Differences Between Middle Ear Infection And Outer Ear Infection
| Middle ear infection | Outer ear infection |
|---|---|
| Middle ear infection Usually affects children | Outer ear infection Usually affects adults aged 45 to 75 |
| Middle ear infection Caused by viruses like colds and flu | Outer ear infection Caused by something irritating the ear canal, such as eczema, water or wearing ear plugs |
| Middle ear infection Affects the middle ear | Outer ear infection Affects the ear canal |
How Do Ear Infection Antibiotics Work
Ear infections are no fun for anyone.
An ear infection occurs when fluid builds up behind your eardrum in the middle part of your ear and causes swelling . This can lead to significant pain and discomfort.
Since most ear infections are caused by bacteria, its typically best to treat individual cases with antibiotics.
But antibiotic treatment isnt appropriate for every ear infection. There are a variety of factors to consider, including:
Recurring ear infections may also require a different approach.
If youre considering ear infection antibiotics for yourself or a loved one, learn more about how these medications work and how they can be both helpful and possibly harmful.
Ear infections are most prevalent in young children. Theyre often the byproducts of upper respiratory infections.
You or your child might experience other symptoms before the ear infection, including:
If an upper respiratory infection is caused by bacteria, then its possible to have an ear infection at the same time.
An ear infection occurs when bacteria gets trapped in your middle ear. Bacteria known as Hemophilus influenza and Streptococcus pneumoniae are the most common bacterial culprits.
But an ear infection may still occur if you have a viral respiratory illness. As you recover, its possible for bacteria to travel to your middle ear and become trapped, leading to a secondary infection in your ears.
Can Ear Infections Affect Hearing
Fluid buildup in the middle ear also blocks sound, which can lead to temporary hearing problems. Kids having a problem might:
- not respond to soft sounds
- need to turn up the TV or radio
- seem inattentive at school
In kids who have otitis media with effusion, the fluid behind the eardrum can block sound, so mild temporary hearing loss can happen, but might not be obvious.
A child whose eardrum has ruptured might have ringing or buzzing in the ear and not hear as well as usual.
Read Also: Does Zpack Help With Sinus Infection
Causes Of A Middle Ear Infection
Middle ear infections are caused by viruses and bacteria, often resulting from other conditions that can cause blockage and swelling of the eustachian tubes that connect the throat and the middle ear. When this happens, a vacuum is created, allowing germs and fluid from the throat to enter the middle ear. A middle ear infection develops when bacteria or viruses grow in this fluid.
Children are more susceptible to middle ear infections than adults, partly because their eustachian tubes are narrower, so they are more easily blocked. Children also have relatively larger adenoids than adults. These are masses of tissue situated at the point where the nose bends into the throat that are vulnerable to infection, swelling and inflammation ââ¬â when this happens, they can block the eustachian tubes and cause a middle ear infection.
How Is An Ear Infection Diagnosed
Once youre at the doctors office, a medical professional will look inside your ear with an otoscope to determine whether you have an infection.
Typical signs include fluid buildup in the ear canal and middle ear, along with a red and inflamed eardrum.
Depending on the severity of your symptoms, your doctor may recommend waiting a few days to see if your ear infection improves.
Some infections resolve on their own. But if the infection is severe, or if symptoms dont improve after this time, then antibiotics may be warranted.
Chronic fluid buildup without an infection warrants additional testing from an ear, nose, and throat specialist.
Its especially important to diagnose young children so that they dont encounter speech and language delays from loss of hearing.
If your doctor recommends antibiotics to treat a severe ear infection, they will likely recommend an oral treatment, such as amoxicillin .
You May Like: How Do Doctors Treat Sinus Infections
How Is A Middle
Your health care provider will take a medical history and do a physicalexam. He or she will look at the outer ear and eardrum with an otoscope.The otoscope is a lighted tool that lets your provider see inside the ear.A pneumatic otoscope blows a puff of air into the ear to check how wellyour eardrum moves. If you eardrum doesnt move well, it may mean you havefluid behind it.
Your provider may also do a test called tympanometry. This test tells howwell the middle ear is working. It can find any changes in pressure in themiddle ear. Your provider may test your hearing with a tuning fork.
Symptoms Of Adult Ear Infections
According to the National Health Service , people with ear infections often develop mild symptoms that clear up on their own. Some common symptoms include ear pain, difficulty hearing, ear discharge, itchiness, swelling, irritation, or redness around the ear, which develops into scaly skin.
With some ear infections, you might experience nausea, ear drainage, or an unexplained heavy feeling in the ear . However, ear infections can also result in more severe symptoms, including the enlargement or swelling of the lymph nodes in front or behind the ears. This can cause you to be feverish or experience severe ear pain, according to Healthline. Lymph nodes play an active role as part of the immune system, ridding your body of harmful substances, per Healthline.
If you’re battling an inner ear infection, you might also experience unexplained dizziness. Inner ear infections like labyrinthitis affect the cochlea, which sends sound waves and signals to the brain’s language processing areas. According to the NHS, an infection can throw these signals out of sync, confusing your brain and leading to symptoms like loss of balance.
Don’t Miss: Chances Of Getting Hiv From Infected Needle
Can Ear Infections Be Prevented
Some lifestyle choices can help protect kids from ear infections:
- Breastfeed infants for at least 6 months to help to prevent the development of early episodes of ear infections. If a baby is bottle-fed, hold the baby at an angle instead of lying the child down with the bottle.
- Prevent exposure to secondhand smoke, which can increase the number and severity of ear infections.
- Parents and kids should wash their hands well and often. This is one of the most important ways to stop the spread of germs that can cause colds and, therefore, ear infections.
- Keep children’s immunizations up to date because certain vaccines can help prevent ear infections.
Get Discounts On Antibiotics Today
When your child has an ear infection and needs antibiotics, the last thing you want to worry about is whether or not you can afford to pay for the prescription. With Easy Drug Card, you can save up to 80% on your prescriptions. Get Your FREE Pre-Activated RX Discount Card INSTANTLY and begin using it immediately at 65,000+ participating pharmacies nationwide, including most large chain stores like Walgreens, CVS, Rite-Aid as well as local neighborhood pharmacies.
Resources:
1) Johns Hopkins Antibiotic Guide
2) Lexicomp
3) Ear Infection, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 5 May 2021,
4) Swimming and Ear Infections,Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 5 May 2021,
Also Check: What Kind Of Antibiotics Are Used For Urinary Tract Infection
Pain Relievers For Earaches
If you or your child is experiencing an infection, youll likely want relief from the pain fast.
For quick relief, your doctor may also suggest reaching for an over-the-counter pain reliever, with or without the addition of antibiotics.
Acetaminophen or ibuprofen could help, though youll always want to check with your doctor to be sure.
Oral Antibiotics Have Risks
- Oral antibiotics are more likely to cause resistant bacteria outside the ear. When that happens, these medicines will not work as well in the future. Illnesses will be harder to cure and more costly to treat.
- Antibiotic eardrops kill the bacteria faster and more completely than oral antibiotics. Drops dont go into the bloodstream, so more medicine reaches the infection.
Don’t Miss: Will Fluticasone Help Sinus Infection
Causes Of Ear Canal Infection
A variety of bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Staphylococcus aureus, can infect the ear canal. Fungal ear canal infection , typically caused by Aspergillus niger or Candida albicans, is less common. Boils are usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
, are particularly prone to acute external otitis.
Common risk factors for ear canal infection include:
-
Injuring the ear canal while cleaning it
-
Getting water in the ear, particularly while swimming
-
Use of earplugs or hearing aids
-
Getting irritants such as hair spray or hair dye in the ear
Use of cotton swabs to clean the ear is a very common risk factor for ear canal infection. Cotton swabs should not be placed in the ear canal.
Infections In The Middle Ear
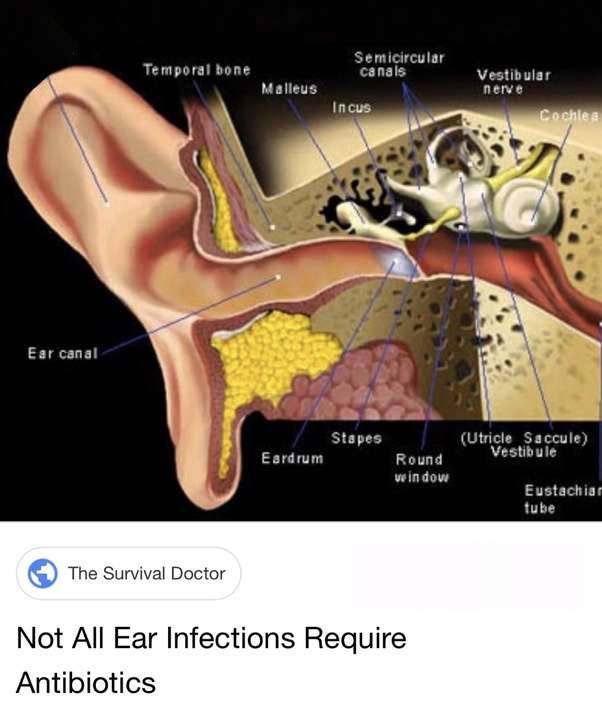
Infections in the middle ear often clear up on their own. Antibiotics make little difference to symptoms, including pain.
Antibiotics might be prescribed if:
- an ear infection does not start to get better after 3 days
- you or your child has any fluid coming out of their ear
- you or your child has an illness that means there’s a risk of complications, such as cystic fibrosis
They may also be prescribed if your child is less than 2 years old and has an infection in both ears.
Recommended Reading: Antibiotics For Uti And Kidney Infection
Ear Infection Home Remedies
There are some home remedies to help your childs ear pain. Ear drops can bring relief, but these should not be used without checking with your childs doctor first. Over-the-counter pain and fever medications such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen are used. However, you should never give aspirin to children. Warm washcloths applied to the outside of the ear may be helpful in reliving some pain. Gargling with salt water may help soothe an aggravated throat and possibly clear the Eustachian tubes. A few drops of warmed olive oil in the ears may soothe ear pain, but it is suggested to speak with your childs doctor beforehand.
Caring For Your Child
- Give your child acetaminophen or ibuprofen for fever, pain, or fussiness. Be safe with medicines. Read and follow all instructions on the label. Do not give aspirin to anyone younger than 18. It has been linked to Reye syndrome, a serious illness.
- If the doctor prescribed antibiotics for your child, give them as directed. Do not stop using them just because your child feels better. Your child needs to take the full course of antibiotics.
- Place a warm cloth on your child’s ear for pain.
- Encourage rest. Resting will help the body fight the infection. Arrange for quiet play activities.
You May Like: Why Am I Getting Sinus Infections All The Time
Why Adults Get Ear Infections
Ear infections are often considered a childhood disease. It almost seems a rite of passage for children to experience repeat ear infections. Then, around the beginning of their teenage years, it often stops entirely. By the time a person hits adulthood, it is quite common to be decades of years removed from the last time he or she experienced an ear infection. It almost seems as though it is impossible for adults to get an ear infection, right? Unfortunately, although not as common in adults as it is in children, it is still possible for adults to suffer an ear infection. In fact, around 20% of ear infections occur in adults. This begs the question, why can adults still get them?
How Adults Get an Ear InfectionAdult ear infections are just like the ear infections a person would have gotten when he or she was a child. Most middle ear infections are caused by either bacteria or viruses. A common cold, the flu, or allergy symptoms that cause congestion and swelling of the nasal passages, throat, and eustachian tubes can sometimes lead to an infection. Anything that makes the nose stuffy has a tendency to cause swelling and blockage of the eustachian tubes. Swelling from colds or allergies can keep the eustachian tubes from opening and this leads to pressure changes and the accumulation of fluid in the middle ear. This pressure and fluid will cause pain and sometimes persistent fluid can lead to an infection.
How Middle Ear Infections Are Treated
Most ear infections clear up within three to five days and don’t need any specific treatment. If necessary, paracetamol or ibuprofen should be used to relieve pain and a high temperature.
Make sure any painkillers you give to your child are appropriate for their age. Read more about giving your child painkillers.
Antibiotics aren’t routinely used to treat middle ear infections, although they may occasionally be prescribed if symptoms persist or are particularly severe.
Read more about treating middle ear infections
You May Like: Can You Get A Yeast Infection From Condoms
When To Seek Medical Advice
Most cases of otitis media pass within a few days, so there’s usually no need to see your GP.
However, see your GP if you or your child have:
- symptoms showing no sign of improvement after two or three days
- a discharge of pus or fluid from the ear some people develop a persistent and painless ear discharge that lasts for many months, known as chronic suppurative otitis media
- an underlying health condition, such as cystic fibrosis or congenital heart disease, which could make complications more likely
Read more about diagnosing middle ear infections
Why Do Kids Get So Many Ear Infections
The NIH points to several reasons why kids are more likely to get ear infections:
- Childrens eustachian tubes are smaller and more level than those of adults. This means its harder for fluid to drain from the ear, so if a childs tubes get blocked by mucus from another respiratory infection, fluid may not drain properly.
- Childrens immune systems are still developing so it can be harder for them to fight infections.
- In children, if bacteria gets trapped in the adenoids , it can cause a chronic infection that gets passed to the eustachian tubes and middle ear.
Read Also: Should You Go To The Doctor For An Ear Infection
Physical And Structural Injuries In The Face And Ears
Serious complications or permanent physical injuries from ear infections are very uncommon, but may include:
- Structural damage. Certain children with severe or recurrent otitis media may be at risk for structural damage in the ear, including erosion of the ear canal.
- Cholesteatomas. Inflammatory tissues in the ear called cholesteatomas are an uncommon complication of chronic or severe ear infections.
- Calcifications. In rare cases, even after a mild infection, some children develop calcification and hardening in the middle and, occasionally, in the inner ear. This may be due to immune abnormalities.
Also Check: Can You Treat Syphilis With Antibiotics
Can You Treat An Ear Infection Without A Doctor

It is possible to treat some types of ear infections without help from a doctor. A middle ear infection may clear up on its own without going to the doctor. Outer ear and inner ear infections may require medical attention depending on the severity of the infection and the bodys ability to fight the infection. Common home remedies and treatments include the use of over-the-counter pain relievers, cold or warm compresses, changes in sleeping positions, and olive oil.
Recommended Reading: How To Tell If My Eczema Is Infected
How Are Ear Infections Treated
Most ear infections go away on their own. You can treat them at home with an over-the-counter pain reliever like acetaminophen , a warm face cloth on the ear, and rest. Your doctor may give you eardrops that can help with pain.
Do not give aspirin to anyone younger than 18.
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. Antibiotics are recommended for children under 6 months old and for children at high risk for complications. But ear infections often get better without them. Talk with your doctor. Whether you use antibiotics will depend on how bad the infection is. For children, it also will depend on the child’s age.
Children may need a follow-up visit in about 4 weeks, even if they feel well. Adults may need one if symptoms get worse.
Minor surgery to put tubes in the ears may help for repeat infections or hearing problems.
Key Points About Ear Infection Remedies
- Ear infections tend to occur in young children, but they can affect anyone.
- Ear infections can either be viral or bacterial. Treating a viral ear infection with conventional antibiotics typically is ineffective and includes undesirable side effects.
- Do ear infections clear up on their own? Yes, they certainly can, especially when you do what you can to boost your or your childs immune system!
7 Natural Remedies for Ear Infections
Don’t Miss: Natural Tooth Pain Relief Infection
What Are The Disadvantages Of Ototopical Antibiotics
Ototopical antibiotics have a few disadvantages as well, which include the following:
Difficult to administer
Direct delivery at the infection site may be difficult or impossible sometimes. The medication may fail to reach the infected area in the middle ear if the ear canal is blocked due to:
- Excessive and hardened earwax
- Block in the ear tubes inserted for fluid drainage from the middle ear
- Swollen or overgrown tissue
Steps must be first taken to clear the blocks before antibiotic administration. Irrigating the ear canal can easily clear a block caused by earwax and other secretions, but an ear tube block and granulation each may require some procedure and other medications.
Inflammation and complications
Ototoxicity is toxicity to the ear from local administration. Ototoxicity can irritate and inflame the mucus membranes of the middle ear. If the antibiotic enters the inner ear, it may lead to:
- Sensitivity reaction
Ototopical antibiotics can cause allergic reactions. Low-grade sensitivity reactions may cause persistent drainage that may be impossible to distinguish from drainage due to infection, making treatment difficult. Some people may also develop cross-sensitivity to related antibiotics.
Absence of systemic effect
Alteration of microenvironment