How Variable Is An Undetectable Viral Load Can This Change Over Time
HIV specialists have decades of experience managing antiretroviral therapy and are confident that you can remain uninfectious as long as you:
- take your medication every day as prescribed, and
- have your viral load checked regularly.
The presence of other sexually transmitted infections can potentially affect viral load, but in the PARTNER study there were no HIV transmissions even when other STIs were present. Those results held through the PARTNER 2 trial as well.
It is however important to remember that HIV treatment can only be successful if you have access to it and are taking it as prescribed.
Phases Of Hiv Infection
Clinical HIV infection undergoes 3 distinct phases: acute seroconversion, asymptomatic infection, and AIDS. Each is discussed below.
Acute seroconversion
Animal models show that Langerhans cells are the first cellular targets of HIV, which fuse with CD4+ lymphocytes and spread into deeper tissues. In humans, rapid occurrence of plasma viremia with widespread dissemination of the virus is observed 4 days to 11 days after mucosal entrance of the virus.
There is no fixed site of integration, but the virus tends to integrate in areas of active transcription, probably because these areas have more open chromatin and more easily accessible DNA. This greatly complicates eradication of the virus by the host, as latent proviral genomes can persist without being detected by the immune system and cannot be targeted by antivirals.
During this phase, the infection is established and a proviral reservoir is created. This reservoir consists of persistently infected cells, typically macrophages, and appears to steadily release virus. Some of the viral release replenishes the reservoir, and some goes on to produce more active infection.
The proviral reservoir, as measured by DNA polymerase chain reaction , seems to be incredibly stable. Although it does decline with aggressive antiviral therapy, the half-life is such that eradication is not a viable expectation.
Asymptomatic HIV infection
AIDS
Sample Collection And Processing
The structured data questionnaire was used to collect the required data for the study. The questionnaire was pre-tested on five patients and errors noticed were corrected prior to the commencement of the study. These five patients were not included in this study. Social demography together with other variables were obtained from patients files and recorded on the questionnaire.
Two mid-stream clean-catch urine samples from all eligible study participants were collected using two wide mouth screw-capped leak proof sterile containers by taking all precautions to avoid contamination. The two samples were taken to KCMC clinical laboratory within 30 minutes of collection. One specimen in each patient was cultured on blood agar and cysteine lactose electrolyte deficient agar . One-microliter disposable loop was used for nucleation on culture media plates then the plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 hours. In case of delay in processing the sample, the samples were kept at 28 °C in a well-monitored refrigerator and cultured within 6 hours.
Antimicrobial susceptibility tests were done for commonly prescribed antibiotics in our set up and zones of inhibition were interpreted using Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute guideline of year 2020 .14 However, owing to the challenges in the availability of antibiotic discs, we did not conduct even number of drug sensitivity tests.
Recommended Reading: Can You Have A Sinus Infection On One Side
Treatment Of Hiv Infection In Infants And Children
-
Antiretroviral drugs: Combination ART most commonly includes 2 nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors plus either a protease inhibitor or an integrase strand transfer inhibitor sometimes a nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor is given with 2 NRTIs
-
Supportive care
Because of the success of combination ART, much of the current focus is on the management of HIV infection as a chronic disease, addressing both medical and social issues. Important long-term medical issues include the need to manage HIV-related and drug-related metabolic complications and to account for age-related changes in drug pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Social issues include the need to cope with peer pressure from noninfected adolescents, ensure school success and appropriate career choice, and educate children about transmission risk. Adolescents often have difficulty seeking and following health care advice and need particular help with treatment adherence. Children and adolescents should be managed in collaboration with experts who have experience in the management of pediatric HIV infection.
How Hiv Affects The Body
HIV attacks the immune system. It specifically attacks the CD4 cells, a subtype of a T cell group. T cells help the body fight off infections.
Without treatment, HIV reduces the number of CD4 cells in the body, increasing a persons risk of getting infections.
If HIV progresses to stage 3, a person will have a higher chance of developing several complications, including an increased risk of developing certain cancers and opportunistic infections.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provides information on where individuals can find their nearest HIV testing center.
Recommended Reading: How Many Stages Of Hiv Infection Are There
Symptomatic Cystitis In Pregnancy
Recommendation.
The diagnosis of cystitis in pregnancy is made based on the presence of lower urinary tract symptoms and laboratory testing. Unlike in nonpregnant patients, urine culture should be routinely obtained to confirm the diagnosis and guide treatment.
Treat cystitis during pregnancy with nitrofurantoin for 7 days or cephalexin for 7 days. Avoid use of nitrofurantoin after 37 weeks gestation because it may increase neonatal jaundice.
How Should Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim Be Stored
- Store sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim oral suspension at room temperature, 68°F to 77°F . Protect the oral suspension from light.
- Store sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim tablets at room temperature, 68°F to 77°F .
- Store sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim injection solution at room temperature, 68°F to 77°F . Do not refrigerate the injection solution.
- Do not use sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim if the original seal of the container is broken or missing.
- Throw away sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim that is no longer needed or expired . Follow FDA guidelines on how to safely dispose of unused medicine.
- Keep sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim and all medicines out of reach of children.
Also Check: What Medicine Is Best For A Yeast Infection
Study Setting And Participants
Data were collected as part of the Antimicrobial Resistance in Gram-negative bacteria from Urinary Specimens study. This was a cross-sectional analysis of consecutively enrolled participants recruited from 10 PHCs in southwest Harare between 1 July 2019 and 24 July 2020. Adult HIV prevalence in Zimbabwe is estimated at 13%. According to national guidelines UTIs should be treated with either a fluoroquinolone or amoxicillin.
Eligibility criteria included age 18years or older, having at least two symptoms suggestive of UTI, onset of symptoms within the previous 2weeks, presence of symptoms within the last 24h, and provision of written informed consent. Those who were discharged from hospital in the previous 72h, who had a urinary catheter in situ or who were enrolled into the study on a previous occasion were excluded.
Interviewer-administered questionnaires determined potential risk factors for AMR and clinical history. Responses were entered in electronic form using the Open Data Kit . HIV status was ascertained by self-report and confirmed by patient-held records.
Treatment Of Acute Hiv Infection
Antiretroviral treatment of chronic HIV infection is well supported and widely recommended. ART for acute HIV infection is controversial. However, treating acute HIV infection has several theoretical advantages, as follows :
-
To relieve symptoms in some symptomatic patients
-
To halt viral evolution at a time of minimal viral diversity, prior to viral adaptations to specific host immune responses
-
To protect developing immune responses from the deleterious effects of sustained HIV viremia
-
To reduce the viral set-point
-
To limit the latent pool of infection
Several studies have shown no benefit for short-term combination antiretroviral therapy during acute infection. However, a 2006 retrospective study found that an initiation of combination therapy within 2 weeks of HIV seroconversion was associated with sustained viral load and CD4 cell count benefits for up to 72 weeks after termination of therapy.
In 2007, another group found that in patients who received 3 months of antiretroviral therapy, the subsequent CD4 cell count decline over 3 years was slower than in patients who did not receive acute therapy. When antiretroviral therapy was started later than 2 weeks after antibody seroconversion, however, patients had a persistent but decreasing CD4 T cell count benefit and a loss of the viral load benefit by week 72 after discontinuation of treatment.
CD4 cell counts appear to deplete very rapidly during acute HIV infection.
Recommended Reading: Group B Streptococcal Infection Medication
Initial Description And Early Spread
In the United States, HIV disease was first described in 1981 among two groups, one in San Francisco and the other in New York City. Numerous young homosexual men presented with opportunistic infections that, at the time, were typically associated with severe immune deficiency: Pneumocystis pneumonia and aggressive Kaposi sarcoma.
HIV itself was not identified for another 2 years. During that time, various other causes were considered, including lifestyle factors, chronic drug abuse, and other infectious agents. The HIV epidemic spread rapidly and silently in the absence of testing.
However, clear clinical implications arose before society became aware of the disease for example, prior to the recognition of HIV, only one case of Pneumocystis pneumonia not clearly associated with immune suppression was diagnosed in the United States between January 1976 and June 1980. In 1981 alone, 42 similar diagnoses were made, and by December 1994, 127,626 cases of Pneumocystis pneumonia with HIV infection as the only identified cause of immune suppression had been reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Also, Kaposi sarcoma is up to 30,000 times more likely to develop in persons with HIV infection than in immunocompetent persons.
Is There Any Treatment Of A Cure For Hiv/aids
Currently, there is no cure for HIV/AIDS. People living with HIV will need lifelong treatment. The best treatments right now are combinations of prescription drugs. These medications include antiviral treatment, protease inhibitors and other drugs that help people who are living with HIV stay healthy. People living with HIV also can stay healthy by doing things like eating properly, exercising and getting enough sleep.
Don’t Miss: Eye Infection And Burning Urination
Seroconversion And Acute Hiv Infection
In the first few weeks after infection with HIV, some people have a short flu-like illness that is called a seroconversion illness. This coincides with the period during which the body first produces antibodies to HIV. The most commonly experienced symptoms are fever, swollen glands, muscle aches and tiredness.
The severity of symptoms at this stage can vary considerably between people they can be so mild as to go unnoticed, or so severe that admission to hospital is needed. They usually go away within two to three weeks.
This early stage of HIV infection is called acute HIV infection. The US public health agency the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention describes it as stage 0.
During acute infection, there are very high levels of HIV in the body , which means that the risk of passing HIV on is higher than at other times.
You can start HIV treatment during acute infection. HIV treatment lowers the amount of virus in the body, which allows the immune system to strengthen and helps prevent illnesses from occurring. Starting HIV treatment in this early phase may have particular benefits in terms of preserving the immune system.
People who start HIV treatment go straight to the chronic stage of infection, described towards the end of the page.
Dhhs Guidelines For Antiretroviral Agents
Current Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in HIV-1Infected Adults and Adolescents, published by US Department of Health and Human Services, recommend starting antiretroviral therapy for all individuals when infection is diagnosed, regardless of stage of infection, as long as barriers to therapy do not exist. Considerations are as follows:
-
The goal of treatment should be the suppression of plasma HIV RNA to below detectable levels
-
Testing for plasma HIV RNA levels and CD4 count and toxicity monitoring should be performed
-
If therapy is initiated before drug-resistance test results are available, a ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitorbased regimen should be used, because clinically significant resistance to protease inhibitors is less common than resistance to non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase and integrase inhibitors in antiretroviral therapynaive persons who harbor drug-resistant virus.
Read Also: Oral Yeast Infection Pill Otc
Prevention Of Adolescent Transmission
Because adolescents are at special risk of HIV infection, they should receive education, have access to HIV testing, and know their serostatus. Education should include information about transmission, implications of infection, and strategies for prevention, including abstaining from high-risk behaviors and engaging in safe sex practices , contraceptive gel, condoms, diaphragms, cervical caps, and contraceptive sponges. Vaginal foams, creams… read more ) for those who are sexually active. Efforts should especially target adolescents at high risk of HIV infection, in particular, black and Hispanic adolescent men who have sex with other men because this is the fastest-growing US demographic of new HIV infections among youth however, all adolescents should receive risk-reduction education.
What Should I Tell My Health Care Provider Before Taking Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim
Before taking sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, tell your health care provider:
- If you are allergic to sulfamethoxazole, sulfonamides , trimethoprim, or any other medicines.
- About any medical conditions you have or have had, including:
- Kidney or liver problems
- Inherited blood disorders: porphyria or glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
- Thyroid problems
Recommended Reading: How Long Does A Uti Infection Last
Chronic Asymptomatic Hiv Infection
This is the stage where there is a balance between the HIV infection and the immune system response, represented by the levels of CD4 and T lymphocyte cells. Many people fall into this category. Swollen or enlarged lymph nodes are commonly present, along with a low number of red blood cells called platelets.
Indications For Art In Children
drugs , including multidrug combination products, available in the… read more .)
Initiation of ART for children is similar to that in adults essentially, all children with HIV infection should be given ART as soon as possible . The goal of therapy is similar to that in adults: suppress HIV replication and maintain or achieve age-normal CD4+ counts and percentages with the least amount of drug toxicity. Before making the decision to initiate therapy, the practitioner should fully assess the readiness of the caregiver and child to adhere with ARV drug administration and discuss the potential benefits and risks of therapy. Because expert opinions on therapeutic strategies change rapidly, consultation with experts is strongly advised.
Don’t Miss: How Do Doctors Treat A Kidney Infection
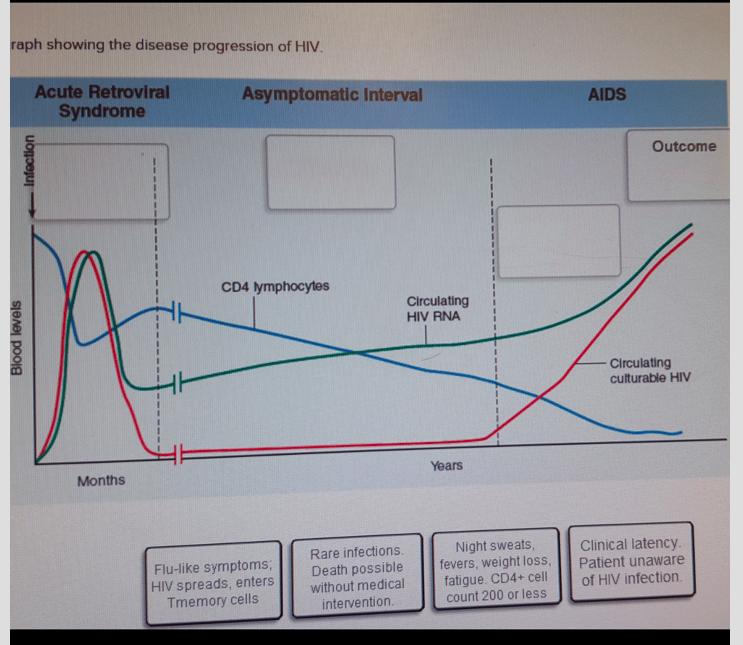
Stages Of Hiv Infection
Stages of Infection
There are four stages of HIV and as with all illnesses, how it progresses, how long it takes and the affect it has on the individual depends on a number of factors for example, general health, lifestyle, diet etc.
Stage 1: Infection
HIV quickly replicates in the body after infection. Some people develop short lived flu-like symptoms for example, headaches, fever, sore throat and a rash within days to weeks after infection. During this time the immune system reacts to the virus by developing antibodies this is referred to as sero-conversion.
Stage 2:Asymptomatic
As the name suggests, this stage of HIV infection does not cause outward signs or symptoms. A person may look and feel well but HIV is continuing to weaken their immune system. This stage may last several years and without a HIV test many people do not know they are infected.
Stage 3:Symptomatic
Over time the immune system becomes damaged and weakened by HIV and symptoms develop. Initially they can be mild but they do worsen, symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, mouth ulcers, thrush and severe diarrhoea. The symptoms are caused by the emergence of opportunistic infections they are referred to as opportunistic infections because they take advantage of a persons weakened immune system. Some examples of opportunistic infections are PCP, toxoplasmosis, TB and kaposi sarcoma.
Stage 4:AIDS/Progression of HIV to AIDS
Viral Load And Being Undetectable
Medical evidence has shown that people on effective HIV treatment cant pass HIV on.
Viral load is the amount of HIV in the blood.
A viral load test shows how much of the virus is in the body by measuring how many particles of HIV are in a blood sample. The results are given as the number of copies of HIV per millilitre of blood for example 200 copies/ml.
You May Like: What Helps Infected Tooth Pain
What Does It Mean To Be Undetectable
HIV medication works by reducing the amount of the virus in the blood to undetectable levels. This means the levels of HIV are so low that the virus cannot be passed on. This is called having an undetectable viral load or being undetectable.
It can take up to six months for some people to become undetectable from when they start treatment.
PARTNER 1 and PARTNER 2 studies provide robust evidence for gay couples and heterosexual couples that the risk of HIV transmission with suppressive ART is effectively zero, which supports the message of the international campaign, U=U .