What Is A Retrovirus
|
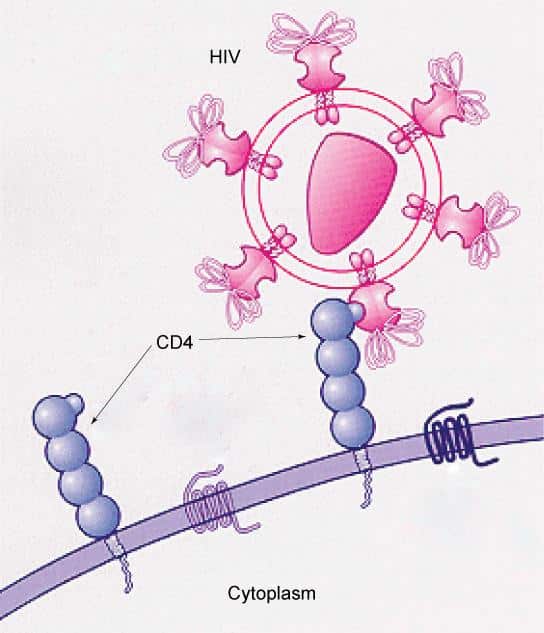
rather than as DNA DNA Genes are segments of deoxyribonucleic acid that contain the code for a specific protein that functions in one or more types of cells in the body. Chromosomes are structures within cells… read more . When HIV enters a human cell, it releases its RNA, and an enzyme called reverse transcriptase makes a DNA copy of the HIV RNA. The resulting HIV DNA is integrated into the infected cells DNA. This process is the reverse of that used by human cells, which make an RNA copy of DNA. Thus, HIV is called a retrovirus, referring to the reversed process. Other RNA viruses , unlike retroviruses, do not make DNA copies after they invade cells. They simply make RNA copies of their original RNA. Each time an HIV-infected cell divides, it makes a new copy of the integrated HIV DNA as well as its own genes. The HIV DNA copy is either
|
HIV-1 originated in Central Africa during the first half of the 20th century when a closely related chimpanzee virus first infected people. The global spread of HIV-1 began in the late 1970s, and AIDS was first recognized in 1981.
Interval Of Mild Or No Symptoms
After the first symptoms disappear, most people, even without treatment, have no symptoms or only occasionally have a few mild symptoms. This interval of few or no symptoms may last from 2 to 15 years. The symptoms that most commonly occur during this interval include the following:
-
Swollen lymph nodes, felt as small, painless lumps in the neck, under the arms, or in the groin
-
White patches in the mouth due to candidiasis
Some people progressively lose weight and have a mild fever or diarrhea.
These symptoms may result from HIV infection or from opportunistic infections that develop because HIV has weakened the immune system.
Transmission Of Hiv Infection
HIV is not transmitted by casual contact or by close, nonsexual contact at work, school, or home. No case of HIV transmission has been traced to the coughing or sneezing of an infected person or to a mosquito bite. Transmission from an infected doctor or dentist to a patient is extremely rare.
HIV is usually transmitted in the following ways:
-
Injection of contaminated blood, as can occur when needles are shared or a health care worker is accidentally pricked with an HIV-contaminated needle
-
Transfer from an infected mother to a child before birth, during birth, or after birth through the mothers milk
-
Medical procedures, such as transfusion of blood that contains HIV, procedures done with inadequately sterilized instruments, or transplantation Overview of Transplantation Transplantation is the removal of living, functioning cells, tissues, or organs from the body and then their transfer back into the same body or into a different body. The most common type of… read more of an infected organ or tissues
HIV is more likely to be transmitted if skin or a mucous membrane is torn or damagedeven if minimally.
|
You May Like: Describe The Relationship Between An Hiv Infection And Aids
What Causes A Cd4 Count To Drop
CD4 cells are part of the immune system. They are present in blood cells and help protect the body from disease. When HIV enters body cells, it reproduces or makes copies of itself. As it does so, it causes CD4 cells to die, leaving the body more prone to infection and disease.
Typically, the more virus thats in the body, the lower the levels of CD4 will be, the more the immune system will be compromised, and the higher the persons risk of infection.
Antiretroviral treatment suppresses the virus and gives CD4 cells a chance to recover. As a person receives treatment, they can expect CD4 levels to rise. In the first year of antiretroviral treatment, you can expect typically to see a persons CD4 count rise by50150 cells/mm3. After that, there will be slower yearly increases.
Cd4 Count And Hiv Treatment
Several different organizations and institutions make recommendations about when to start HIV treatment. The US Department of Health and Human Services , WHO , EACS , BHIVA , and the IAS-USA all recommend that HIV treatment be offered to all people living with HIV, regardless of their CD4 count. Research shows that people living with HIV who start treatment right after diagnosis, while their CD4 counts are still high, have a much lower risk of developing other illnesses or dying.
The DHHS treatment guidelines state:
- HIV treatment is recommended for anyone who is living with HIV, no matter their CD4 count
- HIV treatment is also strongly recommended if you are in one or more of the following situations, no matter your CD4 count:
- You have or had symptoms of AIDS
- You need treatment for hepatitis B and/or hepatitis C
Read Also: Does A Tooth Infection Hurt
What Is It Used For
If you have HIV, a CD4 count may be used to:
- See how HIV is affecting your immune system. CD4 counts can help monitor your risk for developing opportunistic infections or certain cancers. If your risk increases, your provider may give you treatment to help prevent infections.
- Help check how well HIV treatment is working. A CD4 count is used with a test called an HIV viral load test to see if HIV medicines are working. A viral load tests measures how much HIV is in your blood.
- Diagnose AIDS. Without treatment, HIV can lead to a very low CD4 count, which means you have AIDS.
A CD4 count may also be used to:
- Monitor treatment after an organ transplant. If you’ve had an organ transplantation, you’ll need to take medicine to prevent your immune system from attacking the new organ. These medicines are called “anti-rejection” drugs or immunosuppressants. You may also take these medicines to treat certain autoimmune diseases. A low CD4 count means the medicine is working.
- Help diagnose different types of lymphoma. A CD4 count may be used with other tests to find out which type of immune cells are causing lymphoma. The test results help choose the right treatment.
- Help diagnose DiGeorge syndrome. This is an uncommon inherited disorder that often causes immune problems and other health conditions that start at birth.
Diagnosis Of Hiv Infection
-
Tests to detect antibodies to the HIV virus in a sample of blood or saliva
-
Tests to detect HIV RNA in a sample of blood
Early diagnosis of HIV infection is important because it makes early treatment possible. Early treatment enables infected people to live longer, be healthier, and be less likely to transmit HIV to other people.
Doctors usually ask about risk factors for HIV infection Transmission of HIV Infection Human immunodeficiency virus infection is a viral infection that progressively destroys certain white blood cells and can cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome . HIV is transmitted… read more and about symptoms .
Doctors also do a complete physical examination to check for signs of opportunistic infections, such as swollen lymph nodes and white patches inside the mouth , and for signs of Kaposi sarcoma of the skin or mouth.
Don’t Miss: Should I Go To Er For Ear Infection
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The CD4 count is a very useful laboratory parameter when evaluating immunosuppressed patients, especially those with HIV. Nurse practitioners, primary care providers, and other physicians should have some idea about the normal levels of CD4. CD4 counts should be done in all patients first diagnosed with HIV disease. The Public Health Service recommends that all HIV-positive patients be tested every 3 to 6 months. Results can offer insight into the possible diagnosis of AIDS and the risk of opportunistic infections. Also, the test can be an indicator of treatment failure.
Why Is Hiv Therapy So Important
HIV therapy is also called antiretroviral therapy or highly active antiretroviral therapy . It consists of a combination of antiretroviral drugs. Theyre designed to keep the virus from spreading throughout your body by targeting different proteins or mechanisms the virus uses to replicate.
Antiretroviral therapy can make the viral load so low that it cant be detected by a test. This is called an undetectable viral load . If a person is virally suppressed or has an undetectable viral load, their HIV is well managed.
Starting HIV therapy as soon as an HIV diagnosis is received helps allow a person to live a long, healthy life.
Current treatment guidelines provided by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommend that a person living with HIV begin antiretroviral drugs as soon as possible after diagnosis. This is essential to reducing opportunistic infections and preventing complications from HIV.
Effective treatment can also help prevent the transmission of HIV to others. This is also known as treatment as prevention.
According to the
Read Also: Can You Treat A Kidney Infection At Home
Through Blood Transfusions Or Organ Transplants
Currently, HIV infection is rarely transmitted through blood transfusions or organ transplants.
Since 1985 in most developed countries, all blood collected for transfusion is tested for HIV, and when possible, some blood products are treated with heat to eliminate the risk of HIV infection. The current risk of HIV infection from a single blood transfusion is estimated to be less than 1 in about 2 million in the United States. However, in many developing countries, blood and blood products are not screened for HIV or are not screened as stringently. There, the risk remains substantial.
HIV has been transmitted when organs from infected donors were unknowingly used as transplants. HIV transmission is unlikely to occur when corneas or certain specially treated tissues are transplanted.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection
, MD, MAS, University of California, San Diego School of Medicine
-
HIV is transmitted through close contact with a body fluid that contains the virus or cells infected with the virus .
-
HIV destroys certain types of white blood cells, weakening the bodys defenses against infections and cancers.
-
When people are first infected, symptoms of fever, rashes, swollen lymph nodes, and fatigue may last a few days to several weeks.
-
Many infected people remain well for more than a decade.
-
About half of untreated people become ill and develop AIDS, defined by the presence of serious infections and cancers, within about 10 years.
-
Eventually, most untreated people develop AIDS.
-
Blood tests to check for HIV antibody and to measure the amount of HIV virus can confirm the diagnosis.
-
HIV drugs two, three, or more taken togethercan stop HIV from reproducing, strengthen the immune system, and thus make people less susceptible to infection, but the drugs cannot eliminate HIV, which persists in an inactive form.
HIV infections may be caused by one of two retroviruses, HIV-1 or HIV-2. HIV-1 causes most HIV infections worldwide, but HIV-2 causes many HIV infections in West Africa.
Read Also: Can A Tooth Infection Cause A Sinus Infection
What Is A Cd4 Count
A CD4 count is a blood test that measures the number of CD4 cells in a sample of your blood. CD4 cells are a type of white blood cell. They’re also called CD4 T lymphocytes or “helper T cells.” That’s because they help fight infection by triggering your immune system to destroy viruses, bacteria, and other germs that may make you sick.
A CD4 count is mostly used to check the health of your immune system if you are infected with HIV .
HIV attacks and destroys CD4 cells. Without treatment, HIV may destroy so many CD4 cells that your immune system will have trouble fighting off infections. HIV is the virus that causes AIDS . AIDS is the most serious stage of an HIV infection. If you have AIDS, your CD4 count is so low that you may develop serious infections from viruses, bacteria, or fungi that usually don’t cause problems in healthy people. These are called “opportunistic infections,” and they can become life-threatening. AIDS increases your risk of developing certain cancers, too.
Most people with HIV don’t have AIDS. And if they take their HIV medicine as prescribed, they may never develop AIDS.
If you have HIV, a CD4 count can help your health care provider check your risk for serious infections. A CD4 count may also be used to help diagnose and monitor certain other conditions that affect your immune system.
Other names: CD4 lymphocyte count CD4+ count, T4 count, T-helper cell count, CD4 percent
What Else Can Affect Your Cd4 Count
Things other than the HIV virus can influence how high or low your CD4 count is.
An infection like the flu, pneumonia, or a herpes simplex virus can make your CD4 count go down for a while.
Your CD4 count will go way down when you’re having chemotherapy for cancer.
Even things as simple as smoking or changes in sleep or exercise habits can make a difference in the count. Regular alcohol use can also lower CD4 counts.
To get the most accurate and helpful results for your CD4 count, try to:
- Get tested on a normal day after typical sleep and exercise.
- Use the same lab each time.
- Wait for at least a couple of weeks after you’ve been sick or gotten a shot before you get a test.
Recommended Reading: Will Minocycline Treat Sinus Infection
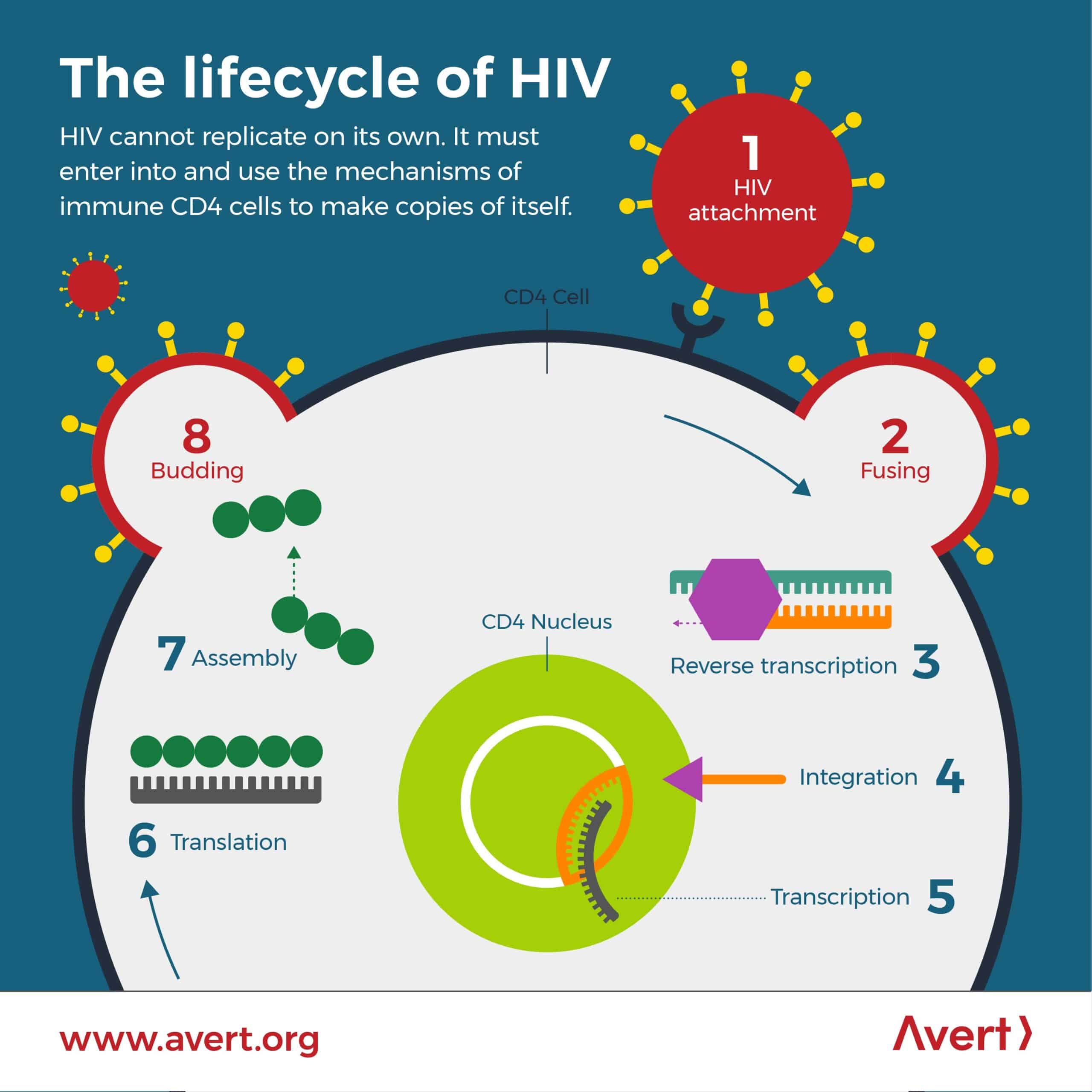
Simplified Life Cycle Of The Human Immunodeficiency Virus
|
Like all viruses, human immunodeficiency virus reproduces using the genetic machinery of the cell it infects, usually a CD4+ lymphocyte.
Drugs used to treat HIV infection were developed based on the life cycle of HIV. These drugs inhibit the three enzymes that the virus uses to replicate or to attach to and enter cells. |
HIV also infects other cells, such as cells in the skin, brain, genital tract, heart, and kidneys, causing disease in those organs.
How Are T Cells Linked To Hiv And Aids
HIV enters its genetic information into helper T cells to make copies of itself. When this happens, the helper T cells die. This severely disrupts the immune response. Low levels of helper T cells mean killer T cells and other white blood cells do not receive as much information about pathogens in the body. As a result, disease-causing bacteria and viruses multiply with minimal detection.
When the amount of helper T cells falls below 200 cells/mm3 , a person may receive an AIDS diagnosis. But healthcare professionals will also take into account other variables such as overall white blood cell count and the percentage of lymphocytes.
AIDS is the most severe stage of HIV. When a person receives an AIDS diagnosis, their immune system is severely compromised, and they are at risk for opportunistic illnesses. The survival rate without treatment at this stage is typically
200 cells/mm3 , they will likely receive an AIDS diagnosis.
When a person has HIV, a healthcare professional will collect a blood sample and request a CD4 count. The CD4 count helps determine how many helper T cells a person has.
But when analyzing a CD4 count, healthcare professionals must take into account that:
- CD4 levels could be lower in the morning
- stress and fatigue may affect CD4 levels
- corticosteroid levels could increase or decrease CD4 levels
The CD4 count helps healthcare professionals monitor HIV progression and if the person is at risk for opportunistic illnesses.
100â150cells/mm3 after 1 year.
Read Also: What Antibiotics Treat Inner Ear Infection
Cd4 Count Vs Viral Load
Theres no direct relationship between CD4 count and viral load.
In the past, doctors used the CD4 count as an indicator of when to start therapy, but advances in HIV medication have changed this. Now it serves as an indicator of immune system stability.
However, in general, a high CD4 count and a low or undetectable viral load are desirable. The higher the CD4 count, the healthier the immune system. The lower the viral load, the likelier it is that HIV therapy is working.
When HIV invades healthy CD4 cells, the virus uses them to make new copies of HIV before destroying them. When HIV remains untreated, the CD4 count decreases, and the viral load increases.
The following chart gives a general idea of what the levels of CD4 and viral load mean for a person with HIV, based on guidelines from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
| How serious is this? |
| After levels remain stable for 2 years. | Up to 6 months interval |