Cdc Study Highlights The Differences In Perceived And Actual Risk
Needlestick injuriesas well as any percutaneous injury that can expose a person to tainted blood or body fluidshave long been a concern to both healthcare workers and the public at large.
Many of the fears have been fueled by media reports which either overstate the risk of acquiring HIV through needlestick injuries or spotlight cases in which victims are reported to be “living in fear” after having received such exposure .
While the perception of risk may be high in cases of needlestick injuries, recent analyses from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggests that the actual risk may be far lowerso low, in fact, that it can now be considered rare.
Against All Odds: What Are Your Chances Of Getting Hiv In These Scenarios
Playing the HIV numbers game is lessand morerisky than you think.
EDITORS NOTE: Although the underlying ideas and messages in this article remain relevant, much HIV prevention research has been published since 2014, notably about there being no risk of transmitting the virus if you are HIV positive and undetectable , as well as the effectiveness of pre-exposure prophylaxis . Go to #Prevention, #PrEP and #Undetectable for the latest related updates.
Liz Defrain
Theres not a lot of certainty in these numbers. But they can be a good tool for understanding risk.
During sex, our risk perception is replaced by love, lust, trust and intimacy.
Liz Defrain
Read More About:
Who Is At Risk For Hiv Infection
Anyone can get HIV, but certain groups have a higher risk of getting it:
- People who have another sexually transmitted disease . Having an STD can increase your risk of getting or spreading HIV.
- People who inject drugs with shared needles.
- Gay and bisexual men.
- Black/African Americans and Hispanic/Latino Americans. They make up a higher proportion of new HIV diagnoses and people with HIV, compared to other races and ethnicities.
- People who engage in risky sexual behaviors, such as not using condoms.
Factors such as stigma, discrimination, income, education, and geographic region can also affect people’s risk for HIV.
You May Like: Gynecologist Recommended Yeast Infection Treatment
Multiple Vulnerabilities Increase Risk In Men And Women
Vaginal sex between partners is one of the most common ways a person can acquire HIV. Both women and men can be put at risk when they have vaginal sex without using a condom.
There are a number of risk factors shared by both partners. There also are reasons for why men may be at risk, and other reasons for why women may be far more likely to become infected with HIV.
This article discusses why vaginal sex presents an HIV risk for both men and women. It explains why anatomical differences, cultural norms, and even how well HIV treatment works can affect that risk.
Nikom1234 / Getty Images
What Are The Chances Of Getting Hiv

HIV continues to be a disease that strikes fear in people. Despite the incredible advances in treatment and prevention, there is still a lot of misinformation, fear, and stigma out there. Understanding the chances of getting HIV through different activities and situations is essential to make informed decisions and understand the risk. You may be surprised.
Also Check: How Do You Get Malware Infections
Does Hiv Affect Women
Yes. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , in 2018, 19% of the new HIV diagnoses in the United States and dependent areas were among women. In addition, 57% of women with HIV were Black/African American.
The most common way that women get HIV is through sex with a male partner who has HIV without using a condom. Most women who have HIV know that they are HIV positive, but some women are not getting the HIV care and treatment they need.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hiv/aids
The first signs of HIV infection may be flu-like symptoms:
- Swollen lymph nodes
These symptoms may come and go within two to four weeks. This stage is called acute HIV infection.
If the infection is not treated, it becomes chronic HIV infection. Often, there are no symptoms during this stage. If it is not treated, eventually the virus will weaken your body’s immune system. Then the infection will progress to AIDS. This is the late stage of HIV infection. With AIDS, your immune system is badly damaged. You can get more and more severe infections. These are known as opportunistic infections .
Some people may not feel sick during the earlier stages of HIV infection. So the only way to know for sure whether you have HIV is to get tested.
Read Also: Will Bladder Infections Go Away On Their Own
Can I Become Infected With Hiv If I Inject Drugs And Share The Needles With Someone Else Without Sterilizing The Needles
We strongly recommend that you use new equipment every time you inject. You can get new equipment from Counterpoint Needle & Syringe Program at Regional HIV/AIDS Connection.
There is a possibility of becoming infected with HIV if you share injecting equipment with someone who has the virus. If HIV infected blood remains inside the needle or in the syringe and someone else then uses it to inject themselves, that blood can be flushed into the bloodstream. Sharing needles, syringes, spoons, filters or water can pass on the virus. Disinfecting equipment between uses can reduce the likelihood of transmission, but does not eliminate it.
How Hard Is It To Contract Hiv For Drug Users
After sex without a condom, sharing needles is the second most common way of getting HIV in many places. People who inject drugs may use a needle or syringe. On average, the risk of HIV transmission from sharing a needle once with an HIV positive person is 0.67%. However, there are factors that can make the actual risk higher, as above. There are several reasons that many drug users share needles. The criminalization of drug use and marginalization of users is one factor. Many places have needle and syringe programs to make clean needles available. However, they are not always accessible.
Recommended Reading: Reduce Swelling From Tooth Infection
How Is Hiv Transmitted Through Needles
HIV isnt transmitted only through sexual contact. Sharing needles also puts a person at higher risk of contracting HIV.
When a needle is injected into a persons body, it breaks the skin barrier. If the needle has already been injected into another person, it can carry traces of their blood, along with any infections they have. The contaminated needle can introduce these infections into the second persons body.
Researchers dont know if having an undetectable viral load reduces the risk of HIV transmission through shared needles, but its reasonable to assume it may provide some risk reduction.
HIV can affect anyone. Whatever their age, gender, sexuality, ethnicity, or race, everyone should take steps to protect themselves. But due to socioeconomic factors, some demographic groups have higher HIV transmission rates and generally are more affected by HIV.
According to the CDC , the general demographic traits most affected by HIV are:
Transgender women are also highly impacted by HIV transmissions as a population, reports the CDC .
These groups are disproportionately affected by HIV, but they arent inherently at greater risk of contracting HIV. An individuals personal risk depends on their behaviors, not on their age, gender, sexuality, ethnicity, race, or any other demographic factor.
Can You Get Hiv/aids From Someones Blood Touching Your Open Sore
HIV transmissions as a result of one persons blood entering another persons open sore or wound are theoretically possible, but in practice hardly ever happen. Only a handful of cases have ever been documented.
If a person is living with HIV and they do not have an undetectable viral load, and their blood directly enters the bloodstream of another person, HIV may be passed on. For example, this is how HIV is usually transmitted when people share syringes or needles used to inject drugs.
However, HIV transmission following limited contactfor example, blood touching an open soreis much less likely.
If you are concerned about an incident in which you had contact with another persons blood, its worth noting a few points:
- If the blood came into contact with undamaged, unbroken skin, there is no HIV risk whatsoever.
- HIV is not transmitted through surface scratches, such as paper cuts.
- A cut or wound that is in the process of healing and scabbing over is unlikely to allow entry of the other persons blood.
- HIV does not survive long outside the body, so the risk from blood left behind on objects is minimal.
- The handful of documented cases of HIV transmission involving fights or accidents have involved serious injuries and profuse bleeding.
Recommended Reading: Yeast Infection Treatment While Breastfeeding
Also Check: Does Boric Acid Pills Cure Yeast Infections
How Does Hiv Work
The full scientific name for HIV is human immunodeficiency virus. Its an infection that attacks the immune system, and it operates like this:
- The virus itself is shaped like a bowling ball covered in tiny spikes
- After HIV enters the bloodstream, it uses those tiny spikes to latch on to white blood cells , the bodys first line of defense against infections
- As soon as HIV gets inside white blood cells, it uses the cells own machinery to create copies of itself, creating effective camouflage that tricks the immune system into leaving it alone
- As HIV creates even more copies of itself, it hijacks a persons immune system
- A weakened immune system means that people living with untreated HIV may start to get all sorts of infections that would never normally make them sickEventually, without proper treatment, HIV leads to AIDS and becomes life-threatening
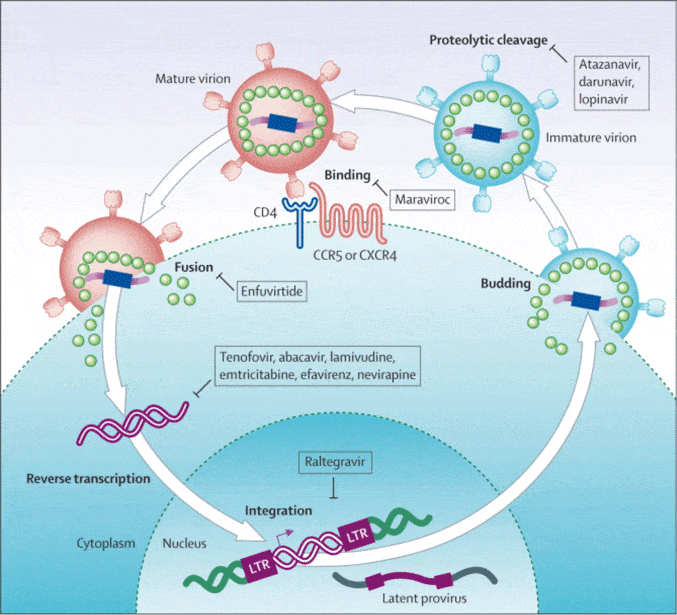
Todays anti-HIV medicines have been designed to address each stage of the infection process.
Some of these medications, which are also called antiretrovirals, stop HIVs spikes from latching on to CD4 cells. Others use different methods to stop HIV from replicating.
These drugs cant completely eradicate the virus from a persons body, but they do successfully stifle its ability to make copies of itself.
Can I Get Pregnant If I Have Hiv
Some people think that HIV hurts your chances of getting pregnant, but this isnt true. If you have HIV and want to become pregnant, talk to your healthcare provider. Together you can make a plan before you try to get pregnant to keep you, your partner and any future children healthy.
HIV can spread to your partner during unprotected sex and to your baby during pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding. Taking ART medications can greatly reduce your risk of transmitting HIV to your baby, especially if you have an undetectable viral load. Your provider may recommend that you dont breastfeed your baby and use formula instead.
Also Check: Can You Do Root Canal On Infected Tooth
Ok But What About My Specific Hiv Risk Question
Over the years, we’ve receivedand our experts have answeredliterally thousands of questions from people concerned about a potential exposure to HIV. Some of them have been extremely detailedbut those details don’t change any of the basic facts about how HIV is and isn’t transmitted.
You can figure out the answer to just about every question that could possibly exist about HIV transmission by reading the rest of our article above. But let’s dive into a handful of the most common kinds of questions we’ve seen over the years:
Can You Get Hiv/aids From Someone’s Blood Touching Your Open Sore
HIV transmissions as a result of one person’s blood entering another person’s open sore or wound are theoretically possible, but in practice hardly ever happen. Only a handful of cases have ever been documented.
If a person is living with HIV and they do not have an undetectable viral load, and their blood directly enters the bloodstream of another person, HIV may be passed on. For example, this is how HIV is usually transmitted when people share syringes or needles used to inject drugs.
However, HIV transmission following limited contactfor example, blood touching an open soreis much less likely.
If you are concerned about an incident in which you had contact with another person’s blood, it’s worth noting a few points:
- If the blood came into contact with undamaged, unbroken skin, there is no HIV risk whatsoever.
- HIV is not transmitted through surface scratches, such as paper cuts.
- A cut or wound that is in the process of healing and scabbing over is unlikely to allow entry of the other person’s blood.
- HIV does not survive long outside the body, so the risk from blood left behind on objects is minimal.
- The handful of documented cases of HIV transmission involving fights or accidents have involved serious injuries and profuse bleeding.
Recommended Reading: How Do Adults Get Ear Infections
When Should I Get Tested For Hiv
If you think you could have HIV or are at risk of HIV, talk to your doctor or sexual health clinic about having a test. Some people at high risk need to be tested regularly.
You should get tested for HIV if:
- you have had unprotected sex with a partner whose HIV status is unknown or who has HIV but does not have a measurable amount of virus in their blood
- you have had unprotected sex with a person from a country that has high rates of HIV infection
- your sexual partner has recently travelled to a country that has high rates of HIV infection and may have had unprotected sex there
- you have had unprotected sex with a sex worker in Africa, Eastern Europe, Southeast Asia or Papua New Guinea
- you have ever shared injecting equipment
Early diagnosis is important and can improve the long-term course of the illness.
It is a good idea to talk to your doctor or sexual health clinic about other STIs at the same time.
Your information will be kept confidential unless there are major concerns for your safety or the safety of others. HIV is a notifiable disease, which means laboratory staff need to inform the government about new cases, but this information is also confidential.
Challenges In Calculating A Number
It isn’t easy for researchers to calculate the risk of transmission from an exposure to HIV through sex. To do this effectively, a group of HIV-negative individuals need to be followed over time and their exposures to HIVboth the number of times they are exposed and the types of exposureneed to be tracked.
As you can imagine, accurately tracking the number of times a person is exposed to HIV is very difficult. Researchers ask HIV-negative individuals enrolled in these studies to report how many times they have had sex in a given period of time, what type of sex they had, how often they used condoms and the HIV status of their partner. Because a person may have trouble remembering their sexual behaviour or may not want to tell the whole truth, this reporting is often inaccurate.
Furthermore, a person does not always know the HIV status of their partner. For this reason, researchers usually enroll HIV-negative individuals who are in stable relationships with an HIV-positive partner . Researchers can then conclude that any unprotected sex reported by a study participant counts as an exposure to HIV.
Also Check: Antibiotics For Ear Infection And Sinus Infection
Where Did Myths About Hiv Come From
The early 1980s were a scary time for people living with HIV. By the spring of 1983, scientists had identified the virus responsible for a mysterious illness called acquired immune deficiency syndrome , but they didnt understand how it passed from person to person.
Initially, some researchers speculated this new infection could be passed through casual contact or even through the air, like tuberculosis. Others theorized it might be hitching a ride with mosquitoes or other insects, like malaria.
But the damage had already been done. Myths about HIV transmission had already taken root, and these myths continue to make life difficult for the 1.1 million people living with HIV today in the United States.
Today we have a solid scientific understanding of HIV transmission. We know that HIV can only be transmitted in very limited circumstances, such as sexual contact or needle sharing. And we have a much better understanding of the way that viral loadthat is, the amount of HIV in a persons bloodstreaminfluences their chances of passing on the virus.
You can use this information to educate yourself, your friends, and your community about the real risk of HIV transmission.
What Are Prep And Pep
PrEP and PEP are medications that can help prevent HIV infection. PrEP stands for pre-exposure prophylaxis. It is recommended for people engaging in behavior that increases their risk of infection. They include serodiscordant couples in which a HIV negative person is in a relationship with someone with HIV. It may also be recommended for those who have sex with multiple partners without condoms. People who have shared needles recently can benefit from it, too.
PEP stands for post-exposure prophylaxis and can help to prevent infection after exposure. Both PrEP and PEP can reduce the risk of HIV infection significantly. PrEP can reduce the risk of infection by more than 90 percent if taken consistently. PEP is an emergency medication and is most effective when taken as soon as possible. A course of PEP should be started within 72 hours of possible HIV exposure.
How hard is it to contract HIV depends on a wide range of factors. It is impossible to calculate an individuals chances of contracting HIV. However, they may fall into certain at-risk groups. The best way to avoid infection is to avoid risky behaviors.
You May Like: Can You Get Sick From A Tooth Infection
How Long Does It Take To Develop The Disease
There is no fixed period between the first contact with HIV and the development of the disease. Signs and symptoms resulting from infection with HIV develop in stages. Many infected individuals may have no symptoms for several years. But others may develop symptoms within three years from the time of infection.
Symptoms of HIV infection are fever, swollen lymph glands in the neck and armpits, sweating, aches, fatigue, unexplained weight loss and diarrhea.
Within eight years, about 50 percent of all infected people develop specific conditions categorized as AIDS. These conditions include a lung disease called “pneumocystis carinii pneumonia,” skin tumours called “Kaposi’s sarcoma,” fungal and viral infections such as candidiasis and herpes zoster, and severe diarrhea.
Some AIDS patients also suffer from dementia resulting in problems with memory and thinking. AIDS patients are prone to various infections of the brain, just as they suffer from an unusually high number of cancers, bacterial and viral infections of other parts of the body.