What Is A Latent Hiv Reservoir
A latent HIV reservoir is a group of immune system cells in the body that are infected with HIV but are not actively producing new virus.
HIV attacks immune system cells in the body and uses the cells own machinery to make copies of itself. However, some HIV-infected immune cells go into a resting or latent state. While in this resting state, the infected cells do not produce new virus. HIV can hide inside these cells for years, forming a latent HIV reservoir but, at any time, cells in the latent reservoir can become active again and start making more virus.
To find out more about how HIV attacks cells, read the HIV Life Cycle fact sheet from HIVinfo.
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can live and long and healthy life and will not transmit HIV to your HIV-negative partners through sex.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Itâs important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
What Are The Types Of Hiv Tests
There are three types of tests used to diagnose HIV infection: antibody tests, antigen/antibody tests, and nucleic acid tests . Your health care provider can determine the appropriate HIV test for you. How soon each test can detect HIV infection differs, because each test has a different window period. The window period is the time between when a person may have been exposed to HIV and when a test can accurately detect HIV infection.
- Antibody tests check for HIV antibodies in blood or oral fluid. HIV antibodies are disease-fighting proteins that the body produces in response to HIV infection. Most rapid tests and home use tests are antibody tests.
- Antigen/antibody tests can detect both HIV antibodies and HIV antigens in the blood.
- NATs look for HIV in the blood.
A persons initial HIV test will usually be either an antibody test or an antigen/antibody test. NATs are very expensive and not routinely used for HIV screening unless the person had a high-risk exposure or a possible exposure with early symptoms of HIV infection.
When an HIV test is positive, a follow-up test will be conducted. Sometimes people will need to visit a health care provider to take a follow-up test. Other times, the follow-up test may be performed in a lab using the same blood sample that was provided for the first test. A positive follow-up test confirms that a person has HIV.
Talk to your health care provider about your HIV risk factors and the best type of HIV test for you.
You May Like: Can You Take Antibiotics For A Viral Infection
Hiv Transmission In Clinical Latency Stage
Although the virus is significantly slowed during the clinical latency stage, it can still be transmitted from person to person.
If an individual is unaware that they are HIV positive or is not regularly taking ART, they can transmit the virus to someone else it will then enter the initial, acute stage in the next person. Getting tested and taking ART as prescribed can reduce an individuals viral load significantly .
Eventually, a persons viral load can become undetectable meaning that the amount of HIV in the blood is so low, that the virus is not detected when tested. Recent research has suggested that those who achieve and maintain an undetectable viral load have virtually no risk of transmitting the virus to an HIV-negative partner.
This idea has been referred to as undetectable = untransmittable or U=U. Therefore, the risk of HIV transmission to an HIV-negative partner can be reduced when an HIV-positive partner is on ART and taking their medications as prescribed.8,9
The Cell Reservoir Of Hiv
Currently, CD4+T cells of resting memory constitute the major reservoir of latent HIV, which has widely been recognized by researchers . However, a study reported that the rate of virus recurrence after the termination of ART therapy is much higher than the replication rate of CD4+T cells, indicating the presence of other reservoirs of latent HIV in addition to CD4+T cells . It has been proved that a variety of cells in circulating blood can also exist in the form of a latent reservoir of HIV after infection, which is associated with a variety of diseases and affect the development of HIV .
Also Check: When To Go To The Er For A Tooth Infection
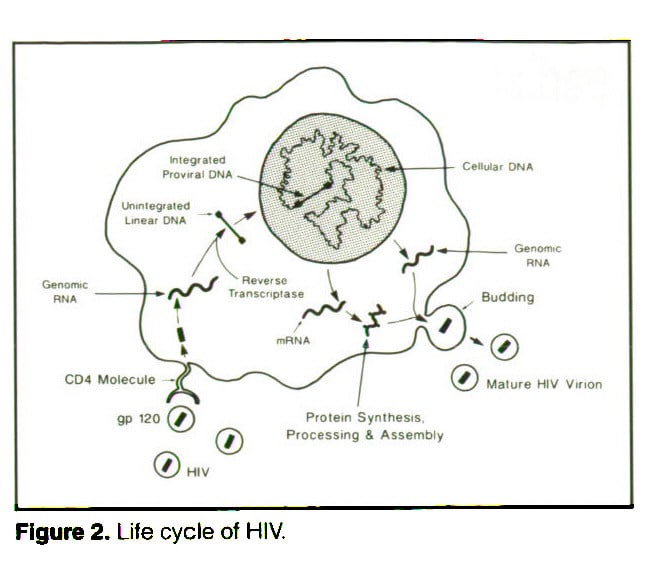
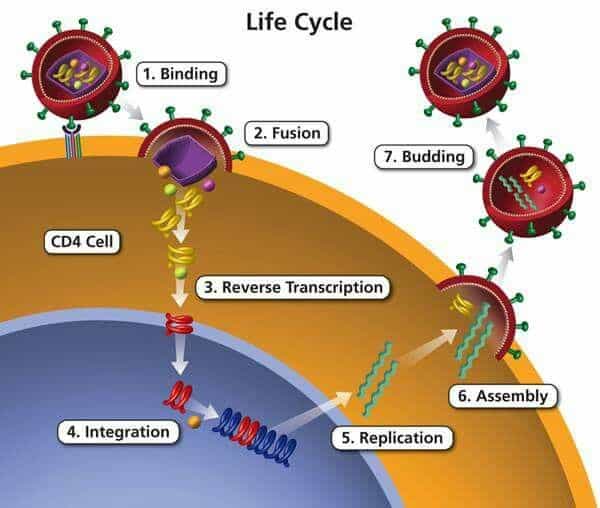
What Are The Seven Stages Of The Hiv Life Cycle
The seven stages of the HIV life cycle are: 1) binding, 2) fusion, 3) reverse transcription, 4) integration, 5) replication, 6) assembly, and 7) budding.
To understand each stage in the HIV life cycle, it helps to first imagine what HIV looks like.
Now, follow each stage in the HIV life cycle as HIV attacks a CD4 cell and uses the machinery of the cell to multiply.
Clinical Latency Stage Of Hiv Infection
The symptoms during ARS may last for a few weeks, according to the National Institutes of Health.
After this point, the infection progresses to the clinical latency stage, a period during which the virus reproduces at very low levels, but it is still active.
Also known as asymptomatic HIV infection or chronic HIV infection, the clinical latency stage typically causes no HIV-related symptoms.
For people who are not taking any anti-retroviral medication for their infection, the clinical latency stage lasts for 10 years, on average, but it may progress quicker.
ART, though, can keep the virus from growing and multiplying, prolonging the clinical latency state for several decades.
It’s important to note that people living with HIV in the clinical latency stage are contagious and can still transmit the virus to other people. But, as the CDC notes, people who take ART exactly as prescribed and maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their HIV negative-partner through sex.
Recommended Reading: When To Go To Urgent Care For Ear Infection
Establishment Of Hiv Infection
After entering the body, the viral particle is attracted to a cell with the appropriate CD4 receptor molecules where it attaches by fusion to a susceptible cell membrane or by endocytosis and then enters the cell. The probability of infection is a function of both the number of infective HIV virions in the body fluid which contacts the host as well as the number of cells available at the site of contact that have appropriate CD4 receptors.
Within the cell, the viral particle uncoats from the envelope to releases its RNA. The enzyme product of the pol gene, reverse transcriptase that is bound to the HIV RNA, provides for reverse transcription of RNA to proviral DNA. It is this HIV proviral DNA which is then inserted into host cell genomic DNA by the integrase enzyme. Once the HIV proviral DNA is within the infected cell’s genome, it cannot be eliminated or destroyed except by destroying the cell itself. The HIV provirus is then replicated by the host cell. The infected cell can then release virions by surface budding, or infected cells can undergo lysis with release of new HIV virions which can then infect additional cells. Antibodies formed against HIV are not protective, and a viremic state can persist despite the presence of even high antibody titers.
First Stage: Acute Hiv Infection Symptoms
Most people don’t know right away when they’ve been infected with HIV. But they may have symptoms within 2 to 6 weeks after theyâve gotten the virus. This is when your body’s immune system puts up a fight. It’s called acute retroviral syndrome or primary HIV infection.
The symptoms are similar to those of other viral illnesses, and they’re often compared to the flu. They typically last a week or two and then go away. Early signs of HIV include:
- Headache and other neurological symptoms
If you have symptoms like these and might have come into contact with someone with HIV in the past 2 to 6 weeks, go to a doctor and ask that you get an HIV test. If you donât have symptoms but still think you might have come into contact with the virus, get tested.
Early testing is important for two reasons. First, at this stage, levels of HIV in your blood and bodily fluids are very high. This makes it especially contagious. Second, starting treatment as soon as possible might help boost your immune system and ease your symptoms.
A combination of medications can help fight HIV, keep your immune system healthy, and keep you from spreading the virus. If you take these medications and have healthy habits, your HIV infection probably wonât get worse.
Don’t Miss: Yeast Infection Vs Chlamydia Discharge
Why Is Hiv Testing Important
Knowing your HIV status can help keep youand otherssafe.
If you are HIV negative:
A negative HIV test result shows that you do not have HIV. Continue taking steps to avoid getting HIV, such as using condoms during sex and, if you are at high risk of getting HIV, taking medicines to prevent HIV . For more information, read the HIVinfo fact sheet on The Basics of HIV Prevention.
If you are HIV positive:
A positive HIV test result shows that you have HIV, but you can still take steps to protect your health. Begin by talking to your health care provider about antiretroviral therapy . People on ART take a combination of HIV medicines every day to treat HIV infection. ART is recommended for everyone who has HIV, and people with HIV should start ART as soon as possible. ART cannot cure HIV, but HIV medicines help people with HIV live longer, healthier lives.
A main goal of ART is to reduce a persons viral load to an undetectable level. An undetectable viral load means that the level of HIV in the blood is too low to be detected by a viral load test. People with HIV who maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partner through sex.
How Is Hiv Transmitted
Human immunodeficiency virus is transmitted by coming in direct contact with certain body fluids of the person infected with HIV. These fluids are as follows
- Receiving blood products that are contaminated with HIV
- Getting stuck with an HIV-contaminated needle
Hence, taking precautions either while having sex or sharing a needle is the best way to prevent HIV.
Also Check: How To Know A Tooth Is Infected
Where Can Someone Get Tested For Hiv
Your health care provider can give you an HIV test. HIV testing is also available at many hospitals, medical clinics, substance use programs, and community health centers. Use CDC’s GetTested treatment locator to find an HIV testing location near you. Getting tested through a professional health care provider is recommended however, there are HIV self-testing kits available. Rapid self-test and mail-in self-test are the two types of HIV self-tests, but state laws regarding self-testing may limit their availability in a location.
A rapid self-test is an oral fluid test done entirely at home or in private. There is currently one U.S. Food and Drug Administration -approved rapid self-test called OraQuick In-Home HIV test. A mail-in self-test requires a person to provide a blood sample from a fingerstick, which is then sent to a lab for testing.
Clinical Significance Of Hiv
Dynamics of viral decay in patients on HAART medications. After initiation of HAART, levels of plasma virus fall rapidly, reflecting the exponential decay of the activated CD4+ T cells that produce most of the plasma virus and the slower decay of a second population of infected cells that have a half-life of about 2 weeks. The second phase decay brings the level of plasma virus down to a new steady state that is below the limit of detection of clinical assays . The average level of residual viremia is around 1 copy/ml. Residual viremia appears to reflect release of virus from stable reservoirs and is not reduced further by treatment intensification. Biological and statistical fluctuations in the level of this residual viremia are occasionally captured in clinical measurements as blips, but these transient elevations do not reflect the evolution of resistant virus.
You May Like: Over The Counter Kidney Infection Medicine Ireland
What Is The Treatment For Hiv
The treatment for human immunodeficiency virus involves a combination of medications known as antiretroviral therapy . ART cannot cure HIV however, it can increase the survival rate of patients.
ART halts the multiplication of the virus and reduces the amount of virus in the body to help the patient stay healthier.
Once the treatment has been started, the patient must remain compliant with the dosage for the medicines to be effective. Noncompliance can result in developing resistance to the medicines.
Cd4+t Lymphocytes Of Resting Memory
CD4+T cells of resting memory are stable reservoirs of latent HIV infection . A previous study stated that there was no significant loss of integrated HIV DNA in resting memory T cells over time, with a half-life of about 25 years . Resting memory T cells can be divided into different subtypes, including primitive T cells and memory T cells . TM cells are divided into central memory T cells , transitional memory T cells , effector memory T cells and stem cell memory T cells . Viral DNA has been detected in all of the above mentioned resting CD4+T cell subpopulations in HIV patients , suggesting that CD4+T lymphocytes of resting memory may be major hosts of latent viral infection.
Compared with TM, viral DNA could be detected in TN cells despite the low frequency of HIV infection . At the same time, data have shown that infected TN cells are treated with drugs that reverse latency. The number of extracellular virions produced by TN in each infected cell was the same as that of TM cells, suggesting that TN cells with latent infection may also be the important source of the virus after treatment interruption or failure, that is, they are important hosts of latent HIV infection, and should not be ignored because of their low infection frequency .
Also Check: Can Cefdinir Treat Yeast Infection
Hiv Latency And The Trouble With Finding A Cure
The Reservoir Of Latent Hiv
- 1Beijing Institute of Hepatology, Beijing Youan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 2Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha, China
- 3Beijing Youan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
The persistence of latent reservoir of the human immunodeficiency virus is currently the major challenge in curing HIV infection. After HIV infects the human body, the latent HIV is unable to be recognized by the bodys immune system. Currently, the widely adopted antiretroviral therapy is also unble to eliminate it, thus hindering the progress of HIV treatment. This review discusses the existence of latent HIV vault for HIV treatment, its formation and factors affecting its formation, cell, and tissue localization, methods for detection and removing latent reservoir, to provide a comprehensive understanding of latent HIV vault, in order to assist in the future research and play a potential role in achieving HIV treatment.
Don’t Miss: Will Vagisil Cure Yeast Infection
Second Stage: Clinical Latency Symptoms
After your immune system loses the battle with HIV, the flu-like symptoms will go away. But thereâs a lot going on inside your body. Doctors call this the asymptomatic period or chronic HIV infection.
In your body, cells called CD4 T cells coordinate your immune systemâs response. During this stage, untreated HIV will kill CD4 cells and destroy your immune system. Your doctor can check how many of these cells you have with blood tests. Without treatment, the number of CD4 cells will drop, and youâll be more likely to get other infections.
Most people don’t have symptoms they can see or feel. You may not realize that you’re infected and can pass HIV on to others.
If youâre taking ART, you might stay in this phase for decades. You can pass the virus on to other people, but itâs extremely rare if you take your medicines.
Detection Of Latent Hiv Reservoirs
At present, detection methods for finding accurate, sensitive, and scalable reservoirs of latent HIV are important in the treatment of reservoirs. Virus outgrowth assay is considered the gold standard for the quantification of latent HIV reservoir. It measures the replicability of the original virus by diluting resting CD4+T cells and activating the intracellular viral gene expression, resulting in inducing the release of HIV from latent infected cells . However, this method is time-consuming, expensive, and requires a large amount of blood culture. Moreover, single stimulation is not sufficient to activate all latent viruses, which underestimates the size of latent HIV reservoir . Detection of HIV DNA based on PCR is relatively simple and rapid method for the detection of the latent reservoir, and provides a supplement for the VOA test . Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction for detection of HIV DNA to determine the amount of HIV DNA carried , digital PCR for detection of HIV DNA for absolute quantitative HIV , and Alu-polymerase chain reaction for detection of HIV integration the amount of DNA is used to evaluate the size of the latent reservoir of HIV . PCR has made rapid development in the determination of latent reservoir of HIV, however, the size of the reservoir may be overestimated because PCR cannot distinguish intact from defective original virus .
Table 1 The different detection methods of latent HIV reservoir.
You May Like: What Are The Best Antibiotics For A Tooth Infection