Ear Pain: About Ear Infection
Ear infections can cause significant pain around, behind, or inside the ear. At times, this ear pain transmits to a sinus or sinuses, jaw, or teeth.
Most of the time, bacteria or viruses cause ear infections. Also, an ear infection can occur when water or different liquids develop in the ear.
An individual with an ear infection may develop different symptoms, for example, earache, congestion, fever, and low energy. The pain of ear infections can be severe and may deteriorate without treatment.
An untreated ear infection can escalate to different areas of the body. Some individuals foster an infection known as mastoiditis, a condition in the mastoid bone close to the ear. When this occurs, an individual may encounter swelling near the ear, hearing issues, or a high fever. Extreme instances of mastitis can be dangerous and need immediate treatment.
Do Inner Ear Infections Hurt
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Other Types Of Ear Infections
Swimmer’s Ear
Acute otitis externa is an inflammation or infection of the outer ear and ear canal. It can be triggered by water that gets trapped in the ear. The trapped water can cause bacteria and fungi to breed. Otitis externa can also be precipitated by overly aggressively scratching or cleaning of ears or when an object gets stuck in the ears.
Otitis externa is generally treated with topical antibiotics, which will cure the infection and help relieve pain. With eardrops, most cases will clear up within 2 to 3 days. If the condition persists, the doctor will need to evaluate and rule out other possible causes.
You May Like: Which Type Of Cell Does Hiv Infect
Signs Of Ear Infection Complications
An ear infection is generally a non-serious condition, with complications being rare. In some cases, however, minor complications can occur. These may include:
- Rupture of the eardrum: Also known as a tympanic membrane rupture, this is one of the most common ear infection complications. The rupture does not hurt and may lead to relief from earache. The rupture will usually heal quickly, but antibiotics may be necessary.
- Hearing loss: The fluid buildup that may occur as a result of infection can persist after the infection itself has resolved. This can cause short-term, but also prolonged hearing loss. Generally, the fluid will disappear naturally, though surgical treatment is available if it persists for longer than roughly three months.
If you are concerned that you may be experiencing a complication of an ear infection, try using the Ada app to find out what the problem may be.
Side Effects Of Antibiotics
- The most common side effects of nearly all antibiotics are gastrointestinal problems, including cramps, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Allergic reactions can occur with all antibiotics, but are especially common with penicillin drugs. These reactions can range from mild skin rashes to rare but severe, even life-threatening, anaphylactic shock.
- Some drugs, including certain over-the-counter medications, interact with antibiotics. Parents should tell the doctor about all medications their child is taking.
You May Like: Best Otc Yeast Infection Medication
Antibiotics And Other Prescriptions
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , using antibiotics by mouth to treat ear infections may not help certain cases of middle ear infections. Antibiotics are not effective against outer ear and viral infections.
The main treatments for outer ear infections are manual cleanings and ear drops. The type of ear drop will depend on what is causing the infection. In the case of malignant otitis externa, intravenous antibiotics are the primary treatment.
Can Allergies Cause Ear Infections
Allergies can also lead to the development of ear infections. People who have seasonal or year long allergies are more likely to experience ear infections than those without.
Environmental allergies can irritate the eustachian tube, which runs from the middle ear to the throat. The eustachian tube helps balance pressure between the outer and inner ear.
An allergy can cause swelling around the eustachian tube, which can prevent fluid from draining away from the middle ear.
If this fluid collects behind the ear drum, it increases the risk of bacteria and viruses growing in the fluid. These bacteria and viruses can cause an ear infection in the middle ear.
Symptoms of a middle ear infection can appear suddenly and may include:
Recommended Reading: Urgent Care Treat Yeast Infections
When Should I Contact My Gp
It’s not always necessary to see your GP if you or your child have earache. Your local pharmacist is always on hand to offer help and advice on how you can manage the problem. The pain will often improve in a few days and there are things you can do to help in the meantime.
You should contact your GP or local out-of-hours service if:
- you or your child also have other symptoms, such as a high temperature , vomiting, a severe sore throat, hearing loss, swelling around the ear, or discharge from the ear
- there is something stuck in your or your child’s ear
- the earache doesn’t improve within a few days
To assess your condition at home use our earache self-help guide.
What Causes The Fluid
Anyone can get fluid trapped behind their eardrum, but it occurs more often in children because of their anatomy. Childrens ear pressure regulating tubes, formally called eustachian tubes, are shorter and flatter than those in adults. The result is that they tend not to function as well. Eustachian tube dysfunction is often associated with allergies, congestion from a cold, enlarged adenoid, cigarette smoke, and oral abnormalities like a cleft palate.
Read Also: Does Urgent Care Do Yeast Infections
What Should I Expect If I Or My Child Has An Ear Infection
Ear infections are common in children. Adults can get them too. Most ear infections are not serious. Your healthcare provider will recommend over-the-counter medications to relieve pain and fever. Pain relief may begin as soon as a few hours after taking the drug.
Your healthcare provider may wait a few days before prescribing an antibiotic. Many infections go away on their own without the need for antibiotics. If you or your child receives an antibiotic, you should start to see improvement within two to three days.
If you or your child has ongoing or frequent infections, or if fluid remains in the middle ear and puts hearing at risk, ear tubes may be surgically implanted in the eardrum to keep fluid draining from the eustachian tube as it normally should.
Never hesitate to contact your healthcare provider if you have any concerns or questions.
Check If It’s An Ear Infection
The symptoms of an ear infection usually start quickly and include:
- discharge running out of the ear
- a feeling of pressure or fullness inside the ear
- itching and irritation in and around the ear
- scaly skin in and around the ear
Young children and babies with an ear infection may also:
- rub or pull their ear
- not react to some sounds
- be irritable or restless
- be off their food
- keep losing their balance
Most ear infections clear up within 3 days, although sometimes symptoms can last up to a week.
If you, or your child, have a high temperature or you do not feel well enough to do your normal activities, try to stay at home and avoid contact with other people until you feel better.
| Inner ear infection | Middle ear infection | Outer ear infection |
|---|---|---|
| Can affect both children and adults | Usually affects children | Usually affects adults aged 45 to 75 |
| Caused by viral or bacterial infections | Caused by viruses like colds and flu | Caused by something irritating the ear canal, such as eczema, water or wearing earplugs |
| Affects parts of the inner ear like the labyrinth and vestibular system, and can lead to labyrinthitis | Affects the eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of the nose | Affects the ear canal |
You May Like: What Is The Best Yeast Infection Medication
What Causes Both Ears To Hurt
A cold, allergies, or a sinus infection can all cause the tubes in your middle ear to get clogged. If your doctor suspects bacteria as the culprit, she may prescribe antibiotics. Bacterial infections can also lead to hearing loss if they go untreated.
When you hear about these problems with your ears, first check to make sure that you aren’t actually seeing things. Ears can be deceiving because they can look healthy even when there is some sort of problem. If you’re unsure whether or not something is wrong, ask for help from someone who knows more about health issues than you do. Your doctor should be able to help you out.
In conclusion, both ears hurting at once could indicate a problem with your ears. Make sure to see your doctor if this happens so he can determine the cause of your pain.
Can Ear Infections Be Prevented
Some lifestyle choices can help protect kids from ear infections:
- Breastfeed infants for at least 6 months to help to prevent the development of early episodes of ear infections. If a baby is bottle-fed, hold the baby at an angle instead of lying the child down with the bottle.
- Prevent exposure to secondhand smoke, which can increase the number and severity of ear infections.
- Parents and kids should wash their hands well and often. This is one of the most important ways to stop the spread of germs that can cause colds and, therefore, ear infections.
- Keep childrens immunizations up to date because certain vaccines can help prevent ear infections.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Over A Kidney Infection
Don’t Miss: Does Uti Antibiotics Cause Yeast Infections
Are Poodles Prone To Ear Infections
Unfortunately, several dog breeds are more susceptible to ear infections than others and poodles are one of them. There are a few reasons why a Poodle is more prone to ear infections than other breeds.
These reasons include:
- Extra hair in the ear canal
- Lack of airflow due to a more extended ear flap
- Prone to allergies
The extra hair and lack of airflow are the main contributors when it comes to poodles and ear infections. This is because hair and lack of airflow allow for moisture and debris to settle in the ear canal. Over time, this creates a breeding ground for yeast and bacteria, which can lead to an infection.
Another contributing factor is allergies, whether seasonal or food-related. Poodles are known to be sensitive on the inside and the outside. When an allergy occurs, it can settle into an ear infection. Finding out whether a poodle has an allergy is essential when it comes to preventing ear infections.
The good news is that there are plenty of preventative measures an owner can take to reduce the chances of ear infections. Proper cleaning and hair removal are two of the best ways to ensure the ears stay healthy and strong.
Treating Outer Ear Infections
The outer ear should be carefully cleaned. That should be followed by the application of antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory medications on your ear.
Antibiotics may be prescribed if your doctor determines that the infection is bacterial.
If you have a viral infection, you may simply need to tend to the irritation on your ear and wait for the infection to resolve itself. Depending on the type of virus involved, more specialized treatment may be necessary.
Dont Miss: Sinus Infection Tooth Pain Antibiotics
You May Like: Lymphocyte Count In Early Hiv Infection
How Do Adults Get Ear Infections
Adults with weakened immune systems and certain medical conditions are more likely to get ear infections. For example, if you have diabetes, it can cause an inflammatory response throughout your body including your middle and inner ear. Having skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis can increase the chance that you get an outer ear infection.
What Are The Goals Of Chronic Otitis Media Surgery
- The goals of surgery are to first remove all of the infected tissue so that it can be safe from recurrent infections.
- The second goal is to recreate a middle ear space with an intact eardrum.
Finally, hearing is to be restored.
- This may seem strange that hearing is the last priority, but if the first two priorities are not met, anything that is done to improve hearing will ultimately fail.
- If hearing is restored, but the infection returns, the hearing will be lost again.
- Likewise, if hearing is restored, but the middle ear space is not recreated, the eardrum will re-stick to the middle ear or the ossicles.
Also Check: Best Over The Counter Treatment For Penile Yeast Infection
Read Also: What To Do When Your Wisdom Tooth Is Infected
When Is An Ear Infection Considered To Be Chronic
If an ear infection lasts for more than three months, its considered chronic. If chronic ear infections arent treated, it can lead to hearing loss and other serious problems. In children, chronic ear infections can affect their ability to achieve developmental milestones, like walking and talking.
Is a chronic ear infection curable?
If your child has an ear infection for a few months and its affecting their ability to hear, your doctor may recommend a minor surgery to put in ear tubes for chronic ear infections.
During ear tube surgery, an ear, nose and throat doctor inserts small plastic or metal tubes into the eardrum. These tubes help drain the built-up fluid that can cause ear infections. Ear tubes usually fall out on their own within about a year.
What Is Middle Ear Infection
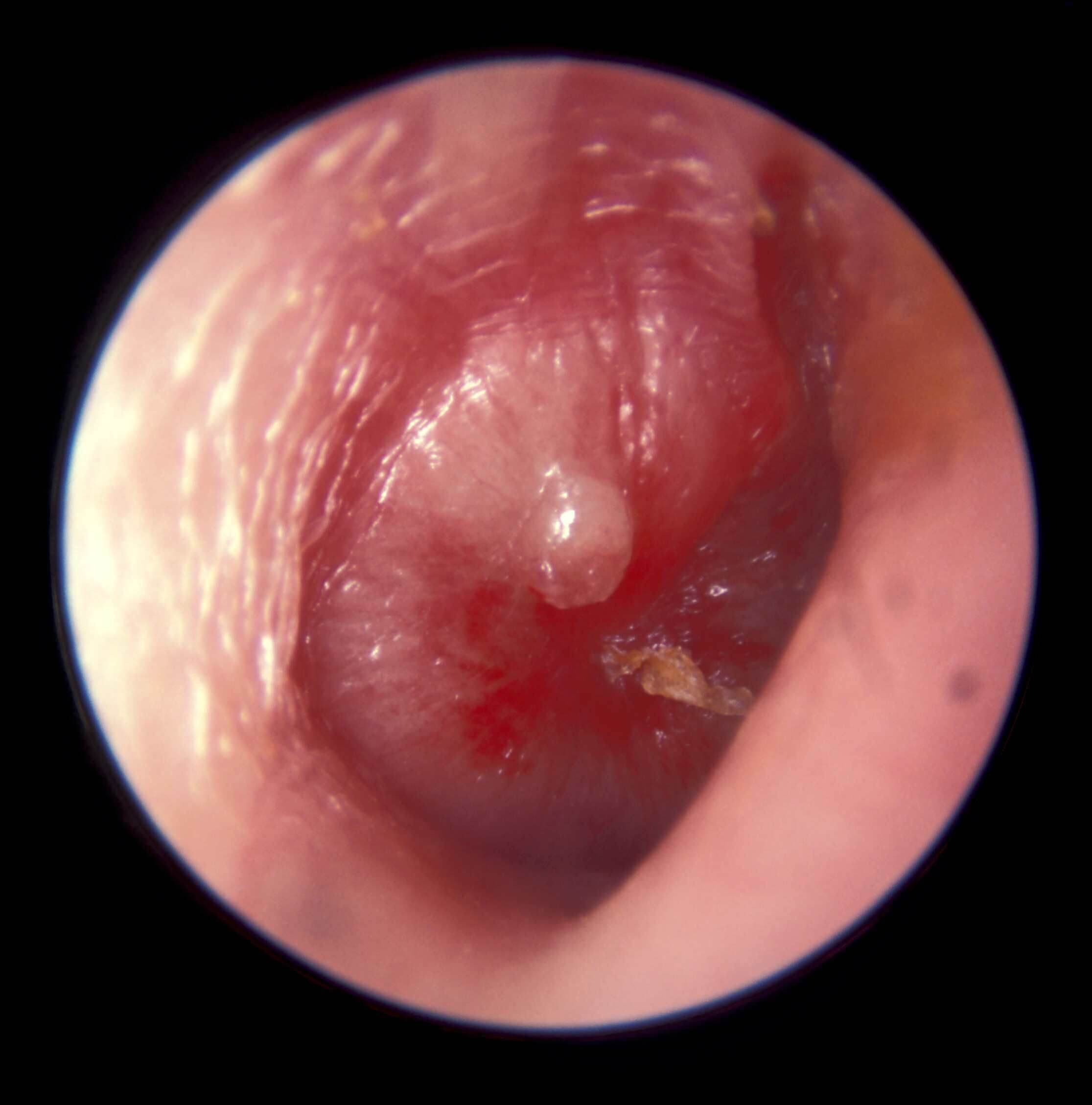
The ear is made up of three different sections: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. These parts all work together so you can hear and process sounds. The outer and middle ear are separated by the eardrum a very thin piece of skin that vibrates when hit by sound waves.
This page deals with middle ear infection , which is the infection / inflammation of the air-filled space behind the eardrum that contains the tiny vibrating bones of the ear. This space can become blocked and filled with mucus , which can become infected, causing inflammation.
There are two types of middle ear infection:
- An acute infection that starts suddenly and lasts for a short period of time and
- A chronic ear infection that does not get better or keeps coming back. Chronic ear infection can result in long-term damage to the ear.
Sometimes gel-like fluid will remain in the middle ear after an ear infection, causing “glue ear“, a relatively common condition that is often undetected among New Zealand pre-schoolers. Glue ear can adversely affect hearing and may take several weeks to resolve.
Outer ear infection is characteristically different to middle ear infection. This is a skin infection in the outer ear canal, which may start as an itch and develop into infection causing inflammation. Sometimes referred to as swimmers ear, this kind of infection can normally be treated effectively with ear drops from your doctor or pharmacist.
Don’t Miss: I Get A Yeast Infection Before Every Period
Symptoms Of Middle Ear Infections
Infection can cause:
- Earache mild to severe pain in the ear or face or pulling at the ear and irritability in an infant
- Fever a high temperature might be the only symptom in babies or young children
- Mild deafness caused by fluid which builds up from the infection
- Ear discharge this happens when the eardrum bursts because of pressure behind it.
Children usually recover from mild infections in three to five hours, although your child may feel tired afterwards.
Are Antibiotics Absolutely Necessary To Treat Ear Infections
No, they are not absolutely necessary, but they are helpful for several reasons:
- Antibiotics will help your child feel better faster by eliminating the bacteria, which in turn reduces the fever and ear pain more quickly. Children generally feel better after one or two days of antibiotics.
- Allowing an ear infection to heal on its own usually subjects a child to four to seven days of fever and ear pain.
- Antibiotics help prevent the very rare, but possible, complications of an ear infection spreading into the brain or bone surrounding the ear.
- New research is suggesting that 80 percent of uncomplicated ear infections will resolve within 4 to 7 days without antibiotics. Parents who choose not to use antibiotics can treat the pain and fever with Auralgan anesthetic ear drops and ibuprofen or acetaminophen, or can try using Xlear® nasal spray as mentioned above.
Read Also: Medicine To Treat Kidney Infection
What Causes Inflammation Of The Outer Ear
Bacteria are the most common cause of an outer ear infection . However, it might be caused by a fungal infection, especially if you’ve previously had antibiotics for a bacterial illness. Non-infectious causes of ear inflammation include allergies, irritants, and skin diseases like eczema.
The ear is surrounded by many sensitive organs – hearing hairs, feeling tympans, and sensing pressure and temperature. Because of this, minor injuries to the ear can lead to inflammation. For example, if you blow your nose too hard and spray tissue into your ears, this could cause pain and swelling. As another example, if you use cotton swabs instead of ear plugs when going through airport security, this could also cause pain and swelling in the ear.
In addition to these things that can cause pain and swelling in the ear, there are certain medical conditions that can lead to ear inflammation without anyone knowing about it. For example, leukemia and lymphoma can cause cancer cells to spread into the blood stream where they can reach any part of the body including the ears. Once in the ears, these cancers can cause severe pain and swelling as well as deafness. Other diseases that can lead to ear inflammation include diabetes, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders such as lupus.
As you can see, inflammation of the ear is very common but not always serious.
About Article Author