Tested Home Remedies For Ear Infections In Adults
1. Salt Compress
Salt can be one of the easily available home remedies for the ear infections. Just heat a cup of salt on pan/double boiler or microwave. Then take out the salt on a cloth and tie from top.When some heat is released, place the salt filled cloth over the affected ear for 5-10 minutes. Repeat the procedure every day. Salt can be replaced with rice.
2. Heating Pad
Heat pad not only relieves pain quickly but also prevents micro-organism infestation. You need to use heating pad or warm water bottle to press against ear. Remember to apply heat for short periods. Start with 5 mins, and then remove. Apply few minutes later again.
3. Make the Best of Garlic
Naturally, garlic has the ability to relieve pain, especially earache. It can be used in different ways. You can prepare garlic oil by frying 2 cloves garlic in oil until blackish, strain and use as ear drops when slightly warm. Otherwise, just boil garlic in some water, crush and add salt, place in cloth piece and place over ear. The simplest way to apply garlic is to eat garlic daily.
4. Apply Basil Oil
Basil also works to relieve ear infections in adults. Minor earache and infections can be treated with basil. Extract juice of 4-5 basil leaves and apply on the ear and surroundings. Dont let it enter into the ear canal. You can also mix holy basil oil with carrier oil. Soak in cotton ball and wipe it inside the ear.
5. Apple Cider Vinegar in Cotton Ball
6. Olive Oil to Clean
7. Tea Tree Oil
Otitis Media In Adults
Otitis media is another name for a middle ear infection. It means an infection behind your eardrum. This kind of ear infection can happen after any condition that keeps fluid from draining from the middle ear. These conditions include allergies, a cold, a sore throat, or a respiratory infection.
Middle ear infections are common in children, but they can also happen in adults. An ear infection in an adult may mean a more serious problem than in a child. So you may need additional tests. If you have an ear infection, you should see your healthcare provider for treatment. If they happen repeatedly, you should see an otolaryngologist or an otologist .
What are the types of middle ear infections?
Infections can affect the middle ear in several ways. They are:
Who is more likely to get a middle ear infection?
You are more likely to get an ear infection if you:
- Smoke or are around someone who smokes
- Have seasonal or year-round allergy symptoms
- Have a cold or other upper respiratory infection
What causes a middle ear infection?
The middle ear connects to the throat by a canal called the eustachian tube. This tube helps even out the pressure between the outer ear and the inner ear. A cold or allergy can irritate the tube or cause the area around it to swell. This can keep fluid from draining from the middle ear. The fluid builds up behind the eardrum. Bacteria and viruses can grow in this fluid. The bacteria and viruses cause the middle ear infection.
What Can I Do To Prevent Ear Infections
Middle ear infections are often a result of a simple cold. While its hard to prevent colds, good hygiene can help lower your chance of catching one.
Keep your child away from cigarette smoke. Exposure to cigarette smoke increases your childs risk of ear infections.
If your child keeps getting ear infections, they may need grommets put in their ears to prevent recurring infection.
Your risk of an outer ear infection may be reduced by:
- ensuring that you or your child drain water out of your ears after swimming
- using ear plugs for swimming if you are prone to these infections
- not putting anything into your ear, not even a cotton bud, even if your ear feels blocked or painful
Read Also: Does Navage Help With Sinus Infections
What It Feels Like To Live With An Incurable Bladder Disease
Nicole Abi-Najem, a 28-year old student from Toronto, has interstitial cystitis, an extremely painful bladder condition that has been likened to having a permanent urinary tract infection.
As told to Katie UnderwoodUpdatedApril 7, 2016
In 2012, I was working out and I went to the bathroom. When I finished peeing, I still felt like I had to go, but I knew that my bladder was empty. Doctors initially thought it was a urinary tract infection, but a test showed there wasnt any bacteria. They gave me antibiotics, but the feeling didnt go away. I went to a urologist, and he performed a cystoscopy to examine the inside of my bladder. He saw nothing. With both those tests clear, a specialist at Womens College Hospital in Toronto eventually concluded that I had interstitial cystitis.
It feels like a never-ending UTI, a migraine of the bladder. Its an enigmatic condition, but what researchers have ascertained so far is that there are several subtypes, which manifest as excruciating pain, urgency and frequency . For some, the only relief from pain comes from voiding, so many sufferers are chained to their toilets, having to pee up to 60 times a day. For me, the symptom is urgency, which is like a tingling, dull feeling in my urethra. I always feel like I have to go, even if I know theres nothing there. The difference between feeling like urinating and knowing I have to is that I feel a kind of dull pressure with the latter.
Related: How to break the bladder infection cycle
Warning Over Five Unusual Covid Symptoms That You May Not Know Yet And When To Seek Emergency Treatment

- 17:34 ET, Jan 12 2022
EXPERTS are warning of unusual Covid symptoms and when to seek emergency treatment as the omicron variant continues to spread in the US.
While fever, cough, and shortness of breath are common signs of a possible coronavirus infection, other strange symptoms are being attributed to the virus.
Doctors say one of the first signs of the omicron variant in particular can be a scratchy throat, followed by headache and fatigue.
Though someone infected with Covid may not experience any of the following symptoms, its important to be aware that they could be signs of an infection.
Dont Miss: Antibiotics For Viral Sinus Infection
Don’t Miss: Which Doctor To Consult For Yeast Infection
How Are Inner Ear Infections Diagnosed
A healthcare provider will perform a balance examination, and possibly, a neurological assessment. Unlike other types of ear infections, inner ear infections cant be properly diagnosed with a visual examination. A comprehensive assessment is necessary to rule out other health conditions, such as stroke, migraine headaches or Menieres disease, which all share similar symptoms.
Symptoms Of Ear Infection In Adults
Symptoms of Outer Ear Infection
- Pain in the affected ear
- Itching in the ear canal
- Swelling or redness of the outer ear
- Excessive discharge from the ear canal
- Feeling of fullness inside the outer ear
- Temporary hearing loss
See your doctor if you are suffering from any of the swimmers ear symptoms, even if they are not severe. Visit the emergency room or call your doctor urgently if you have fever and severe pain.
Symptoms of Middle Ear Infection
- Excessive discharge from the ear
- Temporary hearing loss
See your doctor if you are suffering from the severe ear pain, discharge of fluid or blood, or your symptoms last for more than one day.
You May Like: How To Stop A Tooth Infection Naturally
How Is An Ear Infection Diagnosed
- Ear infections are diagnosed with a patient history and physical examination of the ear with an otoscope, an instrument that is a light with a cone at the tip to visualize inside the ear canal, to check for inflammation in the ear canal.
- Tympanometry may also be performed to check for changes in pressure in the middle ear.
Dizziness Nausea And Vomiting
The Eustachian tube is also responsible for regulating our sense of balance. When we cant balance properly, we often become dizzy. Dizziness can lead to nausea, and nausea can cause vomiting.
Those who have been on the teacup ride at the fair have first-hand experience with this particular domino effect.
Also Check: Can A Infected Tooth Cause A Sore Throat
What Is Interstitial Cystitis/bladder Pain Syndrome
Interstitial cystitis /bladder pain syndrome is a chronic bladder health issue. It is a feeling of pain and pressure in the bladder area. Along with this pain are lower urinary tract symptoms which have lasted for more than 6 weeks, without having an infection or other clear causes.
Symptoms range from mild to severe. For some patients the symptoms may come and go, and for others they dont go away. IC/BPS is not an infection, but it may feel like a bladder infection. Women with IC/BPS may feel pain when having sex. The more severe cases of IC/BPS can affect your life and your loved ones. Some people with IC/BPS have other health issues such as irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, and other pain syndromes.
The bladder and kidneys are part of the urinary system, the organs in our bodies that make, store, and pass urine. You have 2 kidneys that make urine. Then urine is stored in the bladder. The muscles in the lower part of your abdomen hold your bladder in place.
How the Urinary System Works
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Bladder Infections And Other Uti Infections
A person is more likely to get a bladder infection if they dont urinate frequently enough. If they hold their urine in, the bacteria can collect in the bladder and lead to infection. Try to go to the bathroom at least every two to three hours to keep this from happening.
Not drinking enough water is another risk factor for bladder infections because your body doesnt move as much urine through the bladder as quickly.
Risk factors for urethritis include having a sexually transmitted infection or from trauma to the urethra, such as due to the insertion of a urinary catheter.
In addition to these specific risk factors for bladder infections, there are general risk factors for all UTI types. These include:
risk factors for uti
- having diabetes, as a person experiences changes to their immune system that make them more prone to UTIs
- having an enlarged prostate
- having low levels of estrogen, such as when a woman is post-menopausal
- having a history of kidney stones, which can block the flow of urine through the urinary tract
Women are also more likely than men to get UTIs because their urethra is shorter. The bacteria have less distance to go to reach the bladder and can cause infections.
You May Like: Pull Infection Out Of Tooth
Prevention Of Middle Ear Infection
When children are young, you might be able prevent middle ear infections by encouraging children to blow their noses when necessary. This helps to drain the tubes that connect the middle ear to the back of the throat. As children get older, these tubes become larger and drain more easily.
Some children who get recurrent ear infections have grommets put into their eardrums to prevent infection. Grommets are special ventilating tubes that stop fluid from building up behind the eardrum and help preserve hearing. If your child needs grommets, theyll see an ear, nose and throat specialist.
Avoid smoking. Children who are exposed to second-hand smoke are more likely than other children to develop a range of illnesses, including middle ear infections.
What Is Middle Ear Infection
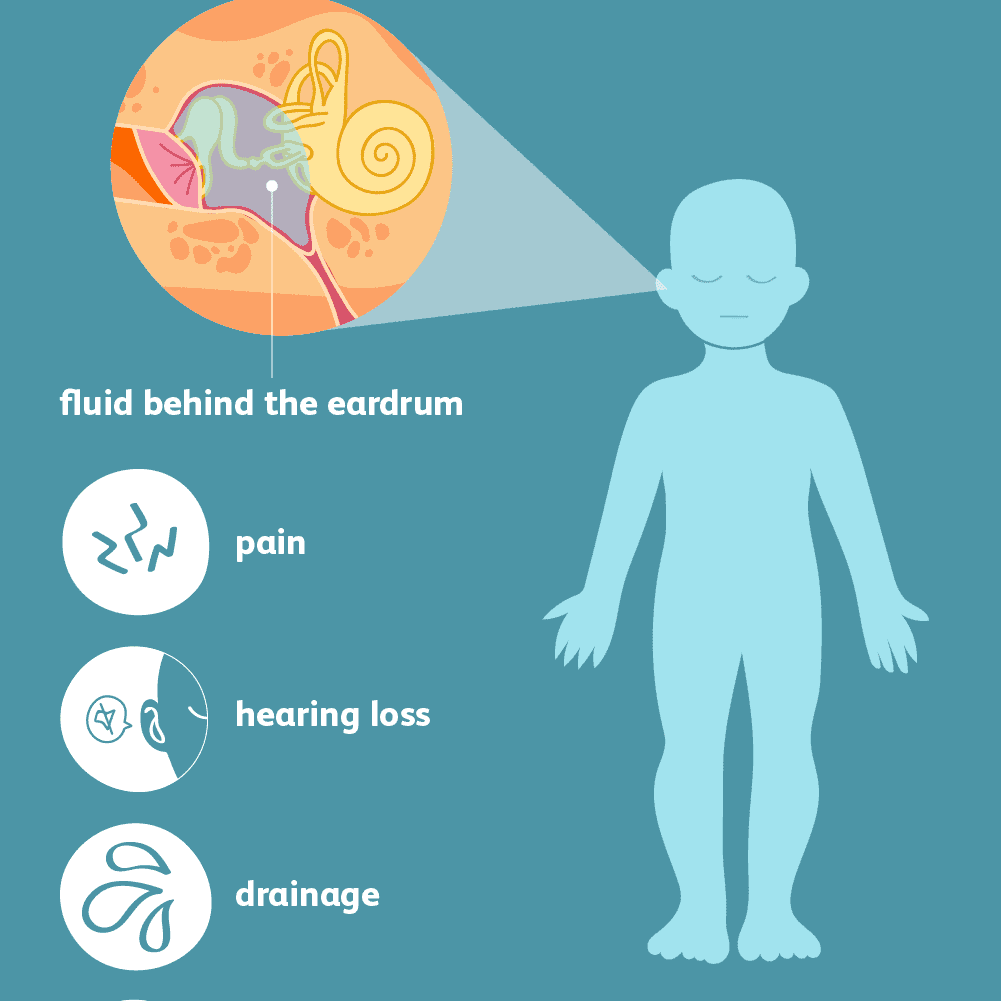
The ear is made up of three different sections: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. These parts all work together so you can hear and process sounds. The outer and middle ear are separated by the eardrum a very thin piece of skin that vibrates when hit by sound waves.
This page deals with middle ear infection , which is the infection / inflammation of the air-filled space behind the eardrum that contains the tiny vibrating bones of the ear. This space can become blocked and filled with mucus , which can become infected, causing inflammation.
There are two types of middle ear infection:
- An acute infection that starts suddenly and lasts for a short period of time and
- A chronic ear infection that does not get better or keeps coming back. Chronic ear infection can result in long-term damage to the ear.
Sometimes gel-like fluid will remain in the middle ear after an ear infection, causing “glue ear“, a relatively common condition that is often undetected among New Zealand pre-schoolers. Glue ear can adversely affect hearing and may take several weeks to resolve.
Outer ear infection is characteristically different to middle ear infection. This is a skin infection in the outer ear canal, which may start as an itch and develop into infection causing inflammation. Sometimes referred to as swimmers ear, this kind of infection can normally be treated effectively with ear drops from your doctor or pharmacist.
You May Like: How Do You Get Rid Of A Tooth Infection Fast
Any Other Recent Innovations In The Treatment Of Ear Infections
Dr. Wang: There’s a procedure I’ve been doing for a few years called Eustachian tube dilation. Using endoscopic guidance through the nose, you insert a balloon in the Eustachian tube, blow it up and leave it there for up to two minutes. This can address the Eustachian tube dysfunction that leads to middle ear infections. I’ve found it works in about 50% of patients, so it doesn’t work for everyone. But it’s so noninvasive, it’s a good place to start with certain patients who are good candidates for it. There’s also a new drug that is almost like a gel that you can squirt into the ear canal. It slowly dissolves and may be easier to get into those really clogged areas than traditional drops.
How Do I Get An Ear Infection
Between your middle ear and your throat there is a passage called the eustachian tube. The eustachian tubes keep pressure from building up by letting air move in and out of your middle ear. When you were young, especially before you turned 3, the eustachian tubes were very small and less able to keep germs out.
The eustachian tubes get longer and usually work better in older kids, but they can still cause problems. If you have allergies or catch a cold, the eustachian tubes can get blocked up and let germs get in the middle ear. Then the number of germs can grow inside your middle ear and cause an infection.
You do not catch ear infections from other people, though you might catch a cold that then leads to an ear infection. If you have an ear infection, you might have ear pain, a fever, or trouble hearing. If you have any of these problems, tell your parent so he or she can take you to the doctor.
p
You May Like: What Antibiotics Treat Uti Infections
What Is An Ear Infection
Ear infections can be either bacterial or viral infections. They can occur in your middle ear, the part of your ear just behind your eardrum, as well as the outer and inner ear. They often clear up on their own but can be painful due to inflammation or fluid buildup.
Ear infections can be chronic or acute. Acute ear infections are painful but short in duration. Chronic ear infections either dont clear up or recur many times. They can cause damage to the middle and inner ear, which is infrequently permanent.
Keep reading to learn about ear infections, including causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Common symptoms of ear infections include:
- mild pain or discomfort inside your ear
- changes in air pressure
Ear infections can also develop from infected adenoids. Your adenoids are glands on the roof of your mouth behind your nose that help protect your body from infections. Infections can spread from these glands to the nearby ends of your Eustachian tubes.
Why Dont Doctors Give Antibiotics For Middle Ear Infections Just In Case
Often, the infection will go away by itself after about 4 days. On average, children who take antibiotics have ear pain for only about 12 hours less than children who dont take antibiotics.
On the other hand, if antibiotics are prescribed, some children will have side effects. Using antibiotics can also cause bacteria to become resistant to them, meaning that the antibiotics might not work in future.
For these reasons, antibiotics are not generally recommended for middle ear infections unless your child is at risk of developing complications. For more information, speak to your doctor or visit the Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care website.
Also Check: My Yeast Infection Is So Painful
How Do You Know If An Ear Infection Is Viral Or Bacterial
It can be difficult to tell, at least in the beginning. If you or your child is recovering from a virus , its probably more likely youre dealing with a viral ear infection. If strep throat or pneumonia has been in the house, theres a greater chance that its bacterial. But thats not always the case.
Symptoms are similar with viral and bacterial infections. One difference is you have a higher fever with a bacterial ear infection. However, fevers can also happen with viral infections.
Often, its a bit of a waiting game. If the ear infection goes away on its own within a week or so, you can assume it was caused by a virus. If it isnt improving after a week, it might be a bacterial infection and you should definitely seek medical treatment.
How Do Ear Infections Happen
A middle ear infection usually happens because of swelling in one or both of the eustachian tubes . The tubes let mucus drain from the middle ear into the throat.
A cold, throat infection, acid reflux, or allergies can make the eustachian tubes swell. This blocks the mucus from draining. Then, or grow in the mucus and make pus, which builds up in the middle ear.
When doctors refer to an ear infection, they usually mean otitis media rather than swimmers ear . Otitis media with effusion is when noninfected fluid builds up in the ear. It might not cause symptoms, but in some kids, the fluid creates a sensation of ear fullness or popping.
Read Also: Kidney Infection Urgent Care Or Er