How Do I Make Sure The Treatment Works
Let the discharge escape: try not to leave balls of cotton wool in the ear canal. If the discharge is heavy, you may need to place some cotton wool lightly in the outer part of the canal to mop it up. If you do this, replace it frequently with a fresh piece.
Use the ear drops correctly: sometimes otitis externa does not clear because ear drops are not used correctly. You have to put them in as often as prescribed to be fully effective. If the drops come out of the ear quickly, they may not work so well. When using drops:
- Lie with the affected ear upwards.
- Put several drops in the ear and remain lying in this position for 1-2 minutes.
- Press the cartilage at the front of the ear canal a few times to push the drops deep inside the ear canal.
Keep your ears dry : this will help the current attack to settle down and help to prevent future attacks . It is best to avoid swimming and getting water in the ears whilst you have otitis externa. Getting more water in the ears will tend to make things worse.
Who Shouldn’t Use Ear Drops
Ear drops can be helpful when treating an ear infection, but there are times when you shouldnât use them. For example, if you or your child has a perforated eardrum, you should avoid the use of certain ototoxic ear drops because fluid from the drops can get deep into the ear and cause more problems.
How Do Ear Infection Antibiotics Work
Ear infections are no fun for anyone.
An ear infection occurs when fluid builds up behind your eardrum in the middle part of your ear and causes swelling . This can lead to significant pain and discomfort.
Since most ear infections are caused by bacteria, its typically best to treat individual cases with antibiotics.
But antibiotic treatment isnt appropriate for every ear infection. There are a variety of factors to consider, including:
- causes
- your age
Recurring ear infections may also require a different approach.
If youre considering ear infection antibiotics for yourself or a loved one, learn more about how these medications work and how they can be both helpful and possibly harmful.
Ear infections are most prevalent in young children. Theyre often the byproducts of upper respiratory infections.
You or your child might experience other symptoms before the ear infection, including:
If an upper respiratory infection is caused by bacteria, then its possible to have an ear infection at the same time.
An ear infection occurs when bacteria gets trapped in your middle ear. Bacteria known as Hemophilus influenza and Streptococcus pneumoniae are the most common bacterial culprits.
But an ear infection may still occur if you have a viral respiratory illness. As you recover, its possible for bacteria to travel to your middle ear and become trapped, leading to a secondary infection in your ears.
Also Check: Yeast Infection From Birth Control Pills
Types Of Middle Ear Infections
Middle ear infections are called otitis media. When otitis media is accompanied by fluid in the middle ear, ear infections are referred to as serous otitis media, or otitis media with effusion.
Middle ear infections often occur after a cold virus or upper respiratory infection. They are also more common in individuals who suffer from allergies or enlarged adenoids , which can inhibit proper functioning of the auditory tube.
Bacteria, viruses, or fungi often enter through the auditory tube, which can then become swollen and blocked with mucus, preventing drainage and ventilation of the middle ear.
The main symptoms of middle ear infections include:
- Ear pain, which may be worse in the morning or cause difficulty sleeping
- Ear drainage
- Trouble hearing
- Fever
A healthcare provider can diagnose a middle ear infection based on symptoms and an examination, which involves looking at the eardrum with an otoscope .
Can Objects Bugs Or Insects In The Ear Cause Outer Ear Infections

Young children often will put foreign objects their ear by accident or while scratching or trying to clean their ear. Often, children who put objects in their ear also have swimmerâs ear . Do not try to remove objects stuck in the ear because it can be difficult. Call your pediatrician to have the object safely removed. Usually this can be done in the office, but sometimes, general anesthesia may be necessary to remove the lodged object if it is stuck deeply in the ear or if the child or adult is uncooperative.
Insects or bugs can be trapped in the ear, for example, small gnats can be caught and stuck in the earwax. Often, bugs and insects can washed out with warm water. Larger insects or bugs may not be able to turn around in the narrow canal. If the insect or bug is still alive, first kill it by filling the ear with mineral oil. This will suffocate the insect, and then see your doctor to have it removed.
Recommended Reading: Does Azo Cure Uti Infections
What Causes An Ear Infection
Ear infections are caused by bacteria and viruses. Many times, an ear infection begins after a cold or other respiratory infection. The bacteria or virus travel into the middle ear through the eustachian tube . This tube connects the middle ear to the back of the throat. The bacteria or virus can also cause the eustachian tube to swell. This swelling can cause the tube to become blocked, which keeps normally produced fluids to build up in the middle ear instead of being able to be drained away.
Adding to the problem is that the eustachian tube is shorter and has less of a slope in children than in adults. This physical difference makes these tubes easier to become clogged and more difficult to drain. The trapped fluid can become infected by a virus or bacteria, causing pain.
Medical terminology and related conditions
Because your healthcare provider may use these terms, its important to have a basic understanding of them:
When Should I See A Specialist To Treat Swimmer’s Ear
If your ear infection has not gone away 10 to 14 days after treatment with antibiotic eardrops, you have lost your hearing, you see pus or other yellow/green matter oozing from your ear, or experience a worsening of any of the symptoms of swimmer’s ear, you should be seen by an ear specialist .
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 01/29/2019.
References
Also Check: Will Yeast Infection Go Away On Own
Diagnosis Of Outer Ear Infection
Your GP will usually be able to diagnose an outer ear infection by asking about your symptoms and examining your ear. They may also ask about your medical history to check if theres anything that could have caused your symptoms.
Your GP may look into your ear using an instrument called an otoscope to check for any signs of infection. They may ask you to move your ear or jaw to see if you feel pain.
If your symptoms are particularly severe or they dont get better after treatment or they come back, your GP may collect some discharge using a cotton swab. This will be sent to a laboratory for testing to find out whether the cause of your ear infection is bacterial or a fungus.
When Should I See A Doctor
A mild ear infection may go away on its own. But most cases of moderate to severe ear pain require a visit to your doctor. You should also see your doctor if youre experiencing ear discharge, fever, or chills.
Children with ear infections may constantly cry due to pain and discomfort. They might also tug or pull at the affected ear. See your doctor if symptoms dont improve within , or if they get worse.
Other signs that you should see a pediatrician include:
- fever of 102.2°F or higher
Don’t Miss: French Bulldog Yeast Infection Treatment
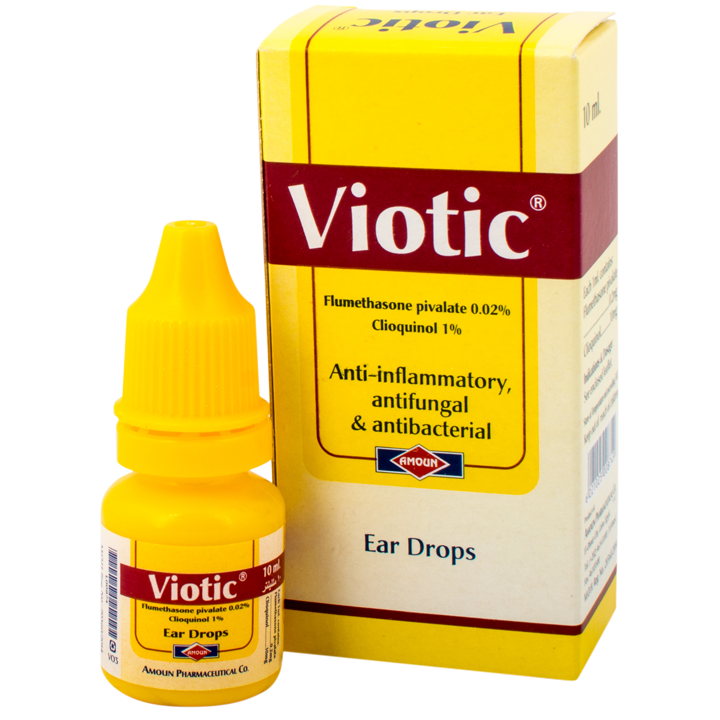
Which Ear Drops Help In The Treatment Of Outer Ear Infections
Some prescription-only ear drops can effectively relieve earache caused by an outer ear infection . There is no evidence that over-the-counter disinfectant ear drops are as effective.
Outer ear infections are among the most common causes of earaches. They are usually caused by bacteria. If the infection only lasts a few days or weeks, it is called acute otitis externa. Painkillers and disinfectant ear drops are some of the more common treatments that are available in pharmacies without a prescription. But prescription-only ear drops for instance, containing antibiotics or steroids are often used too.
Ear Infections In Dogs
If you have ever had an ear infection, you know just how miserable they can be.
These painful infections can not only impact our dogs as well, but they are actually quite common among the canine population.
The shape of a dogs ear canal makes them more prone to the development of ear infections, making this a common factor behind many vet visits.
In this article we will go into the details of ear infections in our canine companions, and help you better understand what this diagnosis means for your pup.
Read Also: Sign For Poop In Sign Language
You May Like: Sinus Infection And Bad Breath
What Are The Disadvantages Of Ototopical Antibiotics
Ototopical antibiotics have a few disadvantages as well, which include the following:
Difficulty in delivery
Direct delivery at the infection site may be difficult or impossible sometimes. The medication may fail to reach the infected area in the middle ear if the ear canal is blocked due to:
- Excessive and hardened earwax
- Block in the ear tubes inserted for fluid drainage from the middle ear
- Swollen or overgrown tissue
Steps must be first taken to clear the blocks before antibiotic administration. Irrigating the ear canal can easily clear a block caused by earwax and other secretions, but an ear tube block and granulation each may require some procedure and other medications.
Ototoxicity
Ototoxicity is toxicity to the ear from local administration. Ototoxicity can irritate and inflame the mucus membranes of the middle ear. If the antibiotic enters the inner ear, it may lead to:
- Vertigo
- Sensitivity reaction
Ototopical antibiotics can cause allergic reactions. Low-grade sensitivity reactions may cause persistent drainage that may be impossible to distinguish from drainage due to infection, making treatment difficult. Some people may also develop cross-sensitivity to related antibiotics.
Absence of systemic effect
Alteration of microenvironment
Check If Its An Ear Infection
The symptoms of an ear infection usually start quickly and include:
- discharge running out of the ear
- a feeling of pressure or fullness inside the ear
- itching and irritation in and around the ear
- scaly skin in and around the ear
Young children and babies with an ear infection may also:
- rub or pull their ear
- not react to some sounds
- be irritable or restless
- be off their food
- keep losing their balance
Most ear infections clear up within 3 days, although sometimes symptoms can last up to a week.
| Inner ear infection |
|---|
Recommended Reading: Autoinsufflation Ear Infection
You May Like: Does Boric Acid Pills Cure Yeast Infections
What Causes Otitis Externa
Otitis externa is an infection of the skin of the ear canal and is very common. The ear canal is a narrow, warm, blind-ended tunnel, which makes it a good protected environment for germs to grow in if they are given a chance. Most infections are caused by a germ . Occasionally, they can be due to a fungal or yeast infection.
Some things can make you more prone to otitis externa – for example:
Substances entering the earIf you regularly get water in an ear then this may provide moisture for germs to grow. It may also cause itching. You may then scratch or poke the ear. This can damage the skin in the ear canal and cause inflammation. Inflamed skin can quickly become infected. A vicious circle may then develop. The inflammation and infection cause more itch, you then scratch more, which then can makes things worse.
If you get shampoo, hairspray or other products into your ear this may have the same effect and may be worse, as the chemicals may additionally irritate the sensitive skin of the canal.
SwimmingOtitis externa is much more common in regular swimmers, due to water getting into the ear canal. In fact, otitis externa is sometimes called swimmer’s ear. It is more likely if you are swimming in water which isn’t clean, such as ponds.
Warm weatherOtitis externa is more likely to develop in hot, humid and ‘sweaty’ weather. It is more common in hot countries.
What Causes An Outer Ear Infection
Swimming can lead to an outer ear infection. The water left inside the ear canal can become a breeding ground for bacteria.
An infection can also occur if the thin layer of skin that lines the ear canal is injured. Intense scratching, using headphones, or placing cotton swabs in your ear can damage this delicate skin.
When this layer of skin becomes damaged and inflamed, it can provide a foothold for bacteria. Cerumen is the ears natural defense against infection, but constant exposure to moisture and scratching can deplete the ear of cerumen, making infections more likely.
Severe pain in the face, head, or neck can signify that the infection has advanced considerably. Symptoms accompanied by a fever or swollen lymph nodes may also indicate advancing infection. If you have ear pain with any of these symptoms, see your doctor right away.
Also Check: Activated Charcoal For Tooth Infection
What Conditions Cause Swimmer’s Ear
Conditions that can lead to swimmer’s ear include:
- Water that gets trapped in the ear canal, for example from swimming or showering often
- Loss of ear wax a natural protectant due to too much water entering the ear canal or removing too much wax when cleaning ears
- Injury to ear caused by putting objects into the ear, such as fingers, pen/pencils, paper clips, hair clips
- Swimming in polluted water
- Other skin conditions that affect the ear canal, such as eczema or psoriasis
Managing Your Symptoms At Home
The advice below should help to relieve your symptoms to some extent and help to prevent complications:
- avoid getting your affected ear wet wearing a shower cap while showering and bathing can help, but you should avoid swimming until the condition has fully cleared
- remove any discharge or debris by gently swabbing your outer ear with cotton wool, being careful not to damage it don’t stick cotton wool or a cotton bud inside your ear
- remove anything from your affected ear that may cause an allergic reaction, such as hearing aids, ear plugs and earrings
- use painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen to relieve ear pain these aren’t suitable for everyone, so make sure you check the information leaflet that comes with the medication first if you’re still unsure, check with your GP, practice nurse or pharmacist
- if your condition is caused by a boil in your ear, placing a warm flannel or cloth over the affected ear can help it heal faster
You May Like: Quick Home Remedies For Sinus Infection
Interactions Between Ofloxacin And Other Medications
Ofloxacin may interact with certain medications or supplements. Always let your doctor and pharmacist know about any other medications or supplements that you are currently taking. The list below does not include all possible drug interactions with ofloxacin . Please note that only the generic name of each medication is listed below.
Using this medicine with any of the following medicines is not recommended. Your doctor may decide not to treat you with this medication or change some of the other medicines you take.
- Bepridil
How To Use Ear Drops
Prior to using ear drops, you should always read the instructions provided to you with your prescription. You can also speak to your pharmacist or doctor for advice on using them. The following instructions will help you use ear drops correctly.
For adults:
- Lie down on a flat surface with a folded towel beneath your head and the affected ear facing the ceiling.
- Pull your earlobe up to straighten out the ear canal.
- Administer the appropriate number of drops into the ear.
- Push the ear flap gently to help ease the drops into the ear.
- Remain in this position for up to two minutes to ensure that the ear canal is fully coated with medicine.
For children:
- Have the child lie on the floor or bed with a towel beneath their head and their affected ear facing the ceiling.
- Hold their head still if they are squirming or fidgeting.
- Pull the earlobe out and down to straighten their ear canal..
- Administer the recommended number of drops
- Press on their ear flap or place a cotton ball gently into the ear and let it remain in position for several minutes to ensure that the medication coats the inside of their ear.
The process for infants is similar to children, but you can also cradle your infant while you administer the drops in an appropriate position that allows the medication to go into their ear properly.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop A Bacterial Infection Without Antibiotics
Frequently Asked Questions About Outer Ear Infections
What is the best way to apply ear drops?What is the best way to apply ear drops?
Youll need to lie down while you put ear drops in, and it can help to have someone else put them in for you.