How Long Does It Take To Show Symptoms Of Hiv
The human immunodeficiency virus is a virus that attacks your bodys immune system. Left untreated, it can lead to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome . Early diagnosis is key to slowing down disease progression.
Symptoms may vary from person to person, but knowing the early symptoms that could present can help you get diagnosed and treated as soon as possible.
This article will discuss the various stages of HIV, how symptoms may present, how testing works, and what to expect if you test positive for the virus.
Verywell / Danie Drankwalter
Who Does Hiv Affect
Its a myth that HIV only infects certain people. Anyone can get HIV if theyre exposed to the virus. Having sex without a condom or sharing needles to inject drugs are the most common ways that HIV spreads.
Some populations are statistically more affected by HIV than others. Groups disproportionately affected by HIV include:
- People who identify as gay, bisexual and men who have sex with men .
- Certain races such as people who are Black or Hispanic.
- Those who exchange sex for money or other items are also at high risk for HIV infection.
While these arent the only populations impacted by HIV, its important to consider that they face unique barriers to accessing preventative care, getting tested, and receiving comprehensive treatment. Homophobia, racism, poverty, and social stigmas around HIV continue to drive inequities and keep people from accessing high-quality healthcare.
How Can I Take Care Of Myself While Living With Hiv
Its very important to take your medications as prescribed and to make sure you dont miss appointments. This is called treatment adherence.
If you miss medications, even by accident, HIV can change how it infects your cells , potentially causing your medications to stop working. If your schedule prevents you from taking medications on time or making it to appointments, talk to your healthcare provider.
Recommended Reading: The Miriam Hospital Hiv/std Clinic
Recommended Reading: Wisdom Teeth Infection After Removal
Can Neurological Complications Develop In Individuals Treated With Antiretroviral Therapy
Even when HIV is well controlled with ART, many infected individuals still develop HIV-associated neurological and cognitive difficulties. This is because many drugs used to combat HIV cannot cross the protective layer called the blood-brain barrier and enter the brain, and even those that can may not completely control the virus in the brain. Antiretroviral drugs can also become toxic after long-term use and cause neurological side effects.
When Is Hiv Contagious
During the clinical latency stage, a person with HIV experiences fewer symptoms. However, they can still transmit the virus to others.
According to the CDC, a person with an undetectable viral load cannot transmit HIV to another individual. This is because HIV treatment suppresses the virus, leaving a low presence of the virus in the blood.
When HIV is not detectable in a test, it is not transmissible.
Don’t Miss: Dr On Demand Ear Infection
Serum Testing For Antigen And Antibody
Patients with suspected acute human immunodeficiency virus infection should undergo serum testing for HIV antibody and HIV antigen using HIV nucleic acid amplification, HIV p24 antigen, fourth-generation enzyme-linked immunoassay , or polymerase chain reaction testing for viral load. Beware of false-positive HIV viral load test results . For more information, see Rapid Testing for HIV and Laboratory Assays in HIV Infection.
What Else Should I Know
Treatment has improved greatly for people with HIV. By taking medicines and getting regular medical care, HIV-positive people can live long and healthy lives.
People with HIV need a medical care team for the best treatment and support.
If you or someone you know has HIV or AIDS it is important to:
- goes to all doctor visits
- takes all medicines exactly as directed
- goes for all follow-up blood tests
- understands what HIV/AIDS is and how it spreads
- is physically active, gets enough sleep, and eats well
Find more information at:
Read Also: Can A Man Give A Woman A Urinary Tract Infection
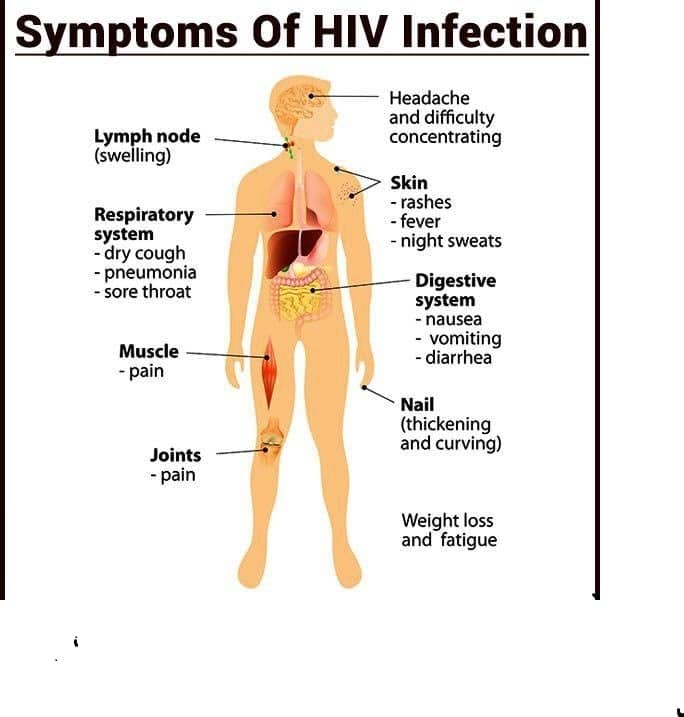
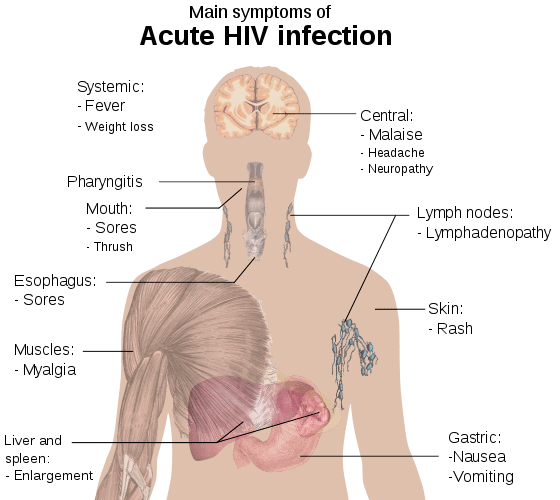
Early Signs And Symptoms Of Hiv
How long does it take to show symptoms of HIV? Some people experience flu-like symptoms at the start of an HIV infection. These early HIV symptoms usually develop within 2-4 weeks in an infected person and may last anywhere from a few days to a few weeks. This early stage of the viral infection is known as an acute HIV infection.
Possible early symptoms include:
Itâs worth keeping in mind that such early symptoms can also be caused by other health conditionsânot just HIV. In short, if youâre experiencing these symptoms, it doesnât necessarily mean that you have HIVâwhich is why STI testing and consulting with your healthcare provider can be helpful next steps to take.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Aids
Having an infection with the HIV virus does not automatically mean that the patient has AIDS. As the HIV virus infects more and more CD4 cells and makes more copies of itself, the patients immune system gets overwhelmed and begins to falter. When the immune system breaks down due to HIV infection, opportunistic infections like fungal infections, pneumonias, and cancers can occur. When this level of HIV infection occurs, it is called AIDS .
Some of the signs and symptoms of progression of HIV to AIDS are:
Read Also: Over The Counter One Day Yeast Infection Pill
What Is Acute Hiv Infection
There are three stages of HIV infection:
- Stage 1:Acute HIVinfection
- Stage 2:Chronic HIV infection
Acute HIV infection is the first stage of the infection. Usually within two to four weeks of infection, two-thirds of those with HIV will experience flu-like symptoms. These symptoms may last for several days or even weeks. However, some people may experience no symptoms at all.
In this stage, there is a large amount of HIV in your blood, which is known as the viral load. Studies have noted incredibly high viral loads during the acute stage, meaning you are more contagious at this time.
Dhhs Guidelines For Antiretroviral Agents
Current Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in HIV-1Infected Adults and Adolescents, published by US Department of Health and Human Services, recommend starting antiretroviral therapy for all individuals when infection is diagnosed, regardless of stage of infection, as long as barriers to therapy do not exist. Considerations are as follows:
-
The goal of treatment should be the suppression of plasma HIV RNA to below detectable levels
-
Testing for plasma HIV RNA levels and CD4 count and toxicity monitoring should be performed
-
If therapy is initiated before drug-resistance test results are available, a ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitorbased regimen should be used, because clinically significant resistance to protease inhibitors is less common than resistance to non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase and integrase inhibitors in antiretroviral therapynaive persons who harbor drug-resistant virus.
Read Also: Meds To Treat Yeast Infection
Treatment Of Acute Hiv Infection
Antiretroviral treatment of chronic HIV infection is well supported and widely recommended. ART for acute HIV infection is controversial. However, treating acute HIV infection has several theoretical advantages, as follows :
-
To relieve symptoms in some symptomatic patients
-
To halt viral evolution at a time of minimal viral diversity, prior to viral adaptations to specific host immune responses
-
To protect developing immune responses from the deleterious effects of sustained HIV viremia
-
To reduce the viral set-point
-
To limit the latent pool of infection
Several studies have shown no benefit for short-term combination antiretroviral therapy during acute infection. However, a 2006 retrospective study found that an initiation of combination therapy within 2 weeks of HIV seroconversion was associated with sustained viral load and CD4 cell count benefits for up to 72 weeks after termination of therapy.
In 2007, another group found that in patients who received 3 months of antiretroviral therapy, the subsequent CD4 cell count decline over 3 years was slower than in patients who did not receive acute therapy. When antiretroviral therapy was started later than 2 weeks after antibody seroconversion, however, patients had a persistent but decreasing CD4 T cell count benefit and a loss of the viral load benefit by week 72 after discontinuation of treatment.
CD4 cell counts appear to deplete very rapidly during acute HIV infection.
The Most Common Symptoms Of Seroconversion Are:
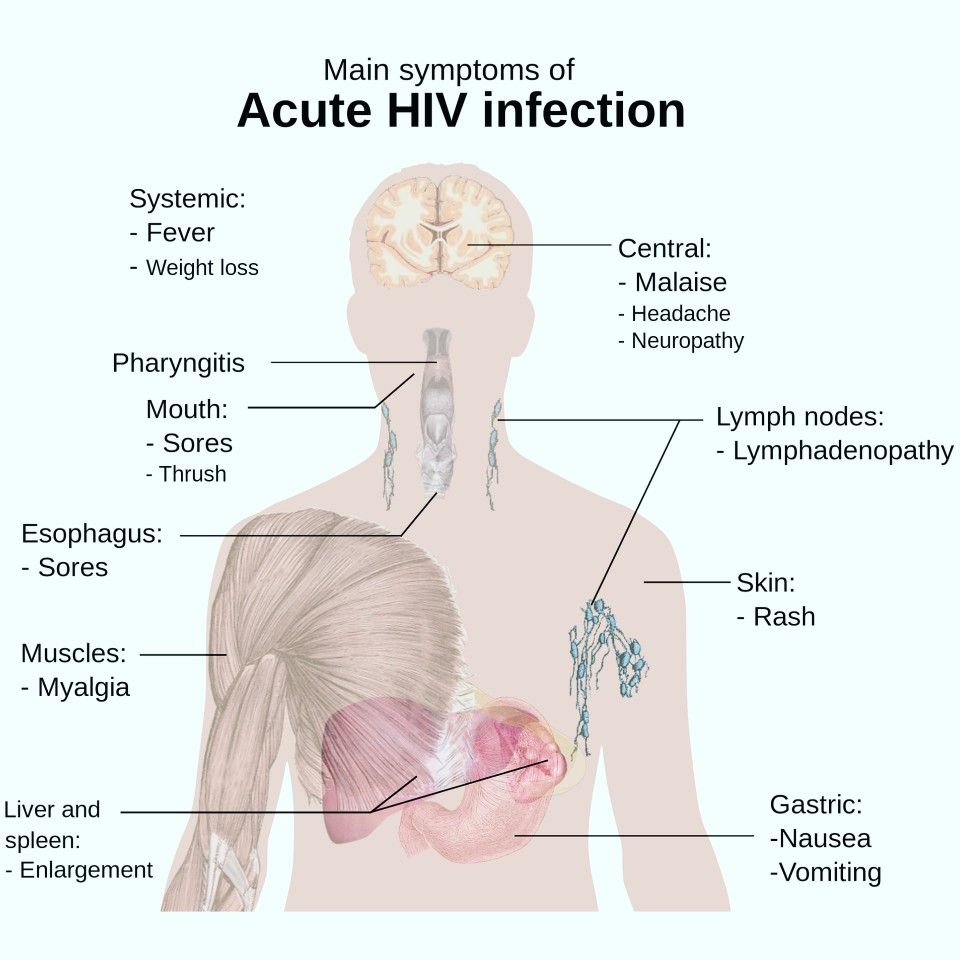
- rash over the body.
Seroconversion is a sign that the immune system is reacting to the presence of the virus in the body. Its also the point at which the body produces antibodies to HIV. Once seroconversion has happened, an HIV test will detect antibodies and give a positive result.
Seroconversion illness happens to most people shortly after infection. It can be severe enough to put someone in hospital or so mild that its mistaken for something like flu although a blocked or runny nose is not usually a symptom.
If you do have HIV, your body fluids are highly infectious during the early weeks and months after transmission. However, once youre on effective treatment and your viral load becomes undetectable you cannot pass on HIV.
It can take up to six months from starting treatment to become undetectable.
Read Also: Chances Of Being Infected With Hiv Without Condom
How Are These Disorders Treated
No single treatment can cure the neurological complications of HIV/AIDS. Some disorders require aggressive therapy while others are treated as symptoms arise.
Neuropathic painchronic pain caused by damage to the nervous systemis often difficult to control. Medicines range from over-the-counter pain killers to anticonvulsant drugs, opiates, and some classes of antidepressants. Inflamed tissue caused by autoimmune or other conditions can press on nerves, causing pain. Such illnesses may be treated with corticosteroids or procedures such as plasma exchange, formally known as plasmapheresis, that clear the blood of harmful substances that cause inflammation.
Treatment options for AIDS- and HIV-related neuropsychiatric or psychotic disorders include antidepressants and anticonvulsants. Psychostimulants may also improve depression and reduce fatigue. Drugs such as cholinesterase inhibitors, which can temporarily improve or stabilize memory and thinking skills in people with dementia, may relieve confusion and slow mental decline. Benzodiazepines may be prescribed to treat anxiety. Psychotherapy may also help some individuals.
Other treatments may include physical therapy and rehabilitation, radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy to shrink cancerous brain tumors that may be related to HIV, antifungal or antimalarial drugs to combat certain bacterial infections associated with the disorder, and penicillin to treat neurosyphilis.
Unlikely Modes Of Transmission
This range of symptoms, typically referred to as acute retroviral syndrome , generally begin within five days of exposure and usually last for around 14 days .
If you have had a recent exposureâsuch as unprotected sex with a partner of unknown statusâthese early signs and symptoms strongly suggest the need for immediate HIV testing.
With that said, not everyone experiences ARS in the same way. The symptoms are non-specific and often mild and are sometimes attributed to other conditions, such as the common cold or simple exhaustion.
According to a 2016 review in Emerging Infectious Diseases, as many as 43% of acute HIV infections are entirely asymptomatic .
Less commonly, some people may develop atypical symptoms of HIV soon after exposure, some of which may be serious. These include tonsillitis, meningitis, herpes zoster , gastric bleeding, and esophageal thrush.
Recommended Reading: Steroid Pack For Sinus Infection
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can live and long and healthy life and will not transmit HIV to your HIV-negative partners through sex.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Its important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
Whats The Outlook For Men Who Have Hiv
Theres no cure for HIV. However, getting a prompt diagnosis and early treatment can slow the progression of the disease and significantly improve quality of life.
HIV is absolutely no longer the death sentence it used to be, says Rymland. I have taken care of patients that were diagnosed in the 80s who have been on treatment and have never been sick. They live full lives. Todays treatment for HIV is easy and effective and, if taken properly, a person can live a long and healthy life and not pass it on to partners.
Indeed, research shows that people with HIV who start treatment before their immune systems are severely damaged might have a nearly normal life expectancy.
You May Like: Activated Charcoal For Tooth Infection
Getting Tested For Hiv
HIV testing is important. Someone living with HIV who isnt getting treatment can still transmit the virus, even if they have no symptoms. Others may pass the virus to others through an exchange of bodily fluids. But todays treatment can effectively eliminate the risk of transmitting the virus to a persons HIV-negative sexual partners.
According to the CDC , antiretroviral therapy can lead to viral suppression. When someone with HIV can maintain an undetectable viral load, they cant transmit HIV to others. The CDC defines an undetectable viral load as fewer than 200 copies per milliliter of blood.
Taking an HIV test is the only way to determine whether the virus is in the body. There are known risk factors that increase a persons chance of contracting HIV. For example, people whove had sex without a condom or shared needles may want to consider seeing their healthcare professional about getting tested.
Is It Safe For Children With Hiv To Receive Routine Immunizations
-
MMR, or measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine, is safe to give to children with HIV, unless they have a severely weakened immune system.
-
DTaP/Td vaccine is safe to give to infants and children with HIV.
-
Hib and Hep B vaccines are safe to give to children with HIV.
-
Hepatitis A and B vaccines are safe to give to HIV-positive children.
-
VZIG should be considered for known HIV-positive children, depending on their immune status.
-
A yearly influenza vaccine is recommended for children with HIV, as well as any individual living in the same household as a child with HIV. There are two types of influenza vaccine children and adults with HIV should receive the shot form of the vaccinenot the nasal spray form, as it contains a live virus. Pneumococcal vaccine can be safely administered to age-appropriate HIV-infected children.
Always consult with your childs doctor regarding immunizations for an HIV-infected child.
Recommended Reading: Tooth Infection And Hip Replacement
How Are Hiv And Aids Treated
Medicines can help people with HIV stay healthy. They can also prevent HIV from progressing to AIDS.
Health care providers prescribe a combination of different medicines for people with HIV and AIDS. They must be taken exactly as prescribed or they wont work. These medicines:
- help keep the number of CD4 cells high
- reduce the viral load of HIV
Regular blood tests will check the number of CD4 cells in the body and the viral load.
If an HIV-positive persons CD4 count gets low, doctors prescribe daily antibiotics. This prevents pneumocystis pneumonia, which happens in people with weakened immune systems.
What Are The Treatments For Hiv/aids
There is no cure for HIV infection, but it can be treated with medicines. This is called antiretroviral therapy . ART can make HIV infection a manageable chronic condition. It also reduces the risk of spreading the virus to others.
Most people with HIV live long and healthy lives if they get and stay on ART. Its also important to take care of yourself. Making sure that you have the support you need, living a healthy lifestyle, and getting regular medical care can help you enjoy a better quality of life.
You May Like: Ear Infection Treatment Adults Over The Counter
Can I Get Pregnant If I Have Hiv
Some people think that HIV hurts your chances of getting pregnant, but this isnt true. If you have HIV and want to become pregnant, talk to your healthcare provider. Together you can make a plan before you try to get pregnant to keep you, your partner and any future children healthy.
HIV can spread to your partner during unprotected sex and to your baby during pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding. Taking ART medications can greatly reduce your risk of transmitting HIV to your baby, especially if you have an undetectable viral load. Your provider may recommend that you dont breastfeed your baby and use formula instead.
Also Check: Can You Stop Hiv Early
How Do I Avoid Passing Hiv On To Someone Else
If you are infected with HIV, the best way to prevent spreading HIV infection to others is to:
- take your medication as prescribed there is a very low risk of passing on HIV if your own infection is under control
- never share needles, syringes and other injecting equipment
If you have HIV infection, you are expected to notify anyone who is at risk of exposure from you:
- Tell people you have had sex or taken drugs with. Your doctor can help you decide who may be at risk and help you to contact them either personally or anonymously.
- Tell anyone you intend to have sex with about your HIV status . This is required by law in some states.
If you are pregnant, talk to your doctor about starting antiretroviral treatment to prevent the infection passing to the baby during pregnancy, childbirth or breastfeeding. Read more about HIV and pregnancy.
Recommended Reading: What Does Hiv Non Reactive Mean
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection Antibiotics Metronidazole