before it leaves the body.
- Urethra: This tube carries the urine from your bladder to the outside of the body.
Treatment Strategies For Recurrent Utis
Recurrent urinary tract infections, defined as three or more UTIs within 12 months, or two or more occurrences within six months, is very common among women these but arent treated exactly the same as standalone UTIs. One of the reasons: Continued intermittent courses of antibiotics are associated with allergic reactions, organ toxicities, future infection with resistant organisms, and more.
Because of this, its strongly recommended that you receive both a urinalysis and urine culture from your healthcare provider prior to initiating treatment. Once the results are in, the American Urological Association suggests that healthcare professionals do the following:
- Use first-line treatments. Nitrofurantoin, TMP-SMX, and fosfomycin are the initial go-tos. However, specific drug recommendations should be dependent on the local antibiogram. An antibiogram is a periodic summary of antimicrobial susceptibilities that helps track drug resistance trends.
- Repeat testing. If UTI symptoms persist after antimicrobial therapy, clinicians should repeat the urinalysis, urine culture, and antibiotic susceptibility testing to help guide further management.
- Try vaginal estrogen. For peri- and post-menopausal women with recurrent UTIs, vaginal estrogen therapy is recommended to reduce risk of future UTIs.
RELATED: The Link Between UTIs and Sex: Causes and How to Prevent Them
You May Like: Can I Go To Urgent Care For Kidney Infection
Treatment From A Gp For Utis That Keep Coming Back
If your UTI comes back after treatment, you may have a urine test and be prescribed different antibiotics.
Your doctor or nurse will also offer advice on how to prevent UTIs.
If you keep getting UTIs and regularly need treatment, a GP may give you a repeat prescription for antibiotics.
If you have been through the menopause, you may be offered a vaginal cream containing oestrogen.
Can A Uti Go Away On Its Own
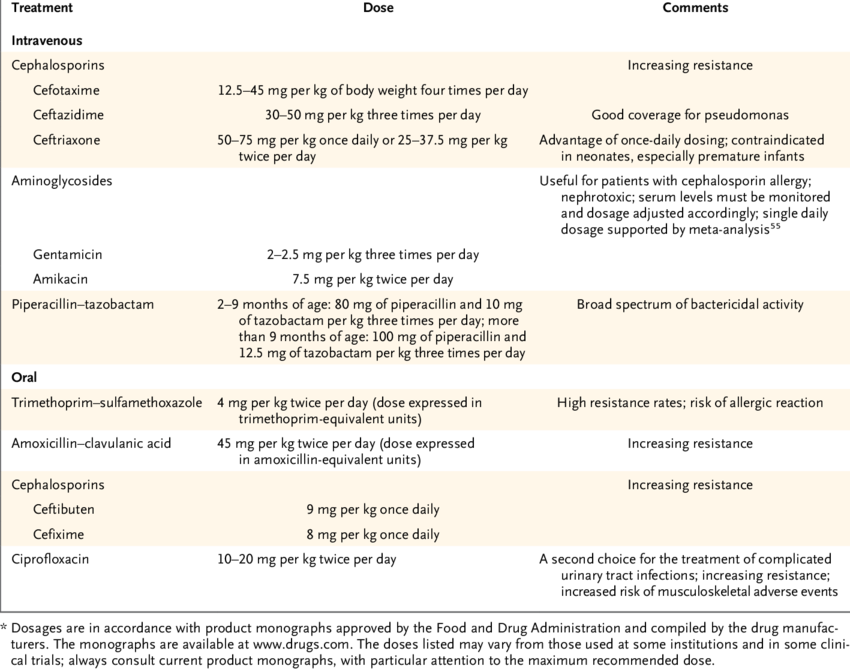
While most patients with a UTI will be prescribed antibiotics, the truth is, uncomplicated urinary tract infections are often self-limiting, meaning they can potentially run their course sans antibiotic treatment, noted a 2018 report in PLoS Medicine.
In fact, that same report found that more than one-half of the women studied experienced a UTI resolution without the use antibiotics. However, since kidney infections occurred in 7 out of 181 women using ibuprofen, the researchers concluded that, at this time, they cannot recommend ibuprofen alone as initial treatment to women with uncomplicated UTIs.
A better idea, for now: Simply wait until a positive urine culture comes back before treating with antibiotics.
Recommended Reading: Kidney And Bladder Infection At The Same Time
What Oral Antibiotics Are Used To Treat An Uncomplicated Uti In Women
The following oral antibiotics are commonly used to treat most uncomplicated UTI infections :
Your doctor will choose your antibiotic based on your history, type of UTI, local resistance patterns, and cost considerations. First-line options are usually selected from nitrofurantoin, fosfomycin and sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim. Amoxicillin/clavulanate and certain cephalosporins, for example cefpodoxime, cefdinir, or cefaclor may be appropriate options when first-line options cannot be used.
Length of treatment for cystitis can range from a single, one-time dose, to a course of medication over 5 to 7 days. Kidney infections may require injectable treatment, hospitalization, as well as a longer course of antibiotic, depending upon severity of the infection.
Sometimes a UTI can be self-limiting in women, meaning that the body can fight the infection without antibiotics however, most uncomplicated UTI cases can be treated quickly with a short course of oral antibiotics. Never use an antibiotic that has been prescribed for someone else.
In men with symptoms that do not suggest a complicated UTI, treatment can be the same as women. In men with complicated UTIs and/or symptoms of prostatitis are not present, men can be treated for 7 days with a fluoroquinolone . Tailor therapy once urine cultures are available.