How Is It Treated
The standard treatment for HIV is a combination of medicines called antiretroviral therapy, or ART. Antiretroviral medicines slow the rate at which the virus multiplies.
Taking these medicines can reduce the amount of virus in your body and help you stay healthy.
Medical experts recommend that people begin treatment for HIV as soon as they know that they are infected.footnote 2, footnote 3
To monitor the HIV infection and its effect on your immune system, a doctor will regularly do two tests:
- Viral load, which shows the amount of virus in your blood.
- CD4+ cell count, which shows how well your immune system is working.
After you start treatment, it’s important to take your medicines exactly as directed by your doctor. When treatment doesn’t work, it is often because HIV has become resistant to the medicine. This can happen if you don’t take your medicines correctly.
Reverse Transcription And Integration
The viral capsid contains the enzymes necessary for the synthesis of new viral particles from the RNA strands by using cellular machinery of the host cell. One of these enzymes is the reverse transcriptase that synthesizes a double stranded DNA molecule from the existing viral ssRNA. The enzyme first creates a single stranded DNA from viral ssRNA, which is termed as reverse transcription. Using this DNA strand as a template, the enzyme then creates the second strand of DNA molecule, thus giving rise to a dsDNA molecule. The virus does not have its own set of nucleotide bases, and uses those present in the cytoplasm of the T-helper cells.
The dsDNA is tightly bound to a viral enzyme called integrase, and is transported into the nucleus by the cellular transport machinery of T-helper cells. Inside the nucleus, integrase enables the integration of the viral DNA into the DNA of T-helper cells. Using this mechanism the virus can hide and stay in the body in a latent state for several years.
Also Check: What Borough Has The Highest Hiv Rate
Challenges In Studying Non
In ART-suppressed individuals the number of latently infected T cell varies from 1 to 10 infectious units per million . Estimation of these numbers in ART-suppressed individuals requires isolation of millions of cells from large volume blood draws . Similar studies on cells from HIV-1 infected people that have low or absent numbers in circulation, or that are principally found in tissues, have been technically challenging or unethical .
Don’t Miss: Can Minocycline Treat Yeast Infection
Strategies For Preventing The Transmission Of Hiv
|
Condoms made of latex provide good protection against HIV , but they are not foolproof. Oil-based lubricants should not be used because they may dissolve latex, reducing the condomâs effectiveness.
Other measures can help. For men, circumcision, an inexpensive, safe procedure, reduces the risk of becoming infected during vaginal intercourse with an infected woman by about half. Whether circumcision reduces the risk of HIV infection in other circumstances is unclear. Because circumcision provides only partial protection against HIV infection, people should also use other measures to prevent HIV infection. For example, if either partner has a sexually transmitted disease or HIV infection, it should be treated, and condoms should be used correctly and consistently.
Read Also: Can You Get Hiv Using Protection
The Biology Of Microglial Cells
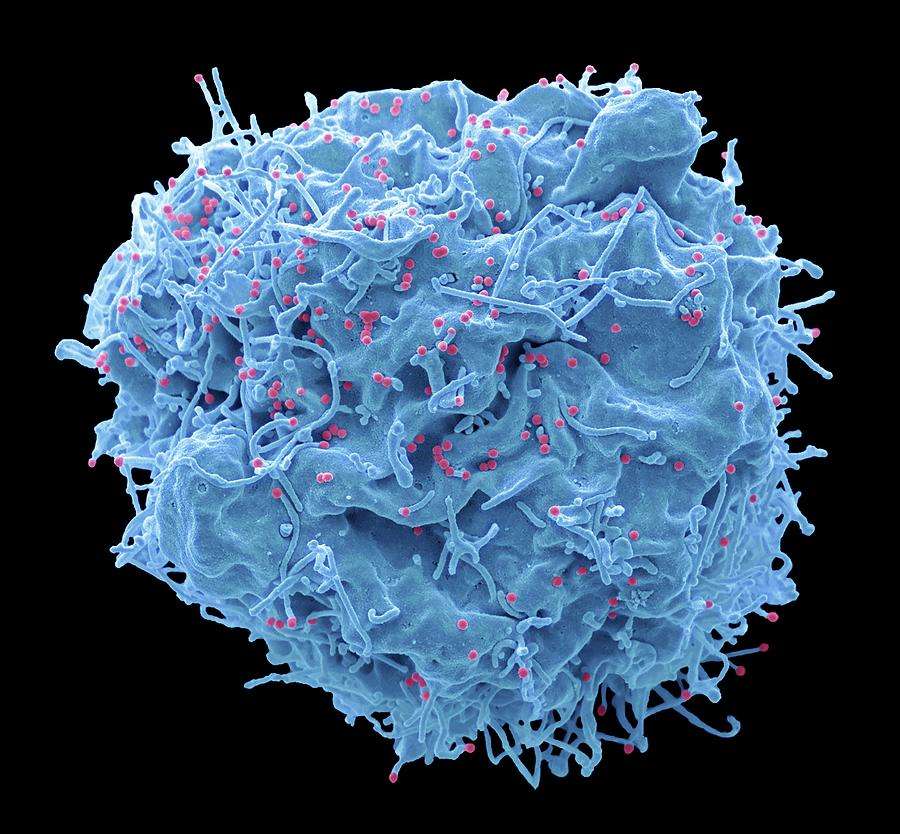
In conclusion, microglial cells fulfill several criteria of a brain reservoir. Most importantly they can subsist for a very long time in the brain and they can colonize the brain parenchyma. Contrary to other potential reservoirs in the brain, these cells divide slowly expanding the viral reservoirs in the brain and thus allowing virus persistence and reseeding of the blood. They are also involved in many functions including immune surveillance. As a consequence, any dysfunction of these cells might explain the occurrence of HAND.
Don’t Miss: Kidney Infection Urgent Care Or Er
How Hiv Infects The Body
HIV is a virus that can cause an HIV infection if it gets into our blood stream.
It then goes on to infect our immune system â the part of our body that keeps you healthy.
It does this by entering T-helper cells so that our immune system canât find and destroy it. Then it makes copies of itself so it can go on to infect other cells.
This is called the HIV lifecycle and it is how the virus multiplies in our body.
Taking antiretroviral drugs is the only way to interrupt the HIV lifecycle and stay healthy.
Entry Via Membrane Fusion
The most well-known example is through membrane fusion. In a number of viruses with a viral envelope, viral receptors attach to the receptors on the surface of the cell and secondary receptors may be present to initiate the puncture of the membrane or fusion with the host cell. Following attachment, the viral envelope fuses with the host cell membrane, causing the virus to enter. Viruses that enter a cell in this manner included HIV, KSHV and herpes simplex virus.
Also Check: Can Ear Infections Clear Up On Their Own
Does Hiv Viral Load Affect Getting Or Transmitting Hiv
Yes. Viral load is the amount of HIV in the blood of someone who has HIV. If taken as prescribed, HIV medicine can reduce a persons HIV viral load very low level, which keeps the immune system working and prevents illness. This is called viral suppression, defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood.
HIV medicine can also make the viral load so low that a standard lab test cant detect it. This is called having an undetectable level viral load. Almost everyone who takes HIV medicine as prescribed can achieve an undetectable viral load, usually within 6 months after starting treatment.
As noted above, people with HIV who take HIV medicine as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load can live long and healthy lives and will not transmit HIVto their HIV-negative partnersthrough sex.
HIV medicine is a powerful tool for preventing sexual transmission of HIV. But it works only if the HIV-positive partner gets and keeps an undetectable viral load. Not everyone taking HIV medicine has an undetectable viral load. To stay undetectable, people with HIV must take HIV medicine as prescribed and visit their health care provider regularly to get a viral load test. Learn more.
Hivs Affect On Receptor Usage
To speculate as to why HIVs have evolved plasticity in their interactions with co-receptors is important. The ability to use multiple functionally redundant contacts with co-receptors could conceivably facilitate immunological escape. Thus, in the face of a neutralising antibody response , the selection of variants with altered envelope sequences would be permitted without compromising the ability of the virus to use a given co-receptor. Furthermore, changes in envelope sequence, that enable the virus to use additional co-receptors while retaining the ability to interact with CCR-5, could be tolerated. It appears that dual-tropic strains that use both CCR-5 and CXCR-4 are less tolerant of perturbations in CCR-5 sequence than are M-tropic strains,, suggesting that acquisition of the ability to utilise CXCR-4 might involve the sacrifice of a degree of functional redundancy and/or affinity in the envelope/CCR-5 interaction.
Recommended Reading: Can Keflex Be Used For Tooth Infection
Hiv Effects On The Kidneys
High blood pressure and diabetes are both related to HIV, and both are major causes of kidney disease. The healthy diet and exercise habits that are good for your heart will help keep your blood pressure and blood sugar under control. That helps protect your kidneys, too.
Some HIV medications can damage your kidneys. If you already have kidney problems, your doctor may want to avoid those drugs or keep a close eye on their effects.
Your doctor will need to check your kidneys regularly because you might not notice the signs of kidney disease.
Recommended Reading: Does Nba Youngboy Have Herpes
Why Does The Immune System Fail To Fight The Hiv Virus
There are various reasons which can contribute to the failure of the immune system to control HIV infection and prevent AIDS development. By infecting CD4+ T cells, HIV is able to replicate predominantly in activated T cells and paralyse one of the main components of adaptive immune system. HIV can also establish latent infection in CD4+ T cells and remain invisible to CD8+ T cells and therefore replication can occur later in the infection and generate new virions. Antigenic mutation within the T-cell epitopes can affect the binding capacity of MHC molecules to the viral peptides, resulting in the inability of the TCRs to recognise the MHC-peptide complex. Finally, HIV is able to hide from anti-HIV antibodies by expressing non-immunogenic glycans on key antibody epitopes.
-
Tests to detect antibodies to the HIV virus in a sample of blood or saliva
-
Tests to detect HIV RNA in a sample of blood
Early diagnosis of HIV infection is important because it makes early treatment possible. Early treatment enables infected people to live longer, be healthier, and be less likely to transmit HIV to other people.
Doctors also do a complete physical examination to check for signs of opportunistic infections, such as swollen lymph nodes and white patches inside the mouth , and for signs of Kaposi sarcoma of the skin or mouth.
Also Check: Natural Medicine For Kidney Infection
How Can I Take Care Of Myself While Living With Hiv
It’s very important to take your medications as prescribed and to make sure you dont miss appointments. This is called treatment adherence.
If you miss medications, even by accident, HIV can change how it infects your cells , potentially causing your medications to stop working. If your schedule prevents you from taking medications on time or making it to appointments, talk to your healthcare provider.
Generalized Epidemics And Global Epidemiology

The HIV infection pandemic is generalized across the adult population in many regions of sub-Saharan Africa, with much of the burden of disease placed on women. In low-income and middle-income countries, approximately half of the people living with HIV infection are women this proportion is higher in sub-Saharan Africa. Most of the transmission events occur as a result of heterosexual transmission from a partner whose HIV status was not known or disclosed . The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS regularly reports on the estimated burden of HIV infection in each country. On a per-capita basis, the countries with highest burden are Swaziland, Lesotho, Botswana and South Africa South Africa is the country with the highest number of HIV-positive people. However, within many countries in this region, large differences in prevalence are evident by geographic region, with South Africa and Kenya being examples. For example, in South Africa, the prevalence of HIV infection in the Western Cape is 7.8%, but 27.9% in KwaZulu-Natal.
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Antibiotics For Ear Infection
Interval Of Mild Or No Symptoms
After the first symptoms disappear, most people, even without treatment, have no symptoms or only occasionally have a few mild symptoms. This interval of few or no symptoms may last from 2 to 15 years. The symptoms that most commonly occur during this interval include the following:
-
Swollen lymph nodes, felt as small, painless lumps in the neck, under the arms, or in the groin
-
White patches in the mouth due to candidiasis
Some people progressively lose weight and have a mild fever or diarrhea.
These symptoms may result from HIV infection or from opportunistic infections that develop because HIV has weakened the immune system.
Make Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet to keep your immune system strong. Heart-healthy eating can help prevent some of the problems, such as high cholesterol, that can be caused by treatment for HIV.
- Learn how to deal with the weight loss that HIV infection can cause.
- Learn how to handle food properly to avoid getting food poisoning. For more information, see the topic Food Poisoning and Safe Food Handling.
- Exercise regularly to reduce stress and improve the quality of your life. Take steps to help prevent HIV-related fatigue.
- Don’t smoke. People with HIV are more likely to have a heart attack or get lung cancer.footnote 23, footnote 24 Cigarette smoking can raise these risks even more.
- Don’t use illegal drugs. And limit your use of alcohol.
Recommended Reading: Under Arm Yeast Infection Treatment
Innate Immune Response To Hiv
Innate immune cells are the first line of defence which HIV encounters upon entry to the body.
Macrophages. Tissue macrophages are one of the target cells for HIV. These macrophages harbour the virus and are known to be the source of viral proteins. However, the infected macrophages are shown to lose their ability to ingest and kill foreign microbes and present antigen to T cells. This could have a major contribution in overall immune dysfunction caused by HIV infection.
Dendritic cells . DCs are large cells with dendritic cytoplasmic extensions. These cells present processed antigens to T lymphocytes in lymph nodes. Epidermal DCs, expressing CD1a and Birbeck granules, are probably among the first immune cells to combat HIV at the mucosal surfaces. These cells transport HIV from the site of infection to lymphoid tissue. The follicular DCs, found in lymphoid tissue, are also key antigen-presenting cells that trap and present antigens on their cell surfaces. In the lymph node follicles, DCs provide signals for the activation of B lymphocytes.
If You Already Have Hiv
If you are infected with HIV, you can greatly lower the risk of spreading the infection to your sex partner by starting treatment when your immune system is still healthy.
Experts recommend starting treatment as soon as you know you are infected.footnote 20
Studies have shown that early treatment greatly lowers the risk of spreading HIV to an uninfected partner.footnote 21, footnote 22
Your partner may also be able to take medicine to prevent getting infected.footnote 16 This is called pre-exposure prophylaxis .
Steps to prevent spreading HIV
If you are HIV-positive or have engaged in sex or needle-sharing with someone who could be infected with HIV, take precautions to prevent spreading the infection to others.
- Take antiretroviral medicines. Getting treated for HIV can help prevent the spread of HIV to people who are not infected.
- Tell your sex partner or partners about your behavior and whether you are HIV-positive.
- Follow safer sex practices, such as using condoms.
Read Also: Can I Use Teladoc For A Yeast Infection
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection
, MD, MAS, University of California, San Diego School of Medicine
-
HIV is transmitted through close contact with a body fluid that contains the virus or cells infected with the virus .
-
HIV destroys certain types of white blood cells, weakening the bodys defenses against infections and cancers.
-
When people are first infected, symptoms of fever, rashes, swollen lymph nodes, and fatigue may last a few days to several weeks.
-
Many infected people remain well for more than a decade.
-
About half of untreated people become ill and develop AIDS, defined by the presence of serious infections and cancers, within about 10 years.
-
Eventually, most untreated people develop AIDS.
-
Blood tests to check for HIV antibody and to measure the amount of HIV virus can confirm the diagnosis.
-
HIV drugs two, three, or more taken togethercan stop HIV from reproducing, strengthen the immune system, and thus make people less susceptible to infection, but the drugs cannot eliminate HIV, which persists in an inactive form.
HIV infections may be caused by one of two retroviruses, HIV-1 or HIV-2. HIV-1 causes most HIV infections worldwide, but HIV-2 causes many HIV infections in West Africa.
You May Like: Is Std And Hiv The Same
Pathology And Pathogenesis Of Hiv Encephalitis
During the later stages of HIV infection, a subset of patients experience nervous system disease. Peripheral macrophage infiltration into brain is a widely observed component of HIV encephalitis . Clinical-pathologic investigation has shown that proliferation and immune activation of infiltrated and resident brain MP correlates better with HAD progression than does the CNS viral load . Perivascular and parenchymal brain macrophages fuse with one another and with resident microglia to form multinucleated giant cells . Pathological signs of a giant cell encephalitis can be found in cortex but preferentially affects subcortical white matter, deep white tracts and basal ganglia. Other histologic findings include microglial nodules, neuronal dropout, diffuse myelin pallor and reactive astrogliosis. Myelin pallor of HIV encephalitis represents disruption of the neuron-oligodendrocyte interaction. The HIV encephalitic brain may appear atrophic with ventricular dilatation but is otherwise unremarkable. Interestingly, the pathological features of HIV-encephalitis do not always correlate with clinical neurologic deficits.
Read Also: Does Cookie Johnson Have Hiv
Recommended Reading: Warning Your Computer Is Infected
Hiv Variation In Different Tissues
Envelope/co-receptor interactions may also influence early post-entry events in some cell types favouring some strains over others. For instance, the observations that both M-tropic and T-tropic SIVMAC strains enter macrophages, while only M-tropic envelopes signal via CCR5 has raised the possibility that co-receptor signalling events induced by a virus entering at the cell surface may be a requirement for replication in some cell types. Signalling during virus entry, however, is controversial and recent data showing that increased expression of CCR5 on the surface of macrophages fully rescues T-tropic SIV replication probably argue against, in this instance.
Thus different cell types in distinct environments will select for or against particular R5 viruses or quasispecies however, the extent this happens and its impact on pathogenesis is unclear.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take For Hiv To Become Aids