How Does Hiv Spread Throughout The Body
HIV cannot reproduce on its own, so it must get into these cells so that it can copy itself.
First, the virus attaches itself to a T-helper cell and fuses with it . It then takes control of the cellâs DNA, makes copies of itself inside the cell, and finally releases more HIV into the blood.
HIV will continue to multiply and spread throughout the body. This is a process called theâ¯HIV lifecycle.
Whats The Difference Between Hiv And Aids
The difference between HIV and AIDS is that HIV is a virus that weakens your immune system. AIDS is a condition that can happen as a result of an HIV infection when your immune system is severely weakened.
You cant get AIDS if you arent infected with HIV. Thanks to treatment that slows down the effects of the virus, not everyone with HIV progresses to AIDS. But without treatment, almost all people living with HIV will advance to AIDS.
What Tests Diagnose Hiv
There are three types of HIV tests: antigen/antibody tests, antibody tests and nucleic acid tests :
Antigen/antibody tests
Antigen tests look for markers on the surface of HIV called p24. Antibody tests look for chemicals your body makes when it reacts to those markers. HIV antigen/antibody tests look for both.
A healthcare provider will take a small sample of blood from your arm with a needle. The blood is sent to a lab and tested for p24 and antibodies to it. An antigen/antibody test is usually able to detect HIV in 18 to 45 days after exposure.
A rapid antigen/antibody test may also be done with a finger prick to draw blood. Youll need to wait at least 18 days after exposure for this type of test to be able to detect HIV. You may need to take the test up to 90 days after exposure for accurate results.
Antibody tests
These tests look for antibodies to HIV in your blood or saliva. This can be done with a blood draw from your arm, a finger prick or with a stick that you rub on your gums to collect saliva.
An antibody test can take 23 to 90 days after exposure to detect HIV. Antibody tests done with a blood draw can detect HIV sooner than those done with saliva or blood from a finger prick.
Nucleic acid tests
NATs look for the HIV virus in your blood. A healthcare provider will take a small sample of blood from your arm with a needle. The blood then is sent to a lab and tested for HIV.
- Viral hepatitis screening.
Recommended Reading: Which Type Of Cell Does Hiv Infect
Do Hiv Medicines Work Against Latent Hiv Reservoirs
HIV medicines prevent HIV from multiplying, which reduces the amount of the virus in the body . Because the HIV-infected cells in a latent reservoir are not producing new copies of the virus, HIV medicines have no effect on them.
People with HIV must take a daily combination of HIV medicines to keep their viral loads low. If a person stops taking their HIV medicines, the infected cells of the latent reservoir can begin making HIV again and the person’s viral load will increase. That is why it is important to continue taking HIV medicines every day as prescribed, even when viral load levels are low.
How Does Hiv Affect The Body
The human immune system involves many types of cells which guard against germs responsible for most diseases. The immune system’s most important guard cells are B-cells and T-cells, which are special white blood cells. B-cells and T-cells cooperate to fight any germ that attacks the human body.
B-cells produce particular proteins, called antibodies, that try to neutralize the invading germ. After a person recovers from an infection, these antibodies continue to circulate in the bloodstream, acting as part of the immune system’s “memory.” Immune system memory explains why a person rarely suffers a second attack from an infectious disease such as measles. If the same germ is encountered again, the antibodies will recognize and neutralize it. T-cells attack the germ directly and try to kill it.
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Yeast Infections While On Farxiga
Where Can Someone Get Tested For Hiv
Your health care provider can give you an HIV test. HIV testing is also available at many hospitals, medical clinics, substance use programs, and community health centers. Use CDC’s GetTested treatment locator to find an HIV testing location near you. Getting tested through a professional health care provider is recommended however, there are HIV self-testing kits available. Rapid self-test and mail-in self-test are the two types of HIV self-tests, but state laws regarding self-testing may limit their availability in a location.
A rapid self-test is an oral fluid test done entirely at home or in private. There is currently one U.S. Food and Drug Administration -approved rapid self-test called OraQuick In-Home HIV test. A mail-in self-test requires a person to provide a blood sample from a fingerstick, which is then sent to a lab for testing.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hiv
Not everyone will have identical symptoms because it depends on the person and what stage of the disease they are in.
There are three stages of human immunodeficiency virus . Each stage has a unique set of symptoms. These include the following
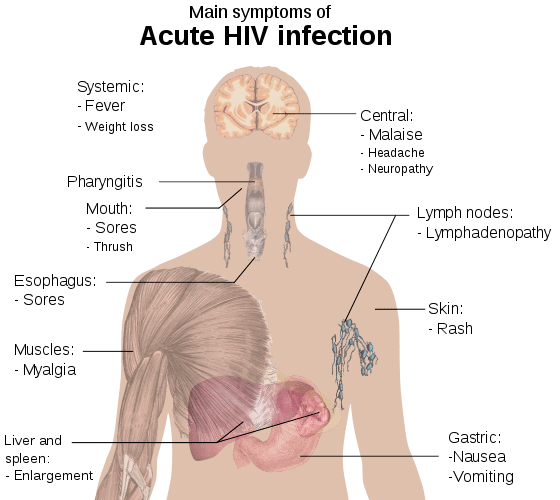
Stage 1: Acute HIV infection
This stage starts around two to four weeks after getting HIV. The symptoms are similar to those of the flu, which last for a week or two. Symptoms include the following
You May Like: Medication For Bladder Infection Over The Counter
Why Is Hiv Testing Important
Knowing your HIV status can help keep youand otherssafe.
If you are HIV negative:
A negative HIV test result shows that you do not have HIV. Continue taking steps to avoid getting HIV, such as using condoms during sex and, if you are at high risk of getting HIV, taking medicines to prevent HIV . For more information, read the HIVinfo fact sheet on The Basics of HIV Prevention.
If you are HIV positive:
A positive HIV test result shows that you have HIV, but you can still take steps to protect your health. Begin by talking to your health care provider about antiretroviral therapy . People on ART take a combination of HIV medicines every day to treat HIV infection. ART is recommended for everyone who has HIV, and people with HIV should start ART as soon as possible. ART cannot cure HIV, but HIV medicines help people with HIV live longer, healthier lives.
A main goal of ART is to reduce a persons viral load to an undetectable level. An undetectable viral load means that the level of HIV in the blood is too low to be detected by a viral load test. People with HIV who maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partner through sex.
Is Hiv Testing Confidential
HIV testing can be confidential or anonymous.
Confidential testing means that your HIV test results will include your name and other identifying information, and the results will be included in your medical record. HIV-positive test results will be reported to local or state health departments to be counted in statistical reports. Health departments remove all personal information from HIV test results before sharing the information with CDC. CDC uses this information for reporting purposes and does not share this information with any other organizations, including insurance companies.
Anonymous testing means you do not have to give your name when you take an HIV test. When you take the test, you receive a number. To get your HIV test results, you give the number instead of your name.
Also Check: Can A Sinus Infection Turn Into An Ear Infection
How Do I Take Care Of Myself With Hiv
The best way to take care of yourself while living with HIV is to follow your treatment plan.
- Make sure to take your medications as prescribed and on time.
- Show up to all appointments so your healthcare team can monitor how youre feeling and know if theres a need to adjust your treatment.
- Follow your healthcare providers recommendations on how to avoid additional illnesses.
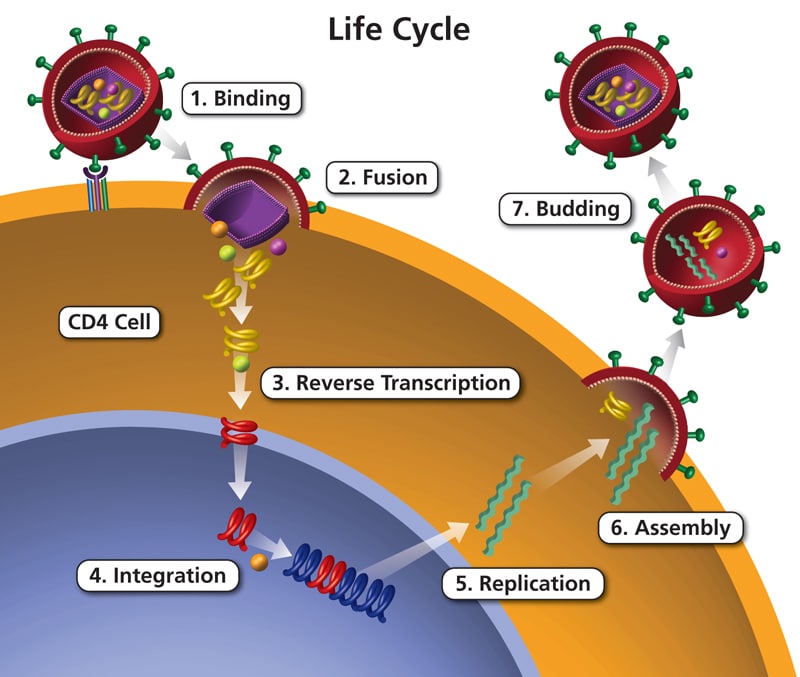
What Is The Hiv Life Cycle
HIV attacks and destroys the CD4 cells of the immune system. CD4 cells are a type of white blood cell that play a major role in protecting the body from infection. HIV uses the machinery of the CD4 cells to multiply and spread throughout the body. This process, which is carried out in seven steps or stages, is called the HIV life cycle.
Read Also: What Cells Are Infected And Destroyed In Hiv Infection
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
- Am I at high risk for HIV?
- What can I do to reduce my risk of HIV?
- How can I make sure I take my medications correctly?
- What can I do to protect myself from other illnesses?
- How can prevent the spread of HIV?
- What do my test results mean?
- What do my blood counts mean?
- What vaccinations should I get?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Treatments have come a long way since the height of the AIDS epidemic. You have the best chance of living a long life if youre diagnosed early and are able to get on and stick with ART medications. People living with HIV today are able to work, have active social lives and families, and pursue fulfilling relationships. In fact, this can have a positive impact on your well-being.
While weve come a long way with treatments, unfortunately, social stigmas around HIV still persist. In addition to the feelings of fear and uncertainty a new diagnosis can bring, you may wonder how those around you will respond. If youre hesitant to get tested or get treatment, or if you just arent sure what your next steps are, you can reach out to a community organization that specializes in HIV. Remember that you are deserving of support, compassion and high-quality healthcare.
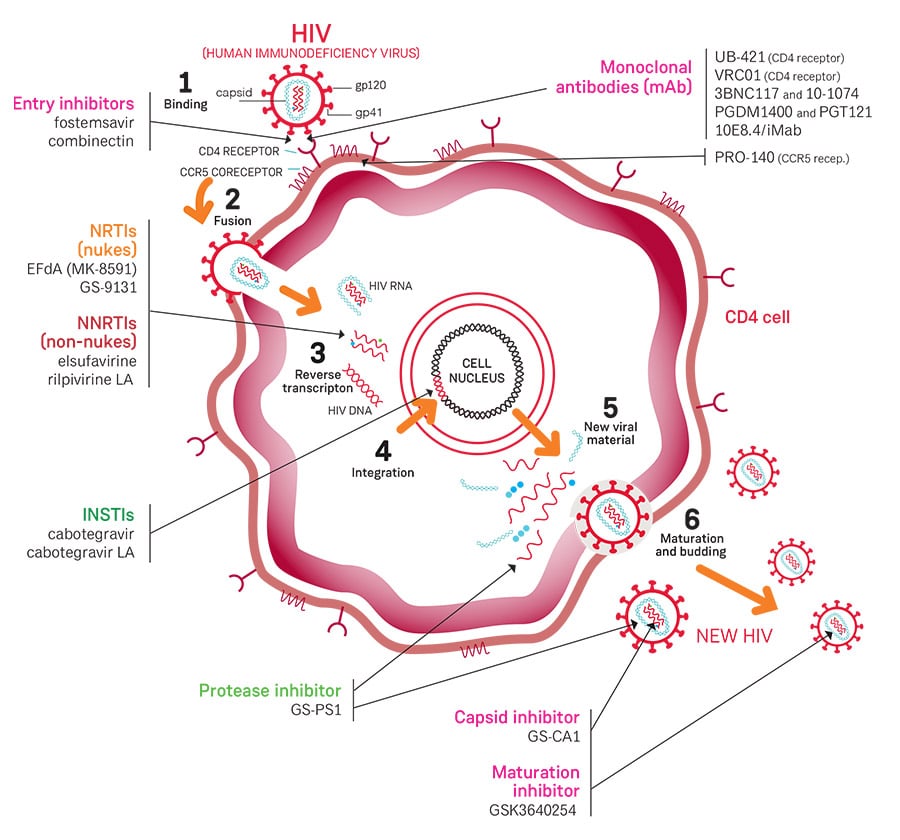
Targeted Antiretroviral Drugs For Each Stage
The primary goals of antiretroviral therapy are to prevent HIV from replicating and suppressing your viral load to a point where its no longer detectable.
Antiretroviral drugs are divided into seven drug classes depending on which part of HIVs lifecycle they interrupt. At least two different drug classes are used during antiretroviral therapy. Each medication typically has two or three of the drugs in it.
Also Check: Antibiotics For Uti Bladder Infection
Can Medications Prevent Hiv
There are medications that can help prevent HIV in people who have been exposed or are at high risk for exposure. These include pre-exposure prophylaxis and post-exposure prophylaxis .
Pre-exposure prophylaxis
PrEP is a pill you take every day if you dont have HIV but are at high risk of getting infected.
- You have a sexual partner with HIV.
- You havent consistently used a condom.
- In the past six months, youve been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease .
PrEP is also recommended if you dont have HIV, you inject drugs and at least one of the following is true:
- You inject drugs with a partner who has HIV.
- You share needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
PrEP is not a replacement for other preventative measures. You should still use condoms and avoid sharing needles to inject drugs while taking PrEP.
Post-exposure prophylaxis
PEP uses HIV medicines to try to prevent an HIV infection soon after you are exposed. PEP is for those who dont have HIV or dont know if they have HIV and think theyve been exposed through consensual sex, sexual assault, shared needles , or work.
You must start PEP within 72 hours of exposure and take it every day for 28 days. PEP is only for emergency use and does not replace other precautions, like condom use.
Can You Get Hiv From Kissing
Since HIV is not spread through spit, kissing is not a common way to get infected. In certain situations where other body fluids are shared, such as if both people have open sores in their mouths or bleeding gums, there is a chance you could get HIV from deep, open-mouthed kissing.
You also dont get HIV from:
- Touching or hugging someone who has HIV/AIDS.
- Public bathrooms or swimming pools.
- Sharing cups, utensils or telephones with someone who has HIV/AIDS.
- Donating blood.
You May Like: Can You Get A Yeast Infection After A Uti
Stage : Seroconversion Illness
The primaryinfection stage only lasts for a number of weeks, during which the person maysuffer from flu-like symptoms such as fever, upset stomach, sore throat ormuscle pain. About one fifth of people would suffer enough to see a doctor butHIV is rarely diagnosed on this alone.
At this point, the immune system is starting to react to the virus by producing HIV antibodies and cytotoxic lymphocytes a process known as seroconversion. A third generation HIV test carried out before this process is complete may be negative or inconclusive.
What Are The Types Of Hiv Tests
There are three types of tests used to diagnose HIV infection: antibody tests, antigen/antibody tests, and nucleic acid tests . Your health care provider can determine the appropriate HIV test for you. How soon each test can detect HIV infection differs, because each test has a different window period. The window period is the time between when a person may have been exposed to HIV and when a test can accurately detect HIV infection.
- Antibody tests check for HIV antibodies in blood or oral fluid. HIV antibodies are disease-fighting proteins that the body produces in response to HIV infection. Most rapid tests and home use tests are antibody tests.
- Antigen/antibody tests can detect both HIV antibodies and HIV antigens in the blood.
- NATs look for HIV in the blood.
A persons initial HIV test will usually be either an antibody test or an antigen/antibody test. NATs are very expensive and not routinely used for HIV screening unless the person had a high-risk exposure or a possible exposure with early symptoms of HIV infection.
When an HIV test is positive, a follow-up test will be conducted. Sometimes people will need to visit a health care provider to take a follow-up test. Other times, the follow-up test may be performed in a lab using the same blood sample that was provided for the first test. A positive follow-up test confirms that a person has HIV.
Talk to your health care provider about your HIV risk factors and the best type of HIV test for you.
Read Also: Difference In Kidney Infection And Uti
First Stage: Acute Hiv Infection Symptoms
Most people don’t know right away when they’ve been infected with HIV. But they may have symptoms within 2 to 6 weeks after theyâve gotten the virus. This is when your body’s immune system puts up a fight. It’s called acute retroviral syndrome or primary HIV infection.
The symptoms are similar to those of other viral illnesses, and they’re often compared to the flu. They typically last a week or two and then go away. Early signs of HIV include:
- Headache and other neurological symptoms
If you have symptoms like these and might have come into contact with someone with HIV in the past 2 to 6 weeks, go to a doctor and ask that you get an HIV test. If you donât have symptoms but still think you might have come into contact with the virus, get tested.
Early testing is important for two reasons. First, at this stage, levels of HIV in your blood and bodily fluids are very high. This makes it especially contagious. Second, starting treatment as soon as possible might help boost your immune system and ease your symptoms.
A combination of medications can help fight HIV, keep your immune system healthy, and keep you from spreading the virus. If you take these medications and have healthy habits, your HIV infection probably wonât get worse.
How Is Hiv Transmitted
Human immunodeficiency virus is transmitted by coming in direct contact with certain body fluids of the person infected with HIV. These fluids are as follows
- Receiving blood products that are contaminated with HIV
- Getting stuck with an HIV-contaminated needle
Hence, taking precautions either while having sex or sharing a needle is the best way to prevent HIV.
Don’t Miss: Will Azo Help A Bladder Infection
Early Symptoms In Primary Hiv
The first noticeable stage is primary HIV infection. This stage is also called acute retroviral syndrome , or acute HIV infection.
It usually causes flu-like symptoms, so its possible for someone in this stage to think they have severe flu or another viral illness rather than HIV. Fever is the most common symptom.
Other symptoms include:
Chronic Hiv Infection With Antiretroviral Treatment
If you take effective HIV treatment, you can live with HIV as a chronic, manageable condition. A chronic health condition is one which continues for a long period of time.
This stage is not included in most descriptions of the stages of infection, which only describe disease progression in the absence of treatment.
However, most people living with HIV who have access to good healthcare are living with HIV as a chronic condition and will continue to do so for the rest of their lives. They are unlikely to fall ill or die as a direct result of HIV.
In order to reach this stage and to remain in it, you need to take HIV treatment and continue to take it, on an ongoing basis. These medications reduce levels of HIV in your body and strengthen the immune system. This usually prevents the symptoms and opportunistic infections described above from occurring.
One of the benefits of effective HIV treatment is that is stops HIV from being passed on. Treatment drastically reduces the amount of HIV in body fluids to the point where there is not enough HIV to transmit the virus to sexual partners.
The chronic infection phase can last for decades. People who start HIV treatment as soon as possible, are able to stick with it and have access to good healthcare are likely to have a similar life expectancy to their peers who dont have HIV.
Also Check: Non Penicillin Antibiotics For Tooth Infection