What Is A Chronic Ear Infection
A chronic ear infection can be caused by an acute ear infection that does not completely go away or repeat ear infections. Acute otitis media is one of the most common types of ear infections. It can become chronic. Otitis media with effusion , which typically occurs in children, can also become chronic.
Otitis media with effusion can occur after an infection has cleared up but fluid remains trapped in the middle ear. When it becomes chronic, it is referred to as chronic chronic otitis media with effusion .
Acute otitis media can also lead to chronic suppurative otitis media , in which ear discharge does not go away or it keeps coming back. CSOM is considered a complication of a middle ear infection. The discharge in CSOM continues to leak out through a hole in the eardrum.
Treating Outer Ear Infections
The outer ear should be carefully cleaned. That should be followed by the application of antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory medications on your ear.
Antibiotics may be prescribed if your doctor determines that the infection is bacterial.
If the infection is fungal, your doctor may prescribe an antifungal medication.
If you have a viral infection, you may simply need to tend to the irritation on your ear and wait for the infection to resolve itself. Depending on the type of virus involved, more specialized treatment may be necessary.
To help prevent an ear infection of any kind, follow these tips:
- Make sure you dry your ears completely after swimming or taking a shower.
- Try quitting smoking, and limit or avoid secondhand smoke when possible.
- Manage your allergies by avoiding triggers and keeping up with allergy medications.
- Wash your hands thoroughly, and try to limit contact with people who have colds or other upper respiratory problems.
- Make sure your vaccines are up to date.
Antibiotics And Other Prescriptions
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , using antibiotics by mouth to treat ear infections may not help certain cases of middle ear infections. Antibiotics are not effective against outer ear and viral infections.
The main treatments for outer ear infections are manual cleanings and ear drops. The type of ear drop will depend on what is causing the infection. In the case of malignant otitis externa, intravenous antibiotics are the primary treatment.
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection Antibiotics Metronidazole
Which Specialties Of Doctors Treat Middle Ear Infections
The majority of children and adults are diagnosed and treated by pediatricians, primary health care doctors, emergency or urgent care medical providers, or other health care professionals. Ear, nose, and throat specialists may be consulted for some individuals.
On rare occasions, a neurologist or neurosurgeon may be needed to treat a severe infection that may extend to other organ systems.
Treating Middle Ear Infections
You may be prescribed antibiotics. Some antibiotics may be taken orally. Others can be applied directly to the site of the infection with ear drops. Medications for pain, such as over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications may also be used to manage your symptoms.
If youre still experiencing cold or allergy symptoms, you may be advised to take a , nasal steroids, or an antihistamine.
Another helpful technique is called autoinsufflation. Its meant to help clear your eustachian tubes. You do this by squeezing your nose, closing your mouth, and gently exhaling. This can send air through the eustachian tubes to help drain them.
Recommended Reading: Homeopathic Remedy For Tooth Infection
What Are The Goals Of Chronic Otitis Media Surgery
The goals of surgery are to:
- First remove all of the infected tissue so that it can be “safe” from recurrent infections.
- Thenrecreate a middle ear space with an intact eardrum.
- Finally, hearing is to be restored.
- This may seem strange that hearing is the last priority, but if the first two priorities are not met, anything that is done to improve hearing will ultimately fail.
- If hearing is restored, but the infection returns, the hearing will be lost again.
- Likewise, if hearing is restored, but the middle ear space is not recreated, the eardrum will re-stick to the middle ear or the ossicles.
How Are Outer Ear Infections Treated
Dr. Wang: Most ENT doctors and primary care physicians will prescribe antibiotic ear drops only. Typically, oral antibiotics are not necessary, and we like to avoid overprescribing them so they continue to work when we actually need them. Occasionally, the opening of the ear may be too inflamed or sticky to get the drops in, so we have to stick a little wick in there to get the drops where they need to go. The provider may prescribe oral antibiotics if the outer ear infection is really severe.
Also Check: Augmentin Antibiotic For Tooth Infection
What’s The Difference Between The Middle Ear Infections We Get As Children Versus The Middle Ear Infections We Get As Adults
Dr. Wang: The underlying causes are usually different. They are more frequent in children because their shorter, more horizontal Eustachian tubes are more likely to get blocked. Also, their adenoids are larger compared to the rest of the throat and can interfere with the opening of the Eustachian tubes. And finally, children’s immune systems are immature and colds and viruses are often passed around day care and school.
Causes Of Ear Infection In Adults
Outer Ear Infection Causes
Swimmer’s ear is frequently caused by bacteria that is usually found in soil and water. Viral or fungal infections are less common. The following conditions can provoke the bacterial growth in your ear:
- Excess moisture in the ear
- Various sensitivity reactions
- Abrasions or scratches in the ear canal
Middle Ear Infection Causes
Most common causes of the middle ear infection are related to swollen or blocked Eustachian tubes, promoting fluids to build up in the middle ear. Examples of such causes are:
- Colds, flu, and sinus infections
- Allergies
- Smoking or inhalation of irritants
- Overgrown or infected adenoids
You May Like: How Do You Get Malware Infections
What Are The Harms Of Fluid Buildup In Your Ears Or Repeated Or Ongoing Ear Infections
Most ear infections dont cause long-term problems, but when they do happen, complications can include:
- Loss of hearing: Some mild, temporary hearing loss usually occurs during an ear infection. Ongoing infections, infections that repeatedly occur, damage to internal structures in the ear from a buildup of fluid can cause more significant hearing loss.
- Delayed speech and language development: Children need to hear to learn language and develop speech. Muffled hearing for any length of time or loss of hearing can significantly delay or hamper development.
- Tear in the eardrum: A tear can develop in the eardrum from pressure from the long-lasting presence of fluid in the middle ear. About 5% to 10% of children with an ear infection develop a small tear in their eardrum. If the tear doesnt heal on its own, surgery may be needed. If you have drainage/discharge from your ear, do not place anything into your ear canal. Doing so can be dangerous if there is an accident with the item touching the ear drum.
- Spread of the infection: Infection that doesnt go away on its own, is untreated or is not fully resolved with treatment may spread beyond the ear. Infection can damage the nearby mastoid bone . On rare occasions, infection can spread to the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord and cause meningitis.
When To Seek Medical Advice
Most cases of otitis media pass within a few days, so there’s usually no need to see your GP.
However, see your GP if you or your child have:
- symptoms showing no sign of improvement after two or three days
- a lot of pain
- a discharge of pus or fluid from the ear some people develop a persistent and painless ear discharge that lasts for many months, known as chronic suppurative otitis media
- an underlying health condition, such as cystic fibrosis or congenital heart disease, which could make complications more likely
Read more about diagnosing middle ear infections
You May Like: Who Can Diagnose A Yeast Infection
Common Symptoms Of Ear Infections
Ear pain is one of the first signs you may have an infection in your ear. Pain can come from swelling in the tissues in and around the ear, as well as from the buildup of pressure on the eardrum. As fluid from the inner and middle ear stop draining naturally, pressure builds against the eardrum. Without treatment, it is even possible for the eardrum to rupture.
Dizziness or vertigo is another sign you may have an ear infection. The delicate structures inside the inner ear are responsible for helping you maintain your balance, so anything that affects the ear will also affect your sense of balance. This dizziness and vertigo can be very frustrating, may cause nausea, and may even prevent you from carrying out daily tasks like driving. In extreme cases, you may not even be able to stand or move about normally due to the extreme disorientation
Unexplained hearing loss is also a common symptom of ear infections. Swelling or a buildup of earwax in the auditory canal can act as an earplug, preventing sounds from reaching the eardrum. Further in, pressure from fluid built up in the middle ear can keep the eardrum from vibrating normally, thus preventing sounds from being transferred deeper into the ear. Finally, swelling in the structures of the inner ear can also prevent sounds from being perceived normally.
What Other Types Of Ear Infections Affect Adults

Dr. Wang: A middle ear infection, or otitis media, is most frequently associated with children, but adults get them as well. This type of ear infection happens when viruses or bacteria get into the middle ear the space behind the eardrum. The middle ear fills with pus or infected fluid. The pus pushes on the eardrum, which can be very painful. Middle ear infections are caused by swelling in one or both of the Eustachian tubes. The Eustachian tubes connect the middle ear to the back of the throat and act as release valves to equalize pressure within the middle ear. When that process is interfered with, that’s when infections can develop.
Also Check: Is There Anything Over The Counter For Ear Infection
Who Is Most Likely To Get An Ear Infection
Middle ear infection is the most common childhood illness . Ear infections occur most often in children who are between age 3 months and 3 years, and are common until age 8. Some 25% of all children will have repeated ear infections.
Adults can get ear infections too, but they dont happen nearly as often as they do in children.
Risk factors for ear infections include:
- Age: Infants and young children are at greater risk for ear infections.
- Family history: The tendency to get ear infections can run in the family.
- Colds: Having colds often increases the chances of getting an ear infection.
- Allergies: Allergies cause inflammation of the nasal passages and upper respiratory tract, which can enlarge the adenoids. Enlarged adenoids can block the eustachian tube, preventing ear fluids from draining. This leads to fluid buildup in the middle ear, causing pressure, pain and possible infection.
- Chronic illnesses: People with chronic illnesses are more likely to develop ear infections, especially patients with immune deficiency and chronic respiratory disease, such as cystic fibrosis and asthma.
- Ethnicity: Native Americans and Hispanic children have more ear infections than other ethnic groups.
Can Adults Still Get Ear Infections
Ear infections and childhood go hand in hand because kids get them so easily. During the early stages of development, their eustachian tubes the passageway between the nose, throat, and ears are small, short, and parallel to the ground, so they dont drain efficiently.
When mucus builds up because of colds or allergies, bacteria set up shop and infect the tissues.
Adults dont get ear infections as frequently as kids do, but that doesnt mean theyre immune to them. Dr. James Lee at Woodstock Family Practice & Urgent Care in Woodstock, Georgia, helps children and adults deal with ear infections and their underlying causes. Heres what you need to know about adult ear infections.
Read Also: Best Remedy For Bladder Infection
It’s Easy To Get The Care You Need
See a Premier Physician Network provider near you.
Though an earache might be something most people remember from childhood, adults are not immune from them.
Ear pain in adults is less likely to be caused by an ear infection than ear pain in children.
In adults, the pain is more likely caused by one of a variety of issues:
- Arthritis of the jaw
- Ear injury from pressure changes
- Hole in the eardrum
- Object stuck in the ear
- Short-term ear infection
- Tooth infection
Symptoms of an earache can include pain, fever, ear drainage, nausea, and vomiting.
When an adult has an earache, its important to treat the root cause of the problem, even if that problem isnt directly related to the ear, such as arthritis of the jaw.
If you experience ear pain that doesnt go away or gets worse within 24 to 48 hours you should call your doctors office.
Also call your doctor if you have severe pain that suddenly stops. This could be a sign that your eardrum has ruptured.
The type of earache you have determines the best treatment:
- For a general earache. Take over-the-counter pain relievers, rest in an upright position instead of lying down, and put a cold pack on the outer ear for 20 minutes
- For ear pain from pressure change. Swallow hard or chew gum
- For earaches caused by other medical issues. Visit your doctor to determine the best treatment on a case-by-case basis. This includes causes such as excess wax buildup, object in ear, sinus infection, sore throat, and tooth infection.
Will Ear Infections Get Better On Their Own
Some ear infections resolve on their own. Often, they get better when the underlying cause goes away. But in some cases, they hang on. If your ear still hurts after your cold clears up or your allergies have calmed down, make an appointment at Woodstock Family Practice & Urgent Care.
If you have the following symptoms, come in right away:
- Severe pain
- Hearing loss
- Fever
When you need urgent care, we offer same-day and walk-in appointments. Dr. Lee may prescribe antibiotics to help you fight the infection, ear drops that go straight to the source, pain relievers, or anti-inflammatories.
More important, he investigates the reason for your ear infections and treats the underlying cause to help you avoid repeat infections.
Left untreated, ear infections can lead to permanent hearing loss, so dont ignore the symptoms. To schedule an appointment, call or book online.
You Might Also Enjoy…
Don’t Miss: How To Fight A Tooth Infection Without Antibiotics
What Are Ear Infections
Ear infections can arise for a variety of reasons and can manifest in many different ways. In adults, ear infections are typically identified by ear pain, fluid draining from the ear, dizziness, and temporary loss of hearing. In children, these infections can also be associated with a fever, fussiness, loss of appetite, and even loss of balance.
Like infections elsewhere in the body, ear infections are caused by the presence of bacteria or viruses inside the ear. Ear infections often occur after upper respiratory infections such as flu, a common cold, or even allergies. Other causes of congestion, stuffiness, and swelling in the nasal passages, including smoking, can contribute to ear infections.
The eustachian tubes are small passages in the head that run from the middle ear to the back of the throat. Normally, these tubes drain fluid from the ear as well as regulate air pressure inside the ear. When these tubes become blocked or obstructed, fluid can build up inside the ear, increasing the chances of infection.
What Do You Suggest For People Who Feel Like There Might Be Moisture In Their Ears
Dr. Wang: You can usually feel it if there’s some water in your ear, right? If you notice that, turn your head to the side and try to shake the water out or let it drain out. You can also place a tissue paper or thin dry cloth around your finger and wipe outside the opening of your ear with your head turned sideways. If you still feel it, or have a history of getting a lot of outer ear infections, use drops to dry out your ears. You can buy Swim-EAR® or other brands over the counter, or you can look up how to make your own by mixing together rubbing alcohol and vinegar. A cool or warm hair dryer may also be effective.
Don’t Miss: Diflucan Dose For Yeast Infection
Spectrum Of Otitis Media
Otitis media is an umbrella term for a group of complex infective and inflammatory conditions affecting the middle ear. All OM involves pathology of the middle ear and middle ear mucosa. OM is a leading cause of healthcare visits worldwide and its complications are important causes of preventable hearing loss, particularly in the developing world.
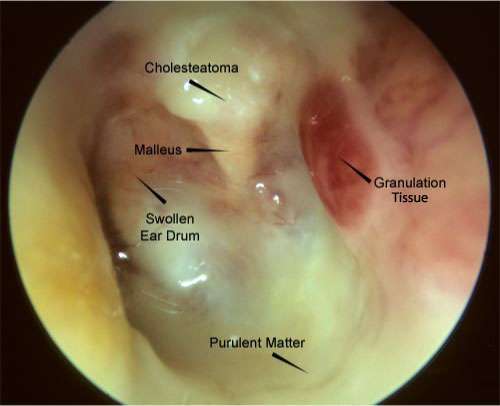
There are various subtypes of OM. These include AOM, OME, chronic suppurative otitis media , mastoiditis and cholesteatoma. They are generally described as discrete diseases but in reality there is a great degree of overlap between the different types. OM can be seen as a continuum/spectrum of diseases:
Symptoms Of Chronic Ear Infections
Someone with a chronic ear infection does not usually have any visible symptoms. However, long-term OME can cause hearing problems and other difficulties, particularly in children. These include:
- delayed responses, or taking a long time to understand speech
- difficulties speaking or reading
- less ability to work independently
Doctors consider OME to be chronic if it lasts for or more.
According to a 2016 guideline, OME usually disappears by itself within 3 months.
They also report that 3040 percent of children experience OME more than once, and 510 percent of episodes last for 1 year or longer.
When someone has CSOM, they have a hole in their eardrum. When the eardrum bursts, it releases tension, so not everyone with CSOM will feel . However, people with AOM or recurrent AOM will likely experience pain.
The symptoms of CSOM include:
- leaking fluid from the ear
- a hole in the eardrum
People with CSOM are unlikely to have a fever.
Chronic ear infections develop from a long-lasting or recurrent acute ear infection. Preventing acute ear infections can help prevent chronic ear infection.
Acute ear infections happen when the eustachian tube, a tube that runs from the middle ear to the back of the throat, becomes clogged.
Children are more likely to be affected by ear infections because these tubes are shorter and narrower, so they become clogged more easily.
Fluid build-up in the middle ear can become infected, which will cause pain and other symptoms.
Causes of ear infections
Also Check: Otc Skin Yeast Infection Treatment