How To Use Ear Drops
Ear drops are not always easy to administer. Follow these steps when using them:
- Lie down on your side with the infected ear facing up.
- Drip your ear drop along the ear canal side .
- Let it slide into the ear canal, and remain still and relaxed for a few minutes.
- Sit up slowly. Avoid sticking anything in your ear to soak up the excess ear drop.
- Let your ear air dry.
Your doctor may decide oral antibiotic treatment is best if:
- The infection has already spread beyond your ear canal
- You have uncontrolled diabetes
- Youve had radiotherapy to your ear
- Its not possible to administer topical antibiotic to the area
You may also treat the ear pain with an oral painkiller such as a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug or Tylenol .
Examples of common NSAIDs include:
What Causes Inner Ear Infections
Infections can happen in any part of the ear, including the inner section. When the inner ear is infected, the problem is sometimes known as labyrinthitis.
The infection can be caused by a virus or bacteria, which usually reach the inner ear after affecting another part of your body.
- Viral Infections: Lots of different viruses can affect the inner ear, including the common cold and flu. The infection usually spread to the inner ear from other parts of the body , so you may start to develop symptoms related to your inner ear after noticing cold-like symptoms. Antibiotics cant help with this type of infection.
- Bacterial Infections: Bacterial infections are less common, especially in adults, but they can happen. Bacteria are more likely to get into the inner ear if the membranes separating it from the inner ear are broken, which might happen if you have a middle ear infection. If the infection is caused by bacteria then taking antibiotics might help.
In some cases, the problem that we call an inner ear infection isnt actually an infection at all. Labyrinthitis can happen when the inner ear becomes inflamed for other reasons, for example if you have an autoimmune condition that causes your immune system to mistakenly attack the tissue. You might need to get treatment for this underlying condition in order to prevent the inner ear problems from returning.
How Do You Know If An Ear Infection Is Viral Or Bacterial
It can be difficult to tell, at least in the beginning. If you or your child is recovering from a virus , its probably more likely youre dealing with a viral ear infection. If strep throat or pneumonia has been in the house, theres a greater chance that its bacterial. But thats not always the case.
Symptoms are similar with viral and bacterial infections. One difference is you have a higher fever with a bacterial ear infection. However, fevers can also happen with viral infections.
Often, its a bit of a waiting game. If the ear infection goes away on its own within a week or so, you can assume it was caused by a virus. If it isnt improving after a week, it might be a bacterial infection and you should definitely seek medical treatment.
Also Check: Strongest Antibiotic For Staph Infection
A Pharmacist Can Help With An Ear Infection
Speak to a pharmacist if you think you have an outer ear infection.
They can recommend acidic eardrops to help stop bacteria or fungus spreading.
- a long-term medical condition such as diabetes or a heart, lung, kidney or neurological disease
- a weakened immune system because of chemotherapy, for example
What Is A Bladder Infection Or Urinary Tract Infection
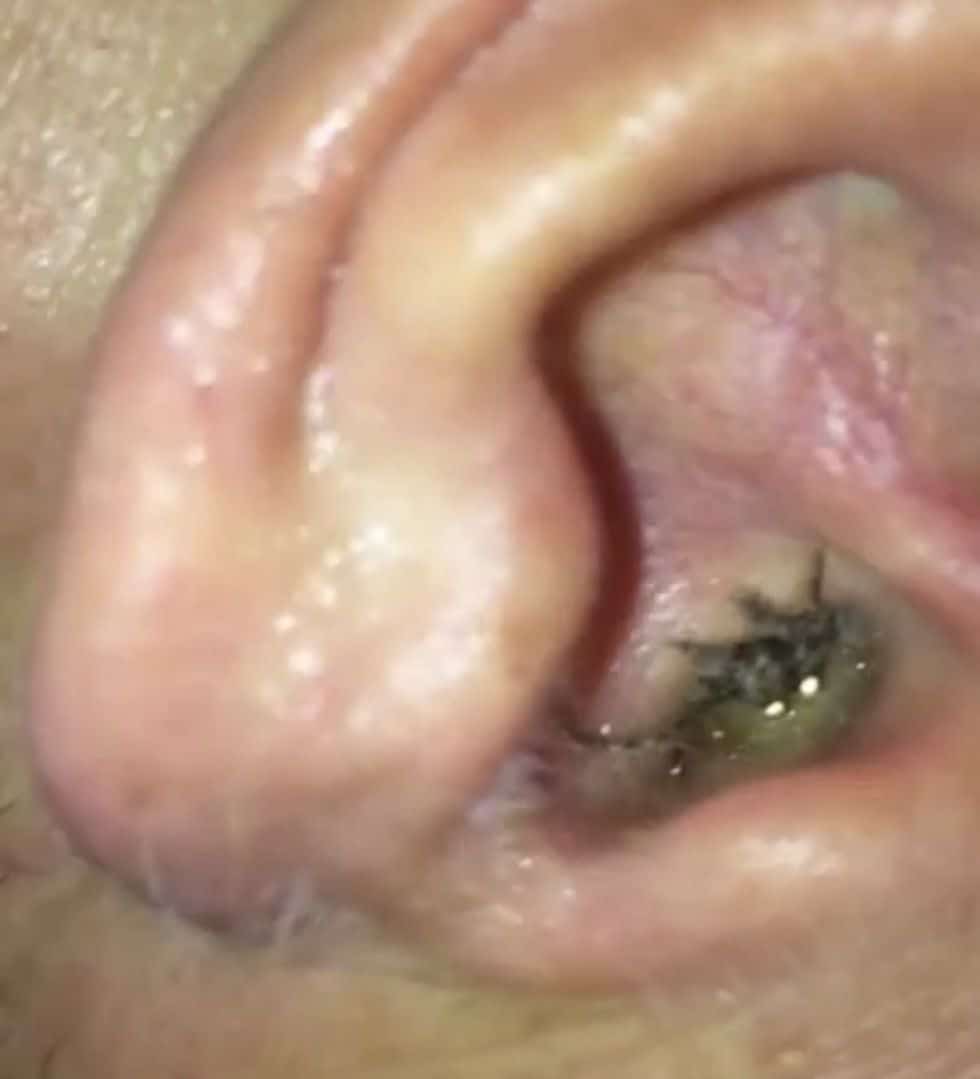
Any infection that affects a part of your urinary tract is known as a urinary tract infection . One that only affects your bladder is a bladder infection. Doctors may narrow it down to the area that is affected, for example:
- If your urethra is affected, it is known as urethritis
- If your bladder is affected it is known as cystitis
- If your kidneys are affected it is known as pyelonephritis. This is a serious infection that can lead to kidney damage if a bladder infection is left untreated.
Read Also: Does Urgent Care Test For Yeast Infections
What Are The Symptoms Of A Middle
Common symptoms of a middle-ear infection in adults are:
-
Pain in 1 or both ears
-
Drainage from the ear
You may also have a fever. Rarely, your balance can be affected.
These symptoms may be the same as for other conditions. Its important totalk with your health care provider if you think you have a middle-earinfection. If you have a high fever, severe pain behind your ear, orparalysis in your face, see your provider as soon as you can.
Infections Inside The Ear
Antibiotics are not usually offered because infections inside the ear often clear up on their own and antibiotics make little difference to symptoms, including pain.
Antibiotics might be prescribed if:
- an ear infection does not start to get better after 3 days
- you or your child has any fluid coming out of the ear
- you or your child has an illness that means there’s a risk of complications, such as cystic fibrosis
They may also be prescribed if your child is less than 2 years old and has an infection in both ears.
If antibiotics are not prescribed, eardrops containing a painkiller and an anaesthetic might be prescribed.
Also Check: When To Get Meds For Sinus Infection
What Should I Do About An Ear Infection
If its only been a couple of days and the only symptom has been ear pain, you dont need to head to the doctor right away. Because many ear infections go away on their own, its likely your doctor will want to wait and see how the symptoms improve before providing prescription medicines.
In the meantime, focus on getting lots of rest. Sleeping strengthens the immune system and helps the body fight off infections and other sickness.
If the ear infection is causing pain or discomfort, there are treatments for ear infections you can try at home. One of the simplest is using a warm compress to dull the pain. Just soak a washcloth in warm water, wring out the excess water and then hold it against the infected ear for up to 20 minutes. If it helps, reapply the compress throughout the day.
If your child is over 3 months old, an over-the-counter medication like acetaminophen can also help with the pain just make sure youre using an age-appropriate dose. If you have questions, contact your doctor or nurse line.
Who Gets A Fungal Ear Infection
Fungal infection of the ear is more common in people living in tropical and subtropical countries. It’s also more common in people who do a lot of water sports such as SCUBA diving and surfing. It occurs more often in the summer than the winter.
About 1 in 8 people with infections of the outer part of the ear have fungal infections.
Recommended Reading: Where To Get Antibiotics For Sinus Infection
How Can I Tell If My Child Has An Ear Infection
Most ear infections happen to children before theyve learned how to talk. If your child isnt old enough to say My ear hurts, here are a few things to look for:
- Tugging or pulling at the ear
- Fussiness and crying
- Fluid draining from the ear
- Clumsiness or problems with balance
- Trouble hearing or responding to quiet sounds
Treating An Ear Infection
Many cases of ear infections improve on their own without medical intervention. Your doctor may want to monitor your symptoms for signs of improvement over the course of a week or two.
For younger children with mild ear pain, doctors often recommend a watch-and-wait approach to monitor symptoms for no longer than 48 hours.
If symptoms dont improve, your doctor may recommend antibiotic treatment or ear drops . In more severe or chronic cases, surgery may be recommended to drain excess fluid from the middle ear.
Ear infections arent contagious. But you can avoid spreading germs that may trigger an ear infection by taking simple preventive measures:
- Wash your hands thoroughly.
Also Check: Cvs Minute Clinic Ear Infection Cost
How Do I Get An Ear Infection
Between your middle ear and your throat there is a passage called the eustachian tube. The eustachian tubes keep pressure from building up by letting air move in and out of your middle ear. When you were young, especially before you turned 3, the eustachian tubes were very small and less able to keep germs out.
The eustachian tubes get longer and usually work better in older kids, but they can still cause problems. If you have allergies or catch a cold, the eustachian tubes can get blocked up and let germs get in the middle ear. Then the number of germs can grow inside your middle ear and cause an infection.
You do not catch ear infections from other people, though you might catch a cold that then leads to an ear infection. If you have an ear infection, you might have ear pain, a fever, or trouble hearing. If you have any of these problems, tell your parent so he or she can take you to the doctor.
p
Where Can I Find Additional Information About Ear Infections
The NIDCD maintains a directory of organizations that provide information on the normal and disordered processes of hearing, balance, smell, taste, voice, speech, and language.
Use the following keywords to help you search for organizations that can answer questions and provide printed or electronic information on ear infections:
Recommended Reading: Infection Control In Dental Laboratory
Risk Factors For Ear Infections
Ear infections occur most commonly in young children because they have short and narrow Eustachian tubes. About of children develop an acute ear infection at some point.
Infants who are bottle-fed also have a higher incidence of ear infections than their breastfed counterparts.
Other factors that increase the risk of developing an ear infection are:
- altitude changes
- Take OTC decongestants like pseudoephedrine .
- Avoid sleeping on the affected ear.
What Happens If My Child Keeps Getting Ear Infections
To keep a middle ear infection from coming back, it helps to limit some of the factors that might put your child at risk, such as not being around people who smoke and not going to bed with a bottle. In spite of these precautions, some children may continue to have middle ear infections, sometimes as many as five or six a year. Your doctor may want to wait for several months to see if things get better on their own but, if the infections keep coming back and antibiotics arent helping, many doctors will recommend a surgical procedure that places a small ventilation tube in the eardrum to improve air flow and prevent fluid backup in the middle ear. The most commonly used tubes stay in place for six to nine months and require follow-up visits until they fall out.
If placement of the tubes still doesnt prevent infections, a doctor may consider removing the adenoids to prevent infection from spreading to the eustachian tubes.
Recommended Reading: Best Otc Male Yeast Infection Treatment
What Causes A Middle
The middle ear connects to the throat by a canal called the eustachiantube. This tube helps even out the pressure between the outer ear and theinner ear. A cold or allergy can irritate the tube or cause the area aroundit to swell. This can keep fluid from draining from the middle ear. Thefluid builds up behind the eardrum. Bacteria and viruses can grow in thisfluid. The bacteria and viruses cause the middle-ear infection.
Who Is At Higher Risk For Ear Infections
- Children less than 5 years old, because they have shorter eustachian tubes.
- Children who attend daycare, because they tend to have more colds.
- Children with allergies.
- Children who are exposed to cigarette smoke. Smoke causes inflammation of the eustachian tube, making ear infections more likely.
- Children who were not breastfed. Breast milk has antibodies that help fight infections.
- Babies who are being bottle-fed, especially if they swallow milk while lying too flat. Milk can enter the eustachian tube and cause inflammation, which increases the risk of an ear infection. Children should be held upright while drinking a bottle. When they are old enough to hold their own bottle well, they should be taught to drink from a regular cup and no longer given a bottle.
- Children with cleft palates, as their eustachian tubes are often inflamed.
- Children of First Nations and Inuit descent, though its not clear why.
- Children with Down syndrome.
You May Like: At Home Ear Infection Care
When To See A Doctor
It is recommended that you see an ENT doctor if the pain worsens or does not stop after two days of medication. Your doctor will probably recommend antibiotics to combat the infection.
Seek immediate medical care in case you notice any of the following:
- Stiff, painful neck
- Feeling faint or dizzy
- Pus, or blood oozing out of the ear
- High fever, even after taking ibuprofen in an effort of how to get rid of ear infection.
- Painful swelling around the ear
- Tinnitus or noise in the ear
For a child who is below six months, it is best to take him/her to a doctor immediately you notice signs of an ear infection. Do not try any home remedies on infants and small children.
Signs of an Ear Infection to Look Out for in Infants
Since they are young and are not able to express how they are feeling, always be alert for the following symptoms of ear infection:
- Child keeps tugging and pulling at the ear due to the pain and discomfort.
- The baby is crying endlessly.
- The baby has difficulty sleeping.
- The baby has fever.
How To Prevent Ear Infections
What can kids do to prevent ear infections? You can avoid places where people are smoking, for one. Cigarette smoke can keep your eustachian tubes from working properly.
You also can try not to catch colds. These steps can help:
- Stay away from people who have colds, if possible.
- Wash your hands regularly.
- Try not to touch your nose and eyes.
Good luck staying clear of colds and keeping those pesky germs out of your ears!
Recommended Reading: Sinus Infection And Hearing Loss
Risk Factors For Contracting An Ear Infection In Adults And Children
- Bottlefeeding: The position of the breastfeeding child is better than that of the bottlefeeding position in terms of the function of the Eustachian tube that leads into the middle ear. If an infant needs to be bottlfed, it’s better to hold the the baby rather than allowing them to lie down with the bottle. Ideally, they should not take the bottle to bed.
- Upper respiratory tract infection: Children often develop upper respiratory infections prior to developing this type of infection. Exposure to groups of children results in more frequent colds, and therefore more earaches.
- Exposure to air with irritants, such as tobacco smoke
- Birth defects: Children with cleft palate or Down syndrome are more prone to ear infections.
- Eustachian tube problems: Any problems with the Eustachian tubes will increase the risk of infection. If the individual has allergies he or she may have swelling and blockage of one or both Eustachian tubes.
- Immunosuppressed: Individuals with suppressed immunosuppression are at increased risk for ear infections.
- Ear infections later in childhood: Children who have episodes of acute infections before six months of age tend to have more later in childhood.
For more information, read our full medical article about ear infection.
Health Solutions From Our Sponsors
What Are The Symptoms Of A Fungal Ear Infection
An explanation of the different types of ear infection and which parts of the ear are involved can be found in the .
This leaflet is about infection of the ear canal with a fungus. Other causes of otitis externa can be found in the .
Typically, the ear starts to look red and the skin on the outer part of the ear becomes scaly. It may start to itch and become quite uncomfortable. You may notice discharge beginning to leak out of the ear.
The itching is often worse with fungal infections than with other types of ear infection. Apart from this the symptoms of a fungal ear infection are often identical to ear infections caused by germs . This means your doctor may prescribe antibiotic ear drops to start with and may only suspect a fungal infection when the treatment doesn’t work.
You May Like: Eye Infection In Dogs Medication
How Do Adults Get Ear Infections
Adults with weakened immune systems and certain medical conditions are more likely to get ear infections. For example, if you have diabetes, it can cause an inflammatory response throughout your body including your middle and inner ear. Having skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis can increase the chance that you get an outer ear infection.
What Are The Symptoms Of An Ear Infection
There are three main types of ear infections. Each has a different combination of symptoms.
- Acute otitis media is the most common ear infection. Parts of the middle ear are infected and swollen and fluid is trapped behind the eardrum. This causes pain in the earcommonly called an earache. Your child might also have a fever.
- Otitis media with effusion sometimes happens after an ear infection has run its course and fluid stays trapped behind the eardrum. A child with OME may have no symptoms, but a doctor will be able to see the fluid behind the eardrum with a special instrument.
- Chronic otitis media with effusion happens when fluid remains in the middle ear for a long time or returns over and over again, even though there is no infection. COME makes it harder for children to fight new infections and also can affect their hearing.
Read Also: Yeast Infection Vs Chlamydia Discharge