Aaos Recommends Prophylactic Antibiotics For Total Knee Replacement Patients
The American Academy of Obstructional Surgeons recommends prophylactic antibiotics in the case of total knee replacement patients. Before and after the procedure, antibiotics should be given 60 minutes prior to the procedure and discontinued within 24 hours. If the patient is at increased risk for infection, the antibiotics should be given for the rest of his or her life.
Are Antibiotics Prescribed After Knee Replacement
There is no definitive answer to this question as it depends on the individual case. Some people may be prescribed antibiotics after knee replacement surgery to help prevent infection, while others may not need them. Your doctor will be able to advise you on whether or not antibiotics are necessary in your case.
A Canadian study on antibiotic prophylaxis for total joint replacement surgery. If it can, Journal of Surgery could be an option. In December 2009, the Journal of Medical Engineering 52: E229-E234. In Canada, opinions about antibiotic use differ greatly from one surgeon to the next. Furthermore, the survey discovered that there is a lack of agreement about the current practice of postoperative wound drainage. Controversy still rages in Canada over best clinical practice for preoperative antibiotic prophylaxis during total joint replacement surgery. Our study examined 590 orthopedic surgeons who are active in Canada.
In total joint replacement surgery, antibiotic prophylaxis should be used. If you are allergic to penicillin, you should take cefuroxime, ceazloin, or cefuroxime, Clindamycin, or vancomycin. IVs should begin one hour after the incision . Before the tourniquet is inflated, completely fill it. If your weight is 80 kg or more, the dose of cefazolin must be double. If operating time exceeds 24 hours or significant blood loss occurs, the dose may be increased. It is not recommended that the duration be longer than 24 hours following surgery.
How Is A Prosthetic Joint Infection Treated
Surgery and antimicrobial treatment are required for the treatment of prosthetic joint infection. The classic surgical options are one-stage or two-stage implants exchange, arthrodesis reconstruction , and debridement with or without implant retention. It is estimated that 11 to 35% of patients fail treatment.
See A Doctor If You Experience These Symptoms
If you have any of these symptoms, you should consult a doctor. In rare cases, the infection can lead to permanent joint damage if not treated.
Also Check: When To Seek Treatment For Sinus Infection
Who Is At Risk Of A Deep Knee Infection
All knee replacement surgery patients have some risk. However, if its been over 2 years since you had your surgery, your chances of developing a deep knee infection decreases significantly. Its more common for people who have had the surgery in the past 24 months to develop this problem.
Youre also at risk of developing a deep infection if you have any of the following health issues:
Skin Infection After Surgery

An SSI that only affects the layers of your skin where your stitches are is called a superficial infection.
Bacteria from your skin, the operating room, a surgeons hands, and other surfaces at the hospital can be transferred into your wound around the time of your surgical procedure. Since your immune system is focused on recovering from surgery, the germs then multiply at the site of your infection.
These types of infections can be painful but usually respond well to antibiotics. Sometimes your doctor may need to open part of your incision and drain it.
Recommended Reading: Best Antibiotic For Severe Sinus Infection
When To Take Antibiotics After Knee Replacement Surgery
Can I take antibiotics after a knee replacement? Most surgeons recommend avoiding invasive dental procedures for 8-12 weeks following knee replacement based on the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons guidelines. By doing so, the risk of bacteria from the blood borne pathogen HBV passing through your new prosthetic knee is reduced. As a result, antibiotics may be required for some procedures. Vascular procedures such as coronary artery bypass grafting and valve replacements, gastrointestinal procedures such as endoscopies and bariatric surgery, and gynecology procedures such as Cesarean sections are also covered.
Staph Infection After Knee Surgery
The likelihood of staph infection after knee or hip joint replacement varies greatly depending on the patientâs immune system, with an incidence ranging from 1.5 to 6% over the course of a lifetime. One of the most common pre-operative risk factors in orthopedics is Staphylococcus aureus .
It is a terrible complication of joint replacement surgery if you get a staph infection. Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most common pre-operative risk factors in orthopedic patients. Because of the aggressive nature of staph bacteria, patients who have it on their skin are more likely to develop chronic skin infections.
Recommended Reading: Oral Steroids For Ear Infection
Whats New In Infection Treatment
There are many different types of knee spacers to treat infected total knee replacements.
Static Spacers
- For severe bone loss, a static spacer is used. This spacer prevents motion at the knee and acts as a fusion. Many surgeons perform this procedure by placing cement within your knee replacement
- Dr. Morton uses an internal rod to provide stability to your knee during this phase. This provides additional stability, preventing your spacer from dislodging during your recovery.
Mobile Spacers
- Mobile spacers are made of cement thats bonded to the ends of your femur and tibia . Newer techniques are performed using mobile implants made of metal and polyethylene components that are surrounded by antibiotic-impregnated cement. These spacers allow for a more functional knee during your temporary spacer phase. Some patients with these spacers find their knee replacement functional enough that they do need a second surgery to their knee.
Watch For Signs Of Infection
You can check for early signs of infection so you can get prompt medical attention to prevent it from getting worse.
Things you can do:
- In the first few weeks after surgery, inspect your incision every day for signs of infection.
- You should take your temperature daily. This can help you identify an infection early. It is best to take your temperature at the same time each day.
It is important to identify an infection right away. Prompt care can keep it from becoming more serious.
If you are diagnosed with an infection, your surgeon can prescribe antibiotics to help it resolve and to prevent it from spreading.
You May Like: What Helps Infected Tooth Pain
Signs And Symptoms Of An Infection After Surgery
If you are recovering from surgery, it is important to take the right steps to prevent infection. Infections after surgical procedures can affect the incision, bladder, lungs, intestines, or bloodstream.
Doing all the right things after surgery can lower your risk of an infection, but it doesnt completely guarantee that you will be infection-free.
This article discusses infections after surgery and how to prevent them. It also looks at types of infections, symptoms, and when you should see a doctor.
Verywell / Joshua Seong
Diagnosing A Knee Infection
Your doctor may be able to tell you have an infection if they see redness and drainage around the surgical incision. They may give you some tests to locate the infection or to learn the type of bacteria causing it.
These tests may include:
- imaging test, such as an X-ray, CT scan, MRI, or bone scan
- joint aspiration, in which your doctor draws fluid from around your knee and tests it in a lab
Also Check: How To Fix A Tooth Infection At Home
What Procedures Require Antibiotics After Hip Replacement
After hip replacement surgery, patients are typically prescribed antibiotics to help prevent infection. The specific type and duration of antibiotic treatment will vary depending on the individual case, but may include antibiotics taken intravenously or orally for a week or more. It is important for patients to take all antibiotics as prescribed and to finish the entire course of treatment even if they are feeling better.
Ways To Reduce Infection After Knee Replacement Surgery
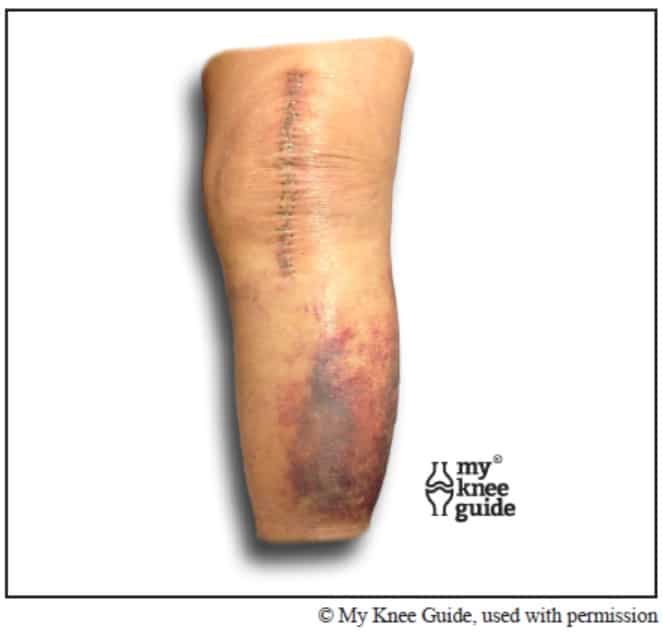
Although infections after knee replacement surgery are rare, orthopedic surgeons in Jacksonville, FL, want their patients to be informed about the risks and how to avoid complications from infection. The more you know about these risks, no matter how low, the better prepared youll be when recovering from surgery.
You May Like: At Home Treatment Sinus Infection
How Long After Knee Replacement Do You Have To Worry About Infection
It is also possible to develop an infection near your artificial knee, also known as a prosthesis or implant. Deep infections, major infections, delayed infections, or late infections are all terms used by doctors. Deep infections after knee replacement are serious and can last for weeks or even years.
A knee replacement is a surgical procedure that is designed to relieve pain and restore function to a knee joint. When a knee replacement is infected, harmful bacteria can enter the wound or body, resulting in a variety of symptoms. A superficial infection may be considered serious depending on the severity of the infection. It can be caused by surgery, other infections in the body, or a variety of other factors that are not known. If caught early, antibiotics may be required to treat the infection. Debridement can be used to treat a deep infection that has not been treated within a few days or weeks.
Prevention Of Knee Infection
You can prevent a knee infection by following simple measures including:
- Discussing with your doctor various ways to prevent infection if you take medications for rheumatoid arthritis or HIV-AIDS, or if you are diabetic.
- Have your joints assessed by your doctor on a regular basis. Check for any sores or cuts which may further lead to infection.
- Do not ignore insect, spider or animal bites.
- Do not ignore any other infections in your body.
- Avoid intravenous drug use.
Also Check: One Night Yeast Infection Treatment
Infected Surgical Incision Symptoms
Be aware of these signs of infection:
- Hot incision: An infected incision may feel warm or hot to the touch. This happens as the body sends infection-fighting blood cells to the site.
- Swelling/hardening of the incision: An infected incision may harden. This happens as the tissue underneath becomes inflamed. The incision may also look swollen or puffy.
- Redness: Some redness at the incision site is normal. The red color should decrease over time. If it becomes redder, it may be infected. Red streaks radiating from the incision to the surrounding skin are a sign that infection is spreading.
- Drainage from the incision: An infected incision may produce foul-smelling drainage or pus. The pus can be blood-tinged, green, white, or yellow. The drainage may also be thick.
- Pain: You should have a slow and steady improvement of your pain as you heal. It is normal to have a mild to moderate increase in pain after activity. You may also notice more pain if you take less pain medication. If pain at the surgery site increases and you don’t know the reason, you may be developing an infection. Tell your surgeon about any significant, unexplained increase in pain.
You can help prevent infection by taking care of your incision.
Preventing A Joint Replacement Infection
You and your care team can reduce risk of infection. While arranging your surgery, speak with your surgeon about infection prevention procedures and what you can do to help reduce your risk. Your doctor may suggest:
- Preoperative testing for bacteria in your nasal passages by a nasal swab.
- Preoperative wash of your skin with a special soap at home before the surgery.
- Giving you antibiotics while you are in the operating room and for at least 24 hours after surgery.
- Recommending preventative antibiotics before you have any procedures that could put you at risk for an infection. Examples include dental surgery or other surgical procedures.
Finally, eat a healthy diet. Malnutrition, not consuming enough nutrients for your needs, can lower your bodys ability to fight infection.
If you suspect sepsis, call 9-1-1 or go to a hospital and tell your medical professional, I AM CONCERNED ABOUT SEPSIS.
Suggested Citation: Sepsis Alliance. . 2022.
Also Check: Lemon Juice And Baking Soda For Urinary Tract Infection
Types And Treatment Of Infection After Knee Replacement
As the authors of this article point out, infection after total knee replacement is the most dreaded and difficult of all complications. Joint infection can be difficult to treat, requiring removal of the implant and revision surgery to put in a second implant.
According to their review of the literature, this problem is increasing not decreasing. Up to two per cent of all senior adults who have this surgery will end up with an infection that requires further treatment. The rate of failure due to infection is double that for revisions so having a second surgery doesnt necessarily mean the end of the problem. In fact, almost 17 per cent of revision total knee arthroplasty procedures end in another surgery.
If this problem isnt turned around in the next 10 years, it is estimated that two-thirds of all revision procedures will be needed because of post-operative infection. Prevention is the key but todays bacteria are stronger and more resistant to antibiotics than ever before. Prevention strategies are not the focus of this article. Instead, surgeons treating patients with this problem will appreciate the review of treatment options provided.
Treatment is based on the infection type and condition of the patient. Treatment choices include: antibiotics, irrigation and debridement, removal and replacement of the implant, arthrodesis , and : amputation. Who gets what treatment? Thats the question these authors try to answer.
What Are The Current Recommendations Regarding Antibiotic Prophylaxis And Artificial Joints
The current recommendations regarding antibiotic prophylaxis and artificial joints are to avoid using them together. Antibiotic prophylaxis is not recommended for patients with artificial joints.
According to the American Dental Association, antibiotics should no longer be given to most dental patients who have orthopedic implants. Prior to 2012, patients undergoing joint replacement procedures were frequently prescribed medication prior to the procedure. Bacteria in the bloodstream are thought to cause infections in the rest of the body. The American Dental Association states that prosthetic joint implant infections are not linked to dental procedures. When antibiotics are used, there is a risk of nausea, upset stomach, and allergic reactions. Antibiotic prophylaxis may benefit patients who have weakened immune systems as a result of dental procedures.
Read Also: Can Uti Medicine Help Yeast Infection
Warning Signs Of An Infection After Surgery
-
Approximately 1 to 4% of people who undergo surgery will develop an infection after surgery. Infections inhibit healing and may cause additional health complications. Be alert for signs of infection after surgery. Prompt medical evaluation and treatment, if necessary, can prevent the infection from progressing. Ignoring or overlooking symptoms of infection could result in another hospital stay. According to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, surgical site infections are the leading cause of hospital readmission after surgery.
Consult your healthcare provider if you notice any of these surgical site infection symptoms:
Do Joint Replacements Put You At Risk For Infection And Sepsis
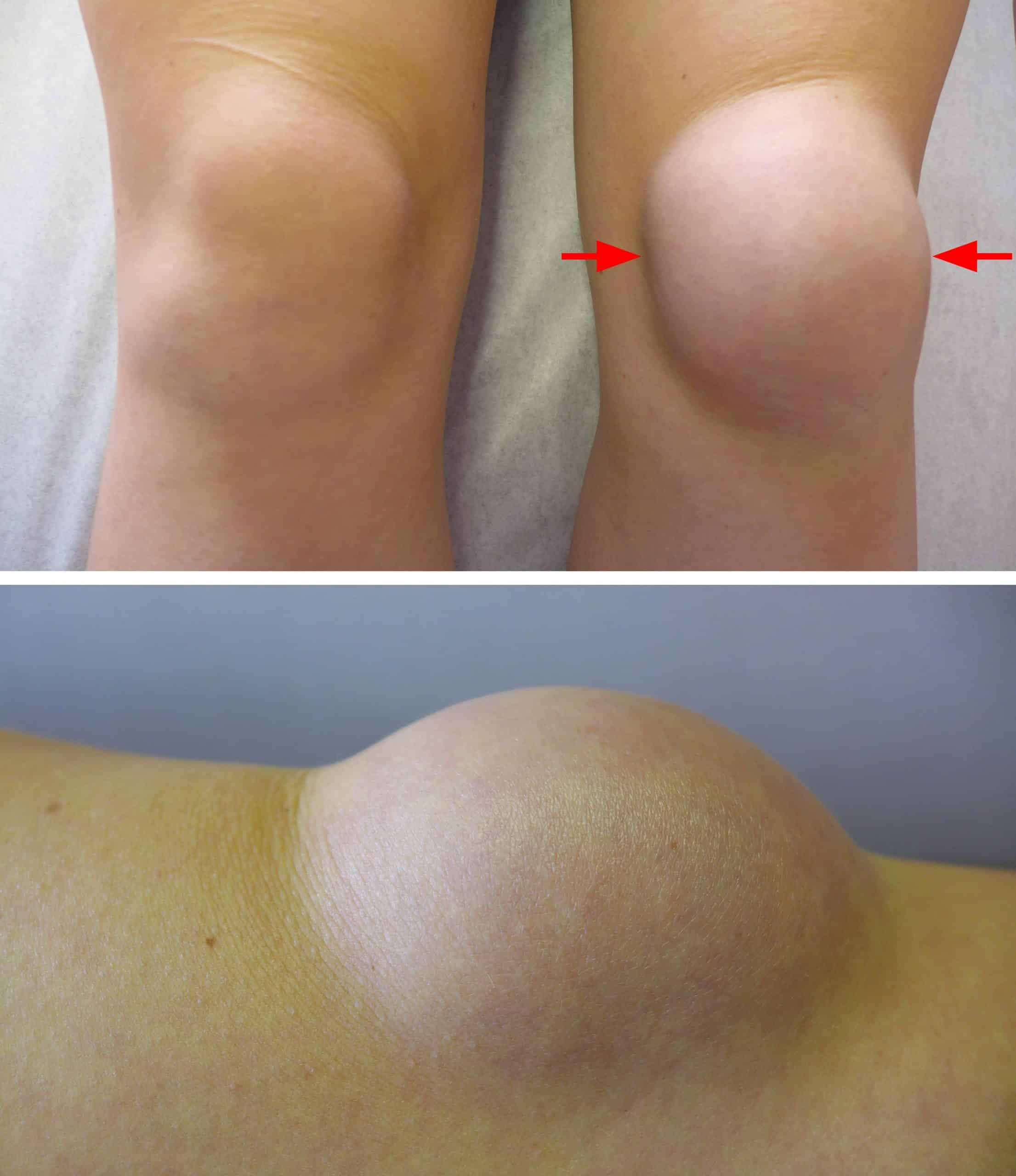
Most people who undergo joint replacements heal well, without any complications. However, any type of surgery does increase your risk of developing an infection, which can in turn cause sepsis.
Risks include developing pneumonia following surgery or contracting a healthcare-acquired infection during your stay in the hospital. As well, some people who undergo joint replacements may be older and/or have underlying disease conditions, such as diabetes or COPD, that may make them susceptible to infections.
Recommended Reading: Can You Use Keflex For Tooth Infection
Organ And Bone Infection After Surgery
An organ and space infection after a surgery involves any organ thats been touched or manipulated as a result of a surgical procedure.
These kinds of infections can develop after an untreated superficial infection or as the result of bacteria being introduced deep in your body during a surgical procedure. These infections require antibiotics, drainage, and sometimes a second surgery to repair an organ or address the infection.
6 percent between 2015 and 2016.
Being aware of your risk prior to surgery is the best way to avoid infection. Your doctor should follow-up to check your incision for signs of infection after most surgeries.
If youre concerned that you might have an SSI, call the doctor right away. The main complications of SSIs come from waiting too long to get treatment.
8 sourcescollapsed
- Anderson DJ, et al. . Strategies to prevent surgical site infections in acute care hospitals: 2014 update.
How Long Do You Have To Take Antibiotics After Hip Replacement
There is no definitive answer to this question as it depends on the individual case. However, it is generally recommended that patients take antibiotics for at least two weeks after hip replacement surgery.
One infection can spread to another if the other is present. Joint replacement patients undergoing dental procedures are prescribed antibiotics by orthopedic surgeons. If a person has artificial hardware in their body after a dental procedure, he or she is more likely to develop an infection. Joint replacement is one type of prosthetic joint infection , which is included in this category. The American Academy of Oss is an organization for orthopedic surgeons. The American Society for Antibiotics has released guidelines for surgeons on how to use prophylactic antibiotics. Unlike the ADA, which focuses primarily on the patients who are not covered by their recommendations, the AAOS goes much deeper into these patients.
Except for immunocompromised patients and cancer patients who appear to have illnesses, there are no exceptions. When you become infected, you may suffer serious consequences. If the joint becomes infected, the patient may need to have another operation to remove the infection and infected tissue from the joint. Because of these unforeseen consequences, surgeons are cautious about infections. Both societies provide evidence supporting their respective recommendations for and against dental prophylactics.
Read Also: Mesh Infection And Hernia Repair A Review