What Can I Expect If I Have Hiv
If youre diagnosed with HIV, its important to know that those living with HIV who follow treatment guidelines can live full lives for nearly as long as those without HIV.
If you have a high CD4 count and an undetectable viral load within a year of starting treatment, research suggests youll have the best outcomes, as long as you continue your treatment plan.
You can improve your outlook by:
- Getting tested as part of routine healthcare or if you think youve been exposed.
- Starting ART soon after being diagnosed.
- Taking your medicine every day.
- Keeping your appointments with your healthcare team.
ART can keep blood levels undetectable but cant entirely rid your body of the virus . If you dont take your medication every day, the virus can start multiplying again and mutate, which may cause your medications to stop working.
Left untreated, it can take about 10 years for HIV to advance to AIDS. If you progress to AIDS and it goes untreated, you can expect to live about three years more.
For those on treatment, if you have a high CD4 count and undetectable viral load within a year of starting treatment, you can expect to live about as long as someone without HIV. If you have a low CD4 count or a detectable viral load within a year of starting treatment, you may live 10 to 20 years less than someone without HIV.
Hiv Diagnosis And ‘window Period’
You wonât know if you have HIV right after youâre infected. It takes time for your body to make antibodies and for antigens to show up.
The âwindow periodâ is the time between when you might have been exposed to HIV and a test can tell for sure you have it. This varies from person to person and test to test. Your testing counselor can tell you more about the window period for the test youâre taking. Here are some general guidelines:
An antibody test can detect HIV 23 to 90 days after youâre exposed to the virus. The window for a test that uses blood from a vein is faster than one that uses oral fluid or blood from a finger stick.
An antigen/antibody test done in a lab on blood from a vein can detect HIV infection within 18 to 45 days. It takes longer if the testâs done with blood from a finger stick.
A nucleic acid test usually has the shortest window: 10 to 33 days. This test is not generally used to diagnose HIV infection unless you have symptoms and a history that suggest you were infected only a few days ago.
If you have a negative test and werenât exposed to the virus during the window period for that test, you can be certain you didnât have HIV when you were tested.
The CDC recommends that all adults have an HIV test at least once, even if theyâre not at risk. If your risk is higher — for example, you have multiple sex partners or use needles for drugs — you should be tested every year.
Do Vaccines Cause Side Effects
Any vaccine can cause side effects. Side effects from vaccines are generally minor and go away within a few days.
Severe reactions to vaccines are rare. Before getting a vaccine, talk to your health care provider about the benefits and risks of the vaccine and possible side effects. Learn about vaccine safety and possible side effects.
Recommended Reading: Can You Treat A Yeast Infection Over The Counter
How Could You Get Hiv From Contact With Blood
The risk of HIV transmission through blood comes when the person has a detectable viral load and their blood enters another persons body or comes into contact with a mucous membrane. These are parts of the body with wet, absorbent skin such as the:
Theres also a risk if blood from a person who has a detectable viral load comes into contact with a cut or broken skin, giving HIV a way through the skin and into someones bloodstream. If blood gets onto skin that isnt broken, there is no risk.
In a medical setting, its possible for HIV to be transmitted by someone accidentally cutting themselves with a blade or needle they have used to treat a person living with HIV.
This is called a needlestick injury. The risk of being infected in this way is very low. However, if someone thinks they have been exposed to HIV through a needlestick injury, post-exposure prophylaxis may be an option.
Stage : Chronic Hiv Infection
In this second phase, HIV is still reproducing at very low levels within the body, and it continues to damage immune cells. People typically do not experience symptoms or get sick from the virus during this stage.
This stage is also known as asymptomatic HIV infection, or clinical latency.
Without medication, the chronic stage of an HIV infection can last for a decade or more. People can still transmit the virus to others during this time.
Antiretroviral therapy slows or stops the progression of HIV. People who take antiretroviral drugs as prescribed may remain in the chronic HIV stage for life and never develop stage 3 HIV.
Recommended Reading: Antibiotics Used To Treat Tooth Infection
Does Hiv Go Away
HIV doesnt go away on its own. It inserts itself into your DNA so your cells think that its a part of you. There can be many years without symptoms after initial infection, but HIV can still be damaging your immune system even if you dont feel sick.
There may be periods while on medication where the virus is not detectable by an HIV test. In these cases, HIV can be hiding in your body, undetected. It can wake up and start destroying your cells again in the future.
This is why continuing to take HIV medication, even if you dont feel sick or the virus is undetectable, is extremely important. Without treatment, HIV will weaken your immune system until you cant fight off other serious illnesses.
Which Vaccines Are Recommended For People With Hiv
The following vaccines are recommended for people with HIV:
Based on age or other circumstances, you provider may recommend other vaccines as well.
Talk to your health care provider about which vaccines are recommended for you. For more details, read this information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention : HIV Infection and Adult Vaccination.
Read Also: Amox Clav 875 Mg Urinary Tract Infection
Has The Introduction Of Antiretroviral Therapy Changed The Cancer Risk Of People Infected With Hiv
The introduction of highly active antiretroviral therapy , also called combination antiretroviral therapy , starting in the mid-1990s greatly reduced the incidence of certain cancers in HIV-infected patients, especially Kaposi sarcoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma . The likely explanation for this reduced incidence is that cART lowers the amount of HIV circulating in the blood, thereby allowing partial restoration of immune system function to fight the viruses that cause many of these cancers.
Although the risk of these AIDS-defining cancers among people infected with HIV is lower than in the past, it is still much higher than among people in the general population . This persistently high risk may reflect the fact that cART does not completely restore immune system functioning. Also, many people infected with HIV are not aware they are infected, have had difficulty in accessing medical care, or for other reasons are not receiving adequate antiretroviral therapy.
The introduction of cART has not reduced the incidence of all HIV-related cancers, and in fact AIDS-defining cancers. For example, the incidence of liver and may be increasing among HIV-infected individuals .
Signs Of Hiv Infection In Children
HIV- infected children may develop a number of signs and symptoms as a result of their HIV infection. However, HIV-infected children may have many years when they have no major health problems and they look, grow and act as other children. After a while the HIV virus may cause certain symptoms. However, some of these signs may also occur in children who have no medical problems at all. Or they may occur in children with other immune system problems.
Some of the more common signs in HIV-infected children include:
- Infections that keep coming back, do not go away or are more severe than in other children
- Swollen glands in more than one area
- White patches in the mouth, on the tongue or in the throat that dont go away
- Repeated fevers
- Slower growth and development than other children the same age
- Diarrhea that continues for several weeks
- Repeated ear infections
- Certain kinds of tumors or cancers
Don’t Miss: Early Stage Of Hiv Infection
How Can I Know If I Have Hiv
You cant tell if someone has HIV just by looking at them, and you may not have any symptoms if youre infected by HIV. The only way to know if you have HIV is to take an HIV test.
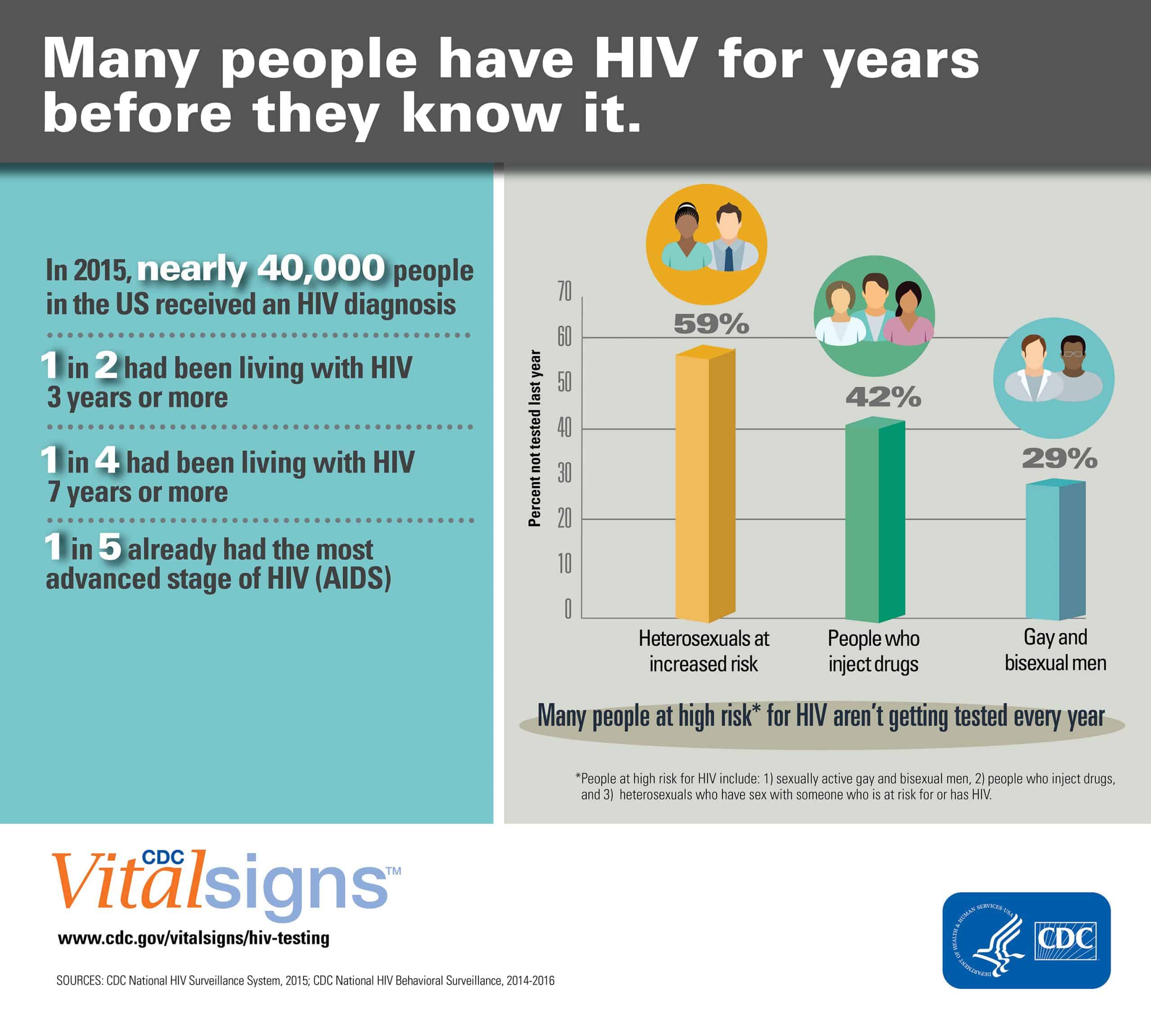
Since nearly 1 out of 7 people with HIV dont know it, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control & Prevention recommends screening people between the ages of 13 to 64 at least once as part of routine healthcare. This test is voluntary and confidential.
Sudden Unexplained Weight Loss
National Human Genome Research Institute
Weight loss is common in people living with HIV during the advanced stages of the disease.
This type of weight loss is more than just a few poundsit’s a sudden, unexplained weight loss of 10% or more of a person’s body weight, in which both fat mass and lean muscle are lost.
The condition is also called HIV wasting syndrome. It’s not as common today as it once was because antiretroviral drugs keep the virus suppressed and allow the immune system to rebuild itself. Wasting is mainly seen in people who have not been treated for HIV.
The exact cause of HIV wasting is unknown, but it is thought that the constant inflammation caused by HIV makes the body burn energy faster and reduces testosterone levels .
Other causes of wasting include malnutrition, chronic diarrhea, tuberculosis, and cancerall of which require urgent diagnosis and treatment.
Recommended Reading: Can Amoxicillin Cure Sinus Infection
How Hiv Infects The Body
HIV infects the immune system, causing progressive damage and eventually making it unable to fight off infections.
The virus attaches itself to immune system cells called CD4 lymphocyte cells, which protect the body against various bacteria, viruses and other germs.
Once attached, it enters the CD4 cells and uses it to make thousands of copies of itself. These copies then leave the CD4 cells, killing them in the process.
This process continues until eventually the number of CD4 cells, also called your CD4 count, drops so low that your immune system stops working.
This process may take up to 10 years, during which time you’ll feel and appear well.
Page last reviewed: 22 April 2021 Next review due: 22 April 2024
Blood Transfusions And Organ Donation

The risk of contracting HIV from a blood transfusion, other blood products, or organ donation is now extremely rare in the United States. All donated blood or blood products in the United States are for several types of bloodborne pathogens, including HIV.
Organ donations are also screened for HIV. Although very rare, its possible for HIV transmission to occur following an organ transplant.
However, testing of organ recipients after surgery can quickly detect transmission so that antiretroviral medications can be started promptly.
Also Check: Can Yeast Infection Spread To Eyes
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
- Am I at high risk for HIV?
- What can I do to reduce my risk of HIV?
- How can I make sure I take my medications correctly?
- What can I do to protect myself from other illnesses?
- How can prevent the spread of HIV?
- What do my test results mean?
- What do my blood counts mean?
- What vaccinations should I get?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Treatments have come a long way since the height of the AIDS epidemic. You have the best chance of living a long life if youre diagnosed early and are able to get on and stick with ART medications. People living with HIV today are able to work, have active social lives and families, and pursue fulfilling relationships. In fact, this can have a positive impact on your well-being.
While weve come a long way with treatments, unfortunately, social stigmas around HIV still persist. In addition to the feelings of fear and uncertainty a new diagnosis can bring, you may wonder how those around you will respond. If youre hesitant to get tested or get treatment, or if you just arent sure what your next steps are, you can reach out to a community organization that specializes in HIV. Remember that you are deserving of support, compassion and high-quality healthcare.
What Tests Diagnose Hiv
There are three types of HIV tests: antigen/antibody tests, antibody tests and nucleic acid tests :
Antigen/antibody tests
Antigen tests look for markers on the surface of HIV called p24. Antibody tests look for chemicals your body makes when it reacts to those markers. HIV antigen/antibody tests look for both.
A healthcare provider will take a small sample of blood from your arm with a needle. The blood is sent to a lab and tested for p24 and antibodies to it. An antigen/antibody test is usually able to detect HIV in 18 to 45 days after exposure.
A rapid antigen/antibody test may also be done with a finger prick to draw blood. Youll need to wait at least 18 days after exposure for this type of test to be able to detect HIV. You may need to take the test up to 90 days after exposure for accurate results.
Antibody tests
These tests look for antibodies to HIV in your blood or saliva. This can be done with a blood draw from your arm, a finger prick or with a stick that you rub on your gums to collect saliva.
An antibody test can take 23 to 90 days after exposure to detect HIV. Antibody tests done with a blood draw can detect HIV sooner than those done with saliva or blood from a finger prick.
Nucleic acid tests
NATs look for the HIV virus in your blood. A healthcare provider will take a small sample of blood from your arm with a needle. The blood then is sent to a lab and tested for HIV.
- Viral hepatitis screening.
Also Check: Can I Get A Kidney Infection Without A Uti
Stage : Acute Hiv Infection
About after HIV enters the body, it can show up as symptoms that last for days or weeks.
During this period, people may experience:
- swollen glands in the throat, groin, or armpits
- sores or ulcers in the mouth or genitals
- nausea, vomiting, or both
This is known as the seroconversion period. Seroconversion is when the body begins to produce antibodies against HIV. This is the bodys natural response to detecting an infection.
In this phase, there tends to be a large amount of HIV in the blood. It replicates rapidly, so the risk of transmitting the virus to others is high.
Not everyone develops symptoms at this stage. Others experience mild flu-like symptoms that largely go unnoticed. This means that people can contract HIV without knowing it, which makes testing very important.
If a person thinks they may have been exposed to HIV, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for advice and to ask them about a preventive medication called post-exposure prophylaxis .
Healthcare professionals can order tests to check for HIV. can detect the virus after 10 days, while others must be taken 90 days after exposure. People often need to take more than one test to get accurate results.
Can Medications Prevent Hiv
There are medications that can help prevent HIV in people who have been exposed or are at high risk for exposure. These include pre-exposure prophylaxis and post-exposure prophylaxis .
Pre-exposure prophylaxis
PrEP is a pill you take every day if you dont have HIV but are at high risk of getting infected.
- You have a sexual partner with HIV.
- You havent consistently used a condom.
- In the past six months, youve been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease .
PrEP is also recommended if you dont have HIV, you inject drugs and at least one of the following is true:
- You inject drugs with a partner who has HIV.
- You share needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
PrEP is not a replacement for other preventative measures. You should still use condoms and avoid sharing needles to inject drugs while taking PrEP.
Post-exposure prophylaxis
PEP uses HIV medicines to try to prevent an HIV infection soon after you are exposed. PEP is for those who dont have HIV or dont know if they have HIV and think theyve been exposed through consensual sex, sexual assault, shared needles , or work.
You must start PEP within 72 hours of exposure and take it every day for 28 days. PEP is only for emergency use and does not replace other precautions, like condom use.
Recommended Reading: What Will A Doctor Prescribe For A Sinus Infection
If I Have Hiv How Can I Keep From Spreading It To Others
The best ways to keep from spreading HIV to others are many of the same ways you use to protect yourself:
- Let sexual partners and anyone you inject drugs with know that you have HIV.
- Follow your treatment plan and dont miss medications. If you have an undetectable viral load, you greatly reduce the risk of transmitting HIV through sex.
- Talk to your sexual partner about taking PrEP.
- Dont share needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
- Limit the number of sexual partners you have.
- If youre pregnant and have HIV, following your treatment plan, including ART medications, can reduce your risk of transmitting the virus to your child.