Should You Treat A Sinus Infection With Antibiotics
Over the past few months Ive seen patient after patient drag themselves to the clinic with coughing, sneezing, headaches and green or yellow nasal discharge, sometimes accompanied by ear and tooth pain. Some people with infection may experience fevers, chills or night sweats signs that the body is fighting a virus or bacteria. These are symptoms I expect as a primary care doctor especially during the spring seasons. They are the telltale signs of sinusitis. But if that sums up symptoms you have, do you need antibiotics? The question may be more complicated than you think.
Each year, more than 30 million Americans endure sinusitis an inflammation of sinus spaces surrounding the nose that makes it difficult to drain fluid that normally flows through the sinuses. Much like a detective weighing clues, us health providers use symptom severity and duration to determine the cause of a patients sickness.
The World Health Organization has called antibiotic resistance one of the biggest threats to global health, saying misuse of antibiotics in humans and animals is accelerating the process.
At a health professionals discretion, antibiotics can be prescribed if a person appears very sick or has any underlying chronic disease that may make them prone to becoming sicker.
You May Like: Waking Up With Sinus Headaches Every Morning
How Do You Catch Ear Infections
Ear infections are often caused by a buildup of bacteria or viruses in the ear canal. This can happen when the Eustachian tubes become blocked due to mucus or fluid buildup, allergies, or a cold. Ear infections can also be caused by swimming in contaminated water and putting objects like cotton swabs in the ear.
What Is A Middle Ear Infection
Middle ear infections are one of the most common childhood problems. Let’s start by talking about infections. An infection happens when germs like bacteria and viruses get inside the body and cause trouble. Germs can get into your ears. The ear is divided into three parts: outer, middle, and inner. When the germs bother your outer ear, it’s called swimmer’s ear.
The middle ear is a small pocket of air behind the eardrum. You have a middle ear infection when germs get into the middle ear and the area fills up with fluid , which contains germ-fighting cells. When the pus builds up, your ear starts to feel like a balloon that is ready to pop, which can really hurt.
Don’t Miss: Can Teladoc Prescribe Antibiotics For Ear Infection
When Is An Ear Infection Considered To Be Chronic
If an ear infection lasts for more than three months, its considered chronic. If chronic ear infections arent treated, it can lead to hearing loss and other serious problems. In children, chronic ear infections can affect their ability to achieve developmental milestones, like walking and talking.
Who Is At Higher Risk For Ear Infections
- Children less than 5 years old, because they have shorter eustachian tubes.
- Children who attend daycare, because they tend to have more colds.
- Children with allergies.
- Children who are exposed to cigarette smoke. Smoke causes inflammation of the eustachian tube, making ear infections more likely.
- Children who were not breastfed. Breast milk has antibodies that help fight infections.
- Babies who are being bottle-fed, especially if they swallow milk while lying too flat. Milk can enter the eustachian tube and cause inflammation, which increases the risk of an ear infection. Children should be held upright while drinking a bottle. When they are old enough to hold their own bottle well, they should be taught to drink from a regular cup and no longer given a bottle.
- Children with cleft palates, as their eustachian tubes are often inflamed.
- Children of First Nations and Inuit descent, though its not clear why.
- Children with Down syndrome.
You May Like: Sinus Infection For 3 Weeks
Signs To Watch Out For In Children
Children between six and eighteen months are at a higher risk of ear infections. If your child is commonly experiencing ear infections around this age, it can lead to developmental to language delays.
As such, you must ensure that you are watching out for the signs of an issue here. If ear infections occur regularly in a child of this age, you must take them to see a doctor so they can get appropriate treatment.
One of the issues is that children during this age are often non-verbal. You might know they are in pain due to their actions or emotions. However, you wont be able to pinpoint the cause of their pain, and they wont be able to tell you.
So, how can you identify if your child suffers from an ear infection?
A child can show several different signs that they are suffering from an ear infection. Some of which are:
-
A problem with balance makes the child stumble or seems more clumsy.
-
Frequent tugging at their ear
Cold And Allergy Remedies
Recent research has questioned the general safety of cough and cold products for children. They are currently banned for use in children under age 4 years. The American College of Chest Physicians recommends against the use of nonprescription cough and cold medicines in children age 14 years and younger.
Also Check: How Hiv Infects Cells Worksheet Answers
Where Can I Find Additional Information About Ear Infections
The NIDCD maintains a directory of organizations that provide information on the normal and disordered processes of hearing, balance, smell, taste, voice, speech, and language.
Use the following keywords to help you search for organizations that can answer questions and provide printed or electronic information on ear infections:
Physical And Structural Injuries In The Face And Ears
Serious complications or permanent physical injuries from ear infections are very uncommon, but may include:
- Structural damage. Certain children with severe or recurrent otitis media may be at risk for structural damage in the ear, including erosion of the ear canal.
- Cholesteatomas. Inflammatory tissues in the ear called cholesteatomas are an uncommon complication of chronic or severe ear infections.
- Calcifications. In rare cases, even after a mild infection, some children develop calcification and hardening in the middle and, occasionally, in the inner ear. This may be due to immune abnormalities.
Don’t Miss: Natural Medicine For Kidney Infection
Final Thoughts On Ear Infections & Treatment
Even though they are uncomfortable, ear infections are relatively common and easy to treat.
If you are in the Starkville, Mississippi region and considered about you or your childs health, be sure to contact us today. We are here for all your needs and concerns.
Ear conditions are usually caused by viruses or bacteria. But the question is, are ear infections contagious? Click here to learn more about them.
How To Prevent Ear Infections
What can kids do to prevent ear infections? You can avoid places where people are smoking, for one. Cigarette smoke can keep your eustachian tubes from working properly.
You also can try not to catch colds. These steps can help:
- Stay away from people who have colds, if possible.
- Wash your hands regularly.
- Try not to touch your nose and eyes.
Good luck staying clear of colds and keeping those pesky germs out of your ears!
Recommended Reading: Antibiotics For Infected Ingrown Hair
Who Is Most Likely To Get An Ear Infection
Anyone can get an ear infection. But youre more likely to get ear infections if you have allergies or other conditions that cause congestion. You may also get more ear infections if you have a weakened immune system and are often sick.
A persons anatomy can also increase their chance of getting an ear infection. Thats why ear infections are more common in young children and in people with birth defects or medical conditions, such as cleft palate or Down syndrome.
What Is An Ear Infection
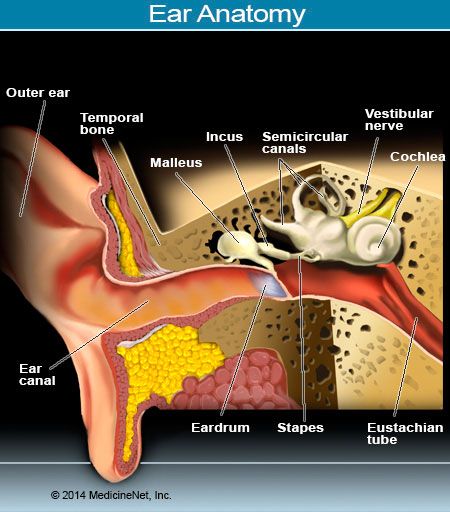
An ear infection, medically referred to as acute otitis media, is an infection that affects the middle ear. It occurs when a blockage of the Eustachian tube – connecting the middle ear with the nasal-sinus cavity – prevents fluid from adequately draining and causes a buildup.
Acute otitis media is considered the most common ear infection and can affect all ages. It is particularly common among children as their Eustachian tubes are shorter and more horizontal than adults.
Middle ear infections can sometimes be mistaken for other conditions that impact the ear or side of the head, like swimmer’s ear. While they generally have similar symptoms, this infection affects the outer ear canal and causes pain when pulling on the earlobe.
Also Check: What Type Of Infection Is Psoriasis
Schedule An Appointment With A Pediatric Ent Specialist Today
Pediatric ENT Associates at Childrens of Alabama specializes in diagnosing head and neck diseases in infants and children. Our highly trained board-certified ear, nose, and throat specialists are leading experts in the field who actively publish medical journals and participate in research. Our team can assess your childs symptoms for an accurate diagnosis and create a personalized treatment plan. Contact us to schedule a consultation and learn more about chronic ear infections in babies.
For your convenience, please fill out the form below to schedule an appointment.
A member of our team will contact you to confirm your desired day and time or offer an alternative day and time that accommodates your schedule.
Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media
In some severe cases after eardrum rupture, perforation may lead to ongoing discharge, which is pus-like. This drainage is often called otorrhea. When this happens, the bacteria involved are most commonly P. aeruginosa or S. aureus. This infection may also spread into the mastoid bone and usually requires injectable antibiotic treatment and sometimes surgery.
Don’t Miss: Medication For Yeast Infection During Pregnancy
Some Steps You Can Take
Whether your sinus infection turns out to be viral or bacterial, you can help to ease your symptoms early on with supportive sinus care:
If your symptoms arent improving after one week, its important to see your doctor. If a bacterial infection is suspected, youll probably need to take an antibiotic to clear up the infection and prevent further complications.
If your infections occur more frequently, and your doctor really wants to establish if they are bacterial or viral, your Otolaryngologist or ear, nose and throat doctor can sample the snot from your nose when youre infected and send it to a laboratory to know for sure.
Note: Antibiotics wont help a viral infection, and taking an antibiotic unnecessarily can do more harm than good. You risk possible side effects and increase your chances of developing antibiotic resistance, which can make future infections harder to treat, says Dr. Sindwani. So its important to wait and see how long your symptoms last.
How Long Are You Contagious With A Sinus Infection
People with a viral sinus infection cant spread the illness to others, but they could pass along virus. catching this from someone who has it will make you more likely for an outbreak as well- contagious up until 2 weeks after symptoms go awayThe passage states that people experiencing Viral Sinonasal Disease cannot infect other individuals due in part because there are no signs or symptoms associated with being infected.
Also Check: When To Use Antibiotics For Sinus Infection
Read Also: Yeast Infection Resistant To Diflucan
Are Ear Infections Contagious In Cats
Ear infections are generally not contagious for humans or other pets, with one exception: those caused by parasites. Parasites like ear mites are highly contagious for other cats in the household. If one cat is affected, talk to your veterinarian about preventative treatment measures for your other cats.
Is Ear Infection Infectious
Ear infections dont carry any risk of spreading. However, viral and bacterial conditions that cause an ear infection may spread between people and. There are three kinds of ear ailments:
- External Ear infection. This is commonly called the swimming ear.
- Labyrinthitis. This is an inflammation of the ears inner part occasionally caused by an infection.
- Middle Ear Disease. This is also called Otitis media. Its the most prevalent kind of ear infection, particularly in children.
Viruses or bacteria may cause ear infections, usually manifest in an ears middle. It could result from an illness like the common flu or cold. Certain diseases are highly infectious. They can spread between people or through the skin.
Influenza, In particular, can be spread through droplets produced by people who speak, sneeze, or cough. You could be infected if infected droplets fall into your mouth or breathe in. It could increase the chance of contracting an ear infection.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Treat A Kidney Infection At Home
Specific Antibiotics Used For Acute Otitis Media
Amoxicillin, a penicillin type of antibiotic, is generally recommended for first-line treatment of AOM. The combination drug amoxicillin-clavulanate is an alternative option. Children who are allergic to penicillin drugs will be prescribed a different antibiotic.
Children who do not respond within 48 to 72 hours to initial treatment with amoxicillin may be given a course of amoxicillin-clavulanate or ceftriaxone. Alternative treatments are ceftriaxone or clindamycin, which may also be accompanied by a different cephalosporin antibiotic.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- How can I keep my child comfortable at night with the pain of an ear infection?
- Is there drainage with an ear infection?
- What is the difference between an ear infection and swimmers ear?
- Is my child a candidate for ear tubes?
- What are the risks and benefits of surgically inserting tubes inside my childs middle ear?
- Should my child get regular hearing tests if they have frequent ear infections?
Don’t Miss: What Is A Infection Control
Living With An Ear Infection
If your child suffers from several ear infections each year, youll want to look out for symptoms every time they have a stuffy nose or congestion.
Never stick anything in your childs ear to relieve the pain of an ear infection, to remove the tubes or remove a foreign object. See your childs doctor to have it removed.
Hearing Loss And Speech Or Developmental Delay
Severe cases of recurrent acute otitis media or persistent otitis media with effusion may impair hearing for a period of time. But the hearing loss is not substantial or permanent for most children.
Hearing loss in children may temporarily slow down language development and reading skills. However, uncomplicated chronic middle ear effusion generally poses no danger for developmental delays in otherwise healthy children.
Rarely, patients with chronic otitis media develop involvement of the inner ear. In these situations, hearing loss can potentially be permanent. Most of these patients will also have problems with vertigo .
Read Also: Oral Antibiotics For Kidney Infection
Causes Of Eustachian Tube Blockages
- Viral infections: Common colds and flu are the biggest triggers, but other upper respiratory infections can also cause the Eustachian tubes to swell.
- Allergies: Pollen, food, or animal dander allergies may obstruct the Eustachian tubes. In some instances, exposure to smoke, fumes, and various airborne toxins may cause the Eustachian tube to swell, leading to ear infections.
- Bacteria: Only cause ear infections in rare circumstances when your immune system is compromised, typically after a viral infection or allergic reaction. This can damage the middle ear and could trigger high fevers and hearing loss. Common ear infection-causing bacteria are contagious and could result in an ear infection if transmitted from one person to another.
How Can I Prevent My Child From Getting An Ear Infection
- Wash your childs hands and your own often to keep germs away.
- If possible, breastfeed your baby.
- Avoid bottle-feeding your baby when they are lying down. Never put your baby to bed with a bottle.
- Transition your baby from a bottle to a cup by 1 year of age.
- Dont smoke, and keep your child away from any second-hand smoke. Exposure to smoke can increase the risk of ear infections.
- Ensure your child gets the pneumococcal vaccine .
- Ensure your child gets a flu shot every year.
- If your child has had many ear infections, try reducing the use of pacifiers . Using a pacifier may increase the risk of repeated ear infections.
Also Check: Is Aids A Viral Infection
What Causes Sinus Infections
The most common cause of sinusitis are viral respiratory infections that lead to swelling and irritation of the sinuses, the most frequent being the common cold.
Other ways to contract a sinus infection include:
- Nasal polyps, or small growths in the lining of the nose, that may be asymptomatic but block the normal sinus pathways
- Any structural change to the nasal cavity, such as a deviated septum or history of sinus or nose surgery
- Hay fever causing swelling to the noses lining, usually during common allergy seasons
While sinus infections are common and most adults will experience one over their lifetimes, there are outside influences that can lead to more frequent cases of sinusitis.
Risk factors for an increased chance of a sinus infection include:
Recommended Reading: Is Advil Cold And Sinus Gluten Free
Side Effects Of Antibiotics
- The most common side effects of nearly all antibiotics are gastrointestinal problems, including cramps, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Allergic reactions can occur with all antibiotics, but are especially common with penicillin drugs. These reactions can range from mild skin rashes to rare but severe, even life-threatening, anaphylactic shock.
- Some drugs, including certain over-the-counter medications, interact with antibiotics. Parents should tell the doctor about all medications their child is taking.
Also Check: How To Diagnose Viral Infection
Treatment Of An Ear Infection
Most episodes of infection in the ear will heal by themselves without the need for medical intervention. However, your physician may wish to observe your symptoms for indications of improvement over the time of a few days or a couple of weeks.
Physicians typically recommend a wait-and-see method for infants and children with moderate ear pain to track symptoms for no more than 48 hours.
If your symptoms do not improve, Your doctor might suggest antibiotic therapy or ear drops for the ear . Surgery could suggest removing excess fluid from the middle of the ear if you have chronic or severe cases.