Myth: A Uti Will Go Away On Its Own
Fact: Asymptomatic bacteriuria, which is a UTI without symptoms, could go away without treatment. However, UTIs with symptoms rarely resolve on their own.
If you are experiencing UTI symptoms, like burning, pain or frequency, talk with your health care team about obtaining a urine culture and the right treatment for you.
How Does It Occur
Normally the urinary tract does not have any bacteria or other organisms in it. Bacteria that cause UTI often spread from the rectum to the urethra and then to the bladder or kidneys. Sometimes bacteria spread from another part of the body through the bloodstream to the urinary tract. Urinary tract infection is less common in men than in women because the male urethra is long, making it difficult for bacteria to spread to the bladder.
Urinary tract infection may be caused by a sexually transmitted disease. Sometimes a stone in the urinary tract blocks the flow of urine and causes an infection. In older men, an enlarged prostate can cause a urinary tract infection by keeping urine from draining out of the bladder completely. Infection might also be caused by the use of a catheter used to drain the bladder or by urethral stricture, which is a narrowing of the urethra by scar tissue from previous infections or surgical procedures.
You may be more likely to have a UTI if you have diabetes or another medical problem that affects the immune system.
Common Bladder Problems And When To Seek Help
Bladder problems can disrupt day-to-day life. When people have bladder problems, they may avoid social settings and have a harder time getting tasks done at home or at work. Common bladder problems include urinary tract infections, urinary incontinence, and urinary retention.
Some signs of a bladder problem may include:
- Inability to hold urine or leaking urine
- Needing to urinate more frequently or urgently
- Pain or burning before, during, or after urinating
- Trouble starting or having a weak stream while urinating
- Trouble emptying the bladder
If you experience any of these symptoms, talk to your health care provider.
Treatment for bladder problems may include behavioral and lifestyle changes, exercises, medications, surgery, or a combination of these treatments and others. For more information on treatment and management of urinary incontinence, visit Urinary Incontinence in Older Adults.
Recommended Reading: How Hiv Infects Cells Worksheet Answers
Appendix 1 Point Of Care Urine Collection Prior To Urine Culture1
Urine Collection
Upon rising or at any time, collect urine in the C& S container provided.
Labelling:
Packaging:
Storage and Transport:
References:
|
Organism |
The report only includes organisms suspected to be uropathogens . This depends on patient demographics, concentration of the specific organism and the specific laboratory protocol. In urine with multiple organisms, identification may not be performed as it may produce misleading results that are not related to the UTI. |
|
Antibiotic susceptibilities |
The report only includes antibiotics that can be used for UTI. The specific antibiotics listed depend on the patient demographics, documented antibiotics and allergies, organism identified, colony count of the organism and the specific laboratory protocol. |
References:
What Is A Uti Anyway
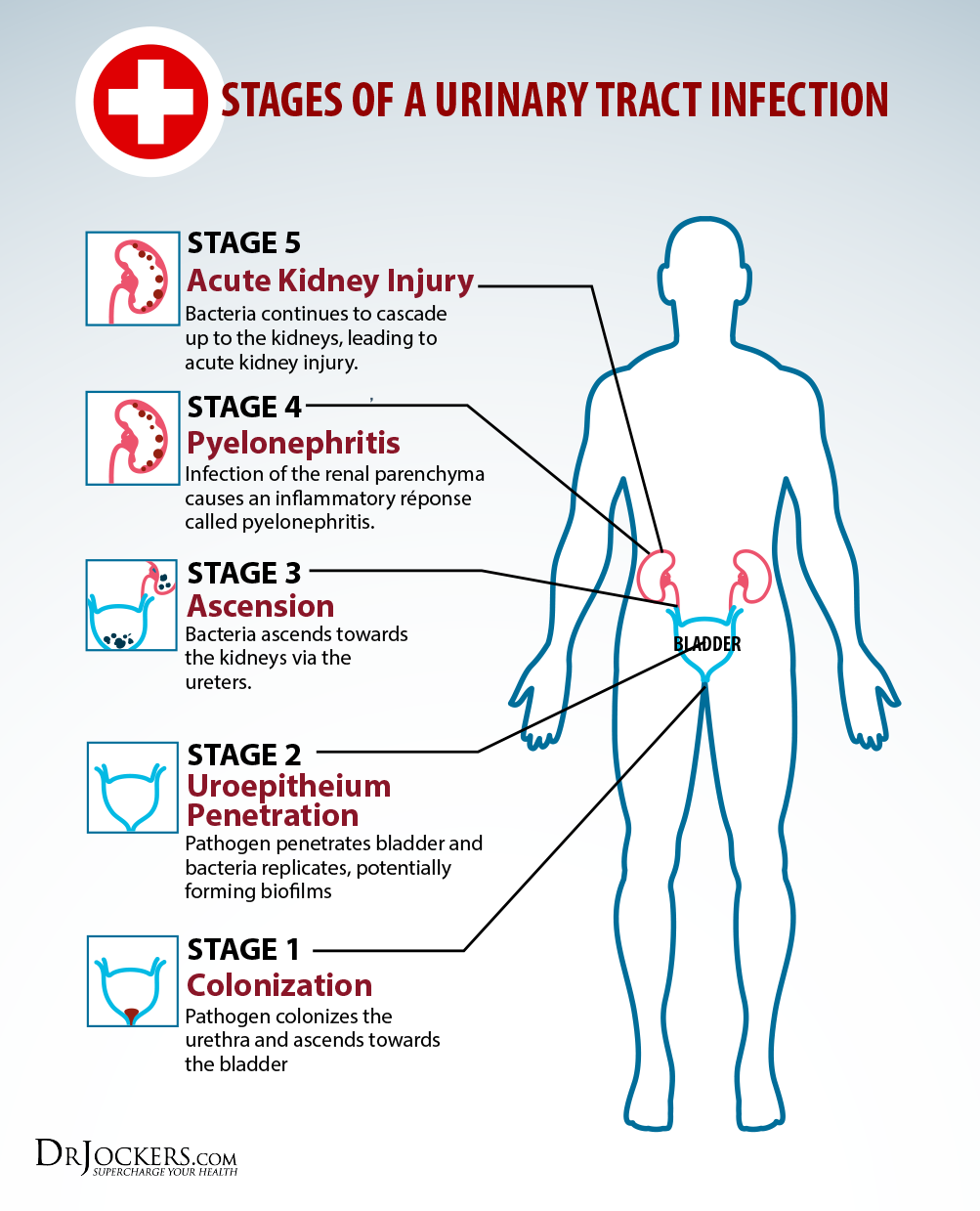
A UTI, or urinary tract infection, happens when bacteria enters into any part of your urinary system, which includes the urethra, the bladder, the kidneys or the uterus. If not flushed out of the system, the bacteria can lead to an infection, or a UTI.
If youve ever had a UTI , you probably havent forgotten the symptoms. UTIs are very unpleasant, to say the least, and are often accompanied with one or more of the following:
-
A burning sensation when urinating
-
A strong urge to urinate often, usually passing only small amounts of urine at a time.
-
Cloudy and/or strong smelling urine
Dont Miss: Types Of Antibiotics For Bladder Infection
You May Like: Will Amoxicillin Help Kidney Infection
Causes Of The Uti That Isnt
Many women may be familiar with the problems of recurrent/frequent urinary tract infections , or even apparent UTI symptoms for which no bacterial infection can be found. This later condition, which one urologist likes to call The UTI That Isnt can be especially frustrating. Lets talk about the possible causes of The UTI That Isnt.
Urethral SyndromeWhile the symptoms of frequency/urgency/pain are present in almost all true UTIs, 30-50% of patients with these symptoms do not have significant bacteria in their urine . However, many of those without bacteria may have white blood cells in their urine. This likely reflects the presence of other infections which may not be bacterial. The presence of white blood cells, no bacteria, and UTI symptoms is the one common description of urethral syndrome.
Once an organism is identified appropriate medications can be given. In a treatment study for chlamydia of the urethra , researchers determined that women may require longer duration of antibiotic dosing than used for vaginal/cervical chlamydia . If urethral symptoms had been present for three weeks or longer, better cure rates were achieved with six days of azythromycin 500mg/day or fourteen days of doxycycline 100mg/twice a day. For those with Ureaplasma, the best dose was also an extended duration of azithromycin 500mg/day for six days.
Whats the bottom line?
What Can Happen If A Uti Is Not Treated
If treated right away, a UTI is not likely to damage your urinary tract. But if your UTI is not treated, the infection can spread to the kidneys and other parts of your body. The most common symptoms of kidney infection are fever and pain in the back where the kidneys are located. Antibiotics can also treat kidney infections.
Sometimes the infection can get in the bloodstream. This is rare but life-threatening.
Also Check: How To Quickly Treat A Yeast Infection
What Causes Interstitial Cystitis
The exact cause of BPS is not clear. However, there are several ideas about what might cause it.
These include:
- damage to the bladder lining, which may mean pee can irritate the bladder and surrounding nerves
- a problem with the pelvic floor muscles used to control peeing
- your immune system causing an inflammatory reaction
Some people who have been diagnosed with BPS , may have a long-term urinary infection in the bladder, which has not been picked up by current urine tests.
BPS may also be associated with chronic conditions such as fibromyalgia, myalgic encephalomyelitis or chronic fatigue syndrome and irritable bowel syndrome .
Uti Signs And Symptoms In Childrenare Different
UTIs are the second most common type of infection in children, behind ear infections. Unfortunately, early symptoms of UTI in young children are not always apparent. And sometimes there are no UTI symptoms at all, or your child is simply unable to articulate the UTI symptoms he or she is experiencing. When it comes to babies under 2 years old, parents need to tune in to these signs of a urinary tract infection:
- Fever A fever of 104°F or higher may be the sole symptom in babies. Its also the most common symptom of UTI during babys first two years.
- Jaundice Up to 18 percent of babies with prolonged or worsening jaundice also have UTIs. When jaundice occurs one full year after birth, its a strong indicator of UTI.
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Crying while urinating
Meanwhile, older children generally have similar symptoms to adults, including urgency, cloudy urine, and pain during urination. For children whove already been toilet trained, bed-wetting is also a sign of a UTI.
Read Also: How Do You Say Urinary Tract Infection In Spanish
Recommended Reading: Infection Control In Hospital Setting
Over The Counter Medications For Urinary Tract Infections
- Brand names listed as examples do not imply better quality over other brands. Generic equivalents may also exist.
- Use only as directed on the package, unless your healthcare provider instructs you to do otherwise.
- OTCs may interact with other medications or be potentially harmful if you have certain medical conditions. Talk to your pharmacist about options that are right for you.
Whats The Difference Between A Urinary Tract Infection And Bladder Infection
A urinary tract infection is a more general type of infection. There are many parts of your urinary tract. A UTI is a term for an infection that takes place throughout the urinary tract. A bladder infection, also called cystitis, is a specific infection. In this infection, bacteria makes its way into the bladder and causes inflammation.
Not all urinary tract infections become bladder infections. Preventing the spread of the infection is one of the most important reasons to treat a UTI quickly when you have symptoms. The infection can spread not only to the bladder, but also into your kidneys, which is a more complicated type of infection than a UTI.
Recommended Reading: Can Yeast Infections Clear On Their Own
What Is A Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria invade the bladder or kidneys. The bacteria can often be found naturally in our bowels or on our skin, but they are harmless there. However, when they get into the urinary tract, they can cause an infection.
Women in general get more UTIs. This is mainly because the female urethra is shorter, which allows bacteria easier access into the bladder.
Typically a woman may have one UTI per year on average. But some women get them more often. If it occurs about four times a year, its considered a recurrent UTI. An estimated 2% to 10% of women get chronic UTIs, according to a review in the journal Climacteric.
UTIs tend to be more common in older men than younger men. This is likely because UTIs in men are often caused by not completely emptying the bladder. This is often due to an enlarged prostate, a condition common in older men.
UTIs are treated with antibiotics and go away quickly.
Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention

Because it does not present with symptoms, this type of UTI can only be diagnosed through a urine culture examination.
Once the condition is isolated, doctors typically prescribe a single dose antibiotic for UTI.
However, except for cases enumerated above, most people without symptoms do not bother to have this procedure done. However there may be instances when bacteria growth does not require treatment because no worrisome symptoms affect the patients daily activities.
Also Check: How To Take Azo Urinary Tract Defense
Recommended Reading: Antibiotic Drops For Eye Infection
Consider Switching Birth Control
Some older research suggests that certain contraceptives may contribute to the cause of UTIs in some women.
If you use diaphragms, spermicides, or nonlubricated condoms and get frequent UTIs, it may be worth talking to your doctor to find other methods of birth control.
Its not uncommon for UTIs to go away on their own with at-home care and without the use of antibiotics.
Some research estimates that 25 to 42 percent of UTIs can go away on their own. This is usually only common in women with no other health issues.
However, there are some serious risks that can come from leaving a UTI untreated, including pyelonephritis and .
UTIs are painful, but with treatment, you can alleviate an infection and prevent recurrent infections. Talk with your doctor if you have symptoms of a UTI. With proper treatment, you should begin to feel better in a few days.
Take your antibiotics as instructed even after your symptoms improve to prevent complications or a secondary infection.
If the UTI doesnt resolve after antibiotic treatment or you end up with multiple episodes of a UTI, your doctor will likely do further testing.
This could be in the form of:
- urodynamic testing
You may be referred to a urologist, depending on the severity of your UTI or if you have chronic infections.
Certain strains of bacteria can cause UTIs. They can range from mild to severe. The degree of severity depends on multiple factors, including:
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Urinary Tract Food
Patient Groups With Asb And Inadequate Evidence To Guide Management
Evidence to guide management of preoperative ASB before nonurologic procedures is limited. A recent study addressed whether preoperative screening for and treatment of ASB in patients undergoing cardiovascular, orthopedic, or vascular procedures confers benefits.66 Among patients with a preoperative culture, patients with bacteriuria and those without bacteriuria were compared for postoperative complications. Surgical site infection was similarly frequent among patients with bacteriuria versus those without, while postoperative UTI was more frequent among patients with bacteriuria . Among the 54 patients with a positive screening culture, a greater proportion of treated patients developed a surgical site infection compared to untreated patients . However, the findings from this small observational study should be interpreted with caution because of the high likelihood of confounding factors.
Also Check: Can Your Jaw Hurt From A Sinus Infection
Complicated Vs Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection
Persistent or recurrent UTI in adults with anatomically and functionally normal urinary tracts leads rarely, if ever, to renal damage. Therefore, it is important to distinguish between complicated and uncomplicated UTI. Complicated UTI implies infections of urinary tracts which are anatomically or functionally altered . Associated conditions complicating UTI are summarized in . Uncomplicated infections occur mainly in otherwise healthy females with structurally normal urinary tract and intact voiding mechanisms. In contrast, complicating factors put individuals of both genders at a higher risk of developing progressive renal damage, bacteraemia, and urosepsis.
Table 1.
Complicated UTI is a clear contraindication against short-term treatment . In such patients antibiotic therapy is recommended for 26 weeks. Furthermore, for accurate treatment of UTI it is important whether the complicating factor could be eliminated during therapy or whether it persists .
Why Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Usually Doesnt Warrant Antibiotics
Clinical studies overwhelming find that in most people, treating asymptomatic bacteriuria with antibiotics does not improve health outcomes.
A 2015 clinical research study found that treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in women was associated with a much higher chance of developing a UTI later on, and that these UTIs were more likely to involve antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Even for frail nursing home residents, there is no proof that treating asymptomatic bacteriuria improves outcomes, but it does increase the presence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Despite the expert consensus that this condition doesnt warrant antibiotics, inappropriate treatment remains very common. A 2014 review article on this topic notes overtreatment rates of up to 83% in nursing homes.
Is there a role for cranberry to treat or manage urine bacteria?
The use of cranberry juice or extract to prevent UTIs has been promoted by certain advocates over the years, and many patients do prefer a natural approach when one is possible.
However, top quality clinical research has not been able to prove that cranberry is effective for this purpose. In a 2016 study of older women in nursing homes, half were given cranberry capsules daily. But this made no difference in the amount of bacteria or white blood cells in their urine.
A 2012 systematic review of high-quality research studies of cranberry for UTI prevention also concluded that cranberry products did not appear to be effective.
You May Like: Severe Ear Infection In Adults
Does Cranberry Juice Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
Many people say that cranberry juice can help treat, or even prevent, a UTI. Researchers are currently looking into the topic, but havent found a definitive answer yet. Healthcare providers recommend drinking lots of fluids if you have, or have a history of getting, a UTI. Adding a glass of unsweetened cranberry juice to your diet isnt a proven way to prevent a UTI, but it typically wont hurt you either.
What Is A Urine Infection And What Causes It
Most urine infections are caused by germs that come from your own bowel. They cause no harm in your bowel but can cause infection if they get into other parts of your body. Some bacteria lie around your back passage after you pass a stool. These bacteria sometimes travel up the tube called the urethra and into your bladder. Some bacteria thrive in urine and multiply quickly to cause infection.
A urine infection is often called a urinary tract infection by healthcare professionals. When the infection is just in the bladder and urethra, this is called a lower UTI. If it travels up to affect one or both kidneys as well then it is called an upper UTI. This can be more serious than lower UTIs, as the kidneys can be damaged by the infection.
Also Check: Nitrofurantoin Help With Tooth Infection
Check If Its A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a UTI may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
Treatment Of Bladder Urinary Tract Infections
![Urinary Tract Conditions [INFOGRAPHIC] Urinary Tract Conditions [INFOGRAPHIC]](https://www.infectiontalk.net/wp-content/uploads/urinary-tract-conditions-infographic-urinary-tract-urinary-tract.jpeg)
The specific intervention depends on the severity of the symptoms. In many instances, healthy patients who have a urinary tract infection but have no symptoms require no treatment at all. Such asymptomatic UTIs typically resolve within two to three days.
If urinary tract infection symptoms are presentsuch as a burning sensation during urination or an increased need to urinatetreatment usually consists of antibiotic medications, which are prescribed for three to 14 days. They include:
- Trimethoprim: Trimethoprim is the standard treatment for urinary tract infections in otherwise-healthy adults. It is one of the more potent UTI antibiotics, so most patients only require a three-day course. Trimethoprim is generally well-tolerated with few side effects, which generally include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea/constipation or stomach pain.
- Nitrofurantoin: Nitrofurantoin is the second most commonly prescribed antibiotic for bladder UTIs. It usually requires a longer course than trimethroprim , and is usually well tolerated but should not be taken by anyone with kidney disease. Side effects include nausea and vomiting.
- Cephalosporins: Cephalosporins are often used as a first-line of treatment in patients that have upper urinary tract infections involving the ureters or kidneys. It is usually taken for seven to 10 days. Side effects include nausea, vomiting, upset stomach and diarrhea.
You May Like: Infection Control In Healthcare Settings