Diabetes And Risk Of Surgical Site Infection: A Systematic Review And Meta
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 October 2015
- Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan School of Public Health, Ann Arbor, Michigan
- Keith S. Kaye
- Division of Infectious Diseases, Wayne State University and Detroit Medical Center, Detroit, Michigan
- Caitlin Knott
- Affiliation:Department of Pharmacy Practice, Eugene Applebaum College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan
- Huong Nguyen
- Affiliation:Department of Pharmacy Practice, Eugene Applebaum College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan
- Affiliation:Department of Pharmacy Practice, Eugene Applebaum College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan
- Richard Evans
- Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan School of Public Health, Ann Arbor, Michigan
- Elizabeth Bertran
- Affiliation:Department of Pharmacy Practice, Eugene Applebaum College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan
- Linda Jaber
- Affiliation:Department of Pharmacy Practice, Eugene Applebaum College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan
- *
- Address correspondence to Emily T. Martin, MPH, PhD, Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan School of Public Health, 1415 Washington Heights, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA 48109-2029 .
Diabetes And Why It Increases Sepsis Risk
According to the National Institutes of Health, diabetes affects over 30 million people in the United States almost 10% of the population. Even more people, 84 million, have what is called pre-diabetes. They have abnormally high blood glucose levels but not high enough to be diagnosed with diabetes. Unfortunately, most people in this large group nine out of 10 dont even know they have pre-diabetes, so they cant make a conscious decision to make lifestyle changes that might reduce their risk of pre-diabetes progressing to diabetes. March 26 is Diabetes Alert Day, held every year on the fourth Tuesday in March. Sepsis Alliance is taking this opportunity to not only share information about diabetes, but how people with diabetes diagnosed or not are at higher risk of developing sepsis than people without the disease. With one in four adults in the U.S. living with diabetes, most of us know at least one person who has this chronic disease.
What treatment you need to treat your diabetes depends on what type you have:
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease offers a Diabetes Risk Test that you can take to judge your risk of developing diabetes. If you are at risk, speak with your doctor or nurse practitioner about what you can do to help yourself.
The signs and symptoms of sepsis can be vague. The most common ones are associated with the mnemonic TIME:
T Temperature higher or lower than normal.
Head And Neck Infections
The two most serious head and neck infections in diabetic persons are invasive external otitis and rhinocerebral mucormycosis.
Invasive external otitis
Invasive external otitis is an infection of the external auditory canal that can extend to the skull base and adjacent regions. It often affects elderly diabetic individuals and the etiologic agent is usually Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Excruciating pain, otorrhea, and hearing loss are the characteristics. Skull base osteomyelitis and cranial nerve involvement may occur. Facial paralysis occurs in 50% of the cases. The best diagnostic method is the magnetic resonance imaging.
Rhinocerebral mucormycosis
Mucormycosis is a rare opportunistic and invasive infection caused by fungi of the class Zygomycetes. The genus most commonly associated with human infections is the Rhizopus, followed by Mucor and Cunninghamella.
This infection occurs in approximately 50% of the cases in individuals with DM due to the greater availability of glucose to the pathogen that causes mucormycosis, the decrease in serum inhibitory activity against the Rhizopus in lower pH, and the increased expression of some host receptors that mediate the invasion and damage to human epithelial cells by Rhizopus.
Periodontitis
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Infection In Your Mouth
Common Infections Outcomes And General Drug Of Choice
In addition to many infections having a worse course in those with diabetes, specific types of infections are also significantly more common in those with diabetes. We will review these diabetes-predominant infections . also provides an overview of common infections and considerations in those with DM.
Mental Health And Diabetes
Living with and managing either type 1 or type 2 diabetes can lead to stress, anxiety and depression. This can affect your blood glucose levels and how you manage your diabetes in general. Over time, this can affect your health.It is important to talk to your doctor if you are going through times of stress, depression or anxiety. Your doctor can refer you to a counsellor or psychologist by providing a diabetes mental health plan. This is Medicare rebated.Other help is available, including:
- online resources
Dont Miss: One Day Yeast Infection Cure
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Doctor Treats Yeast Infection
Research Design And Methods
The Second National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey was a national probability survey of the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population from 1976 to 1980 the NHANES II Mortality Study includes a subsample of 9,252 adults aged 3074 years who were followed passively for mortality through 1992 . All participants in the mortality study underwent complete history, physical, and laboratory testing at the time of the initial survey. The participants were traced through national death and/or social security indexes if a participant was determined to be deceased, the death certificate was retrieved. Participants not determined to be deceased by 31 December 1992 were presumed to be alive. Two participants were excluded because identifying information wasnt available, and 42 participants who were known to be deceased were excluded because a death certificate wasnt available. This resulted in a study population of 9,208 individuals.
What Can Be Done To Avoid Infections
The most important way to prevent infections is to carefully manage your diabetes. Infections and problems fighting infections occur primarily in people with uncontrolled diabetes.
It’s also important to see a podiatrist regularly and practice careful foot care. Don’t walk outside barefoot and always wear shoes and socks inside to avoid minor bumps and scrapes. Your feet should also be examined daily for any blisters, cuts, scrapes, sores or other skin problems that could allow an infection to develop. Meticulous foot and skin care is needed to ensure that minor cuts and scrapes do not turn into ulcerated infections that can migrate into the bloodstream and cause major problems.
Good urinary hygiene, especially for women, can help minimize the possibility of developing urinary tract infections. This includes proper toilet hygiene, prompt urination after sexual intercourse, regular emptying of the bladder, and ample fluid intake.
Yeast infections can often be avoided by good vaginal care. This may include the avoidance of spermicides and douches. Eating foods with active cultures, such as yogurt containing Acidophilus, can be helpful for preventing yeast infections.
Read Also: Clotrimazole And Betamethasone For Yeast Infection
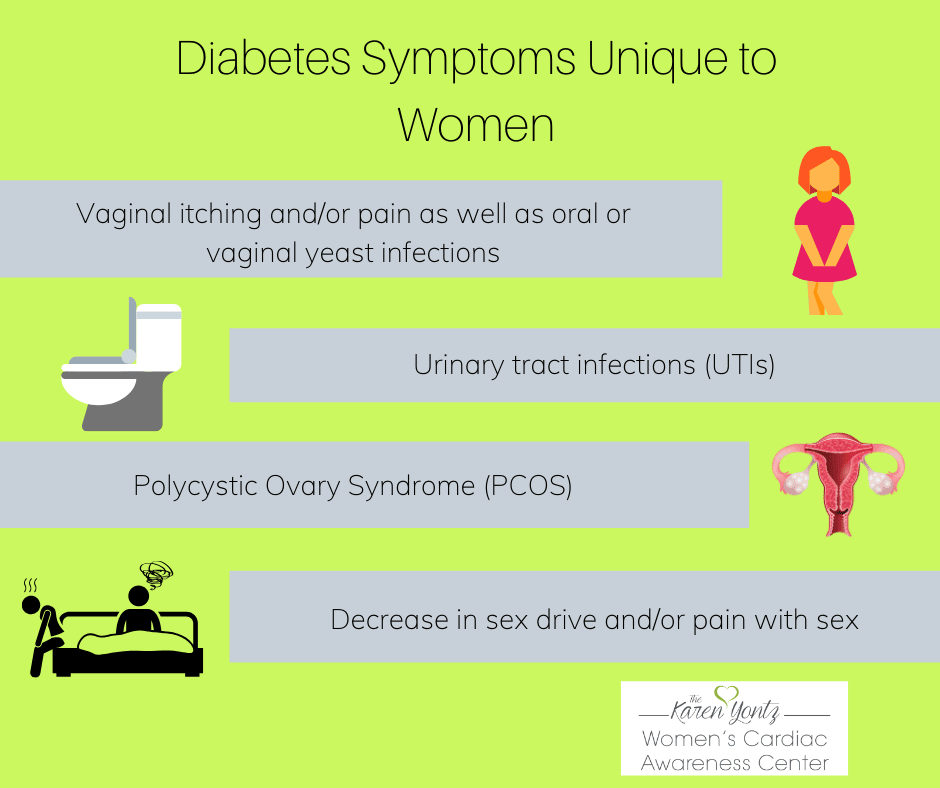
Diabetes And Urinary Tract Infections Things You Need To Know
Modified: Jun 4, 2020 by Tammy Shifflett RN, BSN, CDE, CPT · This post may contain affiliate links ·
In this article we will cover everything you need to know about diabetes and your risk for Urinary Tract Infections. Do you have an increased risk of Urinary Tract Infections now that you have diabetes?
We will cover what a Urinary Tract Infection is, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment guidelines, as well as why they are more common in people with diabetes.
More importantly, we will discuss steps you can take to prevent them!
Contents
Extra Sugars In Yeast
Diabetes can also make it easier for yeast and other pathogens to cling to skin cells and mucus glands. This may be because of the presence of extra sugars, which allow the yeast to colonize at unhealthy levels.
When blood glucose levels are high, the body may excrete extra sugar in the:
Yeast feeds on sugar, making these secretions the most likely factor in overgrowth.
People with diabetes also have increased glycogen levels, a polysaccharide that the body uses to store glucose. Extra glycogen in the vaginal area can lead to an increase in acidity. According to a study published in 2009 in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, this can contribute to yeast growth.
Also Check: Will Teladoc Treat Ear Infection
High Blood Sugar Levels
When blood sugar levels are high, the body starts to get rid of excess sugar through bodily fluids, including vaginal secretions. Yeast gets its energy from sugar, so this vaginal environment makes it easy for yeast to multiply, overgrow, and turn into a yeast infection.
High blood sugar also interferes with immune system functions that help fight off yeast infections. This means uncontrolled diabetes can make it more difficult to prevent and get rid of a vaginal yeast infection.
How Does Illness Affect Diabetes
Illness and infections, as well as other forms of stress, can raise your blood glucose levels. As part of the bodys defence mechanism for fighting illness and infection, more glucose is released into the blood stream. This can happen even if youre off your food or eating less than usual.
People who dont have diabetes just produce more insulin to cope. But when youve got diabetes, your body cant do this. The symptoms of diabetes can add to those of the original illness or infection and make it much worse.
Feeling or being sick, or having diarrhoea can make your blood sugar levels drop, because you’re not absorbing food as usual.
Don’t Miss: Best Antibiotic For Foot Infection
How To Keep Your Legs Healthy:
To help you keep your feet and legs healthy look out for a numbness sensation, a burning pain, an ache thats not so sharp, a less-rough patch of skin, hair loss, a reduction in feeling, swollen ankles or feet, dryness and lack of sweat, certain wounds or cuts that wont heal, and cramping.
Although those symptoms can be taken care of an easy-basis, there are some issues that should grant you into immediate care, like differences in the color and contours of your feet, getting cold feet , blisters, sores, and cuts that are visible but have not feeling or a bad odor coming from a wound. These issues can be very dangerous for a diabetic. Making sure to stay on top of your foot health care is extremely important for your overall health and helping you avoid extreme measures like an amputation.
If there is any change in your healthtake note! Have your doctor go through the symptoms you should personally look out for and try and get some therapeutic, personalized shoes to help you avoid a majority of these issues.
Why Are Infections Hard To Treat In Diabetics
Wound care is a particularly important aspect of diabetic care. Thats because wounds usually take much longer to heal in diabetics than in people with healthy immune systems. A combination of a healthy diet, physical therapy and massage can help reduce the risk of infection.
High blood sugar diabetes can also lead to nerve damage, which causes problems with sensation, particularly in the feet. This sometimes means that injuries go unnoticed, which is dangerous as untreated injuries can lead to infection. Some types of nerve damage can also lead to cracked skin a convenient entry point for infection.
Foot ulcers are very common in diabetics because poor blood circulation means the infected area is difficult to reach. The lack of healing nutrients able to reach infected areas makes patients more vulnerable to fungal and other infections.
Contact us or walk in if you would like to find out more about nursing care and restorative therapy services. We are here to answer all your questions and concerns. Let us know how we could help you with rehab and nursing care for you or your loved one.
Don’t Miss: Antibiotics For Viral Sinus Infection
Diagnosing And Treating Infections
Your healthcare provider may perform one or more tests to diagnose infection, including blood tests, microscopic examination of secretions, urine dipstick tests, X-rays, and physical examination.
Keep the following questions in mind when discussing any possible infections with your healthcare providers:
- For what symptoms should I call the doctor’s office?
- How should I manage my medications during an infection?
- Do antibiotics interact with any of my other medications?
Healthcare providers may prescribe oral or topical antibiotics to treat some infections. Careful blood sugar control is important during any infection to promote healing and prevent further complications related to the infection.
Glycemic Control And Diabetes Therapies
There is good evidence that glycemic control is correlated with infection. A study of 69,318 patients with type 2 DM in Denmark revealed an association between increased risk for community- and hospital-treated infection in those with higher HbA1c â¥10.5% compared with HbA1c 5.5-< 6.4% . Similarly, in a large English cohort there was an increasing risk of infection in parallel with HbA1c for patients with both type 1 and type 2 . In a Taiwanese study looking at outcomes from a community-based health screening program, the authors found that fasting plasma glucose > 200 mg/dL and DM was associated with the highest risk of infection and also a 3-fold higher risk of death than those without DM . Looking at an older population, the risk of certain infections was significantly higher in those with poor glycemic control HbA1c > 8.5% compared with good glycemic control . Intervening to lower glucose appears to mitigate the risks. Zerr et al assessed incidence of sternal wound infection in patients with and without DM before and after implementation of a postoperative continuous IV insulin protocol to keep blood glucose < 200 mg/dL. They found that lower glucose in the first 2 days postoperatively was associated with a decrease in deep wound infection from 2.4% to 1.5% .
Read Also: How To Avoid Bladder Infections After Intercourse
/6yeast Infections Or Thrush
Thrush is a yeast infection that can grow in the different parts of the body like the armpits, finger, mouth and genital area. The condition leads to white discharge, akin to cottage cheese. In the case of diabetes, thrush is generally found around the genitals in men and women, leading to itching, irritation, soreness and stinging during sex or when urinating. Men may also experience an unpleasant smell and difficulty in pulling back the foreskin. Thrust is caused by a type of fungus called candida, which grows in warm and moist conditions.
Gastrointestinal And Liver Infections
The regularity of gastrointestinal motility and sensitivity are important mechanisms of defense against infections. Chronic hyperglycemia contributes to increase the risk of gastrointestinal infectious processes.
Gastritis caused by Helicobater pylori
The association of DM and infection by Helicobacter pylori is controversial. Although some studies showed that some virulent strains of H. pylori are related to macroangiopathy, neuropathy, and microalbuminuria in patients with DM2, there is apparently no relationship between H. pylori infection and these DM complications.
Some data indicate a possible association of H. pylori infection with coronary insufficiency and/or cerebral occlusive vascular disease in adults with DM. Another consequence of this infection is the increase in insulin requirements in children with DM1.
The efficiency of H. pylori eradication is lower in persons with DM, whereas the re-infection rates are seen to be higher.
Oral and esophageal candidiasis
Emphysematous cholecystitis
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C virus is a major public health problem affecting more than 170 million people worldwide and this figure is expected to increase due the lack of a vaccine to prevent it. Approximately 5080% of these patients develop a chronic infection and have a greater chance to progress to cirrhosis.
Hepatitis B
Enteroviruses
Don’t Miss: Boric Acid For Recurrent Yeast Infection
Data Sources And Outcomes
Information on hospitalizations due to bacterial infections and on antimicrobial drug prescription purchases for each participant was drawn from two nationwide registries: the Finnish Hospital Discharge Register, which includes the diagnoses of all in-hospital treatment periods, and the Finnish National Drug Prescription Register, which includes all of the antibiotics purchased from pharmacies outside hospitals. Infections treated in hospitals were classified according to their most common etiology as bacterial, viral, fungal, or as unspecified infections, using the primary and secondary diagnoses from the Hospital Discharge Register, according to the WHO International Classification of Diseases 10th revision. The specific types and sites of the hospital-treated infections are more closely specified in online supplementary table S1. The risk of infections in outpatients was assessed by acquiring information on the annual outpatient prescription purchase frequencies of antibiotics. Antibiotics were identified using the WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System as drugs with an ATC code beginning with J01.
In a subanalysis, the number of antibiotic purchases was compared between patients who had retained a normal AER during the whole follow-up period with their respective sex-matched and age-matched NDCs to separate between the impact of nephropathy and other possible effects of diabetes on antibiotic purchases.
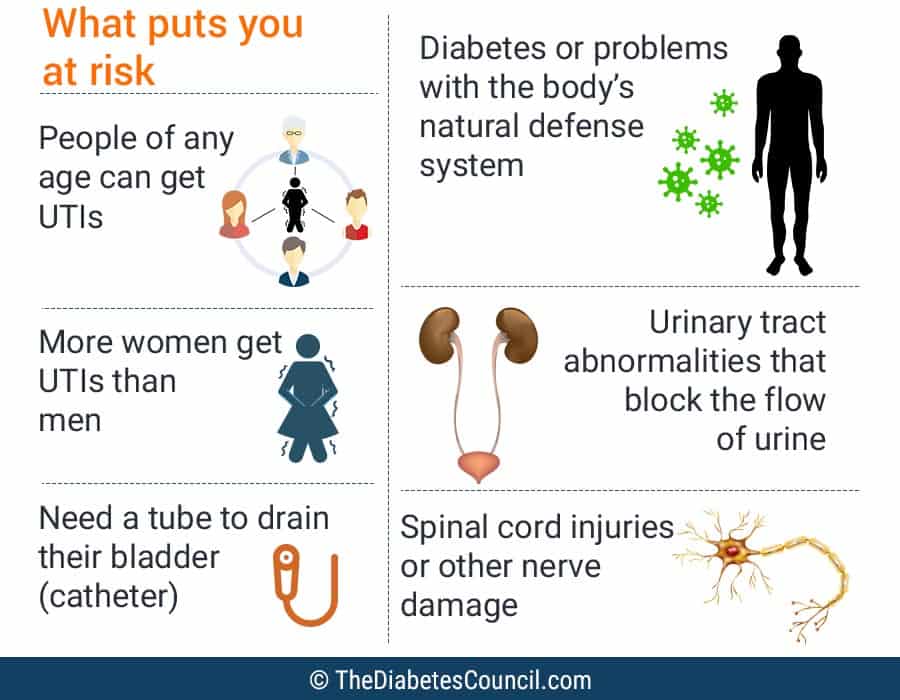
If You Have Diabetes It Is Twice As Likely You Will Develop A Utiwhy
There are many factors that elevate the risk for UTIs for people with diabetes. Common sense would tell us that higher blood sugars increase the risk for all infections.
Well, believe it or not, the jury is still out on that theory for some odd reason. I could not find any recent research anywhere on this theory or for that matter on urinary tract infections in people with diabetes. My hope is more research will be considered since the complications associated with these infections can be life threatening.
According to a study by Nitzan et al Urinary tract infections in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: review of prevalence, diagnosis and management, UTIs are most common and severe with complicated outcomes in people with type 2 diabetes. The study presents the reasons people with diabetes are at a greater risk for urinary tract infections which I will outline here:
Likely Causes of Urinary Tract Infections in People with Diabetes:
- Poor metabolic control
- Use of catheters
- Hospitalizations
Poor metabolic control is not completely understood as a cause of utis yet, so this is a great opportunity for researchers. The extra sugar in the urine builds up, causing the growth of extra bacteria which leads to the infection in the bladder.
We have already discussed a few of these, but lets discuss the ones we havent.
Read Also: How To Get Smell Back After Sinus Infection