How Do I Take Antibiotics
Take antibiotics as directed on the packet or the patient information leaflet that comes with the medication, or as instructed by your GP or pharmacist.
Doses of antibiotics can be provided in several ways:
- oral antibiotics tablets, capsules or a liquid that you drink, which can be used to treat most types of mild to moderate infections in the body
- topical antibiotics creams, lotions, sprays or drops, which are often used to treat skin infections
- injections of antibiotics these can be given as an injection or infusion through a drip directly into the blood or muscle, and are usually reserved for more serious infections
It’s essential to finish taking a prescribed course of antibiotics, even if you feel better, unless a healthcare professional tells you otherwise. If you stop taking an antibiotic part way through a course, the bacteria can become resistant to the antibiotic.
Should I Avoid Antibiotics Altogether
Not at all. Antibiotics can save people’s lives, and if you need them, you should get them as quickly as you can. Since only a doctor can prescribe antibiotics, this means that you should talk to your doctor if you think you might need them .
However, it is the grave over-reliance and inappropriate use of antibiotics that have contributed to the global antibiotic resistance crisis that we face.
A study by the CDC showed that many adults believe that if they are sick enough to see a doctor for a cold, they should get an antibiotic treatment. The study also showed that patients are not aware of the consequences of taking the drugs if they are not needed. And when antibiotics are misused, bacteria can become resistant.
Some Steps You Can Take
Whether your sinus infection turns out to be viral or bacterial, you can help to ease your symptoms early on with supportive sinus care:
If your symptoms arent improving after one week, its important to see your doctor. If a bacterial infection is suspected, youll probably need to take an antibiotic to clear up the infection and prevent further complications.
If your infections occur more frequently, and your doctor really wants to establish if they are bacterial or viral, your Otolaryngologist or ear, nose and throat doctor can sample the snot from your nose when youre infected and send it to a laboratory to know for sure.
Note: Antibiotics wont help a viral infection, and taking an antibiotic unnecessarily can do more harm than good. You risk possible side effects and increase your chances of developing antibiotic resistance, which can make future infections harder to treat, says Dr. Sindwani. So its important to wait and see how long your symptoms last.
You May Like: Amoxicillin Vs Penicillin For Tooth Infection
Q Are There Downsides To Taking Antibiotics
A. Most antibiotics are entirely safe, though there are possible side effects and sometimes a persons response to an antibiotic is unpredictable. Weve also learned that there are good bacteria in the body that help keep us healthy, that we dont want to kill with antibiotics. Doctors try to strike a balance between destroying the harmful bacteria and keeping the healthy ones.
The other concern is antibiotic resistance. When we overuse antibiotics, the bacteria could adapt to them. So, youll need a higher dose or a more potent antibiotic, which comes with a greater risk of side effects or harm.
Conditions Are Often Treated With These Drugs But Shouldn’t Be
Every year doctors prescribe millions of antibiotics. But up to 43 percent of the antibiotics prescribed in doctors offices could be unnecessary, according to a nationally representative study published in the journal BMJ on Dec. 11.
Unless an infection is caused by bacteriawhich is usually not the casethe drugs will have no effect.
And antibiotics can cause serious side effects, says Lauri Hicks, D.O., a medical epidemiologist and head of the Centers for Disease Controls program Get Smart: Know When Antibiotics Work. These can include allergic reactions as well as an infection called C. difficile, which can cause severeand sometimes deadlydiarrhea.
Plus, she says, the more bacteria are exposed to antibiotics, the less likely they are to respond to the drugs. You increase your risk of developing an antibiotic-resistant infection the more antibiotics that you take, Hicks notes.
Doctors know that, but they often prescribe antibiotics anyway, in part because patients expect it.
Here are six conditions where its wise to question the use of antibiotics.
Read Also: Can Ear Infections Heal On Their Own
Which Antivirals Does The Cdc Recommend
The CDC recommends baloxavir marboxil , oseltamivir , peramivir , and zanamivir for flu. They are most effective when given within 48 hours after symptoms start to appear. These flu drugs can decrease the duration of the flu by one to two days if used within this early time period. Oseltamivir , and zanamivir are usually given for a period of five days to treat the flu. For flu prevention, they are typically used for at least 7 days. In some cases, antivirals may be given for longer periods of time. For prevention of flu, antiviral drugs may be given for at least 7 days. In some cases, antivirals may be given for longer periods of time.
Oseltamivir is approved for treatment in those over 2 weeks of age and for prevention in people ages 3 months and older.
Peramivir, given in one intravenous dose, is approved for people ages 2 and older.
Zanamivir, an inhaled medication, is approved for treatment of people ages 7 and older and for prevention in people ages 5 and older.
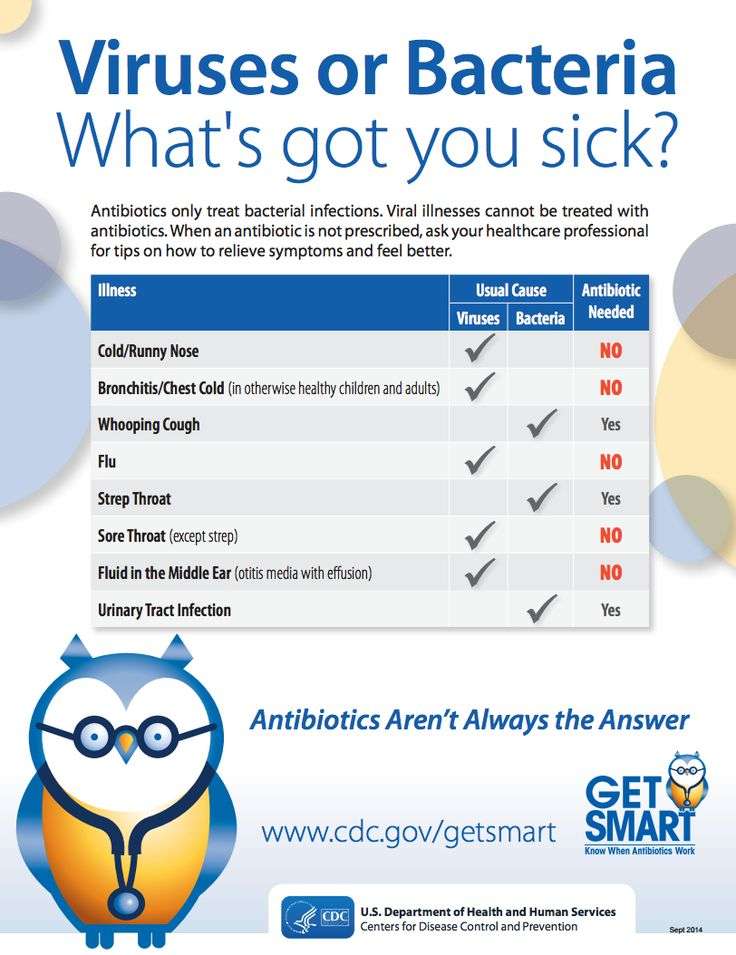
Common Illnesses Caused By Viruses
- flu
- COVID
Most viral illnesses do not need special medication and are self-limiting, meaning your own immune system will kick in and fight off the illness. However, this can take time a cough and cold can last from 7 to 10 days and the flu or COVID might keep you down for 2 to 3 weeks or more.
If you have tested positive for COVID-19, be sure to contact your doctor for further advice. Follow all local, state and federal mandates for quarantine and mask wearing.
If you come down with a viral illness, you should rest, drink plenty of fluids and treat symptoms such as fever or aches and pains. Treatment options include proper doses of pain and fever relievers like over-the-counter acetaminophen or ibuprofen, or as directed by your doctor. If you are diagnosed with a viral illness such as a cough, cold or sore throat, and your symptoms worsen or do not clear up within 10 days, be sure to contact your doctor.
You May Like: What Antibiotic For Ear Infection In Adults
Using Antibiotics Responsibly: Our Commitment
At Atrium Health, we spread antibiotic education to our doctors through our Antimicrobial Support Network and patient care collaborative, which both work with doctors to make sure patients are prescribed the most appropriate antibiotics. The ultimate goal is to improve your care and safety.
About Atrium Health
How To Help Relieve Cold And Upper Respiratory Symptoms
As I said earlier, viral infections can linger for two weeks or more. You may feel terrible for three or four days, but then the symptoms tend to fade away. During this time, you can try over-the-counter medications and home remedies to help relieve your symptoms:If you experience more than one of these symptoms, there are many medications that offer multi-symptom relief. Along with taking medication, stay hydrated and get rest. I know you want to get back to work and your daily life, but your body needs time to heal plus you want to avoid giving the virus to someone else.If you have a fever that lasts more than two or three days, go to the doctor. If your symptoms last more than 10 days, or if you start to get better and then get sick again, see your doctor. Antibiotics are not evil, and we shouldnt fear them. But we do need to use them responsibly to ensure they continue working when we need them for years to come.
- Cough: Expectorant or cough suppressant, steroid nasal spray, humidifier
- Nasal congestion and sinus pressure: Nasal or oral decongestant, steroid nasal spray, humidifier
- Sore throat: Lozenges, humidifier, warm teas with honey and lemon, warm water with salt gargles
- Fever: Acetaminophen,ibuprofen, or aspirin
Our doctors can assess whether an antibiotic would work for you. Schedule an appointment online or call .
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection Natural Medicine
Antibiotics Are Not One
The antibiotics that work for a urinary tract infection arent the same as the ones that will fight strep throat. And the broad-spectrum antibiotics used to fight infections in hospitals arent the same as the very specific antibiotics your doctor may prescribe to treat a bacterial ear infection.
Heres why thats matters: If you take the wrong medication, it wont be effective.
On top of that, it may have unpleasant and unwanted side effects. In most cases, side effects of antibiotics are pretty benign. But, for example, taking those broad-spectrum antibiotics for an extended period of time can put you at risk for C. diff, a severe and hard-to-treat infection.
Colds And Flu: Do You Need Antibiotics
- Health Matters
- Colds and Flu: Do You Need Antibiotics?
As the mercury in the thermometer drops, we see a rise in colds and flu. Coughs, colds, and sore throats make their way through schools and workplaces with people asking, How long will this last? and, Do I need antibiotics? Dr. Mike Gavin, of UR Medicine Primary Care, helps answer these questions.
Besides the fact that they wont be effective against viruses and may be costly, theres another good reason for limiting antibiotic use. Taking them when they arent needed creates antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria become invincible to antibiotics, making them much harder to treat in the future. Overuse and misuse of antibiotics causes antibiotic-resistant bacteria, or superbugs. If more superbugs are created, we will not have any effective antibiotics to treat bacterial infections.
How can we stop the creation of superbugs and, at the same time, make sure a cold is really a viral infection? These facts may help you successfully navigate the winter cold and flu season:
Michael J. Gavin, M.D., cares for adults and children at UR Medicine Primary Cares Tow Path Family Medicine and new patients are welcome. Call 758-0800.
Recommended Reading: Will Amoxicillin Cure A Sinus Infection
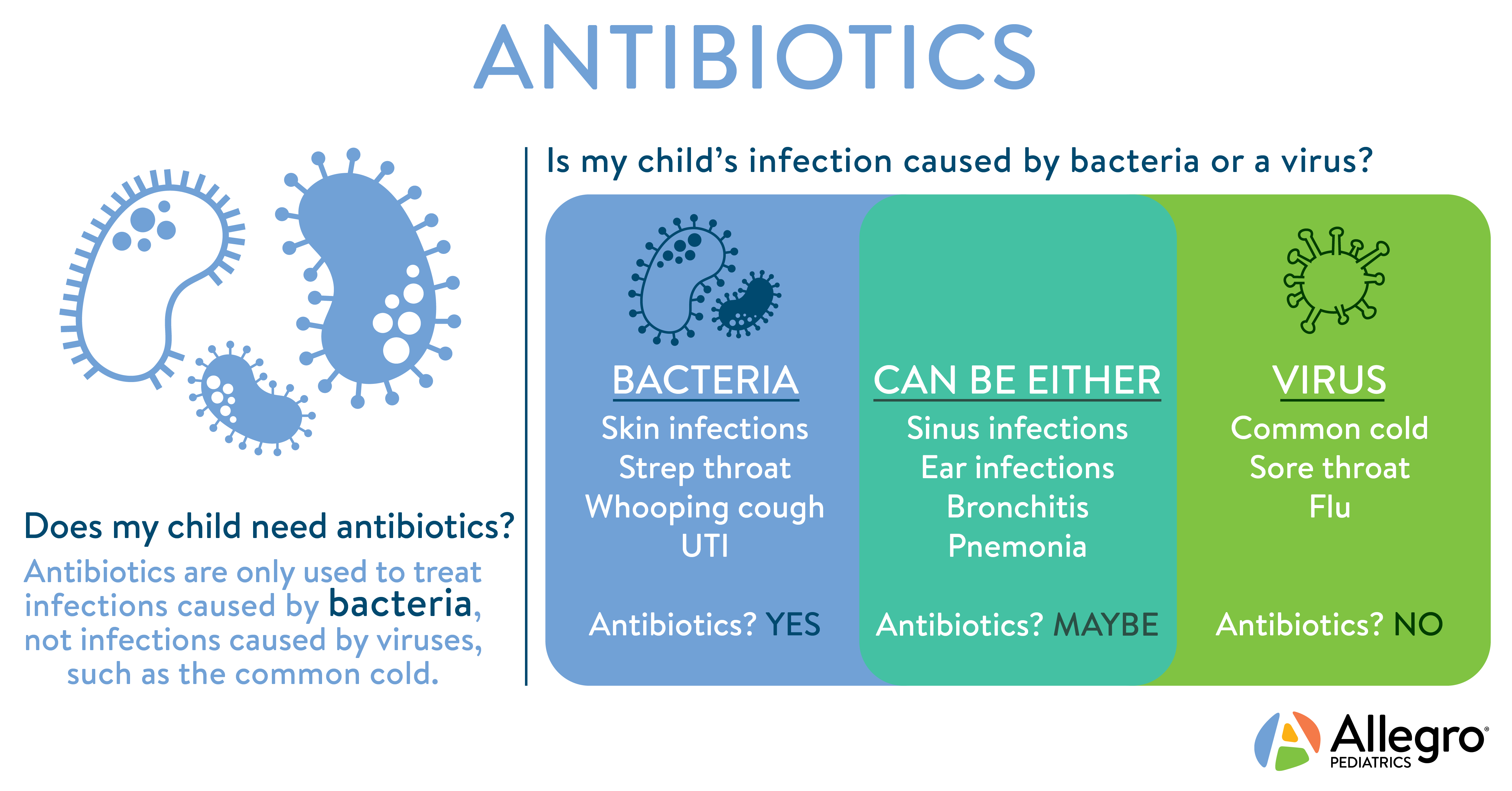
Diagnosis Of Bacterial And Viral Infections
You should consult your doctor if you think you have a bacterial or viral infection. Exceptions include the common cold, which is usually not life-threatening.
In some cases, it’s difficult to determine whether an illness is viral or bacterial because many ailments — including pneumonia, meningitis, and diarrhea — can be caused by either. But your doctor may be able to determine the cause by listening to your medical history and doing a physical exam.
If necessary, they also can order a blood or urine test to help confirm a diagnosis, or a “culture test” of tissue to identify bacteria or viruses. Occasionally, a biopsy of affected tissue may be required.
Antibiotics: When You Need Them And When You Dont
Antibiotics often are seen as wonder drugs. And in many ways they are. Antibiotics revolutionized medicine and have saved countless lives over the past century. Unfortunately, many health care providers now rely too heavily on antibiotics and prescribe them when they arent necessary. Patients also have come to expect and even demand antibiotics every time they get sick.Nearly one-third of the antibiotics prescribed in the United States arent appropriate for the conditions being treated, according to a May 2016 study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association .Why is this a problem? Because its led to a surge in antibiotic-resistant bacteria that are becoming increasingly difficult to treat. In fact, the first bacteria resistant to last-resort antibiotic treatment was identified in the United States in May 2016.If your doctor prescribes an antibiotic , learn which conditions they can treat, why antibiotic resistant infections are so scary, and how doctors and patients can be smarter about antibiotic use.
Also Check: Can Augmentin Be Used For Tooth Infection
How Can Vaccines Help
Many infections can be prevented by following the recommended vaccine schedule as proposed by the CDC, so be sure to keep up-to-date with your vaccines and those of your children. Your doctor and pharmacist can provide more information about important vaccines for you and your family.
Vaccines are readily available in the U.S. to help prevent the COVID-19 infection. These vaccines are safe and effective, can help keep you out of the hospital, and can help prevent severe illness and death. Learn more about the COVID-19 vaccines here.
Accidentally Taking An Extra Dose
There’s an increased risk of side effects if you take 2 doses closer together than recommended.
Accidentally taking 1 extra dose of your antibiotic is unlikely to cause you any serious harm.
But it will increase your chances of getting side effects, such as pain in your stomach, diarrhoea, and feeling or being sick.
If you accidentally take more than 1 extra dose of your antibiotic, are worried or you get severe side effects, speak to your GP or call NHS 111 as soon as possible.
Don’t Miss: Yeast Infection Treatment While Breastfeeding
Antibiotics Dont Work For Everything
Antibiotics fight infections caused by bacteria, but they wont work against infections caused by viruses. That means they are not effective against the flu, the common cold or COVID-19.
If that sounds like common sense, consider this: In a recent survey, one in three surveyed Americans wrongly believed that antibiotics work effectively against colds.
When you visit your doctor, be as specific as possible about all of your symptoms so he or she can narrow down the cause, Dr. Allan says. Figuring out whether its likely a bacterial or viral infection is step one.
For example, symptoms such as a consistently high fever , nasal discharge and severe facial pain may indicate a bacterial sinus infection. Most sinus infections are viral, but if these symptoms linger for many days without improvement, the cause may indeed be bacterial.
Likewise, that same high fever combined with ongoing ear pain may be signs of a bacterial ear infection. In both cases, antibiotics would be appropriate.
But not all infections are bacterial. A stuffy head and low-grade fever might be signs of a virus, for instance. Its critical to work with your doctor to get as clear a diagnosis as possible then proceed with the proper treatment.
That treatment is not always antibiotics. Sometimes easing your symptoms while letting your body fight off a virus is the proper course of action.
But Sometimes Antibiotics For Sinus Infections Are Needed
So how does one judge when it is appropriate to prescribe antibiotics for a sinus infection? There are several sets of official guidelines, which are all similar. When a patient has thick, colorful nasal discharge and/or facial pressure or pain for at least 10 days, they meet criteria for antibiotic treatment. If a patient has had those symptoms, but the symptoms seemed to start improving and then got worse again, then even if its been less than 10 days, they meet criteria for antibiotic treatment.
The authors, however, also suggest that doctors discuss watchful waiting with patients and explain that most sinus infections clear up on their own in one to two weeks, and its a safe option to hold off on antibiotics. The symptoms can then be treated with a cocktail of over-the-counter medications and supportive care, like nasal saline irrigation, nasal steroid sprays, decongestants, and pain medications.
Of course, many patients expect and demand antibiotics for sinus infections, and even those who are open to watchful waiting may hear about the rare but possible complications of things like, oh, brain abscess, and opt to treat.
In the case of my patient above, she met criteria for treatment. She weighed the watchful waiting option against the potential risks of antibiotics for her sinus infection, and chose the prescription. I can tell you from very close follow-up that she improved quickly, though in truth, we will never really know if she would have gotten better anyway.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Over The Counter Medication For Yeast Infection
How Does Antibiotic Resistance Occur
According to the CDC, each year, at least 2.8 million people in the U.S. become infected with bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics and at least 35,000 people die as a direct result of these infections.
In general terms, antibiotic resistance can occur when bacteria learn to fight off the antibiotic.
- Antibiotics work by interfering with the bacterial cell wall and prevent bacteria from making copies of themselves. However, many of these drugs have been widely used for a long period of time, overused, or used inappropriately.
- Antibiotics are designed to kill specific bacteria. But over time bacteria learn to adapt to the medicine, making the drug less effective.
- Bacteria fights back against a drug in many ways:
- by producing enzymes that can inactivate the antibiotic