Who Shouldn’t Use Ear Drops
Ear drops can be helpful when treating an ear infection, but there are times when you shouldnât use them. For example, if you or your child has a perforated eardrum, you should avoid the use of certain ototoxic ear drops because fluid from the drops can get deep into the ear and cause more problems.
When Else Are Antibiotics Needed
Antibiotics can be the right treatment for kids who get a lot of ear infections. Their doctors might prescribe daily antibiotics to help prevent future infections. And younger children or those with more severe illness may need antibiotics right from the start.
The âwait-and-seeâ approach also might not apply to children with other concerns, such as cleft palate, genetic conditions such as Down syndrome, or other illnesses such as immune system disorders.
Ear Infections In Babies And Toddlers
Ear infections in babies and toddlers are extremely common. In fact, according to the National Institutes of Health, five out of six children will experience an ear infection before their third birthday.
Many parents are concerned that an ear infection will affect their childs hearing irreversiblyor that an ear infection will go undetected and untreated, says David Tunkel, M.D., Johns Hopkins Medicine pediatric otolaryngologist . The good news is that most ear infections go away on their own, and those that dont are typically easy to treat.
Don’t Miss: When A Wisdom Tooth Is Infected
Management Of Acute Otitis Media
Treatment Strategy for Acute Otitis Media
Initial presentation
|
Diagnosis established by physical examination findings and presence of symptoms |
|
Treat pain |
|
Children six months or older with otorrhea or severe signs or symptoms : antibiotic therapy for 10 days |
|
Children six to 23 months of age with bilateral acute otitis media without severe signs or symptoms: antibiotic therapy for 10 days |
|
Children six to 23 months of age with unilateral acute otitis media without severe signs or symptoms: observation or antibiotic therapy for 10 days |
|
Children two years or older without severe signs or symptoms: observation or antibiotic therapy for five to seven days |
|
Persistent symptoms |
|
Repeat ear examination for signs of otitis media |
|
If otitis media is present, initiate or change antibiotic therapy |
|
If symptoms persist despite appropriate antibiotic therapy, consider intramuscular ceftriaxone , clindamycin, or tympanocentesis |
Information from reference 8.
Treatment Strategy for Acute Otitis Media
Initial presentation
Information from reference 8.
Which Antibiotic Is Best For An Ear Infection
Two classes of antibiotics are commonly used to treat an infection.
Aminoglycosides
Aminoglycosides have been the main treatment for bacterial ear infections for decades. Two aminoglycosides used in ototopical preparations are:
- Neomycin
- Tobramycin
Though both of the above are commonly used in the United States, only neomycin has FDA approval. Neomycin is effective for gram-positive bacteria but its effectiveness against gram-negative bacteria has declined over years, especially against Pseudomonas, the most common bacteria in ear infections.
Tobramycin is effective for Pseudomonas and other gram-negative bacteria.
Quinolones
Quinolones are the most recently introduced ototopical antibiotics. Most quinolone antibiotics in use are fluoroquinolones, which also contain an atom of fluorine. Fluoroquinolones are considered the best available treatment now for ear infections for two reasons:
- Broad spectrum of activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
- Lack of ototoxicity
Following are some of the FDA-approved fluoroquinolone solutions for external ear infection from Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa:
Ciprofloxacin
Don’t Miss: Will Clindamycin Treat A Bladder Infection
When Antibiotics Are Needed
Antibiotics may be used to treat bacterial infections that:
- are unlikely to clear up without antibiotics
- could infect others
- could take too long to clear without treatment
- carry a risk of more serious complications
People at a high risk of infection may also be given antibiotics as a precaution, known as antibiotic prophylaxis.
When Should I Return To My Healthcare Provider For A Follow
Your healthcare provider will let you know when you need to return for a follow-up visit. At that visit, you or your childs eardrum will be examined to be certain that the infection is going away. Your healthcare provider may also want to test you or your child’s hearing.
Follow-up exams are very important, especially if the infection has caused a hole in the eardrum.
Recommended Reading: Quick Home Remedies For Sinus Infection
What Is The Treatment For Ear Infections
Medications used to treat ear infections include:
- Pseudoephedrine to ease ear pressure
- Antibiotic ear drops for infections of the ear canal
- Neomycin
- Polymyxin B
- Steroid ear drops for infections of the ear canal
- Hydrocortisone
- Oral antibiotics for infections of the middle ear , and severe infections of the outer ear
For mild cases of ear infection, doctors often recommend watching and waiting before starting use of antibiotics, as many cases will go away on their own. Consult your childs pediatrician before giving any over-the-counter medications to your child.
Home remedies to relieve symptoms include:
- Warm compresses applied to the area to help soothe pain
- Over-the-counter pain eardrops
Antibiotics For Acute Middle Ear Infection In Children
Review questions
This review compared 1) the clinical effectiveness and safety of antibiotics against placebo in children with an acute middle ear infection ) and 2) the clinical effectiveness and safety of antibiotics against expectant observation in children with AOM.
Background
AOM is one of the most common infections in early infancy and childhood, causing pain and general symptoms of illness such as fever, irritability and problems feeding and sleeping. By three years of age, most children have had at least one AOM episode. Though AOM usually resolves without treatment, it is often treated with antibiotics.
Study characteristics
The evidence in this review is current to 26 April 2015.
For the review of antibiotics against placebo we included 13 trials from high-income countries with generally low risk of bias. Three trials were performed in a general practice setting, six in an outpatient hospital setting and four in both settings.
For the review of antibiotics against expectant observation, five trials from high-income countries were eligible with low to moderate risk of bias. Two trials were performed in a GP setting and three in an outpatient hospital setting. Four trials reported outcome data that could be used for this review.
Key results
Quality of the evidence
We judged the quality of the evidence to be high for most of the outcomes in the review of antibiotics against placebo .
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection Antibiotics Metronidazole
Should I Take My Child To A Health Professional
If you think your child has an ear infection, take them to your doctor or nurse practitioner. They will ask how your child has been feeling and behaving, and will look inside their ears with a special instrument for signs of infection. Sometimes, the pressure of the pus can cause the eardrum to burst and the pus leaks out of the ear this is a runny ear. Because there is no more pressure on the eardrum, the pain goes away and your child seems to be much better. But the ear infection is still there. Your child will need to see a doctor or nurse practitioner to check if the infection needs to be treated and to make sure the eardrum heals properly.
Who Should Use Antibiotic Eardrops
Antibiotic eardrops can be more effective and safer for:
- People with Swimmers Ear, an infection caused by water in the ear.
- Children who have tubes in their ears. The tubes prevent most infections behind the eardruman area known as the middle ear. If there is an infection, antibiotic eardrops can be given right through the tube.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Treat A Kidney Infection At Home
Accidentally Taking An Extra Dose
Thereâs an increased risk of side effects if you take 2 doses closer together than recommended.
Accidentally taking 1 extra dose of your antibiotic is unlikely to cause you any serious harm.
But it will increase your chances of getting side effects, such as pain in your stomach, diarrhoea, and feeling or being sick.
If you accidentally take more than 1 extra dose of your antibiotic, are worried or you get severe side effects, speak to your GP or call NHS 111 as soon as possible.
You May Like: Hungry In Sign Language
What Are The Advantages Of Ototopical Antibiotics
Administration of antibiotics directly in the ear has several advantages over systemic delivery including the following:
Antibiotic concentration
Topical antibiotic solutions contain vastly greater concentration of antibiotic than the medications administered orally, or even intravenously. The high antibiotic concentration, delivered directly at the site of the infection, is much more effective in killing the bacteria. It also reduces the possibility for development of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains.
The lowest level of drug concentration that can prevent bacterial growth is known as minimum inhibitory concentration . Some drug-resistant bacteria have a high MIC, but ototopical antibiotics far exceed the MIC required for destroying even highly resistant bacteria.
Absence of systemic effects
The absence of systemic effects with topical administration eliminates the risk of systemic antibiotic side effects. The normal beneficial bacteria that live in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts are unaffected. Absence of systemic antibiotics also prevents the natural selection and proliferation of drug-resistant bacteria.
Alteration of microenvironment
Treatment cost
Ototopical antibiotics are generally less expensive than comparable systemic medications.
Read Also: How To Use Goldenseal For Tooth Infection
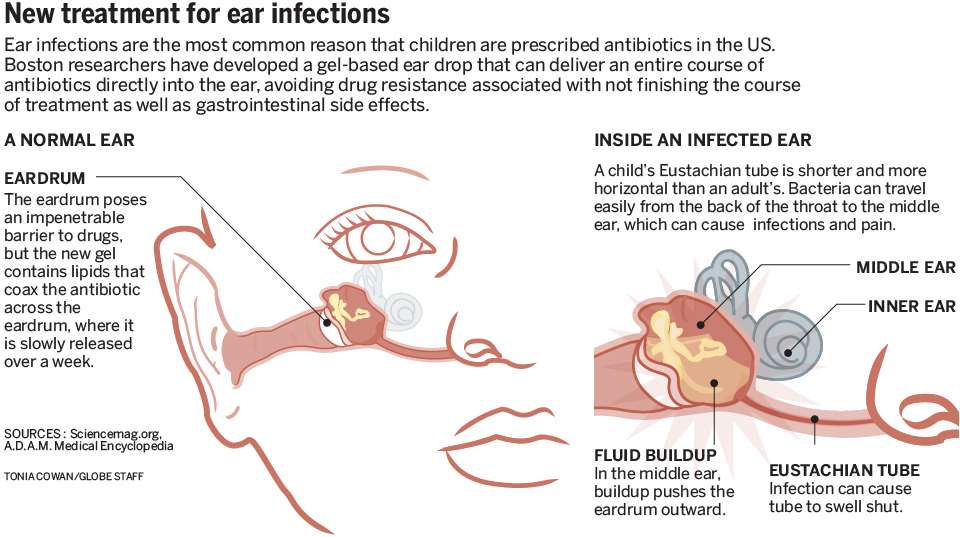
Where Is The Middle Ear
The middle ear is behind the eardrum and is also home to the delicate bones that aid in hearing. These bones are the hammer , anvil and stirrup . To provide the bigger picture, lets look at the whole structure and function of the ear:
The ear structure and function
There are three main parts of the ear: outer, middle and inner.
- The outer ear is the outside external ear flap and the ear canal .
- The middle ear is the air-filled space between the eardrum and the inner ear. The middle ear houses the delicate bones that transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. This is where ear infections occur.
- The inner ear contains the snail-shaped labyrinth that converts sound vibrations received from the middle ear to electrical signals. The auditory nerve carries these signals to the brain.
Other nearby parts
- The eustachian tube regulates air pressure within the middle ear, connecting it to the upper part of the throat.
- Adenoids are small pads of tissue above the throat and behind the nose and near the eustachian tubes. Adenoids help fight infection caused by bacteria that enters through the mouth.
Watchful Waiting Makes Sense In Most Cases
In most children it’s best to wait for two to three days in order to see whether the symptoms improve on their own, and then decide whether to use . This can help avoid side effects. Painkillers will relieve the pain more quickly than antibiotics. If you take a “watchful waiting” approach, it’s a good idea to go to back to the doctor for a check-up.
You May Like: Can You Get Antibiotics For A Viral Infection
How Does Amoxicillin Work
After starting therapy, amoxicillin will begin to work faster than many other antibiotics since it is bactericidal, which means it kills bacteria. This is in contrast to bacteriostatic antibiotics, which slow the growth and reproduction of bacteria but dont kill them directly.
Specifically, amoxicillin works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to what is known as penicillin-binding proteins . These are located inside the bacterial cell wall.
Amoxicillins ability to interfere with PBPs in the cell wall ultimately leads to cell lysis .
Natural Home Remedies For Ear Infection
Armed with facts and my instincts, I have pursued natural and holistic healthcare and remedies for my family for over a decade now.
Weve treated strep throat, tummy bugs, upper respiratory illness, urinary tract infections, and ear infections with natural home remedies such as herbs, essential oils, homeopathy, and using food as medicine.
One day, the facts and my instincts may very well tell me that its time to trust a medical doctor with the care of someone in my family or myself in which case, Ill listen to both!
Ear infections are one of the easiest maladies to treat naturally and at home, however.
If you suspect an ear infection and still feel a trip to the doctor is necessary, by all means, go! But before you fill that prescription for antibiotics for yourself or your child, give some proven, natural home remedies for ear infection a try.
Here are five natural, no-antibiotic treatments for ear infections that work:
Recommended Reading: Doxycycline Dosage For Sinus Infection In Adults
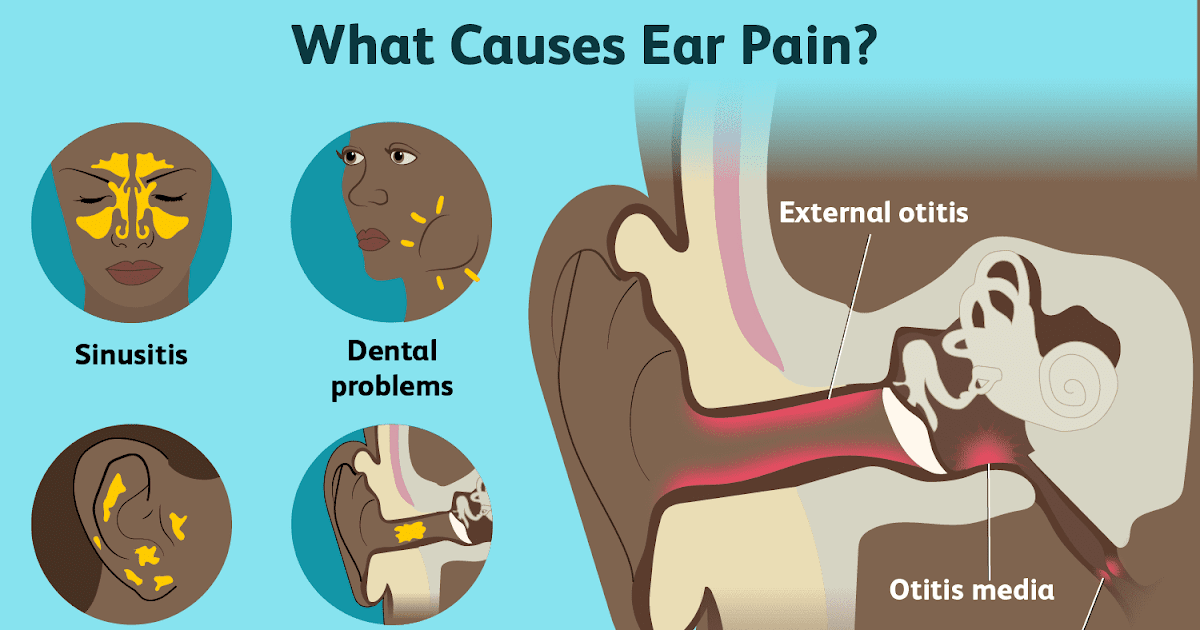
What Causes An Ear Infection
Ear infections are caused by bacteria and viruses. Many times, an ear infection begins after a cold or other respiratory infection. The bacteria or virus travel into the middle ear through the eustachian tube . This tube connects the middle ear to the back of the throat. The bacteria or virus can also cause the eustachian tube to swell. This swelling can cause the tube to become blocked, which keeps normally produced fluids to build up in the middle ear instead of being able to be drained away.
Adding to the problem is that the eustachian tube is shorter and has less of a slope in children than in adults. This physical difference makes these tubes easier to become clogged and more difficult to drain. The trapped fluid can become infected by a virus or bacteria, causing pain.
Medical terminology and related conditions
Because your healthcare provider may use these terms, its important to have a basic understanding of them:
What Are The Treatments For Ear Infections
If your pediatrician recommends antibiotics, shell usually start with amoxicillin, an effective and safe antibiotic for bacterial infections that is one of the most commonly prescribed for young children. Whether or not your doctor opts for antibiotics or a watch-and-wait approach, rest and fluids are key as with any childhood respiratory infection or virus.
For pain relief at home, your pediatrician will usually recommend Acetaminophen for babies under 6 months and Acetaminophen or Ibuprofen for children 6 months and older. Remember that according to the CDC, over-the-counter cough medicines should not be given to children under 4 and should only be given to older children with your doctors approval. Recent research has shown that the negatives of these OTC medicines often outweigh any benefits.
Read Also: Does The Meningitis Vaccine Prevent Infection
Symptoms Of A Middle Ear Infection
In most cases, the symptoms of a middle ear infection develop quickly and resolve in a few days. This is known as acute otitis media. The main symptoms include:
- a lack of energy
- slight hearing loss – if the middle ear becomes filled with fluid
In some cases, a hole may develop in the eardrum and pus may run out of the ear. The earache, which is caused by the build-up of fluid stretching the eardrum, then resolves.
What Can I Do About My Symptoms
- Donât move too quickly you might lose your balance.
- Remove tripping hazards like area rugs and electrical cords. Put non-slip mats in your bath and shower.
- If you start to feel dizzy, lie down right away. People with vertigo often feel better if they lie down in a quiet, darkened room with their eyes closed.
- Drink lots of fluids and eat well. Avoid caffeine, alcohol, salt, and tobacco.
- If you think your meds are making you feel dizzy, talk to your doctor. They may change your dose, have you stop using them, or try something else.
- Donât drive if you have dizzy spells.
Recommended Reading: Can I Sue The Hospital For An Infection
Don’t Miss: Yeast Infection Worse After Monistat
How Is An Ear Infection Diagnosed
Once youre at the doctors office, a medical professional will look inside your ear with an otoscope to determine whether you have an infection.
Typical signs include fluid buildup in the ear canal and middle ear, along with a red and inflamed eardrum.
Depending on the severity of your symptoms, your doctor may recommend waiting a few days to see if your ear infection improves.
Some infections resolve on their own. But if the infection is severe, or if symptoms dont improve after this time, then antibiotics may be warranted.
Chronic fluid buildup without an infection warrants additional testing from an ear, nose, and throat specialist.
Its especially important to diagnose young children so that they dont encounter speech and language delays from loss of hearing.
If your doctor recommends antibiotics to treat a severe ear infection, they will likely recommend an oral treatment, such as amoxicillin .
When You Need Themand When You Dont
Many children get ear infections. The infections are usually in the middle ear behind the eardrum. They may be caused by bacteria or by a virus. Doctors often treat bacterial infections with antibiotics. Antibiotics are strong medicines that kill bacteria.
Infants and some babies and children do need antibiotics.
But using antibiotics too often can be harmful. Heres why:
In most cases, antibiotics are not needed.
- They do not work for ear infections caused by viruses.
- They do not help the pain.
- Usually, viral infections and many bacterial infections go away on their own in two to three days, especially in children who are over two years old.
First, call the doctor and treat the pain.
If you suspect your child has an ear infection, you should call the doctors office and describe the symptoms. Usually, your doctor should ask you to wait a few days before bringing your child in.
The main sign of an ear infection is pain, especially on the first day. Or, a child may have a fever.
Start by giving your child an over-the-counter pain reliever, such as:
- acetaminophen .
- ibuprofen .
Antibiotics do not relieve pain in the first 24 hours. They only have a small effect on pain after that. So, pain relievers are an important treatment, and usually they are the only treatment needed.
When is treatment with antibiotics needed?If the infection is very painful and lasts more than a few days, chances are it is a bacterial infection.
02/2021
You May Like: Can You Pull A Tooth That Is Infected