When To See Your Gp
See your GP if you have a fever and persistent tummy, lower back or genital pain, or if you notice a change to your usual pattern of urination.
Most kidney infections need prompt treatment with antibiotics to stop the infection from damaging the kidneys or spreading to the bloodstream. You may also need painkillers.
If youre especially vulnerable to the effects of an infection for example, if you have a pre-existing health condition or are pregnant, you may be admitted to hospital and treated with antibiotics through an intravenous drip.
After taking antibiotics, you should feel completely better after about two weeks.
In rare cases, a kidney infection can cause further problems. These include blood poisoning and a build-up of pus in the kidney called an abscess.
Donât Miss: Stop Tooth Infection Without Antibiotics
How Are Utis Diagnosed
Only a health care provider can treat urinary tract infections. The first thing a doctor will do is confirm that a person has a UTI by taking a clean-catch urine specimen. At the doctors office, youll be asked to clean your genital area with disposable wipes and then pee into a sterile cup.
The sample may be used for a urinalysis or a urine culture . Knowing what bacteria are causing the infection can help your doctor choose the best treatment.
Read Also: Will Overactive Bladder Go Away
What Are Potential Kidney Infection Complications
Most people recover 100% from a kidney infectionbut there is the possibility of serious complications if one is left untreated. As we mentioned, a kidney infection that doesnt get treated can cause a condition known as sepsis. This happens when your body responds overzealously to an infection, which can lead to a dangerous drop in blood pressure and cause the body to go into shock, according to the NIDDK. This can make your organs fail, which, in the most extreme cases, can lead to death.
Even in non-life-threatening cases, if you have a kidney infection that becomes chronic, you can wind up with permanent kidney damage that can cause problems like kidney disease or high blood pressure. In pregnant people, untreated kidney infections can also increase the risk of having a baby with low birth weight, notes the Mayo Clinic.
All of that sounds scary, but heres whats most important to know: A kidney infection is treatable. Its all about how soon you seek treatment once you start experiencing kidney infection symptoms.
Recommended Reading: What Is Used To Treat Ear Infections
How Are Kidney Infections Treated
A physician will treat the disease based on his or her examination. He or she may start the patient on the standard treatment of a course of antibiotics before the lab tests results are available. The medication may change once the exact strain of bacteria is revealed by the lab tests.
If the treatment is effective, the patient should feel better in two to three days. If not, your healthcare provider will start looking for additional problems. Most antibiotic treatments last for 14 days and it is essential that patients take the pills as recommended for the full 14 days even though symptoms may disappear after a few days. The disappearance of symptoms does not mean all bacteria are killed. Some may remain and the infection may reappear.
There is also a concern that those bacteria that remain may develop resistance to the medication. For some reason the disease is more difficult to treat in men and they may have to take medication for up to six weeks. Patients with severe illness, those that have significant nausea and vomiting, high fevers, significant pain and signs of dehydration may be hospitalized for a few days while the antibiotics are administered intravenously. Urine samples are taken after about six weeks of treatment and examined to insure the bacterial infection is eradicated.
Read Also: Is Pomegranate Juice Good For Your Kidneys
When To Go To The Doctor
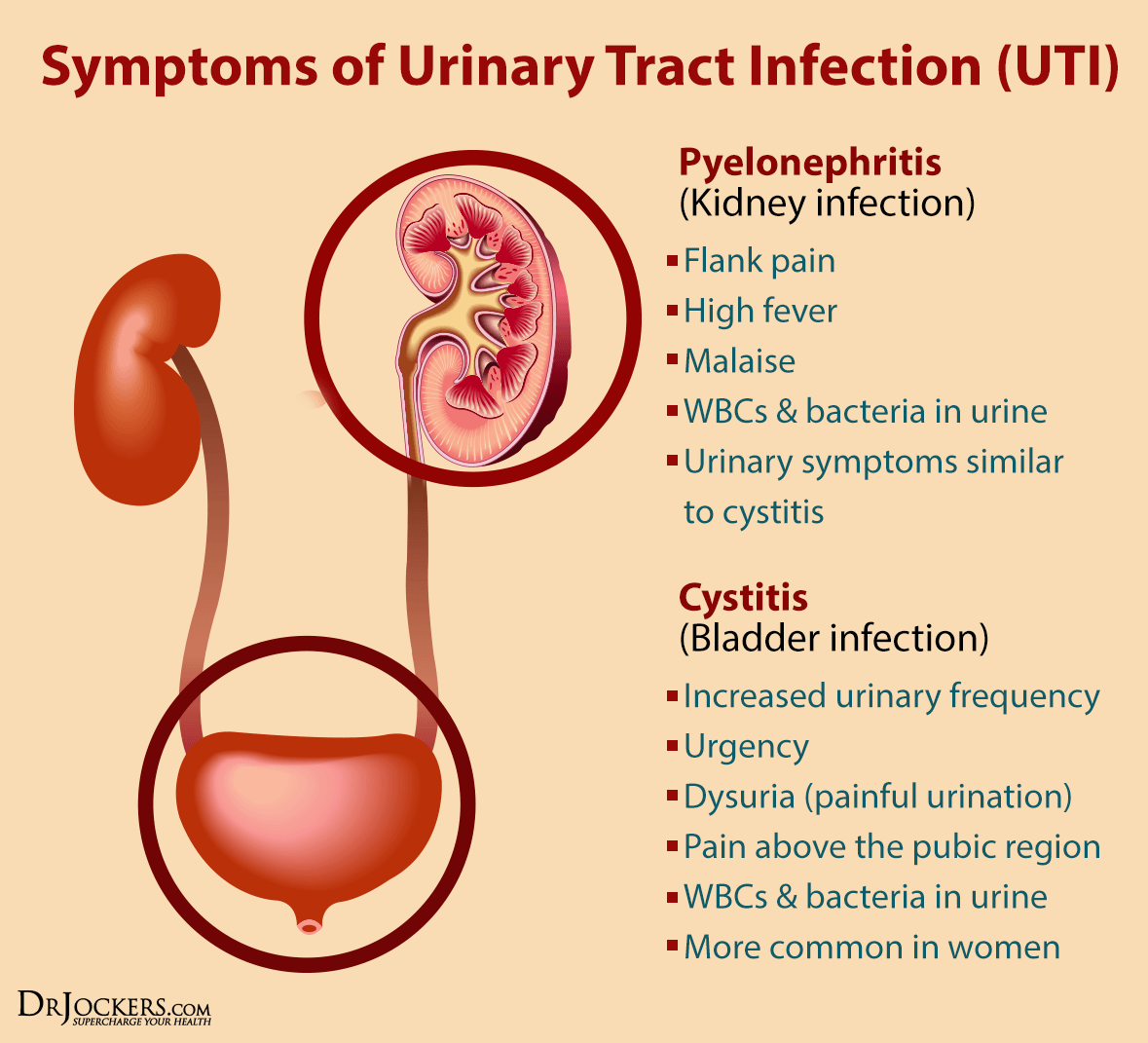
Pain and burning during urination can be caused by multiple conditions that affect the health of our urinary system. Sometimes this condition can also spread from the urinary system to the rest of the body. This is a symptom that should not be ignored. It is important to consult a medical specialist if you notice any of the following:
- Increased need for urination
- Pain, burning, stinging during urination.
- Pain in the lower abdomen or back.
- Smelly, cloudy or dark urine.
- Presence of blood in the urine.
- Fever, tremors and / or chills.
- You are urinating very little or practically nothing.
A doctor to will be able to diagnose your symptoms and treat your infection appropriately. For this diagnosis a doctor will generally conduct several different medical tests, which could include a urinalysis, a urine culture, urethral or vaginal flow analysis, ultrasound of the bladder, kidney or prostate, etc.
Treatment of pain and burning when urinating will depend on the specific case. If the origin stems from a urine infection, antibiotics will usually be administered.
You May Like: How Long Does A Yeast Infection Last Without Treatment
Read Also: Oral Prescription For Yeast Infection
What Are The Types Of Dialysis
Dialysis is a process that does the work of healthy kidneys when you have kidney failure. Dialysis filters wastes, removes extra fluid, and restores the proper balance of chemicals in the blood.
There are two basic types of dialysis: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
- Hemodialysis uses a man-made membrane called a dialyse to clean your blood. You are connected to the dialyse by tubes attached to your blood vessels. Before hemodialysis treatments can begin, your doctor will need to create a site where blood can flow in and out of your body. This is called the dialysis access. In some cases, hemodialysis can be done at home. You will need to be trained, and you will need to make room for the dialysis machine. You may have choices for how often and how long you need dialysis.
- Peritoneal dialysis uses the lining of your belly, which is called the peritoneal membrane, to filter your blood. Before you can begin peritoneal dialysis, your doctor will need to place a catheter in your belly for the dialysis access.
Also Check: Can A Uti Lead To A Yeast Infection
Seek Medical Attention For Utis
It is important to seek medical attention if you think you may have a UTI particularly if you think you may have a bladder or kidney infection, both of which are very serious conditions. Early treatment of urinary infection can help to prevent infection spreading to the bladder or kidneys.
Your doctor will test your urine to check which micro-organism is present. Urinary tract infections usually respond quickly and well to antibiotics.
Also Check: How Do Bladder Infections Happen
Also Check: Emergency Antibiotics For Tooth Infection
How Do Doctors Treat A Kidney Infection
Doctors treat most kidney infections with antibiotics . Doctors will often first prescribe an antibiotic that fights the most common types of kidney infection because it is very important to treat a kidney infection right away. Then, they may change the type of antibiotic after they get the results of your blood or urine tests.
Doctors will prescribe an antibiotic medicine based on:
- What type of bacteria is causing the infection
- How severe the infection is
- If you are you are pregnant
- If you are older than 65
- If you had problems from certain antibiotics in the past, such as allergic reactions
If you have a very serious infection, you may need to stay in the hospital to get antibiotics through an IV . You may also get medicine for pain.
If your kidney infection was caused by a problem with the shape of your urinary tract, you may need to have surgery to correct the problem and prevent future kidney infections.
Treatment For Utis Vs Kidney Infection Treatment
UTIs, including kidney infections, can be treated with a course of antibiotics. The type of antibiotic can depend on the type of bacteria thats causing your infection as well as how severe your infection is.
The doctor will often start you on an antibiotic that works against a wide variety of UTI-causing bacteria. If a urine culture is performed, the doctor may switch your antibiotic to one thats most effective at treating the specific bacterium thats causing your infection.
Simple UTIs can be treated with short 3- to 5-day courses of antibiotics. Treatment for kidney infections generally lasts 7 to 14 days, depending on which class of antibiotic is prescribed.
You may begin to feel better after only a few days on antibiotics. However, you should still make sure that you complete your entire treatment course as prescribed. If you do not take all of your antibiotics, the stronger bacteria may not be killed, causing your infection to persist and flare up again.
If youre pregnant, your doctor may also request a repeat urine sample following a kidney infection, even if your symptoms have resolved. This allows them to check to see whether your infection has completely cleared.
If there are still bacteria present in the sample, you may need another course of antibiotics. Persistence of bacteria can potentially harm an unborn baby.
People with severe kidney infections may need to be hospitalized. In this case, you may receive antibiotics and fluids intravenously.
Recommended Reading: Can Mild Yeast Infection Cure Itself
Treatment From A Gp For Utis That Keep Coming Back
If your UTI comes back after treatment, you may have a urine test and be prescribed different antibiotics.
Your doctor or nurse will also offer advice on how to prevent UTIs.
If you keep getting UTIs and regularly need treatment, a GP may give you a repeat prescription for antibiotics.
If you have been through the menopause, you may be offered a vaginal cream containing oestrogen.
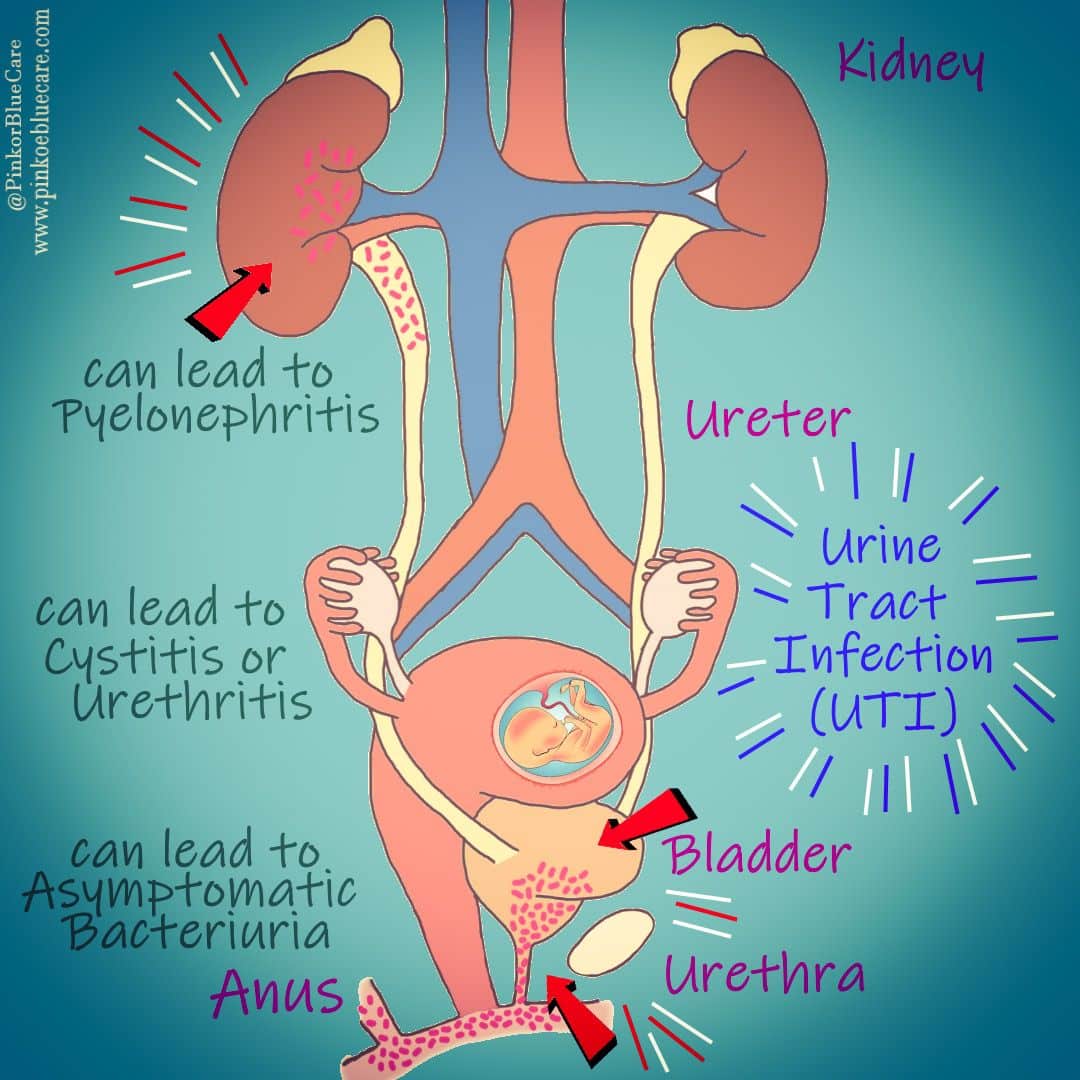
Causes Of Kidney Infection
A kidney infection usually happens when bacteria, often a type called E. coli, get into the tube that carries urine out of your body .
The bacteria travel up to your bladder, causing cystitis, and then up into your kidneys.
E. coli bacteria normally live in your bowel, where they cause no harm.
They can be transferred from your bottom to your genitals during sex or if you’re not careful when wiping your bottom after going to the loo.
A kidney infection can sometimes develop without a bladder infection. For example, if you have a problem with your kidney, such as kidney stones, or if you have diabetes or a weakened immune system.
Read Also: How To Speed Up Yeast Infection Recovery
Top Tips To Prevent Further Kidney Infections
Some of the things that may help include the following:
- Dont hold on to urine. Go to the toilet promptly
- Stay well hydrated and make sure you drink plenty of fluids every day
- Constipation can increase your chances of a bladder or kidney infection, so treat constipation promptly
- Empty your bladder after having sex
- Always make sure that you wipe from front to back after going to the toilet
- Avoid using feminine products such as deodorant sprays or douches in your genital area
Kimberly-Clark Australia makes no warranties or representations regarding the completeness or accuracy of the information. This information should be used only as a guide and should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional medical or other health professional advice.
Arnold, J., McLeod, N., Thani-Gasalam, R. and Rachid, P. . RACGP – Overactive bladder syndrome management and treatment options. Racgp.org.au. Available at:.
Bladderclinic.com.au, . Overactive Bladder . Available at:.
Cherney, K. . Home Remedies for Overactive Bladder. Healthline. Available at:.
Eilber, MD, K. . What Is The Difference Between A Small Bladder And An …. EmpowHER. Available at:
How To Feel Better
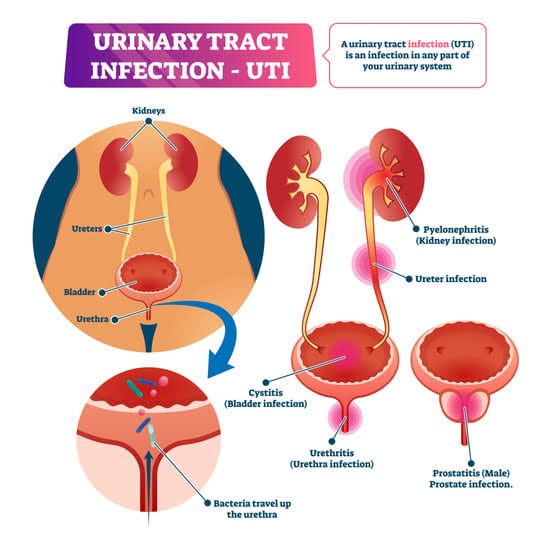
If your healthcare professional prescribes you antibiotics:
- Take antibiotics exactly as your healthcare professional tells you.
- Do not share your antibiotics with others.
- Do not save antibiotics for later. Talk to your healthcare professional about safely discarding leftover antibiotics.
Drink plenty of water or other fluids. Your healthcare professional might also recommend medicine to help lessen the pain or discomfort. Talk with your healthcare professional if you have any questions about your antibiotics.
Read Also: Antibiotics For Viral Sinus Infection
When To See Your Doctor
Kidney pain is almost always a sign that something is wrong with your kidney. You should see your doctor as soon as possible to determine whats causing your pain.
If the condition that has caused kidney pain isnt treated promptly and appropriately, your kidneys can stop working, which is called kidney failure.
Its especially important to see your doctor right away if your pain is severe and started suddenly because this is often caused by a serious problem such as renal vein thrombosis or bleeding into your kidney that needs emergency treatment.
The Pathogen/s Causing Your Symptoms May Not Be In Your Sample
Standard UTI test methods focus on free-floating pathogens .
With every recurrence of UTI, there is an increased risk of an embedded, difficult-to-treat bladder infection. An infection embedded in or attached to the bladder wall is called a biofilm.
Biofilms arent always bad many types of bacteria form these structures naturally and theyre an important part of the gut microbiome.
When bacteria form biofilms in the bladder, they are no longer free-floating. If the bacteria are not floating around in the urine, they will not be passed into your sample on urination.
If the bacteria are not in your sample, they will not be detected.
There are other reasons your sample may not contain detectable levels of bacteria, including over-hydration. If your bladder is frequently flushed and your urine is diluted, your sample may not contain enough of anything a urine culture can detect.
Also Check: Can A Bad Tooth Cause Ear Infection
Prevention And Treatment Of Kidney Infection
-
Occasionally surgery
Antibiotics are started as soon as the doctor suspects pyelonephritis and samples have been taken for laboratory tests. The choice of drug or its dosage may be modified based on the laboratory test results , how sick the person is, and whether the infection started in the hospital, where bacteria tend to be more resistant to antibiotics. Other factors that can alter the choice or dosage of drug include whether the persons immune system is impaired and whether the person has a urinary tract abnormality , including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Blockage can be complete read more ).
Outpatient treatment with antibiotics given by mouth is usually successful if the person has:
-
No nausea or vomiting
Its Almost Impossible To Collect An Uncontaminated Urine Sample
If youve ever had to provide a urine sample for any type of testing, youre probably familiar with the terms midstream and clean-catch. These basically refer to a urine sample that is captured only during the middle timeframe of urination and is free from contamination. There are two issues here.
Second, its really hard to perch over a toilet, separate the labia , and at the same time have a sample collection cup at the ready, and then only capture 30mL or so of urine from a stream that could be hundreds of milliliters in total.
The result of all this difficulty is that up to 1 in 4 urine samples are considered contaminated. Regardless of the type of testing you choose or are recommended, its always best to have an accurate sample.
Also Check: Can A Yeast Infection Cause Bleeding
What Conditions Are Related To Recurrent Utis
Recurrent UTIs sometimes happen along with other conditions, such as:
- vesicoureteral reflux , which is found in 30%50% of kids diagnosed with a UTI. In this congenital condition, pee flows backward from the bladder to the ureters. Ureters are thin, tube-like structures that carry pee from the kidney to the bladder. Sometimes the pee backs up to the kidneys. If it’s infected with bacteria, it can lead to pyelonephritis.
- hydronephrosis, which is an enlargement of one or both kidneys due to backup or blockage of urine flow. It’s usually caused by severe VUR or a blocked ureter. Some kids with hydronephrosis might need to take daily low doses of antibiotics to prevent UTIs until the condition producing hydronephrosis gets better or is fixed through surgery.
But not all cases of recurrent UTIs can be traced back to these body structure-related problems. For example, dysfunctional voiding when a child doesn’t relax the muscles properly while peeing is a common cause of UTIs. Not peeing often enough also can also increase a child’s risk for recurrent infections. Both dysfunctional voiding and infrequent urination can be associated with constipation.
Rarely, unrelated conditions that harm the body’s natural defenses, such as diseases of the immune system, also can lead to recurrent UTIs. Use of a nonsterile urinary catheter can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract and also cause an infection.
Types Of Kidney Infection
Kidney infections can be acute or chronic.
An acute kidney infection is one that goes away after treatment.
A chronic infection comes and goes, or may never go away properly. This type of infection can damage the kidneys. It usually occurs if there is a problem that causes urine to flow backwards from the bladder and up into the kidneys.
Recommended Reading: Kyleena Iud And Yeast Infection
What Is The Outlook For Kidney Infections
With treatment, the outlook for kidney infections is very positive. It is vital that you take all of any prescribed medications for the infection. You may begin feeling better shortly after beginning a treatment, but still need to take the entire prescribed treatment.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 05/22/2019.
References
- National Kidney Foundation. Urinary Tract Infections Accessed 5/23/19.
- National Institute of Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases . Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection Accessed 5/23/19.
Lab Tests For Kidney Infection
The most common lab tests to help diagnose a kidney infection are two types of urine test:
Urinalysis For this test, youll urinate into a container at your doctors office or lab. A sample of your urine will be viewed under a microscope, to look for bacteria or white blood cells, which can indicate an infection.
Its possible for healthy people to have bacteria in their urine, so its important for urinalysis results to be viewed in the context of your symptoms, rather than as definitive evidence of an infection.
Urine Culture To help determine what kind of bacteria are causing your infection and guide your treatment, a sample of your urine may be placed in a container where the bacteria can grow for one to three days.
In some cases, your doctor may order a blood test to look for signs of an infection. This can involve two different tests:
Peripheral Blood Smear For this test, a thin layer of your blood is viewed under a microscope to look for an elevated white blood cell count and for neutrophils, the type of white blood cells that fight infection.
Blood Culture A sample of your blood is placed in a container to encourage bacterial growth, then examined over one to three days for bacteria that would indicate an infection.
While 20 to 30 percent of kidney infections show positive blood culture results, theres little evidence that this testing helps guide treatment or improve outcomes, according to Johns Hopkins Medicine.
Don’t Miss: Ear Nose And Throat Infection