Managing Lower Urinary Tract Infection
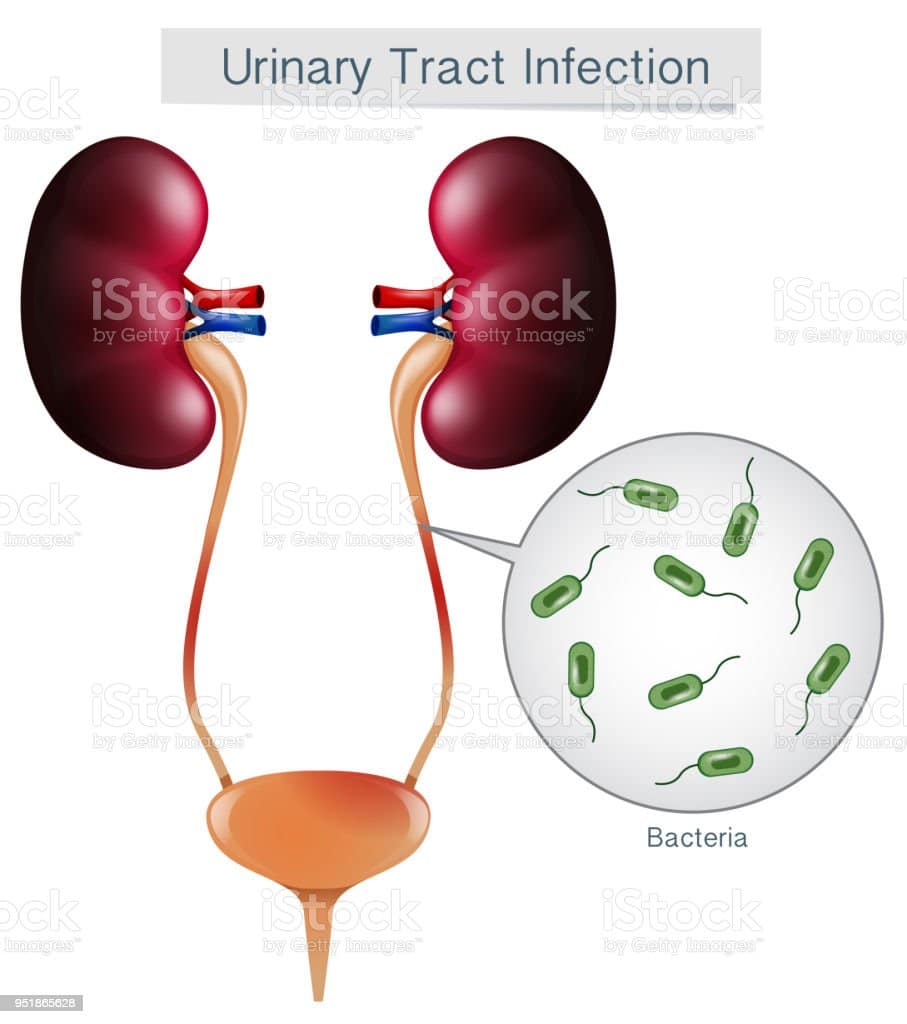
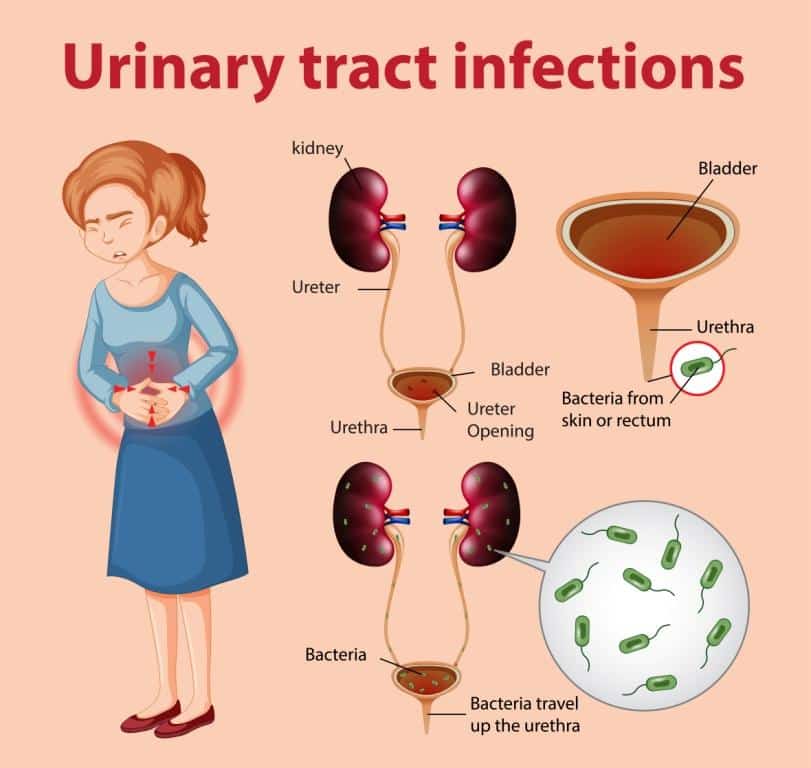
1.1.1 Be aware that lower urinary tract infection is an infection of the bladder usually caused by bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract entering the urethra and travelling up to the bladder.
1.1.2 Give advice about managing symptoms with self-care to all people with lower UTI.
Treatment for women with lower UTI who are not pregnant
1.1.3 Consider a back-up antibiotic prescription or an immediate antibiotic prescription for women with lower UTI who are not pregnant. Take account of:
-
the severity of symptoms
-
the risk of developing complications, which is higher in people with known or suspected structural or functional abnormality of the genitourinary tract or immunosuppression
-
the evidence for back-up antibiotic prescriptions, which was only in non-pregnant women with lower UTI where immediate antibiotic treatment was not considered necessary
-
previous urine culture and susceptibility results
-
previous antibiotic use, which may have led to resistant bacteria
-
preferences of the woman for antibiotic use.
1.1.4 If a urine sample has been sent for culture and susceptibility testing and an antibiotic prescription has been given:
-
review the choice of antibiotic when microbiological results are available, and
-
change the antibiotic according to susceptibility results if bacteria are resistant and symptoms are not already improving, using a narrow-spectrum antibiotic wherever possible.
Treatment for pregnant women and men with lower UTI
1.1.7 For pregnant women with lower UTI:
Duration Of Urinary Tract Infections
Once treatment has started, symptoms of simple bladder infections usually go away within one to two days, though you’ll need to continue taking any course of antibiotics as prescribed. If the infection is complicated and has spread to the kidney, it may take a week or longer before symptoms disappear.
How Relevant Is This To My Practice
Uncomplicated lower UTI remains one of the most commonly treated infections in primary care. The urinary tract is a common source of infection in children and infants and is the most common bacterial infection in children < 2 years of age, both in the community and hospital setting. During the first six months of life, UTIs are more common in boys. The outcome is usually benign, but UTIs can progress to renal scarring in early infancy, especially when associated with congenital anomalies of the urinary tract. Renal scarring may lead to complications in adulthood including hypertension, proteinuria, renal damage and even chronic renal failure, which requires dialysis treatment.
In general, 40% of women develop a UTI at some point in their life. In Singapore, 4% of young adult women are affected and the incidence increases to 7% at 50 years of age. Adult women are 30 times more likely than men to develop a UTI, with almost half of them experiencing at least one episode of UTI during their lifetime. It is reported that one in three women have their first episode of UTI by the age of 24 years. UTIs are most commonly seen in sexually active young women. Other susceptible adults include the elderly and patients requiring urethral catheterisation.
Dont Miss: Monistat Didn T Cure Yeast Infection
You May Like: Can Cialis Cause Urinary Tract Infection
Bladder Infection Vs Uti: Whats The Difference
When it comes to taking care of yourself down there, youre not alone if you have more questions than answers. Many people feel anxious at the mere thought of talking to their doctor about reproductive or sexual health concerns. Things like urinary tract infections and bladder infections happen to a lot of people and are nothing to be ashamed of, but they do need to be addressed ASAP for the sake of your health.
It can be tough to distinguish a UTI from a bladder infection if youve never had one before. Were here to help you out. Well go over the different types of UTIs and bladder infections, what causes each, treatment and prevention strategies, and potential complications to be aware of. Plus, well provide advice on when to seek medical help.
How Is Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosed
In order to ensure a clean urine sample, a physician will likely have you clean your genital area with a special wipe beforehand, and ask that you do a midstream catch of the urine.
If a UTI is diagnosed, youll be treated with antibiotics. Its important to note that false negative results do occur and that almost all women who experience typical UTI symptoms and a negative urine culture actually do have a UTI. 30209-4/fulltext” rel=”nofollow”> 11)
If youve had a prior UTI, your healthcare provider will look at prior cultures to see which bacteria were found, if any, and which antibiotics were used this often guides therapy in recurrent UTIs.
Read Also: Steroid Pack For Ear Infection
Home Remedies For Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
In addition to antibiotics, many people seek natural, at-home remedies to help UTIs. A heating pad can relieve pressure and pain, and wearing loose cotton clothing is recommended. For those with recurrent UTIs, modifying certain habits may help: Choose fragrance-free personal care products to reduce the risk of irritation, and cut back on foods that can irritate the bladder caffeine, alcohol, spicy food, raw onions, citrus fruits, carbonated drinks, and artificial sweeteners.
What Are The Risk Factors For Urinary Tract Infection
Because female urethras are shorter and closer to the rectum, they are more prone to urinary tract infections. As a result, bacteria can enter the urinary tract more easily. Some people are more prone to develop a UTI.
Many other factors that can increase the risk of UTIs include:
- Sexual practice
- Structure-related problems with the urinary tract, such as an enlarged prostate.
- Older adults and young children are more prone to UTIs.
- Poor personal hygiene, as seen in young children learning to use the toilet.
For free treatment under Ayushman Bharat Yojana, Contact Medpho Helpline , or you can also fill out the form below.
Read Also: How Not To Get A Yeast Infection While On Antibiotics
Related Conditions And Causes Of Uti
There are a number of health conditions that share some symptoms with urinary tract infections, including:
The following conditions may make you more susceptible to developing a UTI and increase the severity of symptoms:
Type 2 diabetes
And having a UTI can increase a man’s risk for benign prostatic hyperplasia .
Favorite Sites To Find Docs
SWIU is all about supporting women urologists and the urologic issues that impact women. One of our favorite SWIU perks is their searchable database for prospective patients to find a local female urologist.
An excellent source for overall urinary health info, UCF also offers a tool to help would-be patients find a urologist near them. You can search by zip code, distance, and through eight urinary specialties, including pediatric urology.
You May Like: Do Bacterial Infections Need Antibiotics
How Are Utis Treated
Treatments for UTIs often depend on the severity of the infection. Doctors often divide UTIs into simple and complicated infections.
Bladder infections usually fall into the simple category. Doctors can usually treat them with antibiotics over the course of three to five days. Common antibiotics used to treat bladder infections include trimethoprim, ciprofloxacin, and amoxicillin-clavulanate potassium.
If you have an infection, you should always take all of your antibiotics, even if you feel better. This keeps the infection from coming back.
Complicated UTIs are harder to treat. Kidney infections usually fall into this category. If you have a complicated UTI, you may require IV antibiotics and have to take antibiotics for a week or more.
Pain Relief Vs Antibiotics
New Zealand guidelines do not currently support the use of NSAIDs in favour of antibiotics. The results of two recent large randomised trials found that antibiotics reduce symptom duration on average by around 2 days, and reduce the risk of pyelonephritis. On the beneficial side, around half to two thirds of women who use NSAIDs do not end up needing antibiotics. Shared decision making should used in conjunction with your patient. Kronenberg A, Bütikofer L, Odutayo A, et al. Symptomatic treatment of uncomplicated lower urinary tract infections in the ambulatory setting: randomised, double blind trial. BMJ 2017 359:j4784.
Recommended Reading: Is A Uti The Same Thing As A Bladder Infection
About Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are common infections that can affect the bladder, the kidneys and the tubes connected to them.
Anyone can get them, but they’re particularly common in women. Some women experience them regularly .
UTIs can be painful and uncomfortable, but usually pass within a few days and can be easily treated with antibiotics.
This page is about UTIs in adults. There is a separate article about UTIs in children.
This page covers:
Does Cranberry Juice Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
Many people say that cranberry juice can help treat, or even prevent, a UTI. Researchers are currently looking into the topic, but havent found a definitive answer yet. Healthcare providers recommend drinking lots of fluids if you have, or have a history of getting, a UTI. Adding a glass of unsweetened cranberry juice to your diet isnt a proven way to prevent a UTI, but it typically wont hurt you either.
You May Like: Yeast Infection Treatment While Breastfeeding
Consider Switching Birth Control Methods If You Have Repeat Bladder Infections
If you have trouble with repeat bladder infections, talk with a health care professional about your birth control. Consider switching to a new form of birth control if you use diaphragms, unlubricated condoms, or spermicide, all of which can increase your chances of developing a bladder infection. Consider using lubricated condoms without spermicide or using a nonspermicidal lubricant.
Treating Urinary Tract Infections
Your recommended treatment plan by your GP will depend on whether your infection is in the upper or lower urinary tract.
Both types of urinary tract infection can usually be treated at home using a course of antibiotics.
If an upper UTI is more serious or there is increased risk of complications, you may need hospital treatment.
Don’t Miss: Farxiga Side Effects Yeast Infection
Full Transcript Of Urinary Tract Infections After Bladder Cancer
Stephanie Chisolm:
Hello, and welcome to Urinary Tract Infection After Radical Cystectomy. This is a Patient Insight Webinar from the Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network, and is supported by our sponsors. An untreated urinary tract infections can turn into very serious problems and need immediate care, so BCAN is delighted to welcome nurse practitioner, Krisztina Emodi, from the University of California San Francisco, for a discussion of UTIs after bladder removal. Welcome, Krisztina, its so nice to have you. I know you work with a lot of patients who have UTIs, and this is a really important topic for us, and were really delighted to have you with us.
Krisztina Emodi:
Thank you so much, Stephanie, and thank you to BCAN for having me. I feel like as a nurse practitioner, Im really bridging between our fabulous nursing team and our incredible surgeons, and I have a unique role and opportunity to interact, really with our patients and see the full spectrum of recovery, and all the challenges that come up over time. I would like to address in the next 45 minutes to an hour, just some basic anatomy of what a diversion looks like, distinguishing between an infection versus having asymptomatic bacteria in the urine, understanding some of the diagnostics and treatments as it relates to infections found in bladder cancer patients.
Krisztina Emodi:
Krisztina Emodi:
Krisztina Emodi:
Krisztina Emodi:
Krisztina Emodi:
Krisztina Emodi:
Krisztina Emodi:
Krisztina Emodi:
Krisztina Emodi:
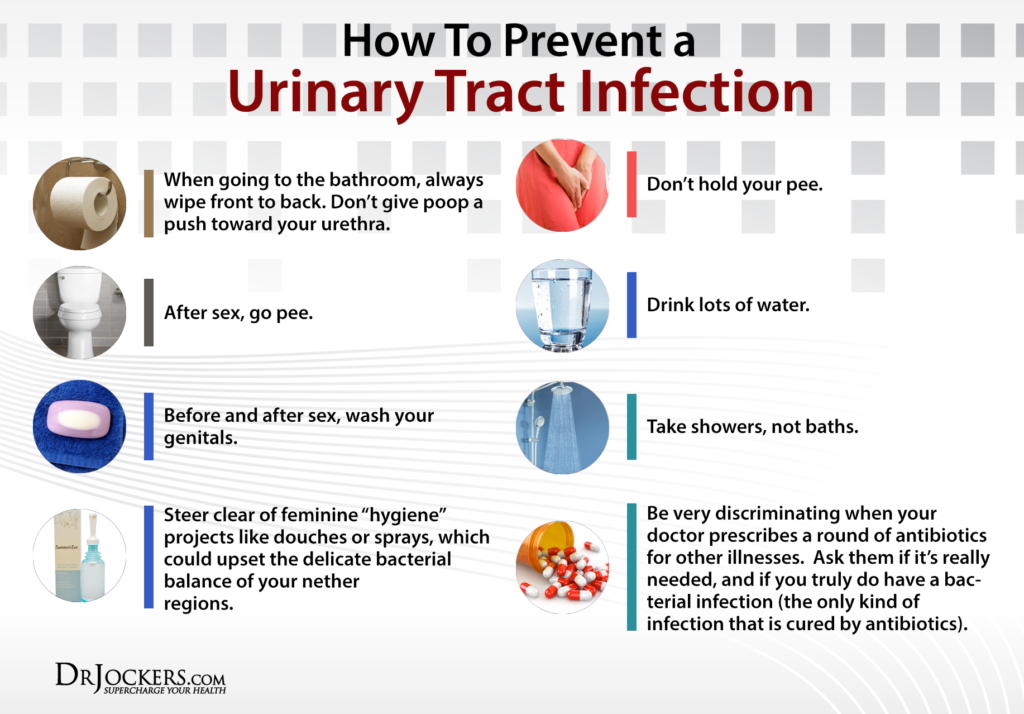
Be Aware Of Your Bathroom Habits
Take enough time to fully empty your bladder when urinatingdont rush it. Urinate after sex to flush away bacteria that may have entered the urethra during sex. Clean the genital area before and after sex.
If youre a woman, wipe from front to back, especially after a bowel movement, to keep bacteria from getting into the urethra.
Also Check: Pentrexyl 500mg For Tooth Infection
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Utis
UTIs can cause such signs as:
- pain, burning, or a stinging sensation when peeing
- an increased urge or more frequent need to pee
- waking up at night a lot to go to the bathroom
- belly pain in the area of the bladder
- foul-smelling pee that may look cloudy or contain blood
If you have any symptoms of a UTI, you’ll need to go to a doctor right away. The sooner you begin treatment, the less uncomfortable you’ll be. Call your doctor’s office or clinic. If you can’t reach your doctor, you can visit an urgent care center or hospital emergency room. The most important thing is to take action as soon as possible.
What If The Infection Does Not Clear Up With Treatment
Most infections clear up with treatment. However, if an infection does not clear up, or if you have repeated infections, you may be given some special tests such as:
-
a type of x-ray called an intravenous pyleogram , which involves injecting a dye into a vein and taking pictures of your kidney and bladder
-
an ultrasound exam, which gives a picture of your kidneys and bladder using sound waves
-
a cytoscopic exam, which uses a hollow tube with special lenses to look inside the bladder.
Also Check: Describe The Relationship Between An Hiv Infection And Aids
Treatment From A Gp For Utis That Keep Coming Back
If your UTI comes back after treatment, or you have 2 UTIs in 6 months, a GP may:
- prescribe a different antibiotic or prescribe a low-dose antibiotic to take for up to 6 months
- prescribe a vaginal cream containing oestrogen, if you have gone through the menopause
- refer you to a specialist for further tests and treatments
In some people, antibiotics do not work or urine tests do not pick up an infection, even though you have UTI symptoms.
This may mean you have a long-term UTI that is not picked up by current urine tests. Ask the GP for a referral to a specialist for further tests and treatments.
Long-term UTIs are linked to an increased risk of bladder cancer in people aged 60 and over.
Favorite Site For Urinary Health Podcasts
Podcasts arent just for politics, laughs, and murder mysteries. The American Urological Association has a fantastic one called, aptly, the Urology Care Podcast, which covers topics like sexual health myths, UTIs, prostate cancer, and more. Currently there are more than 140 episodes to listen to, ranging from about 4 minutes to 28 minutes long.
You May Like: Will Minocycline Treat Sinus Infection
What Can Happen If A Uti Is Not Treated
If treated right away, a UTI is not likely to damage your urinary tract. But if your UTI is not treated, the infection can spread to the kidneys and other parts of your body. The most common symptoms of kidney infection are fever and pain in the back where the kidneys are located. Antibiotics can also treat kidney infections.
Sometimes the infection can get in the bloodstream. This is rare but life-threatening.
Causes Of Utis And Bladder Infections
UTIs and bladder infections occur as a result of bacterial growth in your urinary tract. Your body is naturally home to billions of species of bacteria, and not all of them are bad.
In fact, bacteria help keep your body functioning the way its supposed to. But some bacteria dont belong in sensitive places in your body, and they can trigger some pretty miserable symptoms when they end up in the wrong place.
For example, E. coli, which is most commonly found in your digestive system, is also the most common type of bacteria to cause a UTI or bladder infection.
Several things can increase the risk of UTIs and bladder infections. While some of these risk factors are out of your control, you can control others.
- Sexual intercourse: As fun as sex is, it can increase the risk of developing UTIs. The friction and movement around your genital area during sexual activity can facilitate bacteria moving around down there.
- Hygiene: Things like forgetting to change your underwear, wiping from back to front, or sitting in wet or sweaty clothes for prolonged periods can up your chances of getting a UTI.
- Genetics: Some people are simply more prone to UTIs than others. If someone in your immediate family gets UTIs regularly, youre probably more susceptible to them too.
- Age: Due to urinary incontinence and estrogen deficiency, research shows that women are more likely to get recurrent UTIs after menopause.
Also Check: How To Get Ahead Of A Sinus Infection
When To See A Doctor
Although the body may sometimes fight off a UTI on its own, waiting for this to happen carries risks. UTIs can quickly spread, causing serious kidney infections.
A person should see a doctor for any symptoms of a UTI, particularly if they are pregnant or have an underlying health condition that affects their immune system.
A person with should go to the emergency room for immediate medical care. The symptoms of a kidney infection include:
Can Utis Be Prevented
A few things can help prevent UTIs. After peeing, girls should wipe from front to back with toilet paper. After BMs, wipe from front to back to avoid spreading bacteria from the rectal area to the urethra.
Also, go to the bathroom when needed and don’t hold the pee in. Pee that stays in the bladder gives bacteria a good place to grow.
Keep the genital area clean and dry. Girls should change their tampons and pads regularly during their periods. Bubble baths can irritate the vaginal area, so girls should take showers or plain baths. Avoid long exposure to moisture in the genital area by not wearing nylon underwear or wet swimsuits. Wearing underwear with cotton crotches is also helpful. Skip using feminine hygiene sprays or douches, as these can irritate the urethra.
If you are sexually active, go to the bathroom both before and within 15 minutes after sex. After sex, gently wash the genital area to remove any bacteria. Avoid sexual positions that irritate or hurt the urethra or bladder. Couples who use lubrication during sex should use a water-soluble lubricant such as K-Y Jelly.
Finally, drinking lots of water each day keeps the bladder active and bacteria-free.
UTIs are uncomfortable and often painful, but they’re common and easily treated. The sooner you contact your doctor, the sooner you’ll be able to get rid of the problem.
Recommended Reading: Can An Ear Infection Heal On Its Own