Ear Drops For Ear Tubes
Ear drops are often prescribed after surgery. Begin using these drops on the evening of surgery, as directed by your doctor. Prior to using drops, warm the bottle by either carrying it in your pocket or holding in your hand for a few minutes. After instilling the drops, massage the front of the ear next to the opening of the ear canal several times. This helps to propel the drops into the ear canal and through the tube. Your doctor may recommend additional use of drops if there is drainage for more than 72 hours after surgery since persistent drainage is a sign of ongoing infection. If the drainage continues for more than seven days, or if other symptoms arise, please call our office.
Symptoms Of Middle Ear Infection
A middle ear infection can be triggered soon after your child gets a cough or a runny nose. Symptoms and signs of ear infection in children can include:
- not feeding or eating well
- a cough or runny nose
Older children may tell you that they cant hear properly and their ear feels blocked.
In some children, the eardrum bursts because of the pressure. If this happens you may see fluid or pus coming out of the ear. Although a burst eardrum sounds nasty, your child will probably feel better after it happens because their pain eases.
The symptoms of middle ear infection usually clear up on their own within three days. If youre concerned about your childs symptoms or if they get worse, contact your GP.
Recommended Reading: What Type Of Hearing Loss Does This Simulate
What Is Ear Tube Surgery
Ear tubes are tiny tubes made of metal or plastic. During ear tube surgery, a small hole is made in the eardrums and the tubes are inserted. The opening to the middle ear lets air flow in and out. This keeps air pressure even between the middle ear and the outside, and helps to drain fluid that builds up behind the eardrum.
Most kids wont need surgery to have a tube taken out later. Ear tubes usually fall out on their own, pushed out as the eardrum heals.
Ear tubes are also called tympanostomy tubes, myringotomy tubes, ventilation tubes, or pressure equalization tubes.
Recommended Reading: What To Take With Antibiotics To Prevent Yeast Infection
What Happens If My Child Keeps Getting Ear Infections
To keep a middle ear infection from coming back, it helps to limit some of the factors that might put your child at risk, such as not being around people who smoke and not going to bed with a bottle. In spite of these precautions, some children may continue to have middle ear infections, sometimes as many as five or six a year. Your doctor may want to wait for several months to see if things get better on their own but, if the infections keep coming back and antibiotics arent helping, many doctors will recommend a surgical procedure that places a small ventilation tube in the eardrum to improve air flow and prevent fluid backup in the middle ear. The most commonly used tubes stay in place for six to nine months and require follow-up visits until they fall out.
If placement of the tubes still doesnt prevent infections, a doctor may consider removing the adenoids to prevent infection from spreading to the eustachian tubes.
Dont Miss: How To Turn On Hearing Aid Mode On Iphone
How Do I Know If My Child Has An Ear Infection
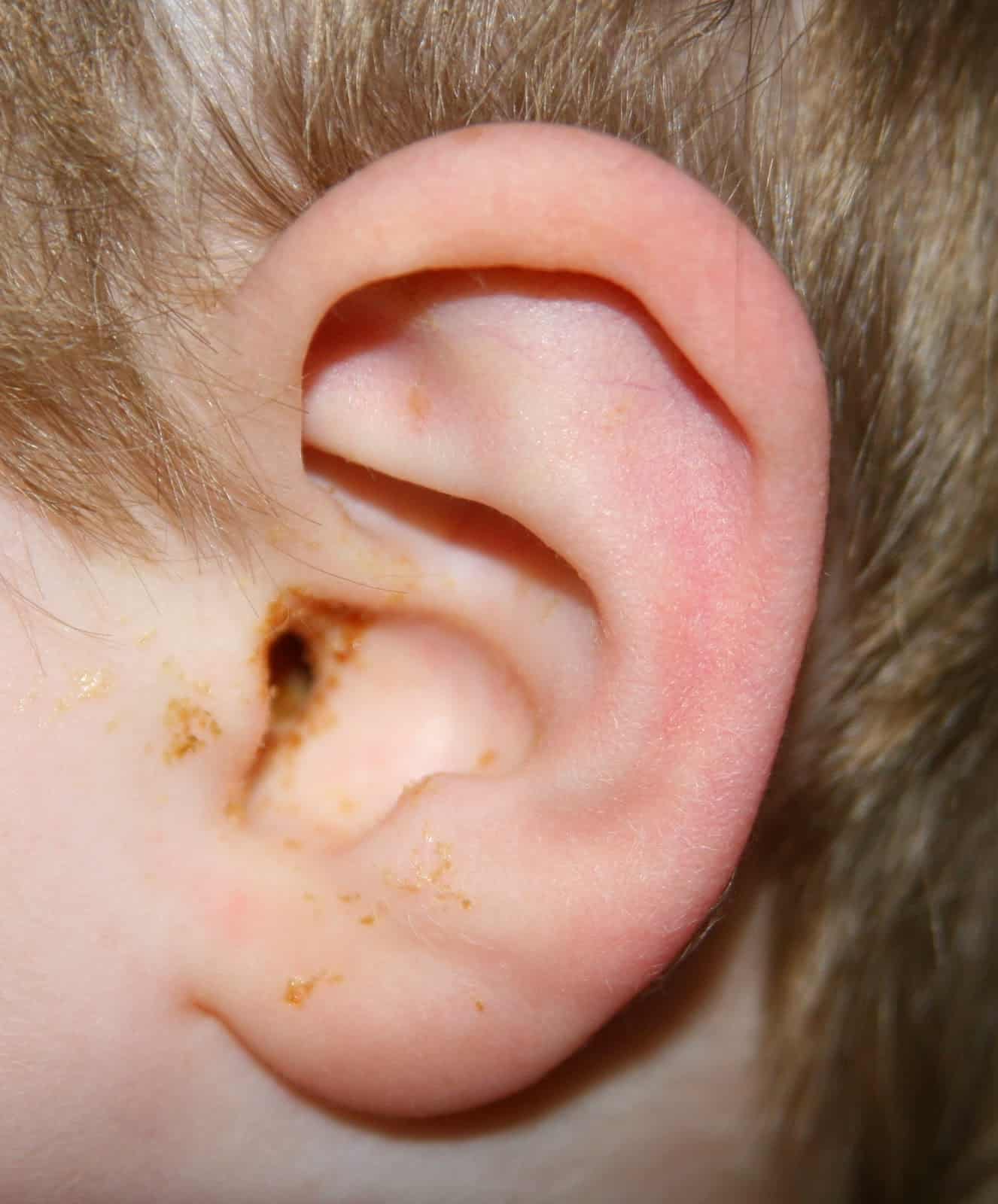
Older children will usually complain of an earache. While younger children might not be able to say they have an earache, they may:
- have an unexplained fever,
- tug or pull at their ears, or
- have trouble hearing quiet sounds.
Some children with an ear infection may also have fluid draining from the ear.
Also Check: 3 Day Z Pack For Sinus Infection
Why It Is Done
Placing tubes in the ears drains the fluid and ventilates the middle ear. Tubes may keep ear infections from recurring while the tubes are in place. They also keep fluid from building up behind the eardrum. Doctors consider surgery to insert tubes:
- If a child has had fluid behind the eardrum in both ears for more than 3 months and has significant hearing loss in both ears.
- If a child has repeat ear infections.
Also Check: Is Tinnitus A Sign Of Hearing Loss
Are There Risks To Ear Tube Surgery
As with any procedure, ear tube surgery can have risks. Possible complications with ear tubes include:
- Ongoing drainage of fluid from the ear, a condition known as otorrhea.
- The hole doesnt heal when the tubes fall out, and youll need another surgery to repair it.
- Scarring or damage to the eardrum, resulting from the surgery or from having frequent ear infections. Very rarely, this can cause changes in hearing.
Recommended Reading: What Antibiotics For Middle Ear Infection
What Happens During Ear Tube Placement
Your child may be given a medication to help him or her relax prior to entering the operating room . In the operating room, the anesthesiologist will usually use a mixture of gas and an intravenous medication for sedation. During the procedure, which typically takes 10 to 15 minutes, your child will be continuously monitored including pulse oximeter and cardiac rhythm . The surgical team is prepared for any emergency. In addition to the surgeon and the anesthesiologist, there will be a nurse and a surgical technician in the room.
After the anesthetic takes effect, the doctor, using an operating microscope, makes a tiny incision in the eardrum through the outer ear canal. There will be no external incisions or stitches. Fluid will be suctioned from the ear, and a tube inserted in the eardrum. Usually, drops will be placed in the ear, and a cotton plug inserted in the ear canal.
An appointment for a follow-up ear check-up is usually arranged 14 to 28 days after the procedure. At this visit, the position and function of the tubes will be assessed.
You can pump them into the ear by pushing on the soft cartilage tissue located in front of the ear canal .
Ear drainage may occur immediately after the procedure or at any time while the tubes are in place.
Yellow clear fluid or mucous may drain for several days to weeks after the surgery.
It is not unusual to see a bloody discharge following surgery. Cotton can be kept in the ear canal and changed as needed to keep dry.
Otitis Media In Adults
Otitis media is another name for a middle ear infection. It means an infection behind your eardrum. This kind of ear infection can happen after any condition that keeps fluid from draining from the middle ear. These conditions include allergies, a cold, a sore throat, or a respiratory infection.
Middle ear infections are common in children, but they can also happen in adults. An ear infection in an adult may mean a more serious problem than in a child. So you may need additional tests. If you have an ear infection, you should see your healthcare provider for treatment. If they happen repeatedly, you should see an otolaryngologist or an otologist .
What are the types of middle ear infections?
Infections can affect the middle ear in several ways. They are:
Who is more likely to get a middle ear infection?
You are more likely to get an ear infection if you:
- Smoke or are around someone who smokes
- Have seasonal or year-round allergy symptoms
- Have a cold or other upper respiratory infection
What causes a middle ear infection?
The middle ear connects to the throat by a canal called the eustachian tube. This tube helps even out the pressure between the outer ear and the inner ear. A cold or allergy can irritate the tube or cause the area around it to swell. This can keep fluid from draining from the middle ear. The fluid builds up behind the eardrum. Bacteria and viruses can grow in this fluid. The bacteria and viruses cause the middle ear infection.
Read Also: Ear Drops For Inner Ear Infection
Pros And Cons Of Ear Tubes
A happier child is almost guaranteed, and thats a relief to parents. For starters, ear infection risk is greatly reduced. The tubes eliminate the chances of a blocked Eustachian tube after ear infection. Less pain means fewer sleep problems and better behavior. Almost immediately, hearing is improved. This, in turn, allows speech to improve.
The main risks are associated with the need for anesthesia. This is a common operation and few children have reactions. If they do, an entire medical team is watching over them for any sign of distress. Your Pediatric ENT doctor will discuss all risks with you.
Can Ear Infection Spread To The Brain
A brain abscess can develop in 3 main ways. These are: an infection in another part of the skull such as an ear infection, sinusitis or dental abscess, which can spread directly to the brain.
Why do I constantly have ear infections?
There are multiple causes of recurrent ear infections or recurrent middle ear infections, ranging from allergies, sinusitis, ear injuries, and bacterial infections due to colds or flu.
How long do ears go empty after a tubal infection?
It just happens when your child has an active ear infection. Drainage will likely occur whenever your child has an upper respiratory or ear infection until the tubes fall out. This usually happens between eight and 14 months after surgery in most cases, he says.
Recommended Reading: Swollen Cheek Due To Tooth Infection
How Ear Tubes Help
There are a few ways that ear tubes help with middle ear problems, including:
- Improved fluid drainage and ventilation Ear infections are more common in small children because the Eustachian tubes in their ears are shorter, narrower and more likely to get clogged. Ear tubes allow fluid to drain and for air to reach the middle ear, reducing the recurrence of infections.
- Less ear pressure and pain Ear pain can happen when fluid collects in your middle ear and pushes against your eardrum. Because ear tubes allow fluid to drain from the middle ear, they can relieve ear pain and that clogged-up feeling.
- Better hearing Fluid that collects behind the eardrum can make it hard to hear. If a child has hearing loss because of an ear infection, it can lead to developmental delays. By improving hearing, ear tubes can help your child reach key milestones sooner.
When Should I Call The Doctor
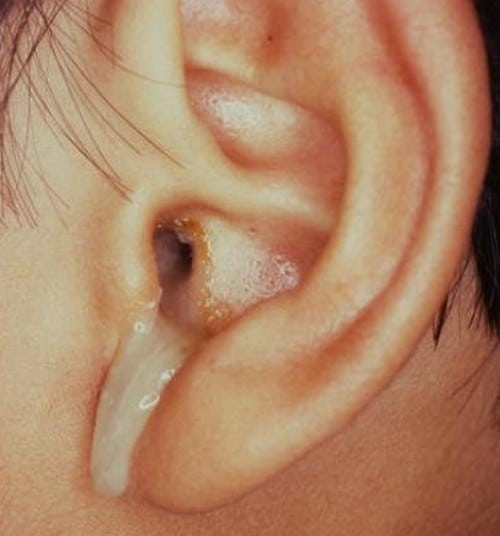
Very rarely, ear infections that dont go away or severe repeated middle ear infections can lead to complications. So kids with an earache or a sense of fullness in the ear, especially when combined with fever, should be seen by their doctors if they arent getting better after a couple of days.
Other things can cause earaches, such as teething, a foreign object in the ear, or hard earwax. Your doctor can find the cause of your childs discomfort and treat it.
You May Like: Herbal Remedies For Tooth Infection
Are There Any Dangers Or Potential Complications
Myringotomy with insertion of ear tubes is an extremely common and safe procedure with minimal complications. When complications do occur, they may include:
- PerforationThis can rarely happen when a tube comes out or a long-term tube is removed and the hole in the ear drum does not close. The hole can be patched through a surgical procedure called a tympanoplasty or myringoplasty.
- ScarringAny irritation of the ear drum , including repeated insertion of ear tubes, can cause scarring called tympanosclerosis or myringosclerosis. In most cases, this causes no problem with hearing and does not need any treatment.
- InfectionEar infections can still occur with a tube in place and cause ear discharge or drainage. However, these infections are usually infrequent, do not cause prolonged hearing loss , and may go away on their own or be treated effectively with antibiotic ear drops. Oral antibiotics are rarely needed.
- Ear tubes come out too early or stay in too longIf an ear tube expels from the ear drum too soon , fluid may return and repeat surgery may be needed. Ear tubes that remain too long may result in perforation or may require removal by an otolaryngologist.
What Is The Purpose Of Ear Tube Placement
Middle ear infections are common in children. When a child has repeated ear infections or fluid build-up in the ears that do not go away easily or there are hearing problems or speech delays, a doctor may recommend surgery to insert an ear tube to allow the eardrum to equalize the pressure.
The surgery, called a myringotomy, is a tiny incision in the eardrum. Any fluid, usually thickened secretions will be removed. In most situations, a small plastic tube is inserted into the eardrum to keep the middle ear aerated for a prolonged period.. These ventilating tubes remain in place for six months to several years. Eventually, they will move out of the eardrum and fall into the ear canal. Your doctor may remove the tube during a routine office visit or it may simply fall out of the ear.
Less common conditions that may call for the placement of ear tubes are malformation of the eardrum or Eustachian tube, Downs syndrome, cleft palate, and barotrauma , according to the American Academy of Otolaryngology.
You May Like: Is Aleve Good For Tooth Infection
Who Are At Risk
The following toddler groups can have a higher susceptibility to develop middle ear infection:
- Prematurely born: Paediatric experts note that infants born prematurely have a higher risk of developing middle ear infections. The high risk is attributed to the slow development of the immune system and eustachian tube not fully developed .
- Exposure to smoke and pollution: Chronic exposure to tobacco smoke and vehicular effluents makes the toddler more susceptible to ear infections.
- Toddlers at daycare: Toddlers who spend a bulk of their time at daycare centers have a higher risk of contracting colds and throat infections, due to droplet infections which can lead to ear infections.
It is vital to spot the symptoms of ear infection in toddlers to initiate quick treatment and mitigate discomfort.
When It Comes To Your Child Where You Take Them Matters
If your child has ear infections, strep throat or other issues that impact their ears, nose or throat, find a pediatric otolaryngologist or click the link below to schedule an appointment.
Steven Goudy, MD, is Medical Director of Otolaryngology at Childrens Healthcare of Atlanta, as well as Professor and Director of Pediatric Otolaryngology at Emory University School of Medicine. He joined Childrens in 2015 by way of Vanderbilt University Childrens Hospital, where he worked for 10 years following his fellowship training in pediatric otolaryngology.
This content is general information and is not specific medical advice. Always consult with a doctor or healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns about the health of a child. In case of an urgent concern or emergency, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency department right away. Some physicians and affiliated healthcare professionals on the Childrens Healthcare of Atlanta team are independent providers and are not our employees.
Recommended Reading: How To Turn Up The Volume On Phonak Hearing Aids
Don’t Miss: Best Over The Counter Medicine For Ear Infection For Adults
Why Do People Get Tubes In Their Ears
Ear tubes are most often placed in children whove had several middle ear infections . Theyre also used to treat buildup of fluid in the middle ear thats lasted longer than three months.
In adults, ear tubes are most commonly used to treat barotrauma a painful condition caused by air pressure changes. In addition to draining fluid from your ear, ear tubes let air in to prevent buildup of fluid in your middle ear.
If these conditions arent treated, they can lead to larger issues, such as difficulties with speech or permanent hearing loss.
Why Is It More Common In Children
Childrens ears have the same basic structure as ours, but their eustachian tubes are narrower and straighter. This makes it difficult for fluid to drain. In severe cases, the fluid is so thick and sticky that it becomes its own type of blockage. This is called glue ear. The tubes are also shorter, making it easier for infections in the nose and throat to travel to the ear.
Additionally, children have developing immune systems and are more prone to infections. They catch more colds, causing more swelling and making it more likely fluid will collect in the ear. Once the fluid is there, its more likely theyll get a secondary infection.
In other children, swelling from lymph tissue called adenoids are to blame. The adenoids are located in the upper back of the throat, above the tonsils, and swell when exposed to germs. Some children experience chronic adenoid inflammation. The swelling can cover the opening to the eustachian tubes in the throat, and infection can travel straight from the adenoids into the middle ear.
You May Like: Can I Get An Infection From A Dental Cleaning
What Are The Symptoms Of An Ear Infection
There are three main types of ear infections. Each has a different combination of symptoms.
- Acute otitis media is the most common ear infection. Parts of the middle ear are infected and swollen and fluid is trapped behind the eardrum. This causes pain in the earcommonly called an earache. Your child might also have a fever.
- Otitis media with effusion sometimes happens after an ear infection has run its course and fluid stays trapped behind the eardrum. A child with OME may have no symptoms, but a doctor will be able to see the fluid behind the eardrum with a special instrument.
- Chronic otitis media with effusion happens when fluid remains in the middle ear for a long time or returns over and over again, even though there is no infection. COME makes it harder for children to fight new infections and also can affect their hearing.