Screening And Diagnostic Tests
If doctors suspect exposure to HIV infection, they do a screening test for HIV. Doctors also recommend that all adults and adolescents, particularly pregnant women, have a screening test regardless of what their risk appears to be. Anyone who is concerned about being infected with HIV can request to be tested. Such testing is confidential and often free of charge.
The current combination screening test tests for two things that suggest HIV infection:
Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system to help defend the body against a particular attack, such as that by HIV. Antigens are foreign substances that can trigger an immune response.
The body takes several weeks to produce enough antibodies to be detected by the test, so results of the antibody test are negative during the first few weeks after the virus enters the body . However, results of the p24 antigen test can be positive as early as 2 weeks after the initial infection. The combination tests can be done quickly by a laboratory. Also, a version of these tests can be done in a doctors office or clinic . If results are positive, doctors do a test to distinguish HIV-1 from HIV-2 and a test to detect the amount of HIV RNA in the blood .
Other, older rapid bedside tests are also available. These tests can be done using a sample of blood or saliva. If results of these rapid screening tests are positive, they are confirmed by ELISA or by repetition of one or more other rapid tests.
How Do I Get Tested For Hiv
A small blood sample, mouth swab, or urine sample is used to test people for HIV. It can take as long as three to six months after initial exposure for the signs of the virus to show up in your blood, and years before you show any symptoms.
You can be tested at a doctor’s office, hospital, community health center, or other health clinic. Some places have mobile testing vans. AIDS services organizations also may provide testing. At-home testing kits are also available.
Depending on where you go, testing may be free. You may be able to choose to take the test without giving your name. Many providers or groups that offer HIV testing also provide counseling.
If you choose to take a test at home, make sure to use a test that has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration . If the test has not been approved by the FDA, it may not give accurate results. Home tests are sold at drugstores and online. Follow up with your doctor to confirm the results of at-home tests and, if necessary, begin treatment.
What Are Hiv And Aids
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome, better known as AIDS, is caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus . AIDS is the most advanced stage of HIV infection.
Over time, the virus attacks and destroys the bodys immune system . Without a fully working immune system, a person is at risk for getting other infections that usually dont affect healthy people. These are called opportunistic infections. People with HIV also have a greater risk of getting certain types of cancer, such as Kaposi sarcoma, lymphoma, and cervical cancer, as well as other health problems. Many of these problems can threaten life.
More than 1 million people in the United States are now living with HIV infection, and nearly 500,000 are living with AIDS. Women account for about 1 out of 4 people infected with HIV in this country. Each year, about 50,000 people become newly infected with HIV in the United States.
Worldwide, about 35 million people are living with HIV/AIDS. More than half of these people live in sub-Saharan Africa. About half are women.
Read Also: Whats The Best Antibiotic For Tooth Infection
Read Also: Oral Antibiotics For Dental Infection
How Can The Risk Of Hiv Spread Be Reduced
- Avoid unprotected sex with someone living with HIV. If one partner is known to be infected or their HIV status is uncertain, using condoms every time, from start to finish, can lower the risk.
- Having injection drug users use clean, sterile needles and supplies: Never share needles. The second most common cause of HIV infection is sharing used needles or drug equipment with injection drug users living with HIV.
- Using pre-exposure prophylaxis : For people who are at high risk of HIV infection, taking medicine is another way to help lower the risk of infection.
- Taking post-exposure prophylaxis : If you have been exposed to HIV, such as from a broken condom or needle stick injury, PEP treatment might reduce the risk of HIV infection. This treatment involves taking anti-HIV drugs every day for 4 weeks. PEP works best if started as soon as possible after exposure, within 72 hours.
- Treatment as prevention: ART greatly reduces the amount of virus in the body, with the goal of being undetectable. Undetectable HIV viral load means HIV is not transmittable and cannot be passed on to others.
- Reducing mother-to-infant transmission: All pregnant women should be tested for HIV. If HIV is diagnosed, treatment with ART should be started right away. Treating the mothers and infants with anti-HIV drugs and avoiding breastfeeding reduces the risk of HIV infection in infants. Also, the baby may need to be delivered by C-section if the mothers HIV levels are high.
How Is Hiv Diagnosed
An HIV antibody test, either from a blood sample or an oral sample , can tell whether you have been infected. A negative test result means no HIV antibodies were found. This usually means you are not infected. However, if you engaged in behavior that could spread the virus within three months of having the test, antibodies may not be detectable and you should be re-tested. A positive test result means antibodies to HIV were found. This means you are infected with the virus and can pass HIV to others even if you have no symptoms. You are infected for life. Even if you think you have a low risk for HIV infection, consider getting tested whenever you have a regular medical check-up.
You May Like: Can You Get Antibiotics For A Viral Infection
Can I Get Pregnant If I Have Hiv
Some people think that HIV hurts your chances of getting pregnant, but this isnt true. If you have HIV and want to become pregnant, talk to your healthcare provider. Together you can make a plan before you try to get pregnant to keep you, your partner and any future children healthy.
HIV can spread to your partner during unprotected sex and to your baby during pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding. Taking ART medications can greatly reduce your risk of transmitting HIV to your baby, especially if you have an undetectable viral load. Your provider may recommend that you dont breastfeed your baby and use formula instead.
Lack Of Symptoms In Early Stages
ARS is common once a person develops HIV. But this isnt the case for everyone as, according to HIV.gov, symptoms may not appear for a decade or longer.
Although the virus replicates quickly in the weeks after contracting it, symptoms in early HIV only tend to show up if the rate of cell destruction is high.
This doesnt mean that cases of HIV without symptoms are less serious or that an asymptomatic person cant transmit the virus to others.
Don’t Miss: What Antibiotics Treat Uti And Kidney Infections
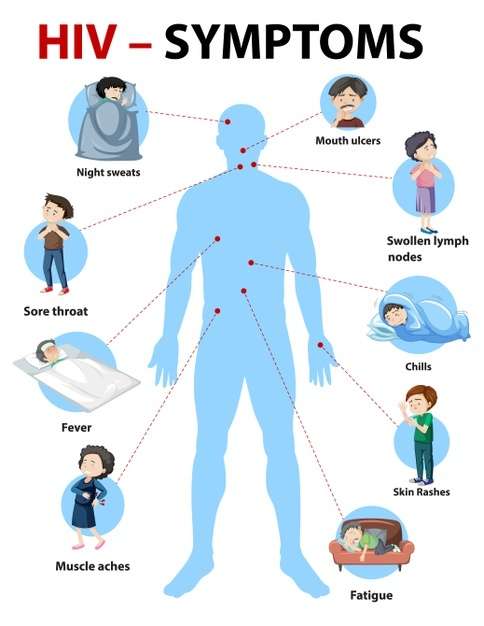
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Aids
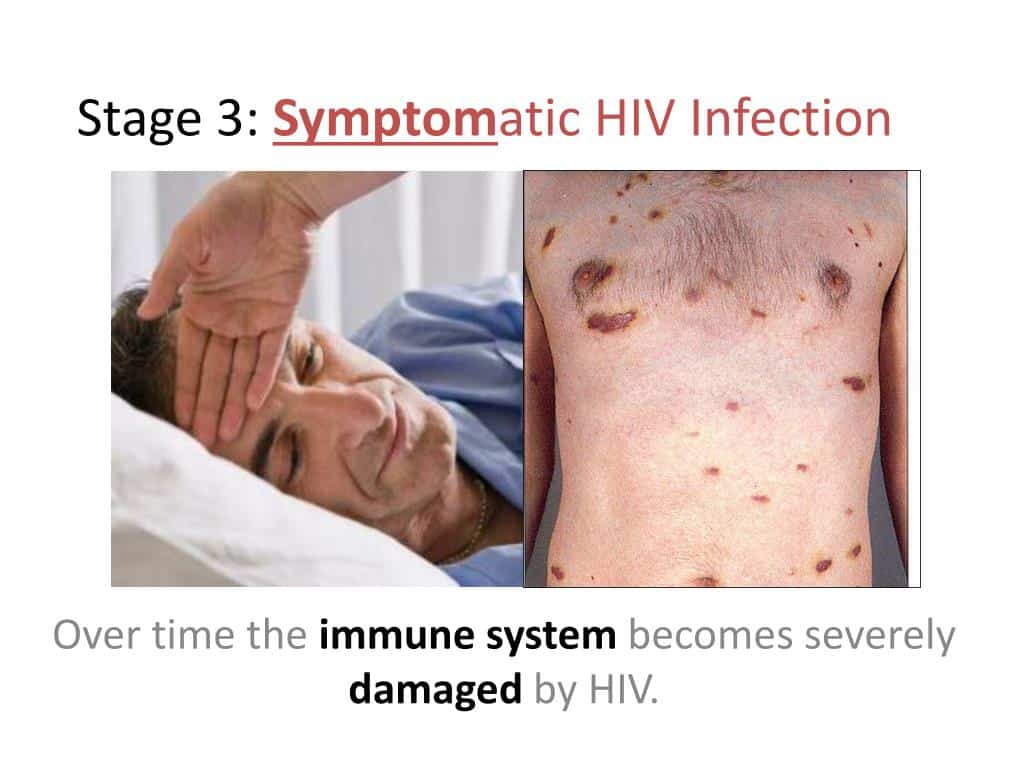
Having an infection with the HIV virus does not automatically mean that the patient has AIDS. As the HIV virus infects more and more CD4 cells and makes more copies of itself, the patients immune system gets overwhelmed and begins to falter. When the immune system breaks down due to HIV infection, opportunistic infections like fungal infections, pneumonias, and cancers can occur. When this level of HIV infection occurs, it is called AIDS .
Some of the signs and symptoms of progression of HIV to AIDS are:
If I Have Hiv How Can I Keep From Spreading It To Others
The best ways to keep from spreading HIV to others are many of the same ways you use to protect yourself:
- Let sexual partners and anyone you inject drugs with know that you have HIV.
- Follow your treatment plan and dont miss medications. If you have an undetectable viral load, you greatly reduce the risk of transmitting HIV through sex.
- Talk to your sexual partner about taking PrEP.
- Dont share needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
- Limit the number of sexual partners you have.
- If youre pregnant and have HIV, following your treatment plan, including ART medications, can reduce your risk of transmitting the virus to your child.
You May Like: Chance Of Catching Hiv From An Infected Person
Is Hiv/aids Different In Older Adults
A growing number of older people are living with HIV/AIDS. One reason is because improved treatments are helping people with the disease live longer. Nearly half of people living with HIV in the United States are age 50 and older. Many of them were diagnosed with HIV in their younger years. However, thousands of older people get HIV every year.
Older people are less likely than younger people to get tested, so they may not know they have HIV. Signs of HIV/AIDS can be mistaken for the aches and pains of normal aging. Older adults might be coping with other diseases and the aches and pains of normal aging, which can mask the signs of HIV/AIDS.
Some older people may feel ashamed or afraid of being tested. Plus, doctors do not always think to test older people for HIV. Some people may not have access to high-quality health facilities and services, which can limit their treatment options. By the time the older person is diagnosed, the virus may be in the late stages and more likely to progress to AIDS.
Remember, if you are at risk, get tested regularly for HIV.
For people who have HIV, it is important to start treatment as soon as possible after diagnosis. Treatment can help reduce the level of HIV in the blood to undetectable levels. When treatment makes HIV undetectable, the possibility of spreading the virus to a sexual partner becomes very low. This is known as treatment as prevention .
Can You Get Hiv From Kissing
Since HIV is not spread through spit, kissing is not a common way to get infected. In certain situations where other body fluids are shared, such as if both people have open sores in their mouths or bleeding gums, there is a chance you could get HIV from deep, open-mouthed kissing.
You also dont get HIV from:
- Touching or hugging someone who has HIV/AIDS.
- Public bathrooms or swimming pools.
- Sharing cups, utensils or telephones with someone who has HIV/AIDS.
- Donating blood.
Read Also: How To Tell If Tooth Infection Has Spread
Latency Can Cause A Break In Symptoms
After initial exposure and possible primary infection, HIV may transition to the clinically latent infection stage. Due to a lack of symptoms in some people, this is also referred to as asymptomatic HIV infection.
According to HIV.gov, latency in HIV infection can last up to 10 or 15 years. This means that the virus is replicating much slower than before. But it doesnt mean that HIV is gone, nor does it mean that the virus cant be transmitted to others.
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can live and long and healthy life and will not transmit HIV to your HIV-negative partners through sex.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Its important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
Don’t Miss: What Kind Of Antibiotics Are Good For Tooth Infection
Diagnosing Acute Hiv Infection
Blood taken during the acute phase of HIV infection may show lymphopenia and thrombocytopenia, but atypical lymphocytes are infrequent. The CD4 count usually remains normal. The HIV-1 antibody tests , the only tests officially used to diagnose established HIV infection, do not become positive until three or four weeks after the infection is acquired.
On the other hand, the quantitative plasma HIV-1 RNA level by polymerase chain reaction , which is 95 to 98 percent sensitive for HIV,8 becomes positive within 11 days of infection.9 During the symptomatic phase of acute HIV infection, the viral RNA shows in excess of 50,000 copies per mL.3 Three instances of false-positive HIV-1-RNA tests have been reported in each instance, however, the person was not having symptoms, and the viral load was less than 2,000 copies per mL.10 The presence of high-titer HIV-I RNA in the absence of HIV antibodies establishes the diagnosis of acute HIV infection.3,11
HIV-1 antibody and viral load tests are readily available through commercial laboratories and should be performed whenever a patient presents with signs and symptoms of acute HIV syndrome and a history that is compatible with HIV infection. If viral RNA quantitation is not available, a serum or plasma p24 antigen test may be used to detect viral infection before the appearance of HIV antibodies.
If I Am Pregnant And Have Hiv Will My Baby Also Have Hiv
Most women with HIV can protect their baby from becoming infected during pregnancy. Proper pre-natal treatment can reduce the risk that an HIV-positive mother will pass the virus to her child to less than 1 percent. The only way these special treatments can be provided is if the health care professionals know the mother is living with HIV. Treatment is most effective when started early in pregnancy. HIV-positive moms should not breastfeed their babies because HIV is sometimes passed this way.
Also Check: Can You Use Keflex For Tooth Infection
What Is The Treatment For Hiv
Individuals who are HIV positive will likely need to see a specialist. As with many other conditions, early detection offers more options for treatment. Today, there are medical treatments that can slow down the rate at which HIV weakens the immune system. However, there are other treatments that can prevent or cure the conditions associated with HIV. Anti-retroviral drug therapy may be given to a pregnant woman, which has proven to greatly reduce the chance of an infant developing HIV. A cesarean section may be recommended to reduce infant transmission from the birth canal. In the U.S., where other feeding options are available, an infected mother should be discouraged from breastfeeding her infant. Consult your childs doctor for more information regarding various drug therapies.
Overview Of The Published Systematic Reviews
Characteristics of the reviews are summarised in Table . The search periods for the published systematic reviews addressed the period 19952013 . Four reviews were restricted to abstracts/papers published in the English language , one was restricted to papers published in English or Spanish , one had no language restrictions and the remaining 4 reviews did not state whether or not the review was restricted by language . The number of articles reviewed ranged from 26 to 852 . The number of generic HRQoL measures identified by the reviews ranged from 0 to 23 and the number of HIV specific measures identified ranged from 1 to 18 .
Don’t Miss: Can Urgent Care Check For Kidney Infection
When To Contact A Doctor
Anyone who is showing symptoms of HIV should contact a doctor as soon as possible. This is especially important if the individual has recently had sexual contact with someone else or shared a needle with someone else.
HIV can remain asymptomatic for a long time. For this reason, anyone who has recently had unprotected sex and is concerned about exposure to HIV should contact a doctor as soon as they can, even if they do not have any symptoms. The same goes for anyone who has recently shared a needle.
It can be difficult to discuss the possibility of having HIV. However, without proper treatment, HIV can be life threatening. In these situations, it is very important for people to put their long-term health first and to discuss the matter with a doctor.
What Tests Diagnose Hiv
There are three types of HIV tests: antigen/antibody tests, antibody tests and nucleic acid tests :
Antigen/antibody tests
Antigen tests look for markers on the surface of HIV called p24. Antibody tests look for chemicals your body makes when it reacts to those markers. HIV antigen/antibody tests look for both.
A healthcare provider will take a small sample of blood from your arm with a needle. The blood is sent to a lab and tested for p24 and antibodies to it. An antigen/antibody test is usually able to detect HIV in 18 to 45 days after exposure.
A rapid antigen/antibody test may also be done with a finger prick to draw blood. Youll need to wait at least 18 days after exposure for this type of test to be able to detect HIV. You may need to take the test up to 90 days after exposure for accurate results.
Antibody tests
These tests look for antibodies to HIV in your blood or saliva. This can be done with a blood draw from your arm, a finger prick or with a stick that you rub on your gums to collect saliva.
An antibody test can take 23 to 90 days after exposure to detect HIV. Antibody tests done with a blood draw can detect HIV sooner than those done with saliva or blood from a finger prick.
Nucleic acid tests
NATs look for the HIV virus in your blood. A healthcare provider will take a small sample of blood from your arm with a needle. The blood then is sent to a lab and tested for HIV.
- Viral hepatitis screening.
Don’t Miss: Oral Prescription For Yeast Infection