Middle Ear Infections In Children
Acute Otitis Media
An inflammation in the middle ear is known as “otitis media.” AOM is a middle ear infection caused by bacteria in the middle ear fluid trapped by a Eustachian tube that is not working well. AOM may develop during or after a cold or the flu. With AOM:
- Middle ear infections are extremely common in children younger than 3. But they are infrequent in adults.
- In children, ear infections often recur, particularly if they first develop in early infancy.
- AOM symptoms improve within 48 to 72 hours with or without antibiotic treatment in most children. There does not appear to be any risks of complications for at least the first 2 to 3 days.
- Even after symptoms subside, fluid may persist in the middle ear for weeks to months after AOM onset.
Otitis Media with Effusion
OME occurs when fluid, called an effusion, becomes trapped behind the eardrum in one or both ears. In chronic and severe cases, the fluid is very sticky and is commonly called “glue ear.” With OME:
- Fluid is present. But there is no infection.
- There is usually no pain. Sometimes the only clue that it is present is a feeling of stuffiness in the ears, which can feel like “being under water.”
- Hearing may be temporarily impaired in children. But most children will not have long-term hearing loss.
Chronic Otitis Media
How Should I Take Amoxicillin And Clavulanate Potassium
Take amoxicillin and clavulanate exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Follow all directions on your prescription label and read all medication guides or instruction sheets.
Amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium may work best if you take it at the start of a meal.
Take the medicine every 12 hours.
Do not crush or chew the extended-release tablet. Swallow the pill whole, or break the pill in half and take both halves one at a time. Tell your doctor if you have trouble swallowing a whole or half pill.
You must chew the chewable tablet before you swallow it.
Shake the oral suspension before you measure a dose. Use the dosing syringe provided, or use a medicine dose-measuring device .
amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium can affect the results of certain medical tests. Tell any doctor who treats you that you are using this medicine.
Use this medicine for the full prescribed length of time, even if your symptoms quickly improve. Skipping doses can increase your risk of infection that is resistant to medication. Amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium will not treat a viral infection such as the flu or a common cold.
Store the tablets at room temperature away from moisture and heat.
Store the liquid in the refrigerator. Throw away any unused liquid after 10 days.
What Is An Ear Infection
There are different types of ear infections. Middle ear infection is an infection in the middle ear.
Another condition that affects the middle ear is called otitis media with effusion. This condition occurs when fluid builds up in the middle ear without causing an infection. Otitis media with effusion does not cause fever, ear pain, or pus build-up in the middle ear.
Swimmers ear is an infection in the outer ear canal. Swimmers Ear is different from a middle ear infection. For more information, visit Swimmers Ear .
You May Like: Best Over The Counter Medicine For Ear Infection For Adults
How Does A Doctor Diagnose A Middle Ear Infection
The first thing a doctor will do is ask you about your childs health. Has your child had a head cold or sore throat recently? Is he having trouble sleeping? Is she pulling at her ears? If an ear infection seems likely, the simplest way for a doctor to tell is to use a lighted instrument, called an otoscope, to look at the eardrum. A red, bulging eardrum indicates an infection.
A doctor also may use a pneumatic otoscope, which blows a puff of air into the ear canal, to check for fluid behind the eardrum. A normal eardrum will move back and forth more easily than an eardrum with fluid behind it.
Tympanometry, which uses sound tones and air pressure, is a diagnostic test a doctor might use if the diagnosis still isnt clear. A tympanometer is a small, soft plug that contains a tiny microphone and speaker as well as a device that varies air pressure in the ear. It measures how flexible the eardrum is at different pressures.
What If My Ear Infection Doesnt Go Away After Antibiotics
If you or your child finish your course of antibiotics, but it seems like the ear infection hasnt gone away, make an appointment with your doctor. Theyll help figure out whats going on and what to do next. Theres a chance that your doctor may prescribe a different type of antibiotic to see if it works better.
Its also possible that the infection is gone but the symptoms arent. This can happen if theres still fluid trapped in the ear, causing a plugged-up feeling, pain or hearing loss. Most of the time the fluid in ears drains within a couple of weeks, but sometimes it sticks around longer.
You May Like: How Can People Know If They Are Infected With Hiv
How Can I Prevent Future Ear Infections
Ear infections generally come after another illness caused by viruses or bacteria. Anything you can do to keep from getting sick or boost your immune system, should also help reduce your chance of ear infections. Here are ways to keep yourself and your family healthy:
Ear infection? Were ready to help.
Who Can And Cannot Take Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin can be taken by most adults and children.
Find out more about giving amoxicillin to children on the Medicines for Children website.
Amoxicillin is not suitable for everyone. To make sure amoxicillin is safe for you, tell your doctor if you:
- have ever had an allergic reaction to amoxicillin or penicillin or any other medicine
- have liver or kidney problems
- have recently had, or are due to have, any vaccinations
Also Check: Can A Uti Lead To A Yeast Infection
Antibiotics For Ear Infections In Adults
If otitis media is characteristic for children, external and internal ear infections are most commonly seen in adults. Cephalexin is considered one of the most effective antibiotics in the treatment of otitis. The severity of the main otitis media symptoms, like pain, inflammation and itching, reduce already on the second day of the antibiotic administration.
Amoxicillin is effective against highly resistant bacteria that cause ear infections. The antibiotic from Penicillins class relieves the basic symptoms of otitis in 7-10 days.
Zithromax is suitable for those, who are experiencing an acute allergy to penicillin. It is an Azithromycin-based drug. The dose of Zithromax 500 mg per day, divided into two doses, is enough to get rid of ear infections symptoms within 3-5 days.
Ciprofloxacin is the most prescribed antibiotic in the treatment of acute inflammatory forms of internal otitis. Ciprofloxacin of 500 mg taken just for a week relieves the symptoms of otitis media.
Cephalexin is suitable for the treatment of acute and chronic forms of external otitis, when pus appears at the inflammation site. To get rid of ear infections, patients should take 250-500 mg of Cephalexin per day, divided into 2 or 4 doses.
You will need a total of 5-10 days to get rid of the main otitis media symptoms with Cefdinir. This antibiotic, just like Cephalexin, belong to the Cephalosporins group. Cefdinir should be taken at a dose of 600 mg once a day .
Who Shouldnt Use Ear Drops
Ear drops can be helpful when treating an ear infection, but there are times when you shouldnât use them. For example, if you or your child has a perforated eardrum, you should avoid the use of certain ototoxic ear drops because fluid from the drops can get deep into the ear and cause more problems.
You May Like: Does Hiv Infect B Cells
What Happens If My Child Keeps Getting Ear Infections
To keep a middle ear infection from coming back, it helps to limit some of the factors that might put your child at risk, such as not being around people who smoke and not going to bed with a bottle. In spite of these precautions, some children may continue to have middle ear infections, sometimes as many as five or six a year. Your doctor may want to wait for several months to see if things get better on their own but, if the infections keep coming back and antibiotics arent helping, many doctors will recommend a surgical procedure that places a small ventilation tube in the eardrum to improve air flow and prevent fluid backup in the middle ear. The most commonly used tubes stay in place for six to nine months and require follow-up visits until they fall out.
If placement of the tubes still doesnt prevent infections, a doctor may consider removing the adenoids to prevent infection from spreading to the eustachian tubes.
Treatment For Otitis Media With Effusion
Otitis media with effusion is fluid behind the middle ear . It usually resolves on its own without treatment, especially when it follows an acute ear infection. Antibiotics are not helpful for most cases of OME.
Clinical practice guidelines for OME recommend the following treatments:
- Watchful Waiting for OME. The child is typically monitored for the first 3 months. If OME lasts longer than 3 months, a hearing test should be conducted. Even if OME lasts for longer than 3 months, the condition generally resolves on its own without any long-term effects on language or development. The doctor will re-evaluate the child at periodic intervals to determine if there is risk for hearing loss.
- Drug Treatment. Antibiotics, decongestants, antihistamines, and corticosteroids do not help and are not recommended for routine management of OME. Antibiotic ear drops are helpful for treating ear infections that may occur in children with tympanostomy tubes. Topical antibiotics work better than oral antibiotics for treating the discharge that can occur with this type of infection.
- Surgery. Ear tube insertion may be recommended when fluid builds up behind your child’s eardrum and does not go away after 3 months or longer. Fluid buildup may cause some hearing loss while it is present. However, most children do not have long-term damage to their hearing or their ability to speak even when the fluid remains for many months.
Tonsillectomy is not recommended for OME treatment.
Recommended Reading: How Do Doctors Treat Sinus Infections
What Causes An Ear Infection
An ear infection usually is caused by bacteria and often begins after a child has a sore throat, cold, or other upper respiratory infection. If the upper respiratory infection is bacterial, these same bacteria may spread to the middle ear if the upper respiratory infection is caused by a virus, such as a cold, bacteria may be drawn to the microbe-friendly environment and move into the middle ear as a secondary infection. Because of the infection, fluid builds up behind the eardrum.
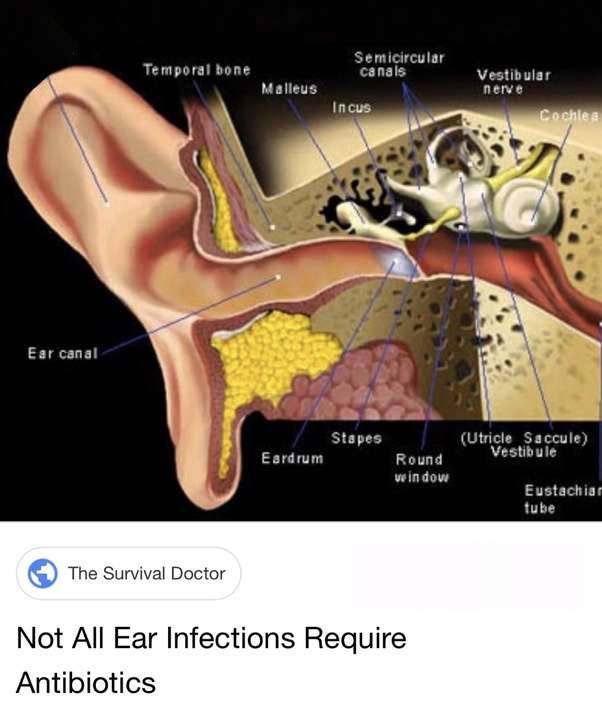
The ear has three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. The outer ear, also called the pinna, includes everything we see on the outsidethe curved flap of the ear leading down to the earlobebut it also includes the ear canal, which begins at the opening to the ear and extends to the eardrum. The eardrum is a membrane that separates the outer ear from the middle ear.
The middle earwhich is where ear infections occuris located between the eardrum and the inner ear. Within the middle ear are three tiny bones called the malleus, incus, and stapes that transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. The bones of the middle ear are surrounded by air.
The inner ear contains the labyrinth, which help us keep our balance. The cochlea, a part of the labyrinth, is a snail-shaped organ that converts sound vibrations from the middle ear into electrical signals. The auditory nerve carries these signals from the cochlea to the brain.
Dangers Of An Unresolved Dental Abscesses
Leaving an abscess untreated will lead to serious medical complications in addition to severe pain. The infection will spread to other parts of your body, including your brain and nearby organs.
A dental abscess infection that travels to the brain is very difficult to treat because of the blood-brain barrier. Its also common for infections to spread into the sinuses.
An infection in your teeth or gums might indicate that you have heart health problems. Researchers believe gum disease is linked to heart disease and heart attack risk.
The infection can also spread to the surrounding bones. Facial bones are especially intolerant to infection. There is a high risk that bone removal will be needed to stop the further spread of the infection.
Even if you have a mild abscess, it can spread and weaken the bones, which creates problems in the future for your teeth.
An untreated abscess also poses a risk for tooth loss. Usually, a root canal and crown are enough to save the affected tooth. However, left untreated, theres a high likelihood your dentist will need to pull the tooth.
One of the most serious issues linked to untreated dental abscesses is . This is an infection in the bloodstream and it puts your entire body at risk.
If the abscess is not treated in time and it ruptures, the infection can spill into your blood and circulate throughout your body. and requires IV antibiotic treatment and long-term hospitalization.
Summary
Recommended Reading: How To Get Over An Ear Infection
Symptoms Of Ear Infections
- The main symptom is an earache.
- Younger children will cry, act fussy or have trouble sleeping because of pain.
- About 50% of children with an ear infection will have a fever.
- Complication: In 5% to 10% of children, the eardrum will develop a small tear. This is from the pressure in the middle ear. The ear then drains cloudy fluid or pus. This small hole most often heals over in 2 or 3 days.
Why Do Kids Get So Many Ear Infections
The NIH points to several reasons why kids are more likely to get ear infections:
- Childrens eustachian tubes are smaller and more level than those of adults. This means its harder for fluid to drain from the ear, so if a childs tubes get blocked by mucus from another respiratory infection, fluid may not drain properly.
- Childrens immune systems are still developing so it can be harder for them to fight infections.
- In children, if bacteria gets trapped in the adenoids , it can cause a chronic infection that gets passed to the eustachian tubes and middle ear.
Read Also: Get Prescription For Yeast Infection Online
Types Of Ear Infections
The most common type of ear infection is called acute otitis media .
AOM infections
AOM is more common in children because they have smaller eustachian tubes. Located between the middle ear and upper throat, these tubes are responsible for fluid drainage.
If this fluid doesnt drain, a buildup and infection may occur. Fluid trapped in the middle ear behind your eardrum may also cause:
Other common infections
Other common types of ear infections include:
- Otitis media with effusion . The infection has cleared up, but fluid may still be stuck in the middle ear.
- Chronic otitis media with effusion . Fluid continues to build up on a recurring basis despite the lack of infection. This chronic condition can lead to serious side effects, such as hearing loss .
- Swimmers ear : occurs in the outer ear when water becomes trapped and promotes bacterial growth in the ear canal.
Otitis Media In Adults
Otitis media is another name for a middle ear infection. It means an infection behind your eardrum. This kind of ear infection can happen after any condition that keeps fluid from draining from the middle ear. These conditions include allergies, a cold, a sore throat, or a respiratory infection.
Middle ear infections are common in children, but they can also happen in adults. An ear infection in an adult may mean a more serious problem than in a child. So you may need additional tests. If you have an ear infection, you should see your healthcare provider for treatment. If they happen repeatedly, you should see an otolaryngologist or an otologist .
What are the types of middle ear infections?
Infections can affect the middle ear in several ways. They are:
Who is more likely to get a middle ear infection?
You are more likely to get an ear infection if you:
- Smoke or are around someone who smokes
- Have seasonal or year-round allergy symptoms
- Have a cold or other upper respiratory infection
What causes a middle ear infection?
The middle ear connects to the throat by a canal called the eustachian tube. This tube helps even out the pressure between the outer ear and the inner ear. A cold or allergy can irritate the tube or cause the area around it to swell. This can keep fluid from draining from the middle ear. The fluid builds up behind the eardrum. Bacteria and viruses can grow in this fluid. The bacteria and viruses cause the middle ear infection.
Don’t Miss: How To Help A Tooth Infection At Home
How Do I Know If My Child Has An Ear Infection
Unfortunately, young children are often unable to communicate their discomfort, forcing parents to identify symptoms via a process of deduction. Most ear infections are preceded by a normal cold. Children may have a runny nose with clear drainage that begins to turn yellow or green at the first signs of infection. Ear infections can also cause many other symptoms usually a combination of at least two of the following:
- Fussiness and irritability, often appearing suddenly
- Grasping or pulling at the ear
- Interruptions in sleep patterns
- Drainage from the ear, often tinged with blood or pus