Antiretroviral Treatment And The Hiv Lifecycle
Antiretroviral treatment for HIV combines several different types of drugs, each of which targets a different stage in the HIV lifecycle. This means that the replication of HIV is stopped on multiple fronts, making it very effective.
If taken correctly, it keeps the immune system healthy, prevents the symptoms and illnesses associated with AIDS from developing, and means that people can enjoy long and healthy lives.
If someone doesnt take their treatment correctly or consistently , the level of HIV in their blood may increase and the drugs may no longer work. This is known as developing drug resistance.
Primary Cell Isolation And Culture
Primary human CD4+ T cells were isolated from peripheral blood by density gradient centrifugation over Lympholyte-H and negative selection using the Dynabeads Untouched Human CD4 T Cells kit according to the manufacturers instructions. Purity was assessed by flow cytometry for CD3 and CD4 and routinely found to be 95%. Cells were activated using Dynabeads Human T-Activator CD3/CD28 beads according to the manufacturers instructions and cultured in RPMI supplemented with 10% FCS, 30 U/ml recombinant human IL-2 , 100units/ml penicillin and 0.1 mg/ml streptomycin at 37°C in 5% CO2.
Proteins And Pathways Regulated By Hiv In Primary T Cells From Multiple Donors
Inter-individual variability is known to affect gene expression during T cell activation . Accordingly, to identify reproducible HIV targets, we analysed primary human CD4+ T cells from three further donors. In each case, mock-infected cells were compared with HIV-infected cells selected using AFMACS 48 hr post-infection . Aside from APOBEC3 proteins, we recently discovered the PPP2R5A-E family of PP2A phosphatase regulatory subunits to be degraded by diverse Vif variants, spanning primate and ruminant lentiviruses . To formally document Vif-dependent changes in primary T cells, both wildtype and Vif-deficient viruses were therefore included. Whilst some donor-dependent differences were apparent, most sample-sample variability was accounted for by HIV infection , and all accessory protein substrates from Figure 2CD and Figure 2figure supplement 1B were significantly depleted by WT HIV . In total, we quantitated 8789 cellular proteins across nine different conditions, of which 650 were significantly regulated by HIV infection and are summarised in an interactive filter table .
Proteins regulated by HIV in primary T cells.
Pathways regulated by HIV in primary T cells.
Read Also: Is There Anything Over The Counter For Ear Infection
Students Color Each Structure And Answer Questions Related To The Model
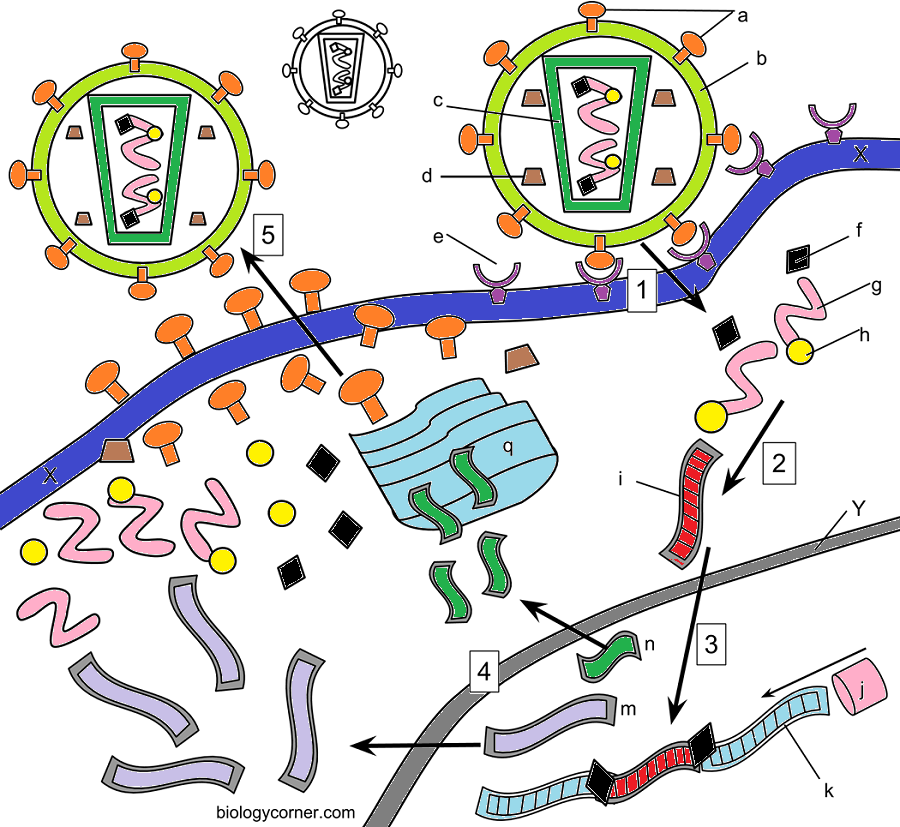
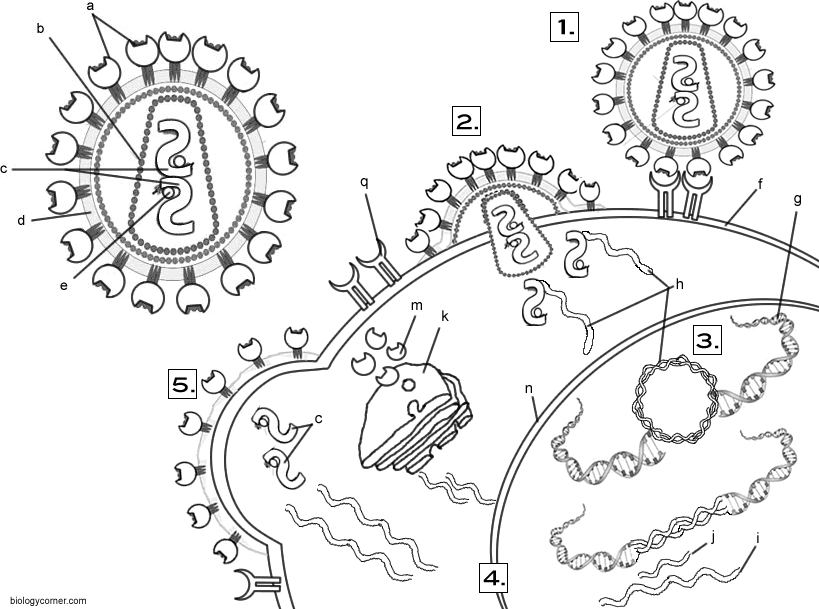
How hiv infects cells coloring worksheet answers. Once infected the T-Helper cell turns into an HIV replicating cell. Answer key and coloring guide to the HIV Worksheet students read about how HIV infects the cell and color a diagram on the life cycle of a virus. A more extensive review of the immune system is available as a Click and Learn resource.
Free Viruses Lesson Plans Labs Worksheets Activities. This chapter provides an overview of the immune system and its associated cells. Students answer introductory questions about bacteria and viruses.
Start studying chapter 3 cells and tissues. The cytoskeleton supports and shapes the cell positions and transports organelles provides strength assists in cell division and aids cell. Once infected the T-Helper cell turns into an HIV replicating cell.
Explain the role of each of the following in HIV infectionprotease assembles the viruses from the proteinsreverse transcriptase converts viral RNA to DNACD4 receptors where the virus fuses with the T helper cells RNA polymerase assembles RNAintegrase fuses viral DNA with host. There are typically 1 million T-cells per one milliliter of blood. Students read about how HIV infects cells answer 3 questions and then color the virus cell parts for 15 keywords.
Students read about how HIV infects cells answer 3 questions and then. The answer key for this activity is located at Teachers Pay Teachers for 125. The video is available for streaming from PBS or Amazon.
Biologycornercom Plant Cell Coloring Answer Key : How Hiv Infects Cells
Biologycorner.com Plant Cell Coloring Answer Key : How HIV Infects Cells – Answer Key by … : How does the shape of a plant cell differ from that of an animal cell?. Animal and plant cell coloring worksheet answers key, we have prepared this post well for you to read and retrieve information from it. Here are some very interesting suggestions about plant cell coloring sheet answer key : Animal cell coloring key animal cell model colouring pages page. Our website always gives you hints for seeing the highest quality pix content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening articles and images that fit your interests. All living things consist of tiny cells, the basic units of life.
Color each part of the cell its designated color. Types of chemical bonds worksheets answer key. Animal cell coloring the answer key to the cell coloring worksheet is available at teachers pay teachers.payments help support biologycorner.com. Cells alive plant cell worksheet answer key with plant and animal cell worksheets choice image worksheet math for kids. Don’t forget to bookmark cell membrane coloring worksheet answer key using ctrl + d or command + d .
Don’t Miss: What Can I Take For Sinus Infection While Breastfeeding
Plant Cell Coloring Answer Key
If you are using mobile phone, you could also use menu drawer from browser. All living things consist of tiny cells, the basic units of life. This is the answer key to the plant cell coloring, which includes a sample cell and answers to the questions. · students may need to use their book or other resources to identify parts. Learn about the most important organelles and structures of the plant cell along with the function of major organelles. Plant and animal cells labeled graphics / brain anatomy diagram quiz, cell membrane coloring worksheet answer key and pogil biology answer key meiosis are some. What question does the endosymbiotic theory attempt to answer? Don’t forget to bookmark cell membrane coloring worksheet answer key using ctrl + d or command + d . How does the shape of a plant cell differ from that of an animal cell? The animal and plant cell labeling key from animal and plant cells worksheet, source:biologycorner.com. Name two things found in a plant cell that are not found in an animal cell: Biologycorner com plant cell coloring. Color each part of the cell its designated color.
X 680 Pixel Type Jpg Download
Don’t forget to bookmark cell membrane coloring worksheet answer key using ctrl + d or command + d . Animal and plant cell coloring worksheet answers key, we have prepared this post well for you to read and retrieve information from it. Students may use their textbook or other. Where do eukaryotic cells come from? Www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/cell_color_plant_key.html this is the answer key to the plant cell coloring, which includes a sample cell and answers to the questions. Cell membrane from cell membrane coloring worksheet answer key, source:biologycorner.com. Biologycorner com animal cell coloring. Plant cell coloring page with labels biology corner. Learn about the most important organelles and structures of the plant cell along with the function of major organelles. Biologycorner.com animal cell coloring key : If you’re searching for biologycorner.com plant cell coloring answer key topic, you have visit the ideal blog. Hopefully fill the posts artikel animal and plant cell coloring worksheet answers key, we write this you can understand.alright, happy reading. Plant cell coloring answers page pages key sheet answer.
Tell the cell what to do b. · students may need to use their book or other resources to identify parts. Plant cell coloring . Lets water pass in and out d. Lets molecules pass in and out c.
Read Also: What Is A Tooth Infection Called
The Animal And Plant Cell Labeling Key From Animal And Plant Cells Worksheet Source: Biologycornercom
If you’re searching for biologycorner.com plant cell coloring answer key topic, you have visit the ideal blog. Lets molecules pass in and out c. Gives the plant structure and support 3. This is the answer key to the plant cell coloring, which includes a sample cell and answers to the questions. I am here to help you find the answers you need quickly so that you can spend less time studying and more time pursuing your passions! Animal and plant cell coloring worksheet answers key, we have prepared this post well for you to read and retrieve information from it. Plant cell coloring . Name two things found in a plant cell that are not found in an animal cell: Where do eukaryotic cells come from? Www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/cell_color_plant_key.html this is the answer key to the plant cell coloring, which includes a sample cell and answers to the questions. Plant cell coloring coloring pages magnificent sheet answer key. Answer key to the animal cell coloring which includes a sample cell and answers to the discussion questions. Color each part of the cell its designated color.
How Do Toxins Enter Cells
The toxins bind to receptors on the surface of susceptible cells and enter them by endocytic uptake. With the exception of pore-forming protein toxins, which compromise the permeability barrier of the target cell plasma membrane, the bacterial toxins act catalytically to modify substrates within mammalian cells.
You May Like: Can Sinus Infection Make Your Head Feel Weird
Virus Vs Bacteria: Any Difference In Symptoms
Symptoms usually reflect the area of the body infected, and the infecting organism. For example, a bacterial infection of the skin may cause a discharge, swelling, pain and redness in a certain area, whereas a viral infection, such as hepatitis C may cause abdominal pain, joint pain, nausea or vomiting, and yellowing of the skin or eyes.
Some illnesses can be caused by either a virus or bacteria, for example pneumonia, meningitis, or diarrhea, and symptoms may be similar, reflecting the body trying to rid itself of the infecting organism, and may include:
- Coughing
Comprehensive Analysis Of Recognised And Novel Vif Targets In Primary T Cells
As predicted, both APOBEC3 and PPP2R5 family proteins were depleted in primary CD4+ T cells infected with WT, but not Vif viruses . Vif-dependent depletion of PPP2R5A-E causes a marked increase in protein phosphorylation in HIV-infected CEM-T4 T cells, particularly substrates of the aurora kinases . AURKB activity is enhanced by activation loop auto-phosphorylation at threonine 232 , antagonised by PP2A-B56 . Accordingly, a marked increase in AURKB T232 phosphorylation is seen in CEM-T4s transduced with Vif as a single transgene . We therefore confirmed depletion of PPP2R5D by immunoblot of AFMACS-selected primary T cells and, as a functional correlate, observed increased AURKB phosphorylation .
Vif-dependent cellular targets in primary T cells.
Besides these known substrates, we also noted differential regulation of several other proteins in primary T cells infected with WT vs Vif viruses . Modest changes in PPP2R1A, PPP2R1B and PPP2CA and PPFIA1 and SGO1 are likely to be secondary to destabilisation of PP2A by PPP2R5 depletion, or reflect proximity of the holoenzyme to the Vif-cullin E3 ligase complex . Conversely, DPH7 and FMR1 are not known to interact physically with PP2A, and show more profound and consistent depletion . We therefore suspected these proteins to be novel Vif substrates.
Read Also: Chances Of Getting Hiv From Infected Needle
Proviruses Generated Are More Difficult To Induce Posing A
The table shows which patient harbored each of these expanded clones, how many times the different integrations sites were isolated, and the fraction of the infected. Proviruses generated are more difficult to induce, posing a. Knowing how this occurs at the molecular level can help us find. What exactly happens when you get an hiv infection? Vodicka, ginger lucero, tatyana m. And slowly feeding fragments of the same sentence which. Hiv infects helper t cells by means of a protein embedded in its envelope called gp120. This image shows the hiv drug maraviroc grabbing hold of ccr5 in an inactive conformation that prevents hiv from using the. Hiv is a virus that damages the immune system. Hiv will slowly reduce the number of these cells. Human immunodeficiency virus presents a complex knot for scientists to unravel. During hiv infection, cd4 t cells in lymphoid tissues initiate a highly inflammatory form of cell death that helps cripple the immune system. The researchers believe the finding is an important lead on how to preserve the immune systems of people infected with the virus that causes aids.
S Of Virus Infections
A virus must take over a cell to replicate. The viral replication cycle can produce dramatic biochemical and structural changes in the host cell, which may cause cell damage. These changes, called cytopathic effects, can change cell functions or even destroy the cell. Some infected cells, such as those infected by the common cold virus , die through lysis or apoptosis , releasing all the progeny virions at once. The symptoms of viral diseases result from the immune response to the virus, which attempts to control and eliminate the virus from the body, and from cell damage caused by the virus. Many animal viruses, such as HIV , leave the infected cells of the immune system by a process known as budding, where virions leave the cell individually. During the budding process, the cell does not undergo lysis and is not immediately killed. However, the damage to the cells that HIV infects may make it impossible for the cells to function as mediators of immunity, even though the cells remain alive for a period of time. Most productive viral infections follow similar steps in the virus replication cycle: attachment, penetration, uncoating, replication, assembly, and release.
Recommended Reading: Infected Sweat Gland Home Remedy
What Are The 4 Main Ways Viruses Cause Tissue Damage
Direct cell damage and death from viral infection may result from diversion of the cells energy, shutoff of cell macromolecular synthesis, competition of viral mRNA for cellular ribosomes, competition of viral promoters and transcriptional enhancers for cellular transcriptional factors such as RNA.
Design And Construction Of The Hiv
AFMACS-based magnetic selection requires the high-affinity 38 amino acid streptavidin-binding peptide to be displayed at the cell surface by fusion to the N-terminus of the truncated Low-affinity Nerve Growth Factor Receptor . Cells expressing this marker may be selected directly with streptavidin-conjugated magnetic beads, washed to remove unbound cells, then released by incubation with the naturally occurring vitamin biotin . To engineer a single round HIV reporter virus encoding SBP-LNGFR, we considered three settings in the proviral construct: fused to the endogenous Env signal peptide or as an additional cistron, downstream of nef and either a P2A peptide or IRES. We used Env-deficient pNL4-3-Env-EGFP as a backbone and, since increased size of lentiviral genome is known to reduce packaging efficiency , tested each approach in constructs from which EGFP was removed and/or the 3 long terminal repeat truncated. Further details relating to construct design are described in the Materials and methods and Supplementary file 1.
Don’t Miss: Natural Remedy For Infection In Urinary Tract
What Happens To Organelles When A Virus Attacks A Cell
Then the viral genome hijacks the host cells machinery, forcing it to replicate the viral genome and produce viral proteins to make new capsids. Next, the viral particles are assembled into new viruses. The new viruses burst out of the host cell during a process called lysis, which kills the host cell.
Stages Of The Hiv Lifecycle
Binding and fusion
HIV attaches to a T-helper cell. It then fuses to it and releases its genetic information into the cell.
The types of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called fusion or entry inhibitor drugs because they stop HIV from entering the cell.
Reverse transcription and integration
Once inside the T-helper cell, HIV converts its genetic material into HIV DNA, a process called reverse transcription. The new HIV DNA then enters the nucleus of the host cell and takes control of it.
The types of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called NRTIs , NNRTIs and integrase inhibitor drugs.
Transcription and translation
The infected T-helper cell then produces HIV proteins that are used to produce more HIV particles inside the cell.
Assembly, budding and maturation
The new HIV is put together and then released from the T-helper cell into the bloodstream to infect other cells and so the process begins again.
The type of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called protease inhibitor drugs.
Don’t Miss: Can I Go To Urgent Care For Kidney Infection
How Hiv Infects Cells
Ingeneral, viruses have very small genomes which means they can encode a very limitednumber of their own proteins. For this reason, most viruses must use the proteinsprovided by their host in order to reproduce and make more viruses. In a way, virusesare parasitic, they bring very little with them and steal what they need fromthe host cell. Because they cannot reproduce on their own, viruses are not consideredliving organisms, they are simply genetic information, either DNA or RNA packagedwithin a protein coat. HIVinfects a particular type of immune system cell, the T Helper Cell. Once infected, the T-Helper cell turns into an HIV replicatingcell. There are typically 1 million T-cells per one milliliter of blood. HIV willslowly reduce the number of these cells until the person develops the diseaseAIDS.
Causes Or Mode Of Infection
The HIV infects the macrophages in the blood. Once they infect, the viral RNA enters the host cell and produces DNA with the help of reverse transcription. This viral DNA, then integrates into the host genome and produces multiple RNA copies by the process of transcription. These RNAs then form multiple copies of the virus and continue the infection in the same way.
At the same time, HIV also enters the T lymphocytes and continues the same set of events as it does in macrophages. This leads to a decrease in the number of helper T lymphocytes. Thus, the immunity of the body is considerably compromised. The immunity is lowered to such an extent that the infected person suffers from even minor infections, which is one of AIDS characteristic symptoms. Other symptoms include bouts of fever, diarrhoea and significant weight loss.
Read Also: Common Urinary Tract Infection Antibiotics