Complications Of A Fungal Ear Infection
A fungal ear infection can cause the following complications:
- Damage to the eardrum. When an eardrum is perforated by a fungus, it usually heals on its own, but it might take several weeks to do so. During this time, you are prone to frequent infections that can be difficult to clear up and that may cause permanent hearing loss.
- Tinnitus and vertigo. The presence of fungi in your ear can result in tinnitus and vertigo. Tinnitus is the perception of ringing or other sounds in your ears when no such noises are present. Its often caused by damage to nerve endings in the inner ear that results from a balance disorder such as vertigo, a viral infection, or inflammation of the middle ear bones.
- Dizziness can be brought on by a fungal ear infection because fungi can infect the semicircular canal of the inner ear, which helps control balance. If you have any type of vertigo, see your doctor right away, if an infection is present, early treatment is vital.
Language Assistant
What Treatment Is Available
Initial treatment begins with cleaning debris and wax from the canal. Once the ear is cleaned specific treatment that is prescribed according to the cause of otitis externa should be administered. Occasionally if swelling in the ear is severe, a wick may be inserted before medication is applied, usually in the form of topical eardrops.
Bacteria
- 2% acetic acid solution inexpensive and effective against most infections but can be irritating to inflamed canal
- Neomycin otic drops effective but can cause contact dermatitis in 15% of patients
- Polymixin B drops avoids potential neomycin sensitisation but is ineffective against Staphylococcus and other gram-positive organisms
- Aminoglycoside drops less irritating than previous preparations but has potential ototoxicity
- Fluoroquinolone drops very effective without causing irritation or sensitisation, no risk of ototoxicity, but is expensive and overuse may cause antibiotic resistance in an important class of antibiotics
- Topical drops that combine antibiotic with steroids may help to reduce inflammation and help resolve symptoms more quickly
- Drops are usually administered 3-4 times daily for 5-7 days. More severe infections may require 10-14 days treatment. Drops should be continued for 3 days more after symptoms disappear.
- Oral antibiotics are rarely indicated except for in severe and persistent otitis externa
Fungi
Systemic dermatological disease, e.g. psoriasis
Contact dermatitis
How Is A Fungal Ear Infection Treated
If the inside of your ear looks really messy, the doctor may suggest a clean-up. This has the odd name of aural toilet. It can be done by a doctor or more usually a nurse. It involves gently clearing the ear of discharge using swabs, a suction tube or syringe. This may need to be done several times a week in the first instance. Aural toileting eases discomfort and also helps ear drops to get to the right place. However, it may be a bit uncomfortable while you’re having it done, and you may need to take some painkillers.
Don’t fiddle with your ear, keep it dry and try to resist scratching inside, however itchy it may be, as this will stop the infection from clearing up. It’s not usually advisable to put a cotton wool plug in the ear unless you get a lot of discharge and you need to keep it under control for the sake of appearances.
Avoid swimming until the condition clears up.
Your doctor may prescribe 5% aluminium acetate ear drops. This is also known as Burow’s solution. It’s not an antifungal but is used to calm down inflammation and help remove any muck in your ear.
Don’t Miss: Sinus Infection Jaw And Tooth Pain
Fungal Ear Infection Causes And Symptoms
The causes of fungal ear infection may depend on various factors such as poor cleaning of the ear canal, chronic inflammation, generic antibiotic therapy carried out for long periods of time and poor general health conditions. The development of fungi determines a peeling of the skin around the ear canal and the presence or a buildup of serous fluid. The colour of the fungal mass varies from white to yellow or black, depending on the species that caused the ear infection. The fungal species can be accurately diagnosed by examining secretion taken out from the ear canal.
Typical of the spring-summer season, otomycosis usually affects only one ear. In the early stages of the infection, symptoms may be absent, but intense itching, mild pain and a feeling of clogged ear generally occurs in the following days. Tinnitus and ear discharge can be associated with these symptoms. But what differentiates otomycosis from any other bacterial otitis externa is the presence of intense pruritus. If the tympanic membrane is undamaged, the infection is localized only in the external auditory canal whilst in the case of a perforated eardrum, the infection can extend all the way to the middle ear.
Infections Inside The Ear
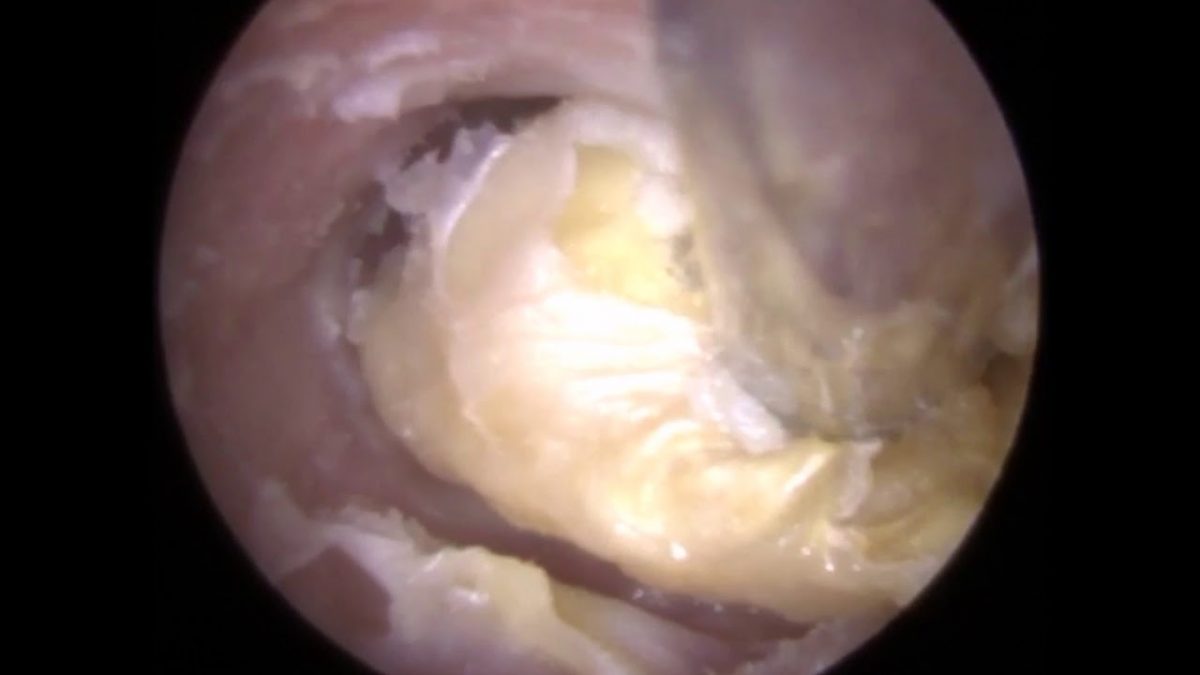
Antibiotics are not usually offered because infections inside the ear often clear up on their own and antibiotics make little difference to symptoms, including pain.
Antibiotics might be prescribed if:
- an ear infection does not start to get better after 3 days
- you or your child has any fluid coming out of the ear
- you or your child has an illness that means there’s a risk of complications, such as cystic fibrosis
They may also be prescribed if your child is less than 2 years old and has an infection in both ears.
Read Also: Can A Sinus Infection Cause A Uti
Who Gets A Fungal Ear Infection
Fungal infection of the ear is more common in people living in tropical and subtropical countries. It’s also more common in people who do a lot of water sports such as SCUBA diving and surfing. It occurs more often in the summer than the winter.
About 1 in 8 people with infections of the outer part of the ear have fungal infections.
Fungal Ear Infection Treatment
Most experts agree that the first step of medical treatment for ear fungus is to have the ear meticulously cleansed. This is usually performed by an ear, nose, and throat specialist over two to three weeks, to ensure a thorough cleaning and drying of the ear is complete before applying ear drops to treat the infection.
The antifungal drops used to destroy the source of the infection are administered over seven to 10 days. This may be extended over several weeks depending on the type and severity of the fungal infection.
Treatment can be a smooth process for most patients. Those with diabetes, and the elderly, must take special care as the infection is easily spread from the external ear canal to the inner ear. From here, the fungal infection may continue and affect the base of the skull on the other side of the inner ear. This would require hospitalization with specialized treatment.
Don’t Miss: Can A Root Canal Get Infected
Treatment Of Ear Canal Infection
-
Removal of infected debris from the ear canal and dry ear precautions
-
Ear drops containing white vinegar and corticosteroids
-
Sometimes ear drops containing antibiotics
-
Rarely antibiotics taken by mouth
To treat ear canal infection due to any cause, a doctor first removes the infected debris from the canal with suction or dry cotton wipes. After the ear canal is cleared, hearing often returns to normal.
Usually, a person with mild ear canal infection is given ear drops containing white vinegar and drops containing a corticosteroid such as hydrocortisone or dexamethasone to use several times a day for up to a week. White vinegar is helpful because bacteria do not grow as well once the normal acidity of the ear canal is restored.
With moderate or severe infection, antibiotic ear drops also are prescribed. If the ear canal is very swollen, a doctor inserts a small wick into the ear canal to allow the antibiotic/corticosteroid ear drops to penetrate. The wick is left in place for 24 to 72 hours, after which time the swelling may have gone down enough to allow the drops to go directly into the ear canal.
People who have severe acute external otitis may need to take antibiotics by mouth, such as cephalexin or ciprofloxacin.
Pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen may help reduce pain for the first 24 to 48 hours, until the inflammation begins to subside.
What Are The Medical Names Of The Fungi
You may hear specific medical terms during your diagnosis and treatment. Most fungal ear infections are caused by the Aspergillus fungus and others by the Candida fungus.
Note you may also come across the terms superior semi-circular canal dehiscence syndrome, SCD, SCDS or SSCD. They all relate to the same thing.
Recommended Reading: Betadine Soak For Infected Finger
A Prospective Analysis Of Otomycosis In A Tertiary Care Hospital
Shuaib Kayode Aremu1* Kayode Rasaq Adewoye2 and Tayo Ibrahim3
1Department of Ear, Nose and Throat, Federal Teaching Hospital, Ido-Ekiti/Afe Babalola University, Nigeria
2Department of Community Medicine, Federal Teaching Hospital, Ido-Ekiti/Afe Babalola University, Nigeria
3Department of Ophthalmology, Federal Teaching Hospital, Ido-Ekiti/Afe Babalola University, Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State, Nigeria
Complications Of Outer Ear Infection
Most outer ear infections clear up quickly with the right treatment. But sometimes an outer ear infection is harder to get rid of, and may continue to cause symptoms for three months or longer. This is called a long-term infection. In time, this can cause your ear canal to become narrowed or blocked, and lead to hearing loss.
Its possible for the infection to spread deeper into your skin or form a large collection of pus . You may need antibiotic tablets to treat this.
Rarely, an outer ear infection can start to affect the skin and cartilage around your ear, and nearby bones. This is called necrotising or malignant otitis externa. It happens when your outer ear infection spreads from your ear to nearby tissues. This can lead to serious infections of your skin, bones, and the membrane surrounding your brain . Most people who develop malignant otitis externa have an underlying problem with their immune system. For instance, they may have a weakened immune system due to HIV/AIDS, diabetes, chemotherapy or taking medicines that suppress the immune system.
If you have malignant otitis, your ear is likely to be very painful. You may also have a high temperature, headache, ear discharge and dizziness. You may notice some loss of movement of the muscles in your face.
If you have these symptoms, its important to seek medical help straight away. Malignant otitis can be life-threatening if it isnt treated.
Read Also: Will An Inner Ear Infection Go Away By Itself
Ear And Eye Infections
Ear Canals.
The ears of many mammals other than humans can be colonized by a commensal yeast, Malassezia pachydermatis, which may proliferate and cause infection under certain circumstances . Candida species, certain Aspergillus species, Pseudallescheria boydii, and a few other organisms also can colonize human or, occasionally, animal external ear canals . A sterile cotton swab is used to collect ear secretions and inoculate plates containing SABC medium. A 10% potassium or sodium hydroxide mount is examined microscopically to verify that any filamentous fungus isolated is producing mycelium and conidiophores in the ear and is not merely a contaminant from an external source.
Eyes.
No fungi colonize any portion of the eye primarily. An extensive and growing list of fungi, however, are known to infect the corneal surface subsequent to a traumatic eye injury, typically a scratch or puncture caused by plant material. After appropriate anesthesia is given corneal scrapings are collected with a suitable sterile scalpel blade and then cultured on SAB . Infection is verified by the presence of fungal filaments in the scrapings when examined in a hydroxide mount or gram smear.
Malcolm D. Richardson, Riina Rautemaa-Richardson, in, 2021
Fungal Infection Of The Ear
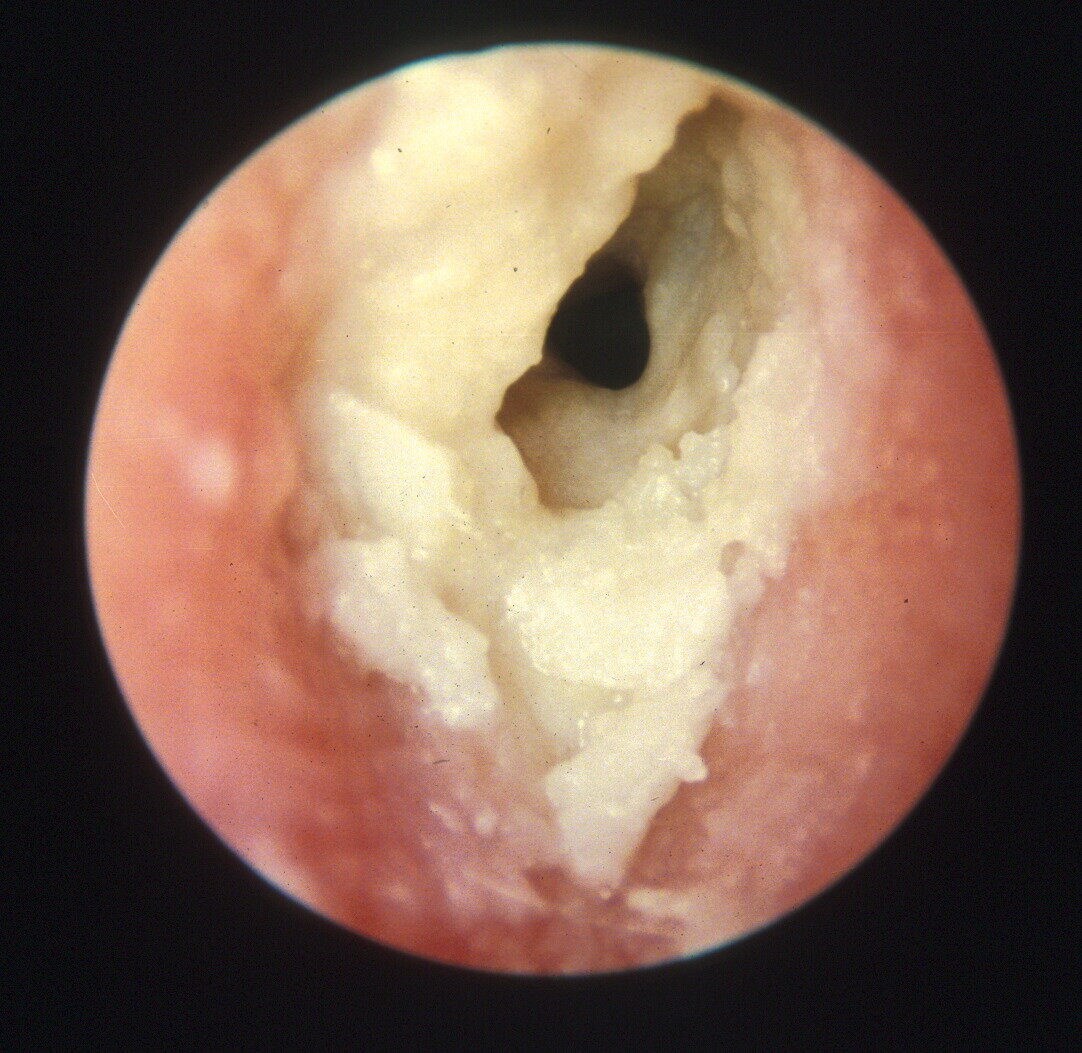
Etiology and Therapy with Bifonazole Cream or Solution
Log in to MyKarger to check if you already have access to this content.
Buy a Karger Article Bundle and profit from a discount!
If you would like to redeem your KAB credit, please log in.
Save over 20%
- Rent for 48h to view
- Buy Cloud Access for unlimited viewing via different devices
- Synchronizing in the ReadCube Cloud
- Printing and saving restrictions apply
USD 8.50
- Access to all articles of the subscribed year guaranteed for 5 years
- Unlimited re-access via Subscriber Login or MyKarger
- Unrestricted printing, no saving restrictions for personal use
The final prices may differ from the prices shown due to specifics of VAT rules.
Also Check: Can You Take Antibiotics For A Viral Infection
How Are Fungal Ear Infections Treated
There are several methods to treat otomycosis your doctor will recommend the best for you.
Cleaning
Effective treatment starts with cleaning the ear to remove any discharge or debris buildup. This should only ever be done by a medical professional do not try this yourself at home. You risk serious or even permanent damage to your ears. The doctor may rinse your ears or use a suction tool or syringe. The process may be uncomfortable if so, your doctor may give you some painkillers.
Your ear is cleaned and dried. This will help inhibit the regrowth of any fungus. Avoid scratching your ear, however itchy it gets. You should avoid swimming until your fungal ear infection has cleared up.
Ear drops
You may be prescribed antifungal ear drops which you will need to use according to your doctors advice this may be several times a day.
These ear drops may include:
- 1% Clotrimazole
- 5% Aluminium acetate
Eardrops may also contain amphotericin B, econazole or miconazole
Topical medications
Antifungals may also be in the form of a cream or ointment that you will need to apply to your outer ear. These will treat the fungus and help relieve any hard crust that may have formed on your outer ear.
Oral medications
Some fungal ear infections may be resistant to ear drops and topical medications and you may have to take oral medications, such as itraconazole or voriconazole.
Do not take oral antifungal medication if you have liver disease.
Otomycosis : Causes Symptoms Treatment And Home Remedies
Otomycosis is a fungal infection in the ears that tends to be a problem for people who live in warm areas of the world. Avid swimmers, individuals who suffer from diabetes, or people who have chronic medical and skin conditions can also experience ear fungus.
Otomycosis is also called mycotic otitis externa or Singapore ear. The infection is usually on the external part of the ear. Aspergillus or Candida is commonly fungi associated with a fungus of the ear, but there are others. Most of the fungi are species that exist in the environment around us, so it is rather easy to come in contact with it. Keep in mind that coming in contact with fungi doesnt mean that you will automatically get otomycosis ear. If you have a weak immune system, you are at a higher risk of getting ear fungus if you come in contact with fungi.
Also Check: Does Ice Help A Tooth Infection
A Pharmacist Can Help With An Ear Infection
Speak to a pharmacist if you think you have an outer ear infection.
They can recommend acidic eardrops to help stop bacteria or fungus spreading.
- a long-term medical condition such as diabetes or a heart, lung, kidney or neurological disease
- a weakened immune system because of chemotherapy, for example
Spike Of Fungal Ear Infections During Covid
In the months of June, July, August, and September 2021 Dr. K. R. Meghanadh saw daily an average of 4 patients with external ear canal fungal infection called Otomycosis. He used to see around 30 patients per month before this spike.
Dr. K. R. Meghanadh said, Due to the spike in these months, I wonder if COVID has any relation with Otomycosis. I observed that only a few were post-COVID, and the number is not significant enough to term this as a post-COVID complication, unlike mucormycosis. I think this is because of the change in lifestyle due to the pandemic. I assume that the time spent in the house has increased and has given people some idle time, leading to increased earbuds usage. Earbuds could be the reason behind this spike, some doctors say it could be because of the season change, but I have not seen such a massive spike in my career due to the change of season. The only difference here is COVID-19 and the changes it brought to our lifestyle. The spike is most probably due to our lifestyle changes.
Using an earbud to clean the ear canal can increase the chance of fungal infection. When the skin inside the ear canal is wet, skin becomes delicate, and the use of an earbud can easily damage the skin, making it susceptible to infection. Using an earbud after a bath can multiply the chances.
Recommended Reading: Can Strep Cause An Ear Infection
Home Treatment For A Fungal Ear Infection That Can Go Wrong
There are commonly 2 remedies used for in-home treatment for ear infections.
oil as ear drops
antibiotic ear drops
Oil for ear infection
Many assume that itching in the ear could be due to dryness of the skin in outer ear canal. However, the itching could be due to fungus also. When people use oil in case of a fungal ear infection, this oil will act as food for the fungus and helps it spread faster.
Antibiotic ear drops for itchy ears
The antibiotic eardrops kill the normal bacteria in the ear canal. Generally, these bacteria and fungi coexist and fight in our ears, controlling each other. Using antibiotic ear drops and killing the bacteria destroys this balance. This environment will be ideal for the fungus to multiply and reach the eardrum.
Outlook For This Condition
In most cases, antifungal treatments are enough to get rid of otomycosis. However, some people dont respond to these treatments, and otomycosis may become chronic. In this case, being under the care of an ear specialist may be helpful.
Continue to follow up with your doctor if your symptoms persist.
If you have diabetes, a weakened immune system, or chronic health problems, getting those conditions under good control is important. Treating any chronic skin conditions, like eczema, is also important.
In addition, continued exposure to the fungus from contaminated water or other sources can cause the infection to return.
There are things you can do to help prevent otomycosis:
Read Also: Can You Fight Off Bacterial Infection Without Antibiotics